Abstract
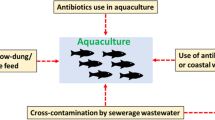
Emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in cultured fishes is one of the major challenges faced in aquaculture. The high prevalence of bacterial infections in fishes leads to frequent use of antibiotics and thus their persistence in the aquatic environment, which in turn results in the proliferation of antibiotic resistant bacteria. The AMR in aquaculture can be transferred to clinically important strains of natural environment through horizontal gene transfer, thereby affecting the whole ecosystem. Most of the cultured fishes, including ornamental possess diverse pathogens exhibiting multiple antibiotic resistance. A thorough understanding of the gene transfer systems such as plasmids, transposons, integrons and gene cassettes can unravel the complexity of antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture. Continuous monitoring programmes, timely detections of the resistant bacteria and implementation of proper regulations are necessary to curb the dissemination of AMR in aquaculture. The present review summarises the antimicrobial use and AMR in cultured fishes, genetic mechanisms involved in the development of resistance, and the management strategies to restrict the spread of AMR in aquaculture.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMR:
-
Antimicrobial Resistance
- ARG:
-
Antimicrobial Resistant Gene
- MGE:
-
Mobile genetic elements
- HGT:
-
Horizontal gene transfer
- MIC:
-
Minimum inhibitory concentration
- MAR:
-
Multiple Antibiotic Resistance
- ESBL:
-
Extended spectrum beta lactamases
- CI:
-
Chromosomal integrons
- MI:
-
Mobile integrons
- MRI:
-
Multidrug resistance integrons
- GC:
-
Gene cassettes
References
Abraham TJ, Manley R, Palaniappan R, Dhevendaran K (1997) Pathogenicity and antibiotic sensitivity of luminous Vibrio harveyi isolated from diseased penaeid shrimp. J Aquacult Trop 121:1–8
Agerso Y, Guardabassi L (2005) Identification of Tet 39, a novel class of tetracycline resistance determinant in Acinetobacter spp. of environmental and clinical origin. J Antimicrob Chemother 55:566–569. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dki051
Agersø Y, Petersen A (2007) The tetracycline resistance determinant Tet 39 and the sulphonamide resistance gene sulII are common among resistant Acinetobacter spp. isolated from integrated fish farms in Thailand. J Antimicrob Chemother 59:23–27. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkl419
Agersø Y, Bruun MS, Dalsgaard I, Larsen JL (2007) The tetracycline resistance gene tet(E) is frequently occurring and present on large horizontally transferable plasmids in Aeromonas spp. from fish farms. Aquaculture 266:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.01.012
Agoba EE, Agyare AFC, Boamah VE, Boakye YD (2017) Antibiotic resistance patterns of bacterial isolates from hatcheries and selected fish farms in the Ashanti region of Ghana. J Microbiol Antimicrob 9:35–46. https://doi.org/10.5897/JMA2017.0387
Akinbowale OL, Peng H, Barton MD (2006) Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria isolated from aquaculture sources in Australia. J Appl Microbiol 100:1103–1113. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.02812.x
Akinbowale OL, Peng H, Grant P, Barton MD (2007) Antibiotic and heavy metal resistance in motile aeromonads and pseudomonads from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farms in Australia. Int J Antimicrob Agents 30:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.03.012
Al-Bahry SN, Mahmoud IY, Al-Belushi KI, Elshafie AE, Al-Harthy A, Bakheit CK (2009) Coastal sewage discharge and its impact on fish withreference to antibiotic resistant enteric bacteria and enteric pathogens as bio-indicators of pollution. Chemosphere 77:1534–1539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.09.052
Alcaide E, Blasco M-D, Esteve C (2005) Occurrence of drug-resistant bacteria in two European eel farms. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3348–3350. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.6.3348-3350.2005
Alderman DJ, Hastings TS (1998) Antibiotic use in aquaculture: development of antibiotic resistance – potential for consumer health risks. Int J Food Sci Technol 33:139–155. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2621.1998.3320139.x
Alekshun MN, Levy SB (2007) Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell 128:1037–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.004
Almeida A, Cunha A, Gomes NCM, Alves E, Costa L, Faustino MAF (2009) Phage therapy and photodynamic therapy: low environmental impact approaches to inactivate microorganisms in fish farming plants. Mar drugs 7:268–313. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7030268
Aoki T, Egusa S, Arai T (1974) Detection of R factors in naturally occurring Vibrio anguillarum strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 6:534–538. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.6.5.534
Ashiru A, Uaboi-Egbeni P, Oguntowo J, Idika C (2011) Isolation and antibiotic profile of Aeromonas species from tilapia fish (Tilapia nilotica) and catfish (Clariasbetrachus). Pak J Nutr 10:982–986. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjn.2011.982.986
Assane IM, Gozi KS, Valladao GMR, Pilarski F (2019) Combination of antimicrobials as an approach to reduce their application in aquaculture: emphasis on the use of thiamphenicol/florfenicol against Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 507:238–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.04.021
Bansemir A, Blume M, Schröder S, Lindequist U (2006) Screening of cultivated seaweeds for antibacterial activity against fish pathogenic bacteria. Aquaculture 252:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.11.051
Baquero F, Negri M-C, Morosini M-I, Blazquez J (1998) Antibiotic-selective environments. Clin Infect Dis 27(Suppl. 1):S5–S11. https://doi.org/10.1086/514916
Bennett PM (2005) Genome plasticity. In: Woodford N, Johnson A (eds) methods in molecular biology, Vol 266. Genomics, proteomics and clinical bacteriology. Humana press Inc., Totowa, pp 71–113
Bennett PM (2008) Plasmid encoded antibiotic resistance: acquisition and transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria. Br J Pharmacol 153(Suppl 1):S347–S357. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0707607
Botrel MA, Haenni M, Morignat E, Sulpice P, Madec JY, Calavas D (2010) Distribution and antimicrobial resistance of clinical and subclinical mastitis pathogens in dairy cows in Rhône-Alpes, France. Foodborne Pathog Dis 7:479–487. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2009.0425
Brunton LA, Desbois AP, Garza M, Wieland B, Mohan CV, Häsler B, Tam CC, Le PNT, Nguyen TP, Van PT et al (2019) Identifying hotspots for antibiotic resistance emergence and selection, and elucidating pathways to human exposure: application of a systems-thinking approach to aquaculture systems. Sci Total Environ 687:1344–1356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.134
Burridge L, Weis JS, Cabello F, Pizarro J, Bostick K (2010) Chemical use in salmon aquaculture: a review of current practices and possible environmental effects. Aquaculture 306:7–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.05.020
Buschmann AH, Tomova A, Lopez A, Maldonado MA, Henriquez LA, Ivanova L, Moy F, Godfrey HP, Cabello FC (2012) Salmon aquaculture and antimicrobial resistance in the marine environment. PLoS One 7:e42724. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042724
Cabello FC (2004) Antibiotics and aquaculture in Chile: implications for human and animal health. Rev Med Chil 132:1001–1006. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0034-98872004000800014
Cabello FC (2006) Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: a growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environ Microbiol 8:1137–1144. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01054.x
Cabello FC, Godfrey HP, Tomova A, Ivanova L, Do¨lz H, Millanao A, Buschmann AH (2013) Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ Microbiol 15:1917–1942. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12134
Cambray G, Sanchez-Alberola N, Campoy S, Guerin E, Da Re S, Gonzalez-Zorn B, Ploy M-C, Barbe J, Mazel D, Erill I (2011) Prevalence of SOS-mediated control of integron integrase expression as an adaptive trait of chromosomal and mobile integrons. Mob DNA 2:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1759-8753-2-6
Castillo D, Higuera G, Villa M, Middelboe M, Dalsgaard I, Madsen L, Espejo RT (2012) Diversity of Flavobacterium psychrophilum and the potential use of its phages for protection against bacterial cold water disease in salmonids. J Fish Dis 35:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2011.01336.x
Castillo D, Christiansen RH, Dalsgaard I, Madsen L, Middelboe M (2015) Bacteriophage resistance mechanisms in the fish pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum: linking genomic mutations to changes in bacterial virulence factors. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:1157–1167. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03699-14
Cattoir V, Nordmann P (2009) Plasmid-mediated quinoloneb resistance in gram-negative bacterial species: an update. Curr Med Chem 16:1028–1046. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986709787581879
Cavalli LS, Brito KCT, Brito BG (2015). One health, one aquaculture: aquaculture under One Health umbrella. J Mar Biol Aquacult 2015:1:1–8.
Chabrillon M, Rico RM, Arijo S, Diaz-Rosales P, Balebona MC, Morinigo MA (2005) Interactions of microorganisms isolated from gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata L., on Vibrio harveyi, a pathogen of farmed Senegalese sole, Solea senegalensis (Kaup). J Fish Dis 28:531–537. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2005.00657.x
Chenia HY (2016) Prevalence and characterization of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Aeromonas spp. isolated from south African freshwater fish. Int J Food Microbiol 231:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.04.030
Chenia HY, Vietze C (2012) Tetracycline resistance determinants of heterotrophic bacteria isolated from a south African tilapia aquaculture system. Afr J Microbiol Res 6:6761–6768. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR10.840
Chiew Y-F, Yeo S-F, Hall LMC, Livermore DM (1998) Can susceptibility to an antimicrobial be restored by halting its use? The case of streptomycine versus Enterobacteriaceae. J Antimicrob Chemother 41:247–251. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/41.2.247
Chuah L, Effarizah ME, Goni AM, Rusul G (2016) Antibiotic application and emergence of multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) in global catfish aquaculture. Curr Environ Health Rep 3:118–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-016-0091-2
Cizek A, Dolejska M, Sochorova R, Strachotova K, Piackova V, Vesely T (2010) Antimicrobial resistance and its genetic determinants in aeromonads isolated in ornamental (koi) carp (Cyprinus carpio koi) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Vet Microbiol 142:435–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.10.001
Dang HY, Zhang XX, Song LS, Chang YQ, Yang GP (2007) Molecular determination of oxytetracycline-resistant bacteria and their resistance genes from mariculture environments of China. J Appl Microbiol 103:2580–2592. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03494.x
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Esteban MA (2017) Beneficial roles of feed additives as immunostimulants in aquaculture: areview. Rev Aquacult 10:950–974. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12209
Declercq AM, Boyen F, Van den Broeck W, Bossier P, Karsi A, Haesebrouck F, Decostere A (2013) Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Flavobacterium columnare isolates collected worldwide from 17 fish species. J Fish Dis 36:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2012.01410.x
Defoirdt T, Sorgeloos P, Bossier P (2011) Alternatives to antibiotics for the control of bacterial disease in aquaculture. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2011.03.004
Deng W, Li N, Zheng H, Lin H (2016) Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in river water in Hong Kong. Ecotox Environ Safe 125:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.12.002
Desriac F, Defer D, Bourgougnon N, Brillet B, Chevalier PL, Fleury Y (2010) Bacteriocin as weapons in the marine animal-associated bacteria warfare: inventory and potential applications as an aquaculture probiotic. Mar Drugs 8:1153–1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8041153
Destoumieux-Garzón D, Mavingui P, Boetsch G, Boissier J, Darriet F, Duboz P, et al. (2018) The one health concept: 10 years old and a long road ahead. Front Vet Sci 5:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2018.00014
Dharmaratnam A, Kumar R, Basheer VS, Sood N, Swaminathan TR, Jena JK (2017) Isolation and characterisation of virulent Serratia marcescens associated with a disease outbreak in farmed ornamental fish, Poecilia reticulata in Kerala, India. Indian J fish 64:71–79. https://doi.org/10.21077/ijf.2017.64.4.71261-10
Dias C, Mota V, Martinez-Murcia A, Saavedra MJ (2012) Antimicrobial resistance patterns of Aeromonas spp. isolated from ornamental fish. J Aquac res Dev 3: 3. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9546.1000131
Dixon BA, Issvoran G (1993) Antibacterial drug resistance in Aeromonas spp. isolated from domestic goldfish and koi from California. J World Aquacult Soc 24:102–104. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.1993.tb00155.x
Dixon BA, Yamashita J, Evelyn F (1990) Antibiotic resistance of Aeromonas spp. isolated from tropical fish imported from Singapore. J Aquat Anim Health 2:295–297. https://doi.org/10.1577/1548-8667(1990)002<0295:AROASI>2.3.CO;2
Dobiasova H, Kutilova I, Piackova V, Vesely T, Cizek A, Dolejska M (2014) Ornamental fish as a source of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes and antibiotic resistance plasmids. Vet Microbiol 171:413–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.02.011
Done HY, Halden RU (2015) Reconnaissance of 47 antibiotics and associated microbial risks in seafood sold in the United States. J Hazard Mater 282:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.075
Done HY, Venkatesan AK, Halden RU (2015) Does the recent growth of aquaculture create antibiotic resistance threats different from those associated with land animal production in agriculture? AAPS J 17:513–524. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-015-9722-z
Duran GM, Marshall DL (2005) Ready-to-eat shrimp as an international vehicle of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. J Food Prot 68:2395–2401. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-68.11.2395
Enne VI, Livermore DM, Stephens P, Hall LM (2001) Persistence of sulphonamide resistance in Escherichia coli in the UK despite national prescribing restriction. Lancet 357:1325–1328. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04519-0
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) 2005. Responsible use of antibiotics in Aquaculture. In: Serrano PH (eds) Available: http://www.fao.org/3/a-a0282e.pdf
FAO/OIE/WHO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Organization for Animal Health/ World Health Organization) 2006. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture and antimicrobial Resistance. Available: http://www.who.int/topics/foodborne_diseases/aquaculture_rep_13_16june2006.pdf. [accessed 18 April 2013]
Furushita M, Shiba T, Maeda T, Yahata M, Kaneoka A, Takahashi Y, Torii K, Hasegawa T, Ohta M (2003) Similarity of tetracycline resistance genes isolated from fish farm bacteria to those from clinical isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5336–5342. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.9.5336-5342.2003
Gao P, Mao D, Luo Y, Wang L, Xu B, Xu L (2012) Occurrence of sulfonamide and tetracycline-resistant bacteria and resistant genes in aquaculture environment. Water Res 46:2355–2364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.02.004
Grave K, Markestad A, Bangen M (1996) Comparison in prescribing patterns of antibacterial drugs in salmonid farming in Norway during the periods 1980–1988 and 1989–1994. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 19:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2885.1996.tb00037.x
Guz L, Grazdzki Z, Krajewska M, Lipiec M, Zabost A, Augustynowicz-Kopec E, Zwolska Z, Szulowski K (2013) Occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Mycobacterium peregrinum in ornamental fish. B. Vet I Pulawy 57:489–492. https://doi.org/10.2478/bvip-2013-0085
Han JE, Kim JH, Cheresca CH, Shin SP, Jun JW, Chai JY, Han SY, Park SC (2012) First description of the qnrS-like (qnrS5) gene and analysis of quinolone resistance-determining regions in motile Aeromonas spp. from diseased fish and water. Res Microbiol 163:73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2011.09.001
Han Y, Wang J, Zhao Z, Chen J, Lu H, Liu G (2017) Fish meal application induces antibiotic resistance gene propagation in mariculture sediment. Environ Sci Technol 51:10850–10860. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02875
Hansson K, Sundström L, Pelletier A, Roy PH (2002) Int I 2 integron integrase in Tn7. J Bacteriol 184:1712–1721. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.184.6.1712-1721.2002
Harikrishnan R, Kim JS, Balasundaram C, Heo MS (2012) Protection of Vibrio harveyi infection through dietary administration of Pueraria thunbergiana in kelp grouper, Epinephelus bruneus. Aquaculture 325:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.10.019
Hatha M, Vivekanandhan AA, Joice GJ, Christol (2005) Antibiotic resistance pattern of motile aeromonads from farm raised freshwater fish. Int J Food Microbiol 98:131–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.05.017
Hesami S, Parkman J, MacInnes JI, Gray JT, Gyles CL, Lumsden JS (2010) Antimicrobial susceptibility of Flavobacterium psychrophilum isolates from Ontario. J Aquat Anim Health 22:39–49. https://doi.org/10.1577/H09-008.1
Heuer OE, Kruse H, Grave K, Collignon P, Karunasagar I, Angulo FJ (2009) Human health consequences of use of antimicrobial agents in aquaculture. Clin Infect Dis 49:1248–1253. https://doi.org/10.1086/605667
Homem V, Santos L (2011) Degradation and removal methods of antibiotics from aqueous matrices - a review. J Environ Manag 92:2304–2347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.05.023
Hooper DC, Jacoby GA (2015) Mechanisms of drug resistance: quinolone resistance. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1354:12–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12830
Huang Y, Michael GB, Becker R, Kaspar H, Mankertz J, Schwarz S, Runge M, Steinhagen D (2014) Pheno- and genotypic analysis of antimicrobial resistance properties of Yersinia ruckeri from fish. Vet Microbiol 171:406–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.10.026
Huang Y, Zhang L, Tiu L, Wang HH (2015) Characterization of antibiotic resistance in commensal bacteria from an aquaculture ecosystem. Front Microbiol 6:914. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00914
Huss HH, Reilly A, Embarek PKB (2000) Prevention and control of hazards in seafoods. Food Control 11:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-7135(99)00087-0
Igbinosa IH, Igumbor EU, Aghdasi F, Tom M, Okoh AI (2012) Emerging Aeromonas species infections and their significance in public health. Sci World J 12:625023. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/625023
Izumi S, Ouchi S, Kuge T, Arai H, Mito T, Fujii H, Aranishi F, Shimizu A (2007) PCR–RFLP genotypes associated with quinolone resistance in isolates of Flavobacterium psychrophilum. J Fish Dis 30:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2007.00797.x
Jacobs L, Chenia HY (2007) Characterization of integrons and tetracycline resistance determinants in Aeromonas spp. isolated from south African aquaculture systems. Int J Food Microbiol 114:295–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2006.09.030
Jacoby GA, Hooper DC (2013) Phylogenetic analysis of chromosomally determined Qnr and related proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:1930–1934. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02080-12
Jagoda SS, Wijewardana TG, Arulkanthan A, Igarashi Y, Tan E, Kinoshita S, Watabe S, Asakawa S (2014) Characterization and antimicrobial susceptibility of motile aeromonads isolated from freshwater ornamental fish showing signs of septicaemia. Dis Aquat Org 109:127–137. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao02733
John N, Hatha AAM (2012) Prevalence, distribution and drug resistance of motile aeromonads in freshwater ornamental fishes. Indian J Fish 59:161–164
Kadowaki T, Yasui Y, Nishimiya O, Takahishi Y, Kohchi C, Soma GI, Inagawa H (2013) Orally administered LPS enhances head kidney macrophage activation with downregulation of IL-6 in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Shellfish Immunol 34:1569–1575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.03.372
Kang C-H, Shin Y, Jang S, Jung Y, So J-S (2016) Antimicrobial susceptibility of Vibrio alginolyticus isolate from oyster in Korea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:21106–21112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7426-2
Kim E, Aoki T (1993) Drug resistance and broad geographical distribution of identical R plasmids of Pasteurella piscicida isolated from cultured yellowtail in Japan. Microbiol Immunol 37:103–109
Kim EH, Yoshida T, Aoki TBB (1993) Detection of R plasmid encoded with resistance to florfenicol in Pasteurella piscicida. Fish Pathol 28:165–170. https://doi.org/10.3147/jsfp.28.165
Kim S-R, Nonaka L, Suzuki S (2004) Occurrence oftetracycline resistance genes tet(M) and tet(S) in bacteriafrom marine aquaculture sites. FEMS Microbiol Lett 237:147–156.
Kim MJ, Hirono I, Kurokawa K, Maki T, Hawke J, Kondo H, Santos MD, Aoki T (2008) Complete DNA sequence and analysis of the transferable multiple-drug resistance plasmids (R plasmids) from Photo- bacterium damselae subsp. piscicida isolates collected in Japan and the United States. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52: 606–611.
Ko WC, Lee HC, Chuang YC, Liu CC, Wu JJ (2000) Clinical features and therapeutic implications of 104 episodes of monomicrobial Aeromonas bacteraemia. J Inf Secur 40:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1053/jinf.2000.0654
Kruse H, Sørum H (1994) Transfer of multiresistance plasmids between bacteria of diverse origin in natural micro-environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:4015–4021
Kumar SR, Ahmed VPI, Parameswaran V, Sudhakaran R, Babu VS, Hameed AS (2008) Potential use of chitosan nanoparticles for oral delivery of DNA vaccine in Asian sea bass (Lates clacrifer) to protect from Vibrio (Listonella) anguillarum. Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:47e56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2007.12.004
Kumar R, Swaminathan TR, Kumar RG, Dharmaratnam A, Basheer VS, Jena JK (2015) Mass mortality in ornamental fish, Cyprinus carpio koi caused by a bacterial pathogen, Proteus hauseri. Acta Trop 149:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2015.05.022
Kumar S, Lekshmi M, Parvathi A, Nayak BB, Varela MF (2017) Antibiotic resistance in seafood borne pathogens. In: Singh OV (ed) Food borne pathogens and antibiotic resistance. Wiley, Hoboken
Labbate M, Case RJ, Stokes HW (2009) The Integron/gene cassette system: an active player in bacterial adaptation. In: Gogarten MB, Gogarten JP, Olendzenski LC (eds) Horizontal gene transfer. Methods in molecular biology, vol 532, pp 103–125
Labee-Lund TM, Sorum H (2001) Class I integrons mediated antibiotic resistance in the fish pathogen Aeromonas salmonicida world-wide. Microb Drug Resist 7:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1089/10766290152652819
Labella A, Gennari M, Ghidini V, Trento I, Manfrin A, Borrego JJ, Lleo MM (2013) High incidence of antibiotic multi-resistant bacteria in coastal areas dedicated to fish farming. Mar Pollut Bull 70:197–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.02.037
Lamari F, Chakroun I, Rtimi S (2017) Assessment of the correlation among antibiotic resistance, adherence to abiotic and biotic surfaces, invasion and cytotoxicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from diseased gilthead sea bream. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 158:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.06.044
Larsson DGJ, Andremont A, Bengtsson-Palme J, Brandt KK, de Roda Husman AM, Fagerstedt P, Fick J, Flach CF, Gaze WH, Kuroda M, Kvint K, Laxminarayan R, Manaia CM, Nielsen KM, Plant L, Ploy M-C, Segovia C, Simonet P, Smalla K, Snape J, Topp E, van Hengel AJ, Verner-Jeffreys DW, Virta MPJ, Wellington EM, Wernersson AS (2018) Critical knowledge gaps and research needs related to the environmental dimensions of antibiotic resistance. Environ Int 117:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.04.041
Lewbart GA (2001) Bacteria and ornamental fish. Seminars in Avian and Exotic Pet Medicine 10:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1053/saep.2001.19543
Li XZ (2005) Quinolone resistance in bacteria: emphasis on plasmidmediated mechanisms. Int J Antimicrob Agents 25:453–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2005.04.002
Li D, Yu T, Zhang Y, Yang M, Li Z, Liu M, Qi R (2010) Antibiotic resistance characteristics of environmental bacteria from an oxytetracycline production wastewater treatment plant and the receiving river. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3444–3451. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02964-09
Li L, Lin S-L, Deng L, Liu Z-G (2013) Potential use of chitosan microparticles for oral delivery of DNA vaccine in black seabream Acanthopagrus schlegelii Bleeker to protect from Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Fish Dis 36:987–995. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12032
Liu X, Steele JC, Meng X-Z (2017) Usage, residue, and human health risk of antibiotics in Chinese aquaculture: a review. Environ Pollut 223:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.01.003
Lozano I, Díaz NF, Muñoz S, Riquelme C (2018) Antibiotics in Chilean aquaculture: a review. Antibiotic Use in Animals p, In, p 21. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.71780
Lulijwa R, Rupia EJ, Alfaro AC (2019) Antibiotic use in aquaculture, policies and regulation, health and environmental risks: a review of the top 15 major producers. Rev Aquacult (in press). https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12344
Lunn AD, Fabrega A, Sanchez-Cespedes J, Vila J (2010) Prevalence of mechanisms decreasing quinolone-susceptibility among Salmonella spp. clinical isolates. Int Microbiol 13:15e20. https://doi.org/10.2436/20.1501.01.107
Luo Y, Mao D, Rysz M, Zhou Q, Zhang H, Xu L, Alvarez PJJ (2010) Trends in antibiotic resistance genes occurrence in the Haihe River, China. Environ Sci Technol 44:7220–7225. https://doi.org/10.1021/es100233w
Marshall SH, Arenas G (2003) Antimicrobial peptides: a natural alternative to chemical antibiotics and a potential for applied biotechnology. Electron J Biotechnol 6:271–284. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol6-issue3-fulltext-1
Marti E, Huerta B, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Barceló D, Marcé R, Balcázar JL (2018) Abundance of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community composition in wild freshwater fish species. Chemosphere 196:115–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.108
McPhearson RM, DePaola A, Zywno SR, Motes ML, Guarino AM (1991) Antibiotic-resistance in gram-negative bacteria from cultured catfish and aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture 99:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(91)90241-X
Michel C, Kerouault B, Martin C (2003) Chloramphenicol and florfenicol susceptibility of fish—pathogenic bacteria isolated in France: comparison of minimum inhibitory concentration, using recommended provisory standards for fish bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 95:1008–1015. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2003.02093.x
Michel C, Matte-Tailliez O, Kerouault B, Bernardet J-F (2005) Resistance pattern and assessment of phenicol agents’ minimum inhibitory concentration in multiple drug resistant Chryseobacterium isolates from fish and aquatic habitats. J Appl Microiol 99:323–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02592.x
Miranda CD, Kehrenberg C, Ulep C, Schwarz S, Roberts MC (2003) Diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in bacteria from Chilean salmon farms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:883–888. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.47.3.883-888.2003
Miranda CD, Tello A, Keen PL (2013) Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in finfish aquaculture environments. Front Microbiol 4:233. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00233
Miranda CD, Godoy FA, Lee MR (2018) Current status of the use of antibiotics and their antimicrobial resistance in the chilean salmon farms. Front Microbiol 9:1284. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01284
Mo WY, Chen Z, Leung HM, Leung AO (2017) Application of veterinary antibiotics in China's aquaculture industry and their potential human health risks. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:8978–8989. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5607-z
Musto J, Kirk M, Lightfoot D, Combs BG, Mwari L (2006) Multi drug resistant Salmonella Java infections acquired from tropical ornamental fish aquarium, Australia, 2003-04. Commun Diseas Intell 30:222–227
Naviner M, Gordon L, Giraud E, Denis M, Mangion C, Le Bris H, Ganiére J-P (2011) Antimicrobial resistance of Aeromonas spp. isolated from the growth pond to the commercial product in a rainbow trout farm following a flumequine treatment. Aquaculture 315:236–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.03.006
Ndi OL, Barton MD (2011) Incidence of class 1 integron and other antibiotic resistance determinants in Aeromonas spp. from rainbow trout farms in Australia. J Fish Dis 34:589–599. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2011.01272.x
Neela FA, Banu MNA, Rahman MA, Rahman MH, Alam MF (2014) Occurrence of antibiotic resistant bacteria in pond water associated with integrated poultry-fish farming in Bangladesh. Sains Malays 44:371–377. https://doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2015-4403-08
Newaj-Fyzul A, Austin B (2015) Probiotics, immunostimulants, plant products and oral vaccines, and their role as feed supplements in the control of bacterial fish diseases. J Fish Dis 14:937–955. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12313
Ngamkala S, Futami K, Endo M, Maita M, Katagiri T (2010) Immunological effects of glucan and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, on probiotic bacterium, on Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus intestine with oral Aeromonas challenges. Fisheries Sci 76:833–840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-010-0280-0
Nguyen TTT, Nguyen HT, Tsaia MA, Byadgi O, Wanga PC, Yoshida T, Chena SC (2017) Genetic diversity virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus dysgalactiae isolates from different aquatic animal sources. Aquaculture 479:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.06.002
Nonaka L, Suzuki S (2002) New Mg2+-dependent oxytetracycline resistance determinant Tet 34 in Vibrio isolates from marine fish intestinal contents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 476:1550–1552. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.46.5.1550-1552.2002
Nonaka L, Ikeno K, Suzuki S (2007) Distribution of tetracycline resistance gene, tet(M), in Grampositive and gram-negative bacteria isolated from sediment and seawater at a coastal aquaculture site in Japan. Microbes Environ 22:355–364. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.22.355
Novotny L, Dvorska L, Lorencova A, Beran V, Pavlik I (2004) Fish: a potential source of bacterial patho- gens for human beings. Vet Med – Czech 49:343–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.10.003
Nya EJ, Austin B (2010) Use of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) as an immunostimulant for the control of Aeromonas hydrophila infections in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Appl Microbiol 108:686–694. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04464.x
Odeyemi OA, Ahmad A (2017) Antibiotic resistance profiling and phenotyping of Aeromonas species isolated from aquatic sources. Saudi J Biol Sci 24:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.09.016
Pan JC, Ye R, Wang HQ, Xiang HQ, Zhang W, Yu XF, Meng DM, He ZS (2008) Vibrio cholerae O139 multiple drug resistance mediated by Yersinia pestis pIP1202-like conjugative plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:3829–3836. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00375-08
Partridge SR, Tsafnat G, Coiera E, Iredell JR (2009) Gene cassettes and cassette arrays in mobile resistance integrons. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:757–784. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00175.x
Pathak SP, Bhattacherjee JW, Ray PK (1993) Seasonal variation in survival and antibiotic resistance among various bacterial populations in a tropical river. J Gen Appl Microbiol 39:4756
Petersen A, Dalsgaard A (2003) Antimicrobial resistance of intestinal Aeromonas spp. and Enterococcusspp. In fish cultured in integrated broiler-fish farms in Thailand. Aquaculture 219:71–82
Petersen A, Andersen JS, Kaewmak T, Somsiri T, Dalsgaard A (2002) Impact of integrated fish farming on antimicrobial resistance in a pond environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6036–6042. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.12.6036-6042.2002
Piotrowska M, Popowska M (2014) The prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes among Aeromonas species in aquatic environments. Ann Microbiol 64:921–934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0911-2
Poirel L, Cattoir V, Nordmann P (2012) Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance; interactions between human, animal, and environmental ecologies. Front Microbiol 3:24. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00024 2
Preena PG, Dharmarathnam A, Raj NS, Kumar TVA, Raja SA, Swaminathan TR (2019a) Antibiotic susceptibility pattern of bacteria isolated from freshwater ornamental fish, guppy showing bacterial disease. Biologia (in press) doi: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00261-8
Preena PG, Dharmarathnam A, Raj NS, Kumar TVA, Raja SA, Nair RR, Swaminathan TR (2019b) Diversity of antimicrobial resistant pathogens from a freshwater rnamental fish farm. Lett Appl Microbiol (in press) doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13231
Rahube TO, Yost CK (2010) Antibiotic resistance plasmids in wastewater treatment plants and their possible dissemination into the environment. Afr J Biotechnol 9:9183–9190. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.2008.00163.x
Rajendiran A, Natarajan E, Subramanian P (2008) Control of Aeromonas hydrophila infection in spotted snakehead Channa punctatus,by Solanum nigrum L., a medicinal plant. J World Aquacult Soc 39:375–383. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.2008.00163.x
Reboucas RH, de Sousa OV, Lima AS, Vasconcelos FR, de Carvalho PB, Silva dos Fernandes Vieira RH (2011) Antimicrobial resistance profile of Vibrio species isolated from marine shrimp farming environments (Litopenaeus vannamei) at Ceara, Brazil. Environ Res 111:21e24. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.66.9.3883-3890.2000
Rhodes G, Huys G, Swings J, Mcgann P, Hiney M, Smith P, Pickup RW (2000) Distribution of oxytetracycline resistance plasmids between aeromonads in hospital and aquaculture environments: implication of Tn1721 in dissemination of the tetracycline resistance determinant Tet a. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3883–3890. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.66.9.3883-3890.2000
Rico A, Jacobs R, Van den Brink PJ, Tello A (2017) A probabilistic approach to assess antibiotic resistance development risks in environ- mental compartments and its application to an intensive aquaculture production scenario. Environ Pollut 231:918–928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.079
Ripabelli G, Sammarco ML, McLauchlin J, Fanelli I (2003) Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance of Vibrio vulnificus and Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Syst Appl Microbiol 26:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1078/072320203322337407
Romero J, Feijoó CG, Navarrete P (2012) Antibiotics in aquaculture — use, abuse and alternatives. In: Carvalho ED David JS Silva RJ (eds) health and environment in aquaculture, pp 159
Rosewarne CP, Pettigrove V, Stokes HW, Parsons YM (2010) Class 1 integrons in benthic bacterial communities: abundance, association with Tn402-like transposition modules and evidence for coselection with heavy-metal resistance. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 72:35–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00823.x
Ruzauskas M, Klimiene I, Armalyte J, Bartkiene E, Siugzdiniene R, Skerniskyte J, Krasauskas R, Suziedeliene E (2018) Composition and antimicrobial resistance profile of gram-negative microbiota prevalent in aquacultured fish. J food safety 38:e12447. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfs.12447
Saavedra MJ, Guedes-Novais S, Alves A, Rema P, Tacão M, Correia A, Martínez-Murcia A (2010) Resistance to β-lactam antibiotics in Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss). Int Microbiol 7:207–211
Sahoo PK, Swaminathan T, Abraham TJ, Kumar R, Pattanayaka S, Mohapatra A, Ratha SS, Patra A, Adikesavalu H, Sood N, Pradhan PK, Das BK, Jayasankar P, Jena JK (2016) Detection of goldfish haematopoietic necrosis herpes virus (cyprinid herpesvirus-2) with multi-drug resistant Aeromonas hydrophila infection in goldfish: first evidence of any viral disease outbreak in ornamental freshwater aquaculture farms in India. Acta Trop 161:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.05.004
Santos L, Ramos F (2018) Antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: current knowledge and alternatives to tackle the problem. Int J Antimicrob Agents 52:135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.03.010
Sarter S, Nguyen HNK, Hung LT, Lazard J, Montet D (2007) Antibiotic resistance in gram-negative bacteria isolated from farmed catfish. Food Control 18:1391–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2006.10.003
Scarano C, Spanu C, Ziino G, Pedonese F, Dalmasso A, Spanu V, Virdis S, De Santis EP (2014) Antibiotic resistance of Vibrio species isolated from Sparus aurata reared in Italian mariculture. New Microbiol 37:329–337. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/47.6.735
Schmidt AS, Bruun MS, Dalsgaard I, Larsen JL (2001a) Characterization of class 1 integrons associated with R-plasmids in clinical Aeromonas salmonicida isolates from various geographical areas. J Antimicrob Chemother 47:735–743. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/47.6.735
Schmidt AS, Bruun MS, Dalsgaard I, Larsen JL (2001b) Incidence, distribution and spread of tetracycline resistance determinants and integron associated antibiotic resistance genes among motile aeromonads from a fish farming environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5675–5682. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.12.5675-5682.2001
Schmidt AS, Bruun MS, Dalsgaard I, Pedersen K, Larsen JL (2000) Occurrence of antimicrobial resistancein fish-pathogenic and environmental bacteria associated with four Danish rainbow trout farms. Appl Environ Microbiol 66: 4908–4915.
Shah SQ, Nilsen H, Bottolfsen K, Colquhoun DJ, Sørum H (2012) DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV mutations in quinolone-resistant Flavobacterium psychrophilum isolated from diseased salmonids in Norway. Microb Drug Resist 18:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2011.0142
Shah SQ, Cabello FC, L’abée-Lund TM, Tomova A, Godfrey HP, Buschmann AH, Sørum H (2014) Antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial resistance genes in marine bacteria from salmon aquaculture and non-aquaculture sites. Environ Microbiol 16:1310–1320. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12421
Sing CK, Khan MZI, Daud HHJM, Aziz AR (2016) Prevalence of Salmonella sp. in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) obtained from farms and wet markets in Kelantan, Malaysia and their antibiotic resistance. Sains Malays 45:1597–1602
Singh AF, Rathore G, Singh V, Mani I, Singh RK, Mishra SK, Mishra BN, Verma OP (2009) Bacterial resistance to oxytetracycline in different life stages of Indian freshwater carp aquaculture system. Int J Microbiol Res 1:25–34. https://doi.org/10.9735/0975-5276.1.1.25-34
Slama KB, Jouini A, Sallem RB, Somalo S, Saenz Y, Estepa V, Boudabous A, Torres C (2010) Prevalence of broadspectrum cephalosporin-resistant Escherichia coli isolates in food samples in Tunisia, and characterization of integrons and antimicrobial resistance mechanisms implicated. Int J Food Microbiol 137:281–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.12.003
Smith P, Hiney MP, Samuelsen OB (1994) Bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents used in fish farming: a critical evaluation of method and meaning. Annu Rev Fish Dis 4:273–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/0959-8030(94)90032-9
Snieszko SF, Bullock GL (1957) Treatment of sulfonamide-resistant furunculosis in trout and determination of drug sensitivity. Fish Bull 125:555–564
Sørum H (2006) Antimicrobial drug resistance in fish pathogens. In: Aarestrup FM (ed) Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria of animal origin. ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp 213–238
Sousa M, Torres C, Barros J, Somalo S, Igrejas G, Poeta P (2011) Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) as carriers of SHV-12 and TEM-52 extended –spectrum beta-lactamases-containing Escherichia coli isolates. Foodborne Pathog Dis 8:1139–1141. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2011.0866
Sreedharan K, Philip R, Singh ISB (2011) Isolation and characterization of virulent Aeromonas veronii from ascetic fluid of oscar Astronotus ocellatus showing signs of infectious dropsy. Dis Aquat Org 1:29–39. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao02304
Sreedharan K, Philip R, Singh ISB (2012) Virulence potential and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of motile aeromonads associated with freshwater ornamental fish culture systems: a possible threat to public health. Braz J Microbiol 43:754–765. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822012000200040
Stalder T, Barraud O, Casellas M, Dagot C, Ploy MC (2012) Integron involvement in environmental spread of antibiotic resistance. Front Microbiol 3:119. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00119
Stokes HW, Gillings MR (2011) Gene flow, mobile genetic elements and the recruitment of antibiotic resistance genes into gram-negative pathogens. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35:790–819. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00273.x
Su HC, Ying GG, Tao R, Zhang RQ, Fogarty LR, Kolpin DW (2011) Occurrence of antibiotic resistance and characterization of resistance genes and integrons in Enterobacteriaceae isolated from integrated fish farms in South China. J Environ Monit 13:3229–3236. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1em10634a
Swain P, Nayak SK, Sasmal A, Behera T, Swain SK, Mishra SS, Sen AK, Das JK, Jayasankar P (2014) Antimicrobial activity of metal based nanoparticles against microbes associated with diseases in aquaculture. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:2491–2502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1674-4
Tamminen M, Karkman A, Lohmus A, Muziasari WI, Takasu H, Wada S et al (2011) Tetracycline resistance genes persist at aquaculture farms in the absence of selec- tion pressure. Environ Sci Technol 45:386–391. https://doi.org/10.1021/es102725n
Tao W, Lee MH, Wu J, Kim NH, Kim J-C, Chung E, Hwang EC, Lee SW (2012) Inactivation of chloramphenicol and florfenicol by a novel chloramphenicol hydrolase. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:6295–6301. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01154-12
Tendencia EA, Pena LD (2001) Antibiotic resistance of bacteria from shrimp ponds. Aquaculture 195:193–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00570-6
Thornber K, Verner-Jeffreys D, Hinchliffe S, Rahman MM, Bass D, Tyler CR (2019) Evaluating antimicrobial resistance in the global shrimp industry. Rev Aquacult (in press). https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12367
Tomova A, Ivanova L, Buschmann AH, Rioseco ML, Kalsi RK, Godfrey HP, Cabello FC (2015) Antimicrobial resistance genes in marine bacteria and human uropathogenic Escherichia coli from a region of intensive aquaculture. Environ Microbiol Rep 7:803–809. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12327
Topp E, Larsson DGJ, Miller DN, Van den Eede C, Virta MPJ (2018) Antimicrobial resistance and the environment: assessment of advances, gaps and recommendations for agriculture, aquaculture and pharmaceutical manufacturing. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 94:fix185. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fix185
Turkson P (2008) Use of drugs and antibiotics in poultry production in Ghana. Ghana J Agric Sci 41:23–33. https://doi.org/10.4314/gjas.v41i1.46142
Vaughan S, Coyne R, Smith P (1996) The critical importance of sample site in the determination of the frequency of oxytetracycline resistance in the effluent microflora of a freshwater fish farm. Aquaculture 139:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(95)01152-8
Vega-Sanchez V, Lat’ıf-Eugen’ın F, Soriano-Vargas E, Beaz Hidalgo R, Figueras MJ, Aguilera-Arreola MG, Castro-Escarpulli G (2014) Re-identification of Aeromonas isolates from rainbow troutand incidence of class 1 integron and β-lactamase genes. Vet Microbiol 172:528–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.06.012
Verner-Jeffreys DW, Welch TJ, Schwarz T, Pond MJ, Woodward MJ, Haig SJ, Rimmer GS, Roberts E, Morrison V, Baker-Austin C (2009) High prevalence of multidrug-tolerant bacteria and associated antimicrobial resistance genes isolated from ornamental fish and their carriage water. PLoS One 4:e8388. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008388
Wang Y, Leung PC, Qian PYGJ-D (2006) Antibiotic resistance and plasmid profile of environmental isolates of Vibrio species from Mai Po nature reserve, Hong Kong. Ecotoxicology 15:371–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-006-0078-0
Watts JEM, Schreier HJ, Lanska L, Hale MS (2017) The rising tide of antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: sources, sinks and solutions. Mari Drugs 15:e158. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060158
Weir M, Rajic A, Dutil L, Cernicchiaro N, Uhland FC, Mercier B, Tusevljak N (2012) Zoonotic bacteria, antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in ornamental fish: a systematic review of the existing researchand survey of aquaculture-allied professionals. Epidemiol Infect 140:192–206. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268811001798
Witte W (1998) Medical consequences of antibiotic use in agriculture. Science 279:996–997. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.279.5353.996
World Health Organization (WHO) 2006. Report of a Joint FAO/OIE/WHO Expert Consultation on antimicrobial use in aquaculture and antimicrobial resistance, Seoul, Republic of Korea. Available at: http://www.who.int/topics/foodbornediseases/aquaculturerep1316june2006.pdf
Wu YR, Gong QF, Fang H, Liang WW, Chen M, He RJ (2013) Effect of Sophora flavescens on non-specific immune response of tilapia (GIFT Oreochromis niloticus) and disease resistance against Streptococcus agalactiae. Fish Shellfish Immunol 34:220–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2012.10.020
Xiao JF, Wang QY, Liu Q, Wang X, Liu H, Zhang YX (2009) Isolation and identification of fish pathogen Edwardsiella tarda from mariculture in China. Aquac Res 40:13e7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.02101.x
Yano Y, Hamano K, Tsutsui I, Aue-Umneoy D, Ban M, Satomi M (2015) Occurrence, molecular characterization, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Aeromonas spp. in marine species of shrimps cultured at inland low salinity ponds. Food Microbiol 47:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2014.11.003
Yoo MH, Huh MD, Kim EH, Lee HH, Jeong HD (2003) Characterization of chloramphenicol acetyltransferasegene by multiplex polymerase chain reaction in multi-drug-resistant strains isolated from aquatic environ-ments.Aquaculture 217:11–21.
Yu JE, Cho MY, Kim JW, Kang HY (2012) Large antibiotic-resistance plasmid of Edwardsiella tarda contributes to virulence in fish. Microb Pathog 52:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2012.01.006
Zhu YG, Zhao Y, Li B, Huang CL, Zhang SY, Yu S, Chen YS, Zhang T, Gillings MR, Su JQ (2017) Continental-scale pollution of estuaries with antibiotic resistance genes. Nat Microbiol 2:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.270
Acknowledgments
The first author acknowledges Department of Science and Technology (DST, SERB) for the Fellowship under National Postdoctoral Fellowship Scheme with Grant number PDF/2017/000378 and Director, National Bureau of Fish Genetic Resources and National Centre for Aquatic Animal Health, Cochin University of Science and Technology for the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Preena, P.G., Swaminathan, T.R., Kumar, V.J.R. et al. Antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: a crisis for concern. Biologia 75, 1497–1517 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00456-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00456-4