Abstract
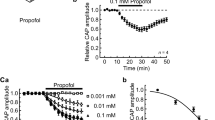
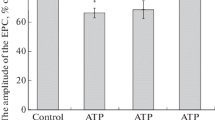
The effect of methylmercuric chloride was investigated on the isolated cervical sympathetic nerve of the rabbit. All concentrations of methylmercury tested decreased both major spikes, S1 and S2, of the electrically evoked compound action potential. The blocking effect is temperature-dependent and not reversible on washing. Despite severe inhibition of the spikes, conduction velocities of the fiber groups involved were not changed. Threefold increases in the Ca2+ concentration in the Locke's bathing solution before exposure to methylmercury markedly slowed the progress of inhibition of both major spikes of the fiber groups in the cervical sympathetic nerve. The results suggest that methylmercury may act by interfering with the normal function of Ca2+ in the nerve.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkadhi KA, Taha MN (1980) Effects of methylmercuric chloride on the superior cervical ganglion of the rabbit. Fed Proc 39: 622
Bakir F, Damaluji SF, Amin-Zaki L, Murtadha M, Khalidi A, Al-Rawi NY, Tikriti S, Dhahir HI, Clarkson TW, Smith JC, Doherty RA (1973) Methylmercury poisoning in Iraq. Science 181: 230–241
Berlin M, Carlson J, Norseth T (1975) Dose-dependence of methylmercury metabolism. Arch Environ Health 30: 307–317
Bishop GH, Heinbecker P (1932) A functional analysis of the cervical sympathetic nerve supply to the eye. Am J Physiol 100: 519–532
Burg R von, Rustam H (1974) Electrophysiological investigations of methylmercury intoxication in humans: Evaluation of peripheral nerve by conduction velocity and electromyography. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 37: 381–391
Cavanagh JB, Chen FCK (1971) The effects of methyl-mercury-dicyandiamide on the peripheral nerves and spinal cord of rats. Acta Neuropathol 19: 208–215
Chang LW, Hartmann HA (1972) Ultrastructural studies of the nervous system after mercury intoxication. II. Pathological changes in the nerve fibers. Acta Neuropathol 20: 316–331
Eccles JC (1935) The action potential of the superior cervical ganglion. J Physiol (Lond) 85: 179–206
Fehling C, Abdulla M, Brun A, Dictor M, Schütz A, Skerfving S (1975) Methylmercury poisoning in the rat: a combined neurological, chemical and histopathological study. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 33: 27–37
Frankenhauser B, Hodgkin AL (1957) The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol (Lond) 137: 218–244
Herman SP, Klein R, Talley FA, Krigman MR (1973) An ultrastructural study of methylmercury-induced primary sensory neuropathy in the rat. Lab Invest 28: 104–118
Huneeus-Cox F, Fernandez HL, Smith BH (1966) Effects of redox and sulfhydryl reagents on the bioelectric properties of the giant axon of the squid. Biophys J 6: 675–689
Jacobs JM, Carmichael N, Cavanagh JB (1975) Ultrastructural changes in the dorsal root and trigeminal ganglia of rats poisoned with methylmercury. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 1: 1–9
Juang MS (1976) An electrophysiological study of the action of methylmercuric chloride and mercuric chloride on the sciatic nerve-sartorius muscle preparation of the frog. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 37: 339–348
Juang MS, Yonemura K (1975) Increased spontaneous transmitter release from presynaptic nerve terminal by methylmercuric chloride. Nature 256: 211–213
Keana JFW, Stämpfli R (1974) Effect of several “specific” chemical reagents on the Na+, K+ and leakage currents in voltage clamped single nodes of Ranvier. Biochim Biophys Acta 373: 18–33
Le Quesne PM, Damaluji SF, Rustam H (1974) Electrophysiological studies of peripheral nerves in patients with organic mercury poisoning. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychol 37: 333–338
Marquis JK, Mautner HG (1974) The effect of electrical stimulation on the action of sulfhydryl reagents in the giant axon of squid; suggested mechanism for the role of thiol and disulfide groups in electrically-induced conformational changes. J Membr Biol 15: 249–260
Miyakawa T, Deshimaru M, Sumiyoshi S, Tersoka A, Udo N, Hattori E, Tetetsu L (1970) Experimental organic mercury poisoning: pathological changes in peripheral nerves. Acta Neuropathol 15: 45–55
Misumi J (1979) Electrophysiological studies in vivo on peripheral nerve function and their application to peripheral neuropathy produced by organic mercury in rats. III. Effects of methylmercuric chloride on compound action potentials in the sciatic and tail nerve in rats. Kumamoto Med J 32: 15–22
Shrager P (1977) Slow sodium inactivation in nerve after exposure to sulfhydryl blocking reagents. J Gen Physiol 69: 183–202
Shrivastav BB, Brodwick MS, Narahashi T (1976) Methylmercury: effects on electrical properties of squid axon membranes. Life Sci 18: 1077–1082
Smith HM (1958) Effects of sulfhydryl blockade on axonal function. J Cell Comp Physiol 51: 161–171
Snyder RD, Seelinge DF (1976) Methylmercury poisoning clinical follow up and sensory nerve conduction studies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychol 39: 701–704
Somjen GG, Herman SP, Klein R (1973) Electrophysiology of methylmercury poisoning. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 186: 579–592
Tsubaki T, Shivakawa K, Hirota K, Kanbayashi K (1977) Neurological aspects of methyl-mercury poisoning in Niigata. In: Tsubaki T, Irukayama K (eds) Minamata Disease. Kodansha Ltd., Tokyo, Japan, pp 145–165
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taha, M.N., Alkadhi, K.A. Effects of methylmercuric chloride on sympathetic preganglionic nerves. Arch Toxicol 50, 141–147 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373396
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373396