Summary
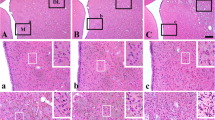
The dorsal hippocampus of cat was investigated by light microscopy and immunohistochemistry following 1 h global cerebral ischemia and various recirculation times from 1 day to 1 year. Complete ischemia was produced by combining hypotension with intrathoracic occlusion of major arteries. Postischemic resuscitation was carried out using an intensive care regimen with continuous neurophysiological monitoring. Brains of controls (n=4) and postischemic animals (n=12) were fixed in formaldehyde and prepared for histology and immunohistochemistry of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). In all post-ischemic animals the hilus and the regio superior of dorsal hippocampus which encompasses the CA1 subfield were severely damaged. Neurons in these regions exhibited the typical sequela of neuronal death. GFAP staining revealed vivid astroglial proliferation in stratum lacunosum-moleculare and stratum oriens. Changes in the regio inferior of dorsal hippocampus, i.e., CA3 subfield, and in dentate gyrus granular layer, were variable. Although most animals exhibited moderate to severe neuronal and glial alterations, groups of surviving cells were observed in the stratum oriens and in the granular layer of dentate gyrus. In one animal the majority of CA3 pyramidal cells and granule cells was preserved. These findings demonstrate that after 1 h of complete cerebral ischemia dorsal hippocampus exhibits two different types of injury: a consistent pattern of selective vulnerability in the hilus and the regio superior, and a variable pattern of non-selective injury in the regio inferior and dentate gyrus. The two patterns can be best explained by intrinsic (pathoclitic) and extrinsic (hemodynamic/edema) factors, respectively and are likely to represent basically different mechanisms of ischemic injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackstad TW (1956) Commissural connections of the hippocampal region in the rat, with special reference to their mode of termination. J Comp Neurol 105:417–521
Blomqvist P, Wieloch T (1985) Ischemic brain damage in rats following cardiac arrest using a long-term recovery model. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 5:420–431
Bodechtel G (1930) Die Topik der Ammonshornschädigung. Z Ges Neurol Psychiatr 123:485–535
Bodsch W, Barbier A, Oehmichen M, Grosse Ophoff B, Hossmann K-A (1986) Recovery of monkey brain after prolonged ischemia. II. Protein synthesis and morphological alterations. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 6:22–33
Brierley JB, Graham DI (1984) Hypoxia and vascular disorders of the central nervous system. In: Adams JH, Corsellis JAN, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology, 4th edn. Arnold, London, pp 125–207
Bureš J, Burešová O (1957) Die anoxische Terminaldepolarisation als Indikator der Vulnerabilität der Groβhirnrinde bei Anoxie und Ischämie. Pflügers Arch 264:325–334
Crain BJ, Westerkam WD, Harrison AH, Nadler JV (1988) Selective neuronal death after transient forebrain ischemia in the mongolian gerbil: a silver impregnation study. Neuroscience 27:387–402
Diemer NH, Siemkowicz E (1981) Regional neurone damage after cerebral ischaemia in the normo- and hypoglycaemic rat. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 7:217–227
Duchen LW (1984) The general pathology of neurons and neuroglia. In: Adams JH, Corsellis JAN, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology, 4th edn. Arnold, London, pp 1–52
Eng LF, DeArmond SJ (1983) Immunohistochemistry of the glial fibrillary acidic protein. Prog Neuropathol 5:19–39
Hirsch H, Scholl H, Paschke KG, Schmid-Schönbein H (1968) Die Veränderung der corticalen Gleichspannung bei kompletter und inkompletter Ischämie des Gehirns. Pflügers Arch 301:334–343
Hossmann K-A (1988) Resuscitation potentials after prolonged global cerebral ischemia in cats. Crit Care Med 16:964–971
Hossmann K-A, Kleihues P (1973) Reversibility of ischemic brain damage. Arch Neurol 29:375–382
Hossmann K-A, Schmidt-Kastner R, Grosse Ophoff B (1987) Revovery of integrative central nervous function after one hour global cerebro-circulatory arrest in normothermic cat. J Neurol Sci 77:305–320
Imdahl A, Hossmann K-A (1986) Morphometric evaluation of post-ischemic capillary perfusion in selectively vulnerable areas of gerbil brain. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 69:267–271
Ito U, Spatz M, Walker JT Jr, Klatzo I (1975) Experimental cerebral ischemia in mongolian gerbils. I. Light microscopic observations. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 32:209–223
Jacob H (1963) Patterns of CNS vulnerability. CNS tissue and cellular pathology in hypoxaemic states. In: Schadé JP, McMenemy WM (eds) Selective vulnerability of the brain in hypoxaemia. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, pp 153–163
Jasper HH, Ajmone-Marsan C (1954) A stereotaxic atlas of the diencephalon of the cat. National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa
Johansen FF, Jørgensen MB, Diemer NH (1983) Resistance of hippocampal CA-1 interneurons to 20 min of transient cerebral ischemia in the rat. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 61:135–140
Johansen FF, Zimmer J, Diemer NH (1987) Early loss of somatostatin neurons in dentate hilus after cerebral ischemia in the rat precedes CA-1 pyramidal cell loss. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 73:110–114
Jørgensen MB, Diemer NH (1982) Selective neuron loss after cerebral ischemia in the rat: Possible role of transmitter glutamate. Acta Neurol Scand 66:536–546
Kirino T (1982) Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res 239:57–69
Kirino T, Sano K (1984) Selective vulnerability in the gerbil hippocampus following transient ischemia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 62:201–208
Kirino T, Tamura A, Sano K (1984) Delayed neuronal death in the rat hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 64:139–147
Koide T, Wieloch TW, Siesjö BK (1986) Chronic dexamethasone pretreatment aggravates ischemic neuronal necrosis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 6:395–404
Lee KS, Tetzlaff W, Kreutzberg GW (1986) Rapid down regulation of hippocampal adenosine receptors following brief anoxia. Brain Res 380:155–158
Paschen W, Schmidt-Kastner R, Djuricic B, Meese C, Linn F, Hossmann K-A (1987) Polyamine changes in reversible cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 49:35–37
Petito CK, Pulsinelli WA (1984) Delayed neuronal recovery and neuronal death in rat hippocampus following severe cerebral ischemia: possible relationship to abnormalities in neuronal processes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 4:194–205
Petito CK, Feldmann E, Pulsinelli WA, Plum F (1987) Delayed hippocampal damage in humans following cardiorspiratory arrest. Neurology 37:1281–1286
Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB, Plum F (1982) Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia. Ann Neurol 11:491–498
Pulsinelli WA, Waldman S, Rawlinson D, Plum F (1982) Moderate hyperglycemia augments ischemic brain damage: a neuropathological study in the rat. Neurology 32:1239–1246
Sapolsky RM, Pulsinelli WA (1985) Glucocorticoids potentiate ischemic injury to neurons: therapeutic implications. Science 229:1397–1400
Schmidt-Kastner R, Hossmann K-A (1988) The distribution of ischemic neuronal damage in the dorsal hippocampus of rat. Acta Neuropathol 76:411–421
Scholz W (1957) Die nicht zur Erweichung führenden unvollständigen Gewebsnekrosen (Elektive Parenchymnekrose). An nervöse Systeme gebundene (topistische) Kreislaufschäden. In: Lubarsch O, Rössle R, Henke F (eds) Handbuch der speziellen pathologischen Anatomie und Histologie, Nervensystem, 1. Teil: Erkrankungen des Zentralen Nervensystems I, Bandteil B. Springer Berlin Göttingen Heidelberg, pp 1284–1383
Simon RP, Swan JH, Griffith T, Meldrum BS (1984) Blockade of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors may protect against ischemic damage in the brain. Science 226:850–852
Simon RP, Griffith T, Evans MC, Swan JH, Meldrum BS (1984) Calcium overload in selectively vulnerable neurons of the hippocampus during and after ischemia: an electron microscopy study in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 4:350–361
Smith M-L, Auer RN, Siesjö BK (1984) The density and distribution of ischemic brain injury in the rat following 2–10 min of forebrain ischemia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 64:319–332
Smith M-L, Kalimo H, Warner DS, Siesjö BK (1988) Morphological lesions in the brain preceding the development of postischemic seizures. Acta Neuropathol 76:253–264
Smith RW, White LE (1975) The fiberarchitectonics of the cat hippocampal formation. J Comp Neurol 123:11–28
Snider RS, Niemer WT (1961) A stereotaxic atlas of the cat brain. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Somogyi P, Hodgson AJ, Smith AD, Nunzi MG, Gorio A, Wu J-Y (1984) Different populations of GABAergic neurons in the visual cortex and hippocampus of cat contain somatostatin- or cholecystokinin-immunoreactive material. J Neurosci 4:2590–2603
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunohistochemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 1–354
Swan JH, Evans MC, Meldrum BS (1988) Long-term development of selective neuronal loss and the mechanism of protection by 2-amino-7-phosphonoheptanoate in a rat model of incomplete forebrain ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:64–78
Thilmann R, Xie Y, Kleihues P, Kiessling M (1986) Persistent inhibition of protein systhesis precedes delayed neuronal death in postischemic gerbil hippocampus. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 71:88–93
Wieloch T (1985) Neurochemical correlates to selective neuronal vulnerability. Prog Brain Res 63:69–85
Wieloch T, Lindvall O, Blomqvist P, Gage FH (1985) Evidence for amelioration of ischaemic neuronal damage in the hippocampal formation by lesions of the perforant path. Neurol Res 7:24–26
Wyss JM, Sripanidkulchai B (1985) The development of ammon's horn and the fascia dentata in the cat: a [3H]thymidine analysis. Dev Brain Res 18:185–198
Xie Y, Seo K, Hossmann K-A (1989) Effect of barbiturate treatment on post-ischemic protein biosynthesis in gerbil brain. J Neurol Sci 92:317–328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt-Kastner, R., Grosse Ophoff, B. & Hossmann, K.A. Pattern of neuronal vulnerability in the cat hippocampus after one hour of global cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol 79, 444–455 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308722
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308722