Summary
-
1.
In the radula protractor ofRapana thomasiana, decrease in the external concentration of Mg increased the rate of rise and the amplitude of the action potential.
-
2.
When the ratio of Ca and Mg in the fluid was kept constant, the variation in the concentration of these cations did not produce any appreciable effect on the rate of rise and the amplitude of the spike potential. The slow component of the potential and contraction were reduced as both cations were increased.
-
3.
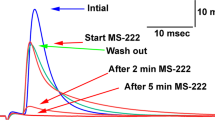
The effect of 5-HT on the radula muscle was examined. At lower concentrations, up to 10−5 M, 5-HT had no apparent effect on the membrane potential and mechanical tension, though the excitability was definitely enhanced. With higher doses over 10−5 M, the membrane depolarized and rhythmical electrical firing and mechanical oscillations were induced.
-
4.
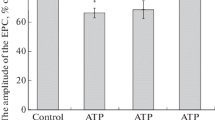
The amplitude of the junctional potential elicited in curarized muscle varied directly with Ca concentration and inversely with Mg concentration.
-
5.
Membrane potential of the muscle was not affected by the change of Mg concentration.
-
6.
The sensitivity of the muscle fiber to the depolarizing action of ACh was virtually unaffected by changing the concentration of Ca or Mg.
-
7.
These results suggest that the concentration of Ca has direct effects and Mg has inverse effects on the amount of transmitter release at the nerve ending.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloomquist, E., Curtis, B. A.: The action of serotonin on calcium-45 efflux from the anterior byssal retractor muscle ofMytilus edulis. J. gen. Physiol.59, 476–485 (1972)
del Castillo, J., Engbaek, L.: The nature of the neuromuscular block produced by magnesium. J. Physiol. (Lond.)124, 370–384 (1954)
del Castillo, J., Stark, L.: The effect of calcium ions on the motor end-plate potentials. J. Physiol. (Lond.)116, 507–515 (1952)
Hagiwara, S., Nakajima, S.: Effects of the intracellular Ca-ion concentration upon the excitability of the muscle fiber membrane of a barnacle. J. gen. Physiol.49, 807–818 (1966)
Hidaka, T., Osa, T., Twarog, B. M.: The action of 5-hydroxytryptamine onMytilus smooth muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)192, 869–877 (1967)
Hill, R. B.: Effects of postulated neurohumoral transmitters on the isolated radula protractor ofBusycon canaliculatum. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.33, 249–258 (1970)
Hill, R. B., Greenberg, M. J., Irisawa, H., Nomura, H.: Electromechanical coupling in a molluscan muscle, the radula protractor ofBusycon canaliculatum. J. exp. Zool.174, 331–348 (1970)
Jenkinson, D. H.: The nature of the antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. (Lond.)138, 434–444 (1957)
Katz, B., Miledi, R.: The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc. roy. Soc. B167, 23–38 (1967a)
Katz, B., Miledi, R.: The timing of Ca-action during neuromuscular transmisson. J. Physiol. (Lond.)189, 535–544 (1967b)
Kobayashi, M.: Electrical and mechanical activities in the radula protractor of a mollusc,Rapana thomasiana. J. comp. Physiol.78, 1–10 (1972a)
Kobayashi, M.: Prolonged depolarization of a molluscan muscle in Ca-free solution. J. comp. Physiol.78, 11–19 (1972b)
Ortiz, C. L., Bracho, H.: Effect of reduced calcium on excitatory transmitter release at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.41A, 805–812 (1972)
Rahamimoff, R.: Role of calcium ions in neuromuscular transmission. In: Calcium and cellular function, A. W. Cuthbert, ed., p. 131–147. London: Macmillan 1970
Wernig, A.: The effects of calcium and magnesium on statistical release parameters at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. (Lond.)226, 761–768 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The author wishes to thank Dr. H. Irisawa for the use of his facilities and for his encouragement.
This research was supported by grants No. 864144 to the author and No. 737002 to H. Irisawa from the Ministry of Education of Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, M. Antagonistic action of Ca and Mg on the neuromuscular transmission and excitation in a molluscan muscle (Radula protractor). J. Comp. Physiol. 94, 17–24 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00610154
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00610154