Abstract
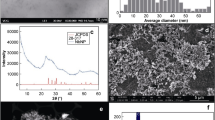
The present study introduces a novel Ni–Mo-MOF-modified screen printed electrode (Ni–Mo-MOF/SPE) to sensitively and rapidly detect amaranth. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was also applied to evaluate the electrochemical behavior of amaranth on the surfaces of bare SPE and Ni–Mo-MOF/SPE, and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) to calculate linearly detection range of amaranth. According to the results, various linear oxidation peak currents were obtained at different concentrations (between 0.15 ± 0.001 and 500.0 ± 0.001 µM) and the limit of detection (LOD) was estimated to be 0.05 ± 0.001 µM in the optimal conditions. Additionally, the efficacy of developed electrode was tested by real samples, the results of which were satisfactory. The proposed Ni–Mo-MOF/SPE not only had special properties such as high selectivity, high sensitivity, cost-effectiveness and rapid response, but also was shown to possess wide applications for sensitively amaranth detection in real samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.R. Barros, P.C. Franco, J.R. Steter, R.S. Rocha, M.R. Lanza, Electro-Fenton degradation of the food dye amaranth using a gas diffusion electrode modified with cobalt(II) phthalocyanine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 722, 46–53 (2014)
M. Wang, M. Cui, M. Zhao, H. Cao, Sensitive determination of Amaranth in foods using graphene nanomeshes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 809, 117–124 (2018)
S. Tvorynska, B. Josypčuk, J. Barek, L. Dubenska, Electrochemical behavior and sensitive methods of the voltammetric determination of food azo dyes amaranth and allura red AC on amalgam electrodes. Food Anal. Methods 12, 409–421 (2019)
S. Jing, H. Zheng, L. Zhao, L. Qu, L. Yu, Electrochemical sensor based on poly (sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) functionalized graphene and Co3O4 nanoparticle clusters for detection of amaranth in soft drinks. Food Anal. Methods 10, 3149–3157 (2017)
L. Li, H. Zheng, L. Guo, L. Qu, L. Yu, A sensitive and selective molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on Pd–Cu bimetallic alloy functionalized graphene for detection of amaranth in soft drink. Talanta 197, 68–76 (2019)
Q. He, J. Liu, X. Liu, G. Li, P. Deng, J. Liang, Manganese dioxide Nanorods/electrochemically reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites modified electrodes for cost-effective and ultrasensitive detection of Amaranth. Colloid. Surf B Biointerfaces 172, 565–572 (2018)
S. Chandran, L.A. Lonappan, D. Thomas, T. Jos, K.G. Kumar, Development of an electrochemical sensor for the determination of amaranth: a synthetic dye in soft drinks. Food Anal. Method. 7, 741–774 (2014)
W.W. Tonica, M.F. Hardianti, S.A. Prasetya, O. Rachmaniah, Determination of Rhodamine-B and Amaranth in snacks at primary school Sukolilo district of Surabaya-Indonesia by thin layer chromatography, in AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 2049 (AIP Publishing LLC, 2018), p. 020043
M. Ma, X. Luo, B. Chen, S. Su, S. Yao, Simultaneous determination of water-soluble and fat-soluble synthetic colorants in foodstuff by high-performance liquid chromatography–diode array detection–electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1103, 170–176 (2006)
X.Q. Li, Q.H. Zhang, K. Ma, H.M. Li, Z. Guo, Identification and determination of 34 water-soluble synthetic dyes in foodstuff by high performance liquid chromatography–diode array detection–ion trap time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 182, 316–326 (2015)
F. Pogacean, M.C. Rosu, M. Coros, L. Magerusan, M. Moldovan, C. Sarosi, S. Pruneanu, Graphene/TiO2-Ag based composites used as sensitive electrode materials for amaranth electrochemical detection and degradation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 165, B3054 (2018)
Y. Gao, L. Wang, Y. Zhang, L. Zou, G. Li, B. Ye, Electrochemical behavior of amaranth and its sensitive determination based on Pd-doped polyelectrolyte functionalized graphene modified electrode. Talanta 168, 146–151 (2017)
M. Wang, Y. Gao, Q. Sun, J. Zhao, Ultrasensitive and simultaneous determination of the isomers of Amaranth and Ponceau 4R in foods based on new carbon nanotube/polypyrrole composites. Food Chem. 172, 873–879 (2015)
K.H. Park, J.H. Choi, A.M. Abd El-Aty, S.K. Cho, J.H. Park, B.M. Kim, J.H. Shim, Determination of spinetoram and its metabolites in amaranth and parsley using QuEChERS-based extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 134, 2552–2559 (2012)
F. Feng, Y. Zhao, W. Yong, L. Sun, G. Jiang, X. Chu, Highly sensitive and accurate screening of 40 dyes in soft drinks by liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 879, 1813–1818 (2011)
A.A. El-Zomrawy, Selective and sensitive spectrophotometric method to determine trace amounts of copper metal ions using Amaranth food dye. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 203, 450–454 (2018)
Q.Q. Hu, H. Gao, Y.M. Wang, W. Ma, D.M. Sun, Simultaneous determination of Carmine and Amaranth based on a poly (L-Arginine)–graphene modified electrode. J. Anal. Chem. 73, 817–823 (2018)
Y. Gao, H. Li, J. Tong, L. Wang, A new voltammetric sensor based on poly (L-cysteine)/GR composite film modified electrode for the sensitive determination of amaranth in wastewater. Environ. Technol. 42, 2385–2390 (2021)
I. Elaissaoui, H. Akrout, S. Grassini, D. Fulginiti, L. Bousselmi, Effect of coating method on the structure and properties of a novel PbO2 anode for electrochemical oxidation of Amaranth dye. Chemosphere 217, 26–34 (2019)
H. Karimi-Maleh, M. Alizadeh, Y. Orooji, F. Karimi, M. Baghayeri, J. Rouhi, S. Tajik, H. Beitollahi, S. Agarwal, V.K. Gupta, S. Rajendran, S. Rostamnia, L. Fu, F. Saberi-Movahed, S. Malekmohammadi, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 60, 816–823 (2021)
M. Sajid, N. Baig, K. Alhooshani, Chemically modified electrodes for electrochemical detection of dopamine: challenges and opportunities. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 118, 368–385 (2019)
H. Karimi-Maleh, M.L. Yola, N. Atar, Y. Orooji, F. Karimi, P.S. Kumar, J. Rouhi, M. Baghayeri, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 592, 174–185 (2021)
M. Singh, N. Jaiswal, I. Tiwari, C.W. Foster, C.E. Banks, A reduced graphene oxide-cyclodextrin-platinum nanocomposite modified screen printed electrode for the detection of cysteine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 829, 230–240 (2018)
I.M. Apetrei, C. Apetrei, A modified nanostructured graphene-gold nanoparticle carbon screen-printed electrode for the sensitive voltammetric detection of rutin. Measurement 114, 37–43 (2018)
Y. Zhang, X. Jiang, J. Zhang, H. Zhang, Y. Li, Simultaneous voltammetric determination of acetaminophen and isoniazid using MXene modified screen-printed electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 130, 315–321 (2019)
W.J. Dang, Y.Q. Shen, M. Lin, H. Jiao, L. Xu, Z.L. Wang, Noble-metal-free electrocatalyst based on a mixed CoNi metal-organic framework for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Alloy. Compd. 792, 69–76 (2019)
Q. Li, H. Guo, R. Xue, M. Wang, M. Xu, W. Yang, W. Yang, Self-assembled Mo doped Ni-MOF nanosheets based electrode material for high performance battery-supercapacitor hybrid device. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 45, 20820–20831 (2020)
K. Zhou, D. Shen, X. Li, Y. Chen, L. Hou, Y. Zhang, J. Sha, Molybdenum oxide-based metal-organic framework/polypyrrole nanocomposites for enhancing electrochemical detection of dopamine. Talanta 209, 120507 (2020)
J. Xu, Q. Ji, X. Yan, C. Wang, L. Wang, Ni (acac) 2/Mo-MOF-derived difunctional MoNi@ MoO2 cocatalyst to enhance the photocatalytic H2 evolution activity of g-C3N4. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 268, 118739 (2020)
Y. Li, K. Pascal, X.J. Jin, Ni–Mo modified metal–organic frameworks for high-performance supercapacitance and enzymeless H2O2 detection. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 22, 5145–5161 (2020)
M. Sheikhshoaie, H. Karimi-Maleh, I. Sheikhshoaie, M. Ranjbar, Voltammetric amplified sensor employing RuO2 nano-road and room temperature ionic liquid for amaranth analysis in food samples. J. Mol. Liq. 229, 489–494 (2017)
M. Bijad, H. Karimi-Maleh, M. Farsi, S.A. Shahidi, Simultaneous determination of amaranth and nitrite in foodstuffs via electrochemical sensor based on carbon paste electrode modified with CuO/SWCNTs and room temperature ionic liquid. Food Anal. Methods 10, 3773–3780 (2017)
Q. Han, X. Wang, Z. Yang, W. Zhu, X. Zhou, H. Jiang, Fe3O4@rGO doped molecularly imprinted polymer membrane based on magnetic field directed self-assembly for the determination of amaranth. Talanta 123, 101–108 (2014)
P. Wang, X. Hu, Q. Cheng, X. Zhao, X. Fu, K. Wu, Electrochemical detection of amaranth in food based on the enhancement effect of carbon nanotube film. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58, 12112–12116 (2010)
J.L. He, W. Kou, C. Li, J.J. Cai, F.Y. Kong, W. Wang, Electrochemical sensor based on single-walled carbon nanotube-TiN nannocomposites for detecting Amaranth. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 10, 10074–10082 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (2020M2D8A206983011). Furthermore, financial support from the Basic Science Research Program (2017R1A2B3009135) through the National Research Foundation of Korea is appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tajik, S., Orooji, Y., Karimi, F. et al. High performance of screen-printed graphite electrode modified with Ni–Mo-MOF for voltammetric determination of amaranth. Food Measure 15, 4617–4622 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-01027-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-01027-0