Abstract
Aims
Potassium deficiency (LK) is a common abiotic stress that affects plant root development. We aimed to identify the role of auxin in LK effects on root growth.
Methods
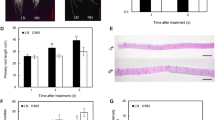
We investigated the effects of LK on the formation and elongation of first- and second-order lateral roots (LRs), auxin concentration, DR5::GUS expression, [3H]IAA transport and the expressions of six PIN genes in roots of tobacco plants. We also examined the effects of exogenous auxin (NAA) and a transport inhibitor (NPA) on LR growth and DR5::GUS expression.
Results
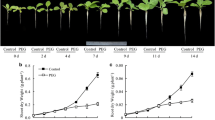
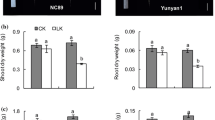
Potassium deficiency reduced root growth, mostly by impairing the formation and elongation of first-order LRs. Indole acetic acid (IAA) concentration and DR5::GUS expression levels decreased in leaves and roots subjected to LK, indicating that LK affected auxin distribution. [3H]IAA transport and the expression levels of PIN genes were reduced by LK, showing that auxin polar transport was inhibited by LK. Application of NAA to LK-treated plants increased first-order LR formation and elongation to levels similar to the control, an outcome that was consistent with the similarity in DR5::GUS expression levels between treatments. NPA acted in a converse manner.
Conclusions
Potassium deficiency inhibited LR formation and elongation in tobacco plants by shifting auxin distribution.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armengaud P, Breitling R, Amtmann A (2004) The potassium-dependent transcriptome of Arabidopsis reveals a prominent role of jasmonic acid in nutrient signaling. Plant Physiol 136:2556–2576. doi:10.1104/pp. 104.046482
Barber SA (1995) Potassium, in soil nutrient bioavailability. In: A Mechanistic Approach. Wiley, New York, pp 231–232
Blakeslee JJ, Peer WA, Murphy AS (2005) Auxin transport. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:494–500. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2005.07.014
Cai J, Chen L, Qu H, Lian J, Liu W, Hu Y, Xu G (2012) Alteration of nutrient allocation and transporter genes expression in rice under N, P, K, and Mg deficiencies. Acta Physiol Plant 34:939–946. doi:10.1007/s11738-011-0890-x
Cao Y, Glass AD, Crawford NM (1993) Ammonium inhibition of Arabidopsis root growth can be reversed by potassium and by auxin resistance mutations aux1, axr1, and axr2. Plant Physiol 102:983–989. doi:10.1104/pp. 102.3.983
Casimiro I, Marchant A, Bhalerao R, Beeckman T, Dhooge S, Swarup R, Graham N, Inzé D, Sandberg G, Casero PJ, Bennett M (2001) Auxin transport promotes Arabidopsis lateral root initiation. Plant Cell 13:843–852. doi:10.1105/tpc.13.4.843
Clarkson DT, Hanson JB (1980) The mineral nutrition of higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 31:239–298. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp. 31.060180.001323
De Smet I, Vanneste S, Inze D, Beeckman T (2006) Lateral root initiation or the birth of a new meristem. Plant Mol Biol 60:871–887. doi:10.1007/s11103-005-4547-2
Den Herder G, Van Isterdael G, Beeckman T, De Smet I (2010) The roots of a new green revolution. Trends Plant Sci 15:600–607. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2010.08.009
Dolan L (2013) Pointing PINs in the right directions: a potassium transporter is required for the polar localization of auxin efflux carriers. New Phytol 197:1027–1028. doi:10.1111/nph.12151
Dolan L, Davies J (2004) Cell expansion in roots. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:33–39. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2003.11.006
Drew MC (1975) Comparison of the effects of a localized supply of phosphate, nitrate, ammonium and potassium on the growth of the seminal root system, and the shoot in barley. New Phytol 75:490–749. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1975.tb01409.x
Dubrovsky JG, Sauer M, Napsucialy-Mendivil S et al (2008) Auxin acts as a local morphogenetic trigger to specify lateral root founder cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 25:8790–8794. doi:10.1073/pnas.0712307105
Forde BG (2002) Local and long-range signaling pathways regulating plant responses to nitrate. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:203–224. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.100301. 135256
Friml J (2003) Auxin transport-shaping the plant. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:7–12. doi:10.1016/S1369526602000031
Gruber BD, Giehl RFH, Friedel S et al (2013) Plasticity of the Arabidopsis root system under nutrient deficiencies. Plant Physiol 163:161–179. doi:10.1104/pp. 113.218453
Hammer GL, Dong ZS, McLean G, Doherty A, Messina C, Schusler J, Zinselmeier C, Paszkiewicz S, Cooper M (2009) Can changes in canopy and/or root system architecture explain historical maize yield trends in the US Corn Belt? Crop Sci 49:299–312. doi:10.2135/cropsci2008.03.0152
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) Circular California Agricultural Experiment Station. In: The water-culture method for growing plants without soil, 2nd edit. pp 32
Hochholdinger F, Park WJ, Sauer M, Woll K (2004) From weeds to crops: genetic analysis of root development in cereals. Trends Plant Sci 9:42–48. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2003.11.003
Jia Y, Yang X, Feng Y, Jilani G (2008) Differential response of root morphology to potassium deficient stress among rice genotypes varying in potassium efficiency. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 9:427–434. doi:10.1631/jzus.B0710636
Jiang F, Li CJ, Jeschke WD, Zhang FS (2001) Effect of top excision and replacement by 1-naphthylacetic acid on partition and flow of potassium in tobacco plants. J Exp Bot 52:2143–2150. doi:10.1093/jexbot/52.364.2143
Jung JY, Shin R, Schachtman DP (2009) Ethylene mediates response and tolerance to potassium deprivation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:607–621. doi:10.1105/tpc.108.063099
Kazan K (2013) Auxin and the integration of environmental signals into plant root development. Ann Bot 112:1655–1665. doi:10.1093/aob/mct229
Kellermeier F, Chardon F, Amtmann A (2013) Natural variation of Arabidopsis root architecture reveals complementing adaptive strategies to potassium starvation. Plant Physiol 161:1421–1432. doi:10.1104/pp. 112.211144
Kim MJ, Ciani S, Schachtman DP (2010) A peroxidase contributes to ROS production during Arabidopsis root response to potassium deficiency. Mol Plant 3:420–422. doi:10.1093/mp/ssp121
Kuchenbuch R, Claassen N, Jungk A (1986) Potassium availability in relation to soil-moisture. 1. Effect of soil-moisture on potassium diffusion, root-growth and potassium uptake of onion plants. Plant Soil 95:221–231. doi:10.1007/BF02375075
Leigh RA, Wyn Jones RG (1984) A hypothesis relating critical potassium concentrations for growth to the distribution and function of this ion in the plant cell. New Phytol 97:1–13. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1984.tb04103.x
Liebersbach H, Steingrobe B, Claassen N (2004) Roots regulate ion transport in the rhizosphere to counteract reduced mobility in dry soil. Plant Soil 260:79–88. doi:10.1023/B:PLSO.0000030191.92338.6a
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-△△C T method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Ljung K, Bhalerao RP, Sandberg G (2001) Sites and homeostatic control of auxin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis during vegetative growth. Plant J 28:465–474. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2001.01173.x
Ma L, Wu WH, Wang Y (2012) Transcriptome analysis of rice root responses to potassium deficiency. BMC Plant Biol 12:161. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-12-161
Mi GH, Chen FJ, Wu QP, Lai NW, Yuan LX, Zhang FS (2010) Ideotype root architecture for efficient nitrogen acquisition by maize in intensive cropping systems. Sci China Life Sci 53:1369–1373. doi:10.1007/s11427-010-4097-y
Nam YJ, Tran LSP, Kojima M, Sakakibara H et al (2012) Regulatory roles of cytokinins and cytokinin signaling in response to potassium deficiency in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 7:e47797. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047797
Peret B, Swarup K, Ferguson A, Seth M, Yang Y, Dhondt S, James N, Casimiro I, Perry P, Syed A (2012) AUX/LAX genes encode a family of auxin influx transporters that perform distinct functions during Arabidopsis development. Plant Cell 24:2874–2885. doi:10.1105/tpc.112.097766
Rigas S, Ditengou FA, Ljung K et al (2013) Root gravitropism and root hair development constitute coupled developmental responses regulated by auxin homeostasis in the Arabidopsis root apex. New Phytol 197:1130–1141. doi:10.1111/nph.12092
Schmidt GW, Delaney SK (2010) Stable internal reference genes for normalization of real-time RT-PCR in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) during development and abiotic stress. Mol Genet Genomics 283:233–241. doi:10.1007/s00438-010-0511-1
Schroeder JI, Ward JM, Gassmann W (1994) Perspectives on the physiology and structure of inward-rectifying K+ channels in higher plants: biophysical implications for K+ uptake. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 23:441–471. doi:10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.002301
Shin R, Schachtman DP (2004) Hydrogen peroxide mediates plant root cell response to nutrient deprivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:8827–8832. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401707101
Song W, Sun H, Li J, Gong X, Huang S, Zhu X, Zhang Y, Xu G (2013) Auxin distribution is differentially affected by nitrate in roots of two rice cultivars differing in responsiveness to nitrogen. Ann Bot 112:1383–1393. doi:10.1093/aob/mct212
Sun H, Tao J, Liu S, Huang S, Chen S, Xie X, Yoneyama K, Zhang Y, Xu G (2014) Strigolactones are involved in phosphate and nitrate deficiency-induced root development and auxin transport in rice. J Exp Bot 65:6735–6746. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru029
Tao LZ, Cheung AY, Wu HM (2002) Plant Rac-like GTPases are activated by auxin and mediate auxin-responsive gene expression. Plant Cell 14:2745–2760. doi:10.1105/tpc.006320
Ulmasov T, Murfett J, Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ (1997) Aux/IAA proteins repress expression of reporter genes containing natural and highly active synthetic auxin response elements. Plant Cell 9:1963–1971. doi:10.1105/tpc.9.11.1963
Vanneste S, Firml J (2009) Auxin: a trigger for change in plant development. Cell 136:1005–1016. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.001
Vicente-Agullo F, Rigas S, Desbrosses G, Dolan L, Hatzopoulos P et al (2004) Potassium carrier TRH1 is required for auxin transport in Arabidopsis roots. Plant J 40:523–535. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02230.x
Wisniewska J, Xu J, Seifertova D, Brewer PB, Ruzicka K, Blilou I, Rouquie D, Benkova E, Scheres B, Friml J (2006) Polar PIN localization directs auxin flow in plants. Science 312:883–883. doi:10.1126/science.1121356
Zazimalova E, Murphy AS, Yang H, Hoyerova K, Hosek P (2010) Auxin transporters-why so many? Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2:a001552. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a001552
Zhang Z, Wang Q, Li Z, Duan L, Tian X (2009) Effects of potassium deficiency on root growth of cotton seedlings and its physiological mechanisms. Acta Agron Sin 35:718–723. doi:10.1016/S1875-2780(08)60079-6
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China, the Key Laboratory of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, Ministry of Agriculture, P. R. China (no. 2013–5), Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201203013) and the China Scholarship Council (CSC). The English in this document has been checked by at least two professional editors, both native speakers of English. For a certificate, please see: http://www.textcheck.com/certificate/Wm8KJB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guillermo Santa Maria.
Wenjing Song and Shangjun Liu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table S1
The primers for qRT-PCR of NtL25 and six NtPIN genes. (PDF 4 kb)
Supplementary Fig S1
Phenotypes of first-order LR with its second-order LR in response to K+ deficiency. (PDF 30 kb)
Supplementary Fig S2
Histochemical localization of DR5::GUS in topmost fully expanded leaf and leaf primordium. (PDF 26 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Liu, S., Meng, L. et al. Potassium deficiency inhibits lateral root development in tobacco seedlings by changing auxin distribution. Plant Soil 396, 163–173 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2579-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2579-1