Summary
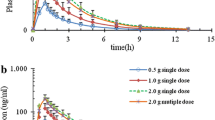
The pharmacokinetics of cefadroxil suspension were studied in 30 children, 13 months to 12 years of age (mean age, 5.7 years). Average peak concentrations in serum of 11 to 14 µg/ml and of 7 to 10 µg/ml after 15- and 10-mg/kg doses, respectively, were not substantially affected by the feeding status. The serum half-life values were 1.3 to 1.5 h. Cefadroxil was detected in saliva of all children 2 h after 15-mg/kg doses: the levels ranged from 0.17 to 2.6 µg/ml (mean, 0.46 µg/ml). The average concentrations in urine were 1,700 and 2,620 µg/ml at 0 to 2 and 2 to 4 h, respectively, after 15-mg/kg doses. In a randomized controlled study of 50 children with impetigo, cefadroxil was as effective as penicillin G in curing existing lesions and in preventing development of new lesions. Cefadroxil may be useful for therapy of mucocutaneous and urinary tract infections in infants and children.
Zusammenfassung
Die Pharmakokinetik von Cefadroxil Suspension wurde bei 30 Kindern im Alter von 13 Monaten bis zwölf Jahren (mittleres Alter 5,7 Jahre) untersucht. Nach Dosen von 15 mg/kg Körpergewicht betrugen die Serumspitzenkonzentrationen im Durchschnitt 11–14 mcg/ml, nach 10 mg/kg 7–10 mcg/ml. Sie wurden von der Nahrungsaufnahme nicht wesentlich beeinflußt. Die Serumhalbwertszeiten lagen bei 1,3 bis 1,5 Stunden. Zwei Stunden nach Gabe einer Dosis von 15 mg/kg war Cefadroxil im Speichel von allen Kindern nachweisbar; die Spiegel lagen zwischen 0,17 und 2,6 mcg/ml (Mittelwert 0,46 mcg/ml). Die mittleren Urinkonzentrationen nach Dosen von 15 mg/kg betrugen nach 0–2 beziehungsweise 2–4 Stunden 1700 und 2620 mcg/ml. In einer randomisierten kontrollierten Studie an 50 Kindern mit Impetigo war Cefadroxil bezüglich der Heilung bestehender Läsionen und der Prävention der Entwicklung neuer Läsionen ebenso wirksam wie Penicillin G. Cefadroxil dürfte für die Behandlung von Haut-, Schleimhaut- und Harnwegsinfektionen bei Säuglingen und Kindern geeignet sein.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Buck, R. E., Price, K. E. Cefadroxil, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 11 (1977) 324–330.
Hartstein, A. I., Patrick, K. E., Jones, S. R., Miller, M. J., Bryant, R. E. Comparison of pharmacological and antimicrobial properties of cefadroxil and cephalexin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 12 (1977) 93–97.
Pfeffer, M., Jackson, A., Ximenes, J., Perche de Menezes, J. Comparative human oral clinical pharmacology of cefadroxil, cephalexin, and cephradine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 11 (1977) 331–338.
Ritschel, W. A. Handbook of basic pharmacokinetics. p. 235–243. Drug Intelligence Publications, Hamilton 1976.
Simon, H. J., Yin, E. J. Microbioassay of antimicrobial agents. Appl. Microbiol. 19 (1970) 573–579.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ginsburg, C.M., McCracken, G.H., Clahsen, J.C. et al. Clinical pharmacology of cefadroxil in infants and children. Infection 8 (Suppl 5), S577–S579 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01639673
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01639673