Abstract
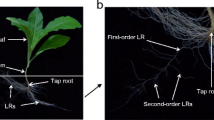
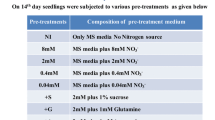
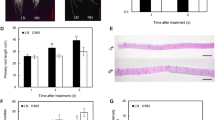
Potassium (K+) is a major limiting element of plant growth, and crops often suffer from low-K+ (LK) stress. Although nitric oxide (NO) is a signaling molecule involved in plant root adaptation to the environment, it remains unclear whether it participates in root growth regulated by LK conditions. Two tobacco cultivars (Nicotiana tabacum L.) exhibiting variant growth features under LK were used in this study. We investigate the effects of LK on root growth, NO accumulation, nitrate reductase (NR) activity and effects of a NO Donor (SNP and NONOate), NO scavenger (cPTIO), NR inhibitor (tungstate), and NO synthase inhibitor (L-NAME) on elongation of first-order lateral roots (LR). Compared with control treatment, the LK-tolerant cultivar NC89 maintained plant growth under LK at 14 days, whereas the dry weight was reduced significantly in the LK-susceptible cultivar Yunyan1. Low-K+-inhibited root growth, mostly by impairing first-order LR formation and elongation was only recorded in cv. Yunyan1. NO accumulation increased in root tips even when cv. Yunyan1 was subjected to LK at day 1. LK-induced NO was generated by the NR pathway during early LK. Application of SNP and NONOate to control-treated plants decreased first-order LR elongation to levels similar to LK treatment in cv. Yunyan1, whereas cPTIO, L-NAME, and tungstate application had the opposite effect. Further results suggested that NO might be involved in auxin-mediated LR elongating as plants respond to LK. In conclusion, NO generated by the NR pathway may be involved in the inhibition by LK stress of first-order LR elongation in tobacco plants.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armengaud P, Breitling R, Amtmann A (2004) The potassium-dependent transcriptome of Arabidopsis reveals a prominent role of jasmonic acid in nutrient signaling. Plant Physiol 136:2556–2576. doi:10.1104/pp.104.046482
Bai S, Yao T, Li M et al (2014) PIF3 is involved in the primary root growth inhibition of Arabidopsis induced by nitric oxide in the light. Mol Plant 4:616–625. doi:10.1093/mp/sst142
Barber SA (1995) Potassium. In: Soil nutrient bioavailability: a mechanistic approach. Wiley, New York, pp 231–232
Ben-zioni A, Vaadia Y, Herman Lips S (1970) Correlations between nitrate reduction, protein synthesis and malate accumulation. Physiol Plant 23:1039–1047. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1970.tb08878.x
Ben-zioni A, Vaadia Y, Herman Lips S (1971) Nitrate uptake by roots as regulated by nitrate reduction products of the shoot. Physiol Plant 24:288–290. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1971.tb03493.x
Bright J, Desikan R, Hancock JT, Weir IS, Neill SJ (2006) ABA-induced NO generation and stomatal closure in Arabidopsis are dependent on H2O2 synthesis. Plant J 45:113–122. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02615.x
Chen WW, Yang JL, Qin C et al (2010) Nitric oxide acts downstream of auxin to trigger root ferric-chelate reductase activity in response to iron deficiency in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 154:810–819. doi:10.1104/pp.110.161109
Correa-Aragunde N, Graziano M, Lamattina L (2004) Nitric oxide plays a central role in determining lateral root development in tomato. Planta 218:900–905. doi:10.1007/s00425-003-1172-7
Drew MC (1975) Comparison of the effects of a localized supply of phosphate, nitrate, ammonium and potassium on the growth of the seminal root system, and the shoot in barley. New Phytol 75:490–749. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1975.tb01409.x
Fan M, Huang Y, Zhong Y et al (2014) Comparative transcriptome profiling of potassium starvation responsiveness in two contrasting watermelon genotypes. Planta 239:397–410. doi:10.1007/s00425-013-1976-z
Fernández-Marcos M, Sanz L, Lewis DR, Muday GK, Lorenzo O (2011) Nitric oxide causes root apical meristem defects and growth inhibition while reducing PIN-FORMED 1 (PIN1)-dependent acropetal auxin transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:18506–18511. doi:10.1073/pnas.1108644108
Freschi L (2013) Nitric oxide and phytohormone interactions: current status and perspectives. Front Plant Sci 4:398. doi:10.3389/fpls.2013.00398
Gas E, Flores-Pérez Ú, Sauret-Güeto S et al (2009) Hunting for plant nitric oxide synthase provides new evidence of a central role for plastids in nitric oxide metabolism. Plant Cell 21:18–23. doi:10.1105/tpc.108.065243
Gierth M, Mäser P, Schroeder JI (2005) The Potassium Transporter AtHAK5 Functions in K+ deprivation-induced high-affinity K+ uptake and AKT1 K+ channel contribution to K+ uptake kinetics in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol 137:1105–1114. doi:10.1104/pp.104.057216
Gruber BD, Giehl RFH, Friedel S, Wirén N (2013) Plasticity of the Arabidopsis root system under nutrient deficiencies. Plant Physiol 163:161–179. doi:10.1104/pp.113.218453
Guo FQ, Crawford NM (2005) Arabidopsis nitric oxide synthase1 is targeted to mitochondria and protects against oxidative damage and dark-induced senescence. Plant Cell 17:3436–3450. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.037770
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. In: Circular California Agricultural Experiment Station 2nd edit. pp 32
Hochholdinger F, Park WJ, Sauer M, Woll K (2004) From weeds to crops: genetic analysis of root development in cereals. Trends Plant Sci 9:42–48. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2003.11.003
Jung JY, Shin R, Schachtman DP (2009) Ethylene mediates response and tolerance to potassium deprivation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:607–621. doi:10.1105/tpc.108.063099
Kellermeier F, Chardon F, Amtmann A (2013) Natural variation of Arabidopsis root architecture reveals complementing adaptive strategies to potassium starvation. Plant Physiol 161:1421–1432. doi:10.1104/pp.112.211144
Kolbert Z, Bartha B, Erdei L (2008) Exogenous auxin-induced NO synthesis is nitrate reductase- associated in Arabidopsis thaliana root primordial. J Plant Physiol 165:967–975. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2007.07.019
Kolbert Z, Ortega L, Erdei L (2010) Involvement of nitrate reductase (NR) in osmotic stress-induced NO generation of Arabidopsis thaliana L. roots. J Plant Physiol 167:77–80. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2009.08.013
Kuchenbuch R, Claassen N, Jungk A (1986) Potassium availability in relation to soil-moisture. Plant Soil 95:221–231. doi:10.1007/BF02375075
Leigh RA, Wyn JRG (1984) A hypothesis relating critical potassium concentrations for growth to the distribution and function of this ion in the plant cell. New Phytol 97:1–13. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1984.tb04103.x
Liebersbach H, Steingrobe B, Claassen N (2004) Roots regulate ion transport in the rhizosphere to counteract reduced mobility in dry soil. Plant Soil 260:79–88. doi:10.1023/B:PLSO.0000030191.92338.6a
Lira-Ruan V, Mendivil SN, Dubrovsky JG (2013) Heuristic aspect of the lateral root initiation index: a case study of the role of nitric oxide in root branching. Appl Plant Sci 1(10):1300029. doi:10.3732/apps.1300029
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–△△C T method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lombardo MC, Graziano M, Polacco JC, Lamattina L (2006) Nitric oxide functions as a positive regulator of root hair development. Plant Signal Behav 1:28–33. doi:10.4161/psb.1.1.2398
Ma L, Wu WH, Wang Y (2012) Transcriptome analysis of rice root responses to potassium deficiency. BMC Plant Biol 12:161. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-12-161
Manoli A, Begheldo M, Genre A, Lanfranco L, Trevisan S, Quaggiotti S (2014) NO homeostasis is a key regulator of early nitrate perception and root elongation in maize. J Exp Bot 65:185–200. doi:10.1093/jxb/ert358
Meng ZB, Chen LQ, Suo D, Li GX, Tang CX, Zheng SJ (2012) Nitric oxide is the shared signalling molecule in phosphorus-and iron-deficiency-induced formation of cluster roots in white lupin Lupinus albus. Ann Bot 109:1055–1064. doi:10.1093/aob/mcs024
Moreau M, Lee GI, Wang Y, Crane BR, Klessig DF (2008) AtNOS/A1 is a functional Arabidopsis thaliana cGTPase and not a nitric oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 283:32957–32967. doi:10.1074/jbc.M804838200
Muday GK, Rahman A, Binder BM (2012) Auxin and ethylene: collaborators or competitors? Trends Plant Sci 17:181–195. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2012.02.001
Ogawa T, Fukuoka H, Yano H, Ohkawa Y (1999) Relationships between nitrite reductase activity and genotype-dependent callus growth in rice cell cultures. Plant Cell Rep 18:576–581. doi:10.1007/s002990050625
Okada T, Nakayama H, Shinmyo A, Yoshida K (2008) Expression of OsHAK genes encoding potassium ion transporters in rice. Plant Biotechnol 25:241–245. doi:10.5511/plantbiotechnology.25.241
Pagnussat GC, Lanteri ML, Lamattina L (2003) Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP are messengers in the indole acetic acid-induced adventitious rooting process. Plant Physiol 132:1241–1248. doi:10.1104/pp.103.022228
Pyo YJ, Gierth M, Schroeder JI, Cho MH (2010) High-affinity K+ transport in Arabidopsis: AtHAK5 and AKT1 are vital for seedling establishment and postgermination growth under low-potassium conditions. Plant Physiol 153:863–875. doi:10.1104/pp.110.154369
Ree KV, Gehl B, Chehab EW et al (2011) Nitric oxide accumulation in Arabidopsis is independent of NOA1 in the presence of sucrose. Plant J 68:225–233. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04680.x
Ruan L, Zhang J, Xin X et al (2015) Comparative analysis of potassium deficiency-responsive transcriptomes in low potassium susceptible and tolerant wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Sci Rep 5:10090. doi:10.1038/srep10090
Santa-María GE, Rubio F, Dubcovsky J et al (1997) The HAK1 gene of barley is a member of a large gene family and encodes a high-affinity potassium transporter. Plant Cell 9:2281–2289. doi:10.1105/tpc.9.12.2281
Sanz L, Fernández-Marcos M, Modrego A et al (2014) Nitric oxide plays a role in stem cell niche homeostasis through its interaction with auxin. Plant Physiol 166:1972–1984. doi:10.1104/pp.114.247445
Schachtman DP, Shin R (2007) Nutrient sensing and signaling: NPKS. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:47–69. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103750
Schmidt GW, Delaney SK (2010) Stable internal reference genes for normalization of real-time RT-PCR in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) during development and abiotic stress. Mol Genet Genom 283:233–241. doi:10.1007/s00438-010-0511-1
Schroeder JI, Ward JM, Gassmann W (1994) Perspectives on the physiology and structure of inward-rectifying K+ channels in higher plants: biophysical implications for K+ uptake. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 23:441–471. doi:10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.002301
Shin R, Schachtman DP (2004) Hydrogen peroxide mediates plant root cell response to nutrient deprivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:8827–8832. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401707101
Song W, Liu S, Meng L et al (2015) Potassium deficiency inhibits lateral root development in tobacco seedlings by changing auxin distribution. Plant Soil 396:163–173. doi:10.1007/s11104-015-2579-1
Spalding EP, Hirsch RE, Lewis DR, Qi Z, Sussman MR, Lewis BD (1999) Potassium uptake supporting plant growth in the absence of AKT1 channel activity. J Gen Physiol 113:909–918. doi:10.1085/jgp.113.6.909
Srivastava N, Gonugunta VK, Puli MR, Raghavendra AS (2009) Nitric oxide production occurs downstream of reactive oxygen species in guard cells during stomatal closure induced by chitosan in abaxial epidermis of Pisum sativum. Planta 229:757–765. doi:10.1007/s00425-008-0855-5
Sun H, Li J, Song W et al (2015) Nitric oxide generated by nitrate reductase increases nitrogen uptake capacity by modulating lateral root formation and inorganic nitrogen uptake rate in rice. J Exp Bot 66:2449–2459. doi:10.1093/jxb/erv030
Sun H, Bi Y, Tao J et al (2016) Strigolactones are required for nitric oxide to induce root elongation in response to nitrogen and phosphate-deficiency in rice. Plant Cell Environ 39:1473–1484. doi:10.1111/pce.12709
Terrile MC, París R, Calderón-Villalobos LIA et al (2012) Nitric oxide influences auxin signaling through S-nitrosylation of the Arabidopsis TRANSPORT INHIBITOR RESPONSE 1 auxin receptor. Plant J 70:492–500. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04885.x
Trevisan S, Manoli A, Quaggiotti S (2014) NO signaling is a key component of the root growth response to nitrate in Zea mays L. Plant Signal Behav 9:28290. doi:10.4161/psb.28290
Wang Y, Wu W (2013) Potassium transport and signaling in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:451–476. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120153
Wang Y, Wu W (2015) Genetic approaches for improvement of the crop potassium acquisition and utilization efficiency. Curr Opin Plant Biol 25:46–52. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2015.04.007
Wang BL, Tang XY, Cheng LY et al (2010) Nitric oxide is involved in phosphorus deficiency-induced cluster-root development and citrate exudation in white lupin. New Phytol 187:1112–1123. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03323.x
Wang C, Chen H, Hao Q et al (2012) Transcript profile of the response of two soybean genotypes to potassium deficiency. PLoS ONE 7:e39856. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039856
Wilson ID, Neill SJ, Hancock JT (2008) Nitric oxide synthesis and signalling in plants. Plant Cell Environ 31:622–631. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01761.x
Xia J, Kong D, Xue S, Tian W, Li N, Bao F, Hu Y, Du J, Wang Y, Pan X, Wang L, Zhang X, Niu G, Feng X, Li L, He Y (2014) Nitric oxide negatively regulates AKT1-mediated potassium uptake through modulating vitamin B6 homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:16196–16201. doi:10.1073/pnas.1417473111
Xia X, Fan X, Wei J, Feng H, Qu H, Xie D, Miller AJ, Xu G (2015) Rice nitrate transporter OsNPF2.4 functions in low-affinity acquisition and long-distance transport. J Exp Bot 66:317–331. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru425
Xie Y, Mao Y, Lai D, Zhang W, Zheng T, Shen W (2013) Roles of NIA/NR/NOA1-dependent nitric oxide production and HY1 expression in the modulation of Arabidopsis salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 64:3045–3060. doi:10.1093/jxb/ert149
Yang T, Zhang S, Hu Y et al (2014) The role of a potassium transporter OsHAK5 in potassium acquisition and transport from roots to shoots in rice at low potassium supply levels. Plant Physiol 166:945–959. doi:10.1104/pp.114.246520
Zhang Z, Wang Q, Li Z, Duan L, Tian X (2009) Effects of potassium deficiency on root growth of cotton seedlings and its physiological mechanisms. Acta Agron Sin 35:718–723. doi:10.1016/S1875-2780(08)60079-6
Zhao D, Tian Q, Li L, Zhang W (2007) Nitric oxide is involved in nitrate-induced inhibition of root elongation in Zea mays. Ann Bot 100:497–503. doi:10.1093/aob/mcm142
Zhao M, Chen L, Zhang L, Zhang W (2009) Nitric reductase-dependent nitric oxide production is involved in cold acclimation and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 151:755–767. doi:10.1104/pp.109.140996
Zhou B, Guo Z, Xing J, Huang B (2005) Nitric oxide is involved in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant activities in Stylosanthes guianensis. J Exp Bot 56:3223–3228. doi:10.1093/jxb/eri319
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (31672225, 31471936, and 3601818), The Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP-TRIC03), Science Foundation for Young Scholars of Tobacco Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (No. 2016A03), Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201203013), China Tobacco General Project: Soil Nutrient Changes and Recovery with Variable Fertilization after Land Reclamation (2013-149), and by the China Scholarship Council (CSC). The English in this document has been checked by at least two professional editors, both native speakers of English. For a certificate, please see: http://www.textcheck.com/certificate/DNhvtC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Wenjing Song and Ren Xue contributed equally to this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
344_2017_9711_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary table 1 The primer of genes for qRT-PCR. Supplementary Fig S1 Effect of NO donor SNP on elongation of root development and NO accumulation in cv. NC89. Supplementary Fig S2 Effect of NO donor SNP on elongation of root development and NO accumulation in cv. Yunyan1. Supplementary Fig S3 The expression of CYCB1;1 gene in tobacco roots. (DOCX 891 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Xue, R., Song, Y. et al. Differential Response of First-Order Lateral Root Elongation to Low Potassium Involves Nitric Oxide in Two Tobacco Cultivars. J Plant Growth Regul 37, 114–127 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-017-9711-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-017-9711-9