Summary
-
1.
The contributions made by the coprodeum and by the colon to transepithelial transport were assessed in vivo, in the domestic fowl. Functional differences were established between these two epithelia that were neither revealed by previous in vitro nor in vivo studies.
-
2.
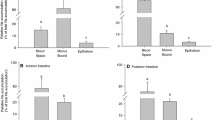
With iso-osmotic perfusion, net colonic sodium ion flux (mucosa→serosa) was five times greater than the flux measured in coprodeum,J Na=100±24 μEq/kg·h and 19±6.3 μEq/kg·h, respectively.
-
3.
Concomitant with net sodium ion flux was a solute-linked water flow, which in the colon averaged 176±34 μl/kg·h, but was virtually undetectable in the coprodeum (13±11 μl/kg·h).
-
4.
Net chloride ion absorption accompanied sodium ion transport and was significantly higher in the colon than in the coprodeum (P<0.01).
-
5.
Sodium transport-independent K+ secretion (serosa→mucosa) was observed with all treatments and in both coprodeum and colon. The magnitudes of the fluxes were not significantly different.
-
6.
The coprodeum functions as a storage site for ureteral urine. Active modification of water and electrolyte composition of urine and chymus takes place almost exclusively in the colon.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- m-s :
-
mucosa→serosa
- s-m :
-
serosa→mucosa
- ECPD :
-
electrochemical potential difference
- P os :
-
osmotic permeability
References
Bindslev N (1981) Water transport in the hen lower intestine during dehydration. In: Ussing HH, Bindslev N, Lassen, NA, Sten-Knudsen O (eds) Water transport across epithelia, Alfred Benzon Symposium 15, Munksgaard, Copenhagen, pp 468–484
Bindslev N, Skadhauge E (1971a) Salt and water permeability of the epithelium of the coprodeum and large intestine in the normal and dehydrated fowl(Gallus domesticus). In vitro Perfusion studies. J Physiol 216:735–752
Bindslev N, Skadhauge E (1971b) Sodium chloride absorption and solute-linked water flow across the epithelium of the coprodeum and large intestine in the normal and dehydrated fowl(Gallus domesticus). In vivo perfusion studies. J Physiol 216:753–768
Choshniak I, Munck BG, Skadhauge E (1977) Sodium chloride transport across the chicken coprodeum. Basic characteristics and dependence on sodium chloride intake. J Physiol 271:489–504
Frizzell R, Koch MJ, Schultz SG (1976) Ion transport by rabbit colon: I. Active and passive components. J Membr Biol 27:297–316
Fromm M, Hegel U (1978) Segmental heterogeneity of epithelial transport in rat large intestine. Pflügers Arch 378:71–83
Lind J, Munck BG, Olsen O, Skadhauge E (1980) Effects of sugars, amino acids and inhibitors on electrolyte transport across hen colon at different sodium chloride intakes. J Physiol 305:315–325
Lyngdorf-Henriksen P, Munck BG, Skadhauge E (1978) Sodium chloride transport across the lower intestine of the chicken. Dependence on sodium chloride concentration and effect of inhibitors. Pflügers Arch 378:161–165
Salas-Coll CA, Kermode JC, Edmonds CJ (1976) Potassium transport across the distal colon in man. Clin Sci Mol Med 51:287–297
Skadhauge E (1967)In vivo perfusion studies of the cloacal water and electrolyte reabsorption in the fowl (Gallus domesticus). Comp Biochem Physiol 23:483–551
Skadhauge E (1968) The cloacal storage of urine in the rooster. Comp Biochem Physiol 24:7–18
Skadhauge E (1981) Osmoregulation in birds. In: Farner DS (ed) Zoophysiology, vol 12. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Skadhauge E (1982) A quantitative survey of salt and water excretion. Comp Biochem Physiol [A] 71 (in press)
Skadhauge E, Thomas DH (1979) Transepithelial transport of K+, NH +4 , inorganic phosphate and water by hen (Gallus domesticus) lower intestine (colon and coprodeum) perfused luminallyin vivo. Pflügers Arch 379:237–243
Thomas DH (1982) Salt and water excretion by birds: the lower intestine as an integrator of renal and intestinal excretion. Comp Biochem Physiol [A] 71 (in press)
Thomas DH, Skadhauge E (1979) Dietary Na+ effects on transepithelial transport of NaCl by hen (Gallus domesticus) lower intestine (colon and coprodeum) perfused luminallyin vivo. Pflügers Arch 379:229–236
Ussing HH, Johansen B (1969) Anomalous transport of sucrose and urea in toad skin. Nephron 6:317–328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rice, G.E., Skadhauge, E. The in vivo dissociation of colonic and coprodeal transepithelial transport in NaCl depleted domestic fowl. J Comp Physiol B 146, 51–56 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688716
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688716