Abstract
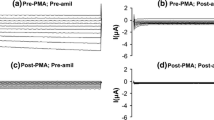
Increases in intracellular calcium (Ca2+) inhibit renal sodium (Na+) absorption in cortical collecting ducts, but the precise mechanism is unclear. We, therefore, studied the effects of raising intracellular Ca2+ (using 10 µmol/L A23187, a Ca2+ ionophore) on wild-type and Liddle-mutated human epithelial Na+ channels (hENaC) expressed in Xenopus oocytes, using the dual-electrode voltage clamp technique. A23187 decreased amiloride-sensitive Na+ current by 55 % in oocytes expressing wild-type hENaC, an effect prevented by co-exposure to 50 μmol/L W-7 (to inhibit the Ca2+/calmodulin complex). By contrast, co-exposure to 50 μmol/L calphostin (to inhibit protein kinase C) or 5 μmol/L KN-62 (to inhibit Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II) had no effect on the decrease in amiloride-sensitive Na+ current elicited by A23187 alone. Whereas A23187 reduced amiloride-sensitive Na+ current in oocytes expressing wild-type hENaC, it had no similar effect in those expressing Liddle-mutated hENaCs, suggesting that the activity of individual Na+ channels in situ was unchanged by the rise in intracellular Ca2+. These data suggest that the A23187-induced rise in intracellular Ca2+ inhibited wild-type hENaC through a W-7-sensitive mechanism, which likely reflected enhanced removal of Na+ channels from the cell membrane by endocytosis. We, therefore, propose that Na+ absorption in cortical collecting duct cells is inhibited by Ca2+, possibly when complexed with calmodulin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreil H, Loffing J, Rebhun JF et al (1999) Defective regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel by Nedd4 in Liddle’s syndrome. J Clin Invest 103:667–673
Alli AA, Bao HF, Alli AA et al (2012) Phosphatidylinositol phosphate-dependent regulation of Xenopus ENaC by MARCKS protein. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 303:F800–F811
Båtshake B, Nilsson C, Sundelin J (1995) Molecular characterization of the mouse prostanoid EP1 receptor gene. Eur J Biochem 231:809–814
Blődow A, Ngezahayo A, Ernst A et al (2003) Calmodulin antagonists suppress gap junction coupling in isolated Hensen cells of the guinea pig cochlea. Pflüg Arch 446:36–41
Boton R, Singer D, Dascal N (1990) Inactivation of calcium-activated chloride conductance in Xenopus oocytes: roles of calcium and protein kinase C. Pflüg Arch 416:1–6
Bourinet E, Fournier F, Nargeot J et al (1992) Endogenous Xenopus-oocyte Ca-channels are regulated by protein kinases A and C. FEBS Lett 299:5–9
Breyer MD, Breyer RM (2000) Prostaglandin E receptors and the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F12–F23
Breyer M, Jacobson H, Breyer R (1996) Functional and molecular aspects of renal prostaglandin receptors. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:8–17
Canessa CM, Horisberger JD, Rossier BC (1993) Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature 361:467–470
Doolan CM, Harvey BJ (1996) Rapid effects of steroid hormones on free intracellular calcium in T84 colonic epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 271:C1935–C1941
Farr TJ, Coddington-Lawson SJ, Snyder PM et al (2000) Human Nedd4 interacts with the human epithelial Na+ channel: WW3 but not WW1 binds to Na+ channel subunits. Biochem J 345:503–509
Frindt G, Palmer LG, Windhager EE (1996) Feedback regulation of Na channels in rat CCT. IV. Mediation by activation of protein kinase C. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 270:F371–F376
Funk C, Furchi L, FitzGerald G et al (1993) Cloning and expression of a cDNA for the human prostaglandin E receptor EP1 subtype. J Biol Chem 268:26767–26772
Goulet CC, Volk KA, Adams CM et al (1998) Inhibition of the epithelial Na+ channel by interaction of Nedd4 with a PY motif deleted in Liddle’s syndrome. J Biol Chem 273:30012–30017
Hartwig JH, Thelen M, Rosen A et al (1992) MARCKS is an actin filament crosslinking protein regulated by protein kinase C and calcium/calmodulin. Nature 356:618–622
Hartzell HC, Rinderknecht A (1996) Calphostin C, a widely used protein kinase C inhibitor, directly and potently blocks L-type Ca channels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 270:C1293–C1299
Harvey BJ, Higgins M (2000) Nongenomic effects of aldosterone on Ca2+ in M-1 cortical collecting duct cells. Kidney Int 57:1395–1403
Hébert RL, Jacobson HR, Breyer MD (1991) Prostaglandin E2 inhibits sodium transport in rabbit cortical collecting duct by increasing intracellular calcium. J Clin Invest 87:1992–1998
Ishikawa T, Marunaka Y, Rotin D (1998) Electrophysiological characterization of the rat epithelial Na+ channel (rENaC) expressed in MDCK cells. Effects of Na+ and Ca2+. J Gen Physiol 111:825–846
Ling BN, Kokko KE, Eaton DC (1992) Inhibition of apical Na+ channels in rabbit cortical collecting tubules by basolateral prostaglandin E2 is modulated by protein kinase C. J Clin Invest 90:1328–1334
Lott JS, Coddington-Lawson SJ, Teedale-Spittle PH et al (2002) A single WW domain is the predominant mediator of the interaction between the human ubiquitin-protein ligase Nedd4 and the human epithelial sodium channel. Biochem J 361:481–488
Masson M, Spezzatti B, Chapman J et al (1992) Calmodulin antagonists chlorpromazine and W-7 inhibit exogenous cholesterol esterification and sphingomyelinase activity in human skin fibroblast cultures. Similarities between drug-induced Niemann-Pick type C lipidoses. J Neurosci Res 31:844–888
Means AR, Van Berkum MF, Bagchi et al (1991) Regulatory functions of calmodulin. Pharmacol Ther 50:255–270
Miledi R, Parker I (1984) Chloride current induced by injection of calcium into Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol 357:173–183
Miledi R, Parker I, Woodward RM (1989) Membrane currents elicited by divalent cations in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol 417:173–195
Nalefski EA, Falke JJ (1996) The C2 domain calcium-binding motif: structural and functional diversity. Protein Sci 5:2375–2390
Okazaki K, Ishikawa T, Inui M et al (1994) KN-62, a specific Ca++/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase inhibitor, reversibly depresses the rate of beating of cultured fetal mouse and cardiac myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:1319–1324
Palmer LG, Frindt G (1987) Effects of cell Ca and pH on Na channels from the rat cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 253:F333–F339
Plant PJ, Yeger H, Staub O et al (1997) The C2 domain of the ubiquitin protein ligase Nedd4 mediates Ca2+-dependent plasma membrane localization. J Biol Chem 272:32329–32336
Rothstein A, Mack E (1992) Volume-activated calcium uptake: its role in cell volume regulation of Madin–Darby canine kidney cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 262:C339–C347
Sengupta P, Ruano MJ, Tebar F et al (2007) Membrane-permeable calmodulin inhibitors (e.g. W-7/W-13) bind to membranes, changing the electrostatic surface potential. Dual effect of W-13 on epidermal growth factor receptor activation. J Biol Chem 282:8474–8486
Shimkets RA, Warnock DG, Bositis CM et al (1994) Liddle’s syndrome: heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the β-subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell 79:407–414
Staub O, Dho S, Henry PC et al (1996) WW domains of Nedd4 bind to the proline-rich PY motifs in the epithelial Na+ channel deleted in Liddle’s syndrome. EMBO J 15:2371–2380
Staub O, Abriel H, Plant P et al (2000) Regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel by Nedd4 and ubiquitination. Kidney Int 57:809–815
Stokes JB, Kokko JP (1977) Inhibition of sodium transport by prostaglandin E2 across the isolated, perfused rabbit collecting tubule. J Clin Invest 59:1099–1104
Thomas AP, Bird GS, Hajnόczky G et al (1996) Spatial and temporal aspects of cellular calcium signalling. FASEB J 10:1505–1517
Toh H, Ichikawa A, Narumiya S (1995) Molecular evolution of receptors for eicosanoids. FEBS Lett 361:17–21
Tohda M, Nakamua J, Hidaka H et al (1991) Inhibitory effects of KN-62, a specific inhibitor of Ca/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, on serotonin-evoked Cl− current and 36Cl− efflux in Xenopus oocytes. Neurosci Lett 129:47–50
Tokuda S, Niisato N, Morisaki S et al (2002) Calmodulin-dependent regulation of hypotonicity-induced translocation of ENaC in renal epithelial A6 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 298:619–623
Watabe A, Sugimoto Y, Irie A et al (1993) Cloning and expression of cDNA for a mouse EP1 subtype of prostaglandin E receptor. J Biol Chem 268:20175–20178
Weber WM, Liebold KM, Reifarth FW et al (1995) The Ca2+-induced leak current in Xenopus oocytes is indeed mediated through a Cl− channel. J Membr Biol 148:263–275
Acknowledgments
Supported by a project grant from the British Heart Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robins, G.G., Sandle, G.I. Calcium Rapidly Down-Regulates Human Renal Epithelial Sodium Channels Via a W-7-Sensitive Mechanism. J Membrane Biol 247, 729–737 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9698-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9698-0