Summary
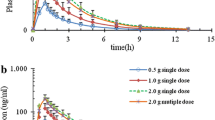
Pharmacological and antimicrobial properties of cefadroxil, a new cephalosporin antibiotic, were compared with cephalexin. Absorption and excretion were studied in 20 healthy men. Peak concentrations of the drugs in serum were similar after ingestion of single 500 mg tablets. The concentration of cefadroxil in serum was more sustained than that of cephalexin. Levels of cefadroxil in serum after a dose of 1000 mg were approximately twice those after a 500 mg dose through 6 h. Each drug administered in a dose of 500 mg every 6 h for 24 h resulted in concentrations in serum that were similar to a single dose without accumulation. Ninety-three percent of the cefadroxil and 85% of the cephalexin were excreted in urine after ingestions of single 500 mg tablets. The urine concentration of cefadroxil was more sustained than cephalexin. Minimal inhibitory and minimal bactericidal concentrations for clinical isolates were comparable with each drug. Cefadroxil compares favorably with cephalexin in this study. Sustained levels of cefadroxil in serum and urine suggest that this drug may be given at less frequent intervals than cephalexin.
Zusammenfassung
Die pharmakologischen und antimikrobiellen Eigenschaften von Cefadroxil, einem neuen Cephalosporin-Antibiotikum, wurden mit denen von Cephalexin verglichen. Resorption und Ausscheidung wurden bei 20 gesunden Männern untersucht. Die Spitzenkonzentrationen der Medikamente im Serum nach Einnahme einer einzelnen 500-mg-Tablette waren ähnlich. Die Konzentration von Cefadroxil im Serum hielt länger an als die von Cephalexin. Die Serumspiegel von Cefadroxil über sechs Stunden nach einer Dosis von 1000 mg waren annähernd zweimal so hoch wie nach einer 500-mg-Dosis. Bei jeder der Substanzen führte die Gabe einer Dosis von 500 mg alle sechs Stunden über einen Zeitraum von 24 Stunden zu Serumkonzentrationen, die denjenigen einer Einzeldosis ohne Kumulation ähnlich waren. Nach Einnahme einer einzigen 500-mg-Tablette wurden 93% von Cefadroxil und 85% von Cephalexin im Urin ausgeschieden. Die Urinkonzentration von Cefadroxil hielt über einen längeren Zeitraum an als die von Cephalexin. Die minimalen Hemmkonzentrationen und minimalen bakteriziden Konzentrationen für klinische Isolate waren bei den beiden Medikamenten vergleichbar. Cefadroxil schneidet beim Vergleich mit Cephalexin in dieser Studie gut ab. Langanhaltende Spiegel von Cefadroxil im Serum und Urin lassen annehmen, daß die Substanz weniger häufig verabreicht werden kann als Cephalexin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Bell, S. M. The significance of sensitivity test ofStaphylococcus aureus to cephaloridine. Med. J. Aust. 2 (1974) 902–904.
Bennett, J. V., Brodie, J. L., Benner, E. J. et al. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl. Microbiol. 14 (1966) 170–177.
Buck, R. E., Price, K. E. Cefadroxil, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 11 (1977) 324–330.
Charney, E., Dynum, R., Eldredge, D. et al. How well do patients take oral penicillin? A collaborative study in private practice. Pediatrics 40 (1967) 188–195.
Ericsson, H. M., Sherris, J. C.: Antibiotic sensitivity testing: report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. Sect. B Suppl. 217 (1971).
Landes, R. R. Single daily doses of tobramycin in therapy of urinary tract infections. J. Infect. Dis. 134 (1976) S 142-S 145.
Matsen, J. M., Barry, A. L. Susceptibility testing: diffusion test procedures. p. 418–427. In:E. H. Lennette, E. H. Spaulding, andJ. P. Truant (ed.), Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 2nd ed. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D. C. 1974.
Mohler, D. N., Wallin, D. G., Drefus, E. G. Treatment streptococcal disease. I. Failure of patients to take penicillin by mouth as prescribed. N. Engl. J. Med. 252 (1955) 1116–1118.
Pfeffer, M., Jackson, A., Ximenes, J. et al. Comparative human oral clinical pharmacology of cefadroxil, cephalexin, and cephradine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 11 (1977) 331–338.
Regamey, C., Libke, R. D., Engleking, E. R. et al. Inactivation of cefazolin, cephaloridine, and cephalothin by methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant strains ofStaphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 131 (1975) 291–294.
Ronald, Q. R., Boutros, P., Mourtada, H. Bacteriuria localization and response to single dose therapy in women. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 235 (1976) 1854–1856.
Stamey, T. A., Fair, W. R., Timothy, M. M. et al. Serum versus urinary antimicrobial concentrations in cure of urinary tract infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 291 (1974) 1159–1163.
Turck, M., Anderson, K. N., Smith, R. H. et al. Laboratory and clinical evaluation of a new antibiotic — cephalothin. Ann. Intern. Med. 63 (1965) 199–211.
Weinstein, L., Schlesinger, J. Treatment of infective endocarditis. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 16 (1973) 275–302.
Westlake, W. J. The use of balanced incomplete block designs in comparative bioavailability trials. Biometrics 30 (1974) 319–327.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Erstveröffentlichung: Antimicrob. Chemother. 12 (1977) 93.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartstein, A.I., Patrick, K.E., Jones, S.R. et al. Comparison of pharmacological and antimicrobial properties of cefadroxil and cephalexin. Infection 8 (Suppl 5), S588–S591 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01639676
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01639676