Summary
Cell bodies of sensory neurons of the rat's hypoglossal nerve were demonstrated by the somatopetal horseradish peroxidase (HRP) transport technique. Labelled perikarya were found within the second and third cervical spinal ganglia and in the vagal sensory ganglia.
After application of HRP to the cut peripheral trunk of the hypoglossal nerve about 200 labelled cell bodies were counted in each animal. The vast majority of the axons from cervical spinal ganglion cells reach the hypoglossal nerve via the descending ramus (N. descendens hypoglossi). However, there may exist an additional pathway, probably via the cervical sympathetic trunk.
Application of HRP to the medial and lateral end branches led to a labelling of much fewer spinal ganglion cells while the number of labelled vagal sensory neurons remained unchanged. Thus, it is suggested that the majority of the cervical afferents of the hypoglossal nerve originates within the extrinsic tongue musculature and the geniohyoid muscle, whereas the vagal afferents may perhaps derive exclusively from the intrinsic muscles.
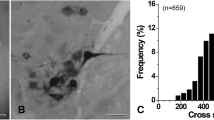
Histograms of the mean diameters of labelled cell bodies show a predominance of very small perikarya. This contrasts with the diameter distribution of sensory perikarya labelled after HRP application to nerves supplying other skeletal muscles. It is therefore assumed that the afferent component of the hypoglossal nerve is composed mainly of small-calibre axons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker, D.: The Morphology of Muscle Receptors, in: Muscle Receptors, Handbook of Sensory Physiologie, Vol. III/2, (C.C. Hunt ed.), 1–190, Berlin: Springer 1974
Barron, D.H.: A note on the course of the proprioceptor fibers from the tongue. Anat. Rec. 66, 11–15 (1936)
Blom, S.: Afferent influences on tongue muscle activity. Acta physiol. scand. 49 (Suppl. 170), 7–97 (1960)
Bowman, J.P., Combs, C.M.: Discharge patterns of lingual spindle afferent fibers in the hypoglossal nerve of the rhesus monkey. Exp. Neurol. 21, 105–119 (1968)
Bowman, J.P., Combs, C.M.: The thalamic projection of hypoglossal afferents in the rhesus monkey. Exp. Neurol. 25, 509–520 (1969a)
Bowman, J.P., Combs, C.M.: The cerebrocortical projection of hypoglossal afferents. Exp. Neurol. 23, 291–301 (1969b)
Boyd, J.D.: The sensory component of the hypoglossal nerve in the rabbit. J. Anat. 75, 330–346 (1941)
Coggeshall, R.E., Galbraith, S.L.: Categories of axons in mammalian rami communicantes, part II. J. Comp. Neurol. 181, 349–360 (1978)
Cooper, S.: Muscle spindles in the intrinsic muscles of the human tongue. J. Physiol. (London) 122, 193–202 (1953)
Cooper, S.: Afferent impulses in the hypoglossal nerve on stretching the cat's tongue. J. Physiol. (London) 126, 32 P (1954)
Corbin, K.B., Harrison, F.: The sensory innervation of the spinal accessory and tongue musculature in the rhesus monkey. Brain 62, 191–197 (1939)
Dault, S.H., Dale Smith, R.: A quantitative study of the nucleus of the mesencephalic tract of the trigeminal nerve of the cat. Anat. Rec. 165, 79–88 (1969)
Downman, C.B.B.: Afferent fibers of the hypoglossal nerve. J. Anat. 73, 387–395 (1939)
Egel, R.T., Bowman, J.P., Combs, C.M.: Calibre spectra of the lingual and hypoglossal nerves of the rhesus monkey. J. Comp. Neurol. 134, 163–174 (1968)
Elfvin, L.-G., Dalsgaard, C.J.: Retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase in afferent fibers of the inferior mesenteric ganglion of the guinea pig. Identification of the cells of origin in dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res. 126, 149–153 (1977)
Fitzgerald, M.J.T., Sachithanandan, S.R.: The structure and source of lingual proprioceptors in the monkey. J. Anat. 128, 523–552 (1979)
Froriep, A., Beck, W.: Ueber das Vorkommen dorsaler Hypoglossuswurzeln mit Ganglion, in der Reihe der Säugetiere. Anat. Anz. 10, 688–696 (1895)
Graham, R.C., Karnovsky, M.J.: The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: Ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J. Histochem, Cytochem. 14, 291–302 (1966)
Gruber, H., Mayr, R., Zenker, W.: Quantitative Untersuchungen an peripheren Nerven. Verh. Anat. Ges. 67, 427–429 (1973)
Hanson, J., Widén, L.: Afferent fibers in the hypoglossal nerve of cat. Acta Physiol. Scand. 79, 24–36 (1970)
Hedger, J.H., Webber, R.H.: Anatomical study of the cervical sympathetic trunk and ganglia in the albino rat (Mus norvegicus albinus). Acta Anat. 96, 206–217 (1976)
Hinsey, J.C., Corbin, K.B.: Observations on the peripheral course of the sensory fibers in the first four cervical nerves of the cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 60, 37–44 (1934)
Kristensson, K., Olsson, Y., Sjöstrand, J.: Axonal uptake and retrograde transport of exogenous proteins in the hypoglossal nerve. Brain Res. 32, 399–406 (1971)
Langworthy, O.R.: Problems of tongue innervation: course of proprioceptive nerve fibers, autonomic innervation of skeletal musculature. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 35, 239–246 (1924a)
Langworthy, O.R.: A study of the innervation of the tongue musculature with particular reference to the proprioceptive mechanism. J. Comp. Neurol. 36, 273–297 (1924b)
Law, M.E.: Lingual proprioception in pig, dog and cat. Nature 174, 1107–1108 (1954)
Lindquist, Ch., Martensson, A.: Reflex responses induced by stimulation of hypoglossal afferents. Acta Physiol. Scand. 77, 234–240 (1969)
Lodge, D., Duggan, A.W., Biscoe, T.J., Caddy, K.W.T.: Concerning recurrent collaterals and afferent fibers in the hypoglossal nerve of the rat. Exp. Neurol. 41, 63–75 (1973)
Morimoto, T., Kawamura, Y.: Discharge patterns of hypoglossal afferents in a cat. Brain Res. 35, 539–542 (1971)
Nakamura, Y.: Possible afferent components in the hypoglossal nerve influencing the trigeminal monosynaptic reflex of the cat. Anat. Rec. 160, 399 (1968)
Neuhuber, W., Niederle, B., Zenker, W.: Somatopetal transport of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in the peripheral and central branches of dorsal root ganglion cells. Cell Tissue Res. 183, 395–402 (1977)
Niederle, B., Mayr, R.: Course of denervation atrophy in type I and type II fibers of rat extensor digitorum longus muscle. Anat. Embryol. 153, 9–21 (1978)
Oldfield, B.J., McLachlan, E.M.: Uptake and retrograde transport of HRP by axons of intact and damaged peripheral nerve trunks. Neurosci. Lett. 6, 135–141 (1977)
Oldfield, B.J., McLachlan, E.M.: Localization of sensory neurons traversing the stellate ganglion of the cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 182, 915–922 (1978)
Richmond, F.J.R., Anstee, G.C.B., Sherwin, E.A., Abrahams, V.C.: Motor and sensory fibers of neck muscle nerves in the cat. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 54, 294–304 (1976)
Richmond, F.J.R., Scott, D.A., Abrahams, V.C.: Distribution of motoneurons to neck musles, biventer cervicis, splenius and complexus in cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 181, 451–463 (1978)
Sauerland, E.K., Mizuno, N.: Hypoglossal nerve afferents: elicitation of a polysynaptic hypoglossolaryngeal reflex. Brain Res. 10, 256–258 (1968)
Takata, M., Fujita, S., Shohara, E.: Postsynaptic potentials in the hypoglossal motoneurons set up by hypoglossal nerve stimulation. Jpn. J. Physiol. 29, 49–60 (1979)
Tanaka, T.: Afferent projections in the hypoglossal nerve to the facial neurons of the cat. Brain Res. 99, 140–144 (1975)
Tarkhan, A.A.: Ein experimenteller Beitrag zur Kenntnis der proprioceptiven Innervation der Zunge. Z. Anat. Entw. gesch. 105, 349–358 (1936)
Tarkhan, A.A., Abou-el-Nage, I.: Sensory fibers in the hypoglossal nerve. J. Anat. 81, 23–32 (1947)
Weddell, G., Harpman, J.A., Lambley, D.C., Young, L.: The innervation of the musculature of the tongue. J. Anat. 74, 255–267 (1940)
Whitwam, J.G., Kidd, C., Fussey, I.F.: Activity in efferent sympathetic nerves evoked by stimulation of the hypoglossal nerve. Brain Res. 14, 756–758 (1969)
Yee, J., Harrison, F., Corbin, K.B.: The sensory innervation of the spinal accessory and tongue musculature in the rabbit. J. Comp. Neurol. 70, 305–315 (1939)
Zapata, P., Torrealba, G.: Mechanosensory units in the hypoglossal nerve of the cat. Brain Res. 32, 349–367 (1971)
Zimny, R., Sobusiak, T., Matlosz, Z.: The afferent components of the hypoglossal nerve. J. f. Hirnforsch. 12, 83–100 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the “Hartmann Müller-Stiftung, Zürich”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuhuber, W., Mysicka, A. Afferent neurons of the hypoglossal nerve of the rat as demonstrated by horseradish peroxidase tracing. Anat Embryol 158, 349–360 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301822
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301822