Abstract
Background
Since 1969, 49 cases have been presented on ring chromosome 4. All of these cases have been characterized for the loss of genetic material. The genes located in these chromosomal regions are related to the phenotype.
Case presentation
A 10-year-old Ecuadorian Mestizo girl with ring chromosome 4 was clinically, cytogenetically and molecularly analysed. Clinical examination revealed congenital anomalies, including microcephaly, prominent nose, micrognathia, low set ears, bilateral clinodactyly of the fifth finger, small sacrococcygeal dimple, short stature and mental retardation. Cytogenetic studies showed a mosaic karyotype, mos 46,XX,r(4)(p16.3q35.2)/46,XX, with a ring chromosome 4 from 75 to 79% in three studies conducted over ten years. These results were confirmed by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Loss of 1.7 Mb and gain of 342 kb in 4p16.3 and loss of 3 Mb in 4q35.2 were identified by high-resolution mapping array.
Conclusion
Most cases with ring chromosome 4 have deletion of genetic material in terminal regions; however, our case has inv dup del rearrangement in the ring chromosome formation. Heterogeneous clinical features in all cases reviewed are related to the amount of genetic material lost or gained. The application of several techniques can increase our knowledge of ring chromosome 4 and its deviations from typical “ring syndrome.”
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Ring chromosomes are rare genetic anomalies in humans that result from the breakage in both ends of a chromosome with the subsequent fusion of the broken ends. This breakage can occur through several cytogenetic mechanisms: breakage in one or both arms of the chromosome with the subsequent fusion of the broken ends or an inversion-duplication-deletion rearrangement (inv dup del) [1,2,3], leading to loss and gain of genetic material and altered phenotypes. On the other hand, without loss of genetic material, a complete ring chromosome can be formed by fusion of subtelomeric segments or telomere-telomere fusion [4, 5].
Usually, the phenotype of the cases with ring chromosome 4, r(4), presents low birth weight, growth retardation and microcephaly. In addition, there are many features similar to those in Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome or similar to cases in which a partial deletion of the short arm of chromosome 4 is observed.
Since 1969, ring chromosome 4 has been described in 49 cases with different clinical findings depending on the amount of genetic material lost in the ring [3, 5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51].
In this report, we present the clinical, cytogenetic and molecular findings of a 10-year-old female patient with a ring chromosome 4 after the third follow-up study.
Case presentation
The proband is a 10-year-old Ecuadorian girl. According to the ancestry profile of the Ecuadorian population, she is a Mestizo with 72% Native American, 25% European and 3% African ancestry. She is the third child of healthy and non-consanguineous parents. Both parents were 22 years old at the time of her birth. There was an abortion threat at the second month of pregnancy and urinary tract infection during the first trimester of the pregnancy. The patient was born by caesarean section at 40 weeks of gestation with an APGAR of 8–9, weight of 2940 g (below the 10th percentile), length of 47 cm (below the 10th percentile), and head circumference of 32 cm (below the 5th percentile). Upon physical examination, she showed sufficient suckling, good gastric tolerance and loud crying. Additionally, she displayed microcephaly, beaked nose, micrognathia, low-set ears, bilateral clinodactyly of the fifth finger and a 0.5 mm sacrococcygeal dimple. At the age of eight months, magnetic resonance imaging with contrast of her lumbar spine revealed a small fistulous tract that communicated the sacral region with the coccyx; in addition, the presence of lipoma, tethered spinal cord and meningocele was discarded. At the age of two, a computerized axial tomography scan with three-dimensional images of her brain was performed without showing any defects.
Cultures of peripheral blood lymphocytes were taken according to standard techniques. A hundred metaphases were studied in the patient. Patient’s karyotype ten days after birth revealed a mosaicism with ring chromosome 4: mos 46,XX,r(4)(p16q35)[65]/45,XX,-4[5]/46,XX,dic r(4)[5]/46,XX[20]. At the age of five, a second cytogenetic analysis was performed, revealing the following karyotype: mos 46,XX,r(4)(p16q35)[66]/45,XX,-4[6]/46,XX,dic r(4)[5]/46,XX[16].
Patient follow-up included a third clinical and cytogenetic evaluation at the age of 10. Her physical examination showed a height of 125 cm (below the 5th percentile) and a weight of 35 kg (below the 75th percentile). Additionally, she presented mental retardation and a pleasant personality (Fig. 1).
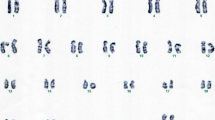
The karyotype was refined to mos 46,XX,r(4)(p16.3q35.2)[58]/45,XX,-4[7]/46,XX,dic r(4)[7]/46,XX[10] (Fig. 2).
The parents’ karyotypes were normal, 46,XX and 46,XY.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis was performed on the patient’s culture to confirm the cytogenetic findings. Specific probes were used for the regions 4p16.3 (Chr4: 492,870–793,359), 4q35.2 (Chr4: 190,183,811–190,408,149) and for the human chromosome 4 centromere probe (Chr4: 48,461,959–49,066,696). All probes were purchased from Agilent and used according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Agilent, USA). The patient’s results showed 46,XX,r(4).ish r(4)(p16.3q35.2)(492,870–793,359-,190,183,811–190,408,149-). The chromosome 4 centromere probe showed two hybridization signals. The 4p and the 4q probe showed one signal in each region (Fig. 3).
FISH findings in chromosome 4. a Patient’s metaphase that shows two green signals corresponding to the centromere region and one red signal corresponding to 4p16.3 region. b Patient’s metaphase that shows two green signals corresponding to the centromere region and one red signal corresponding to 4q35.2 region. c Green signals are shown corresponding to the centromere region and a red signal corresponding to 4q
We decided to determine the status of the chromosomal regions involved in ring formation with single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays. SNP mapping array was performed using the CytoScan 750 K Cytogenetics Array (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA, USA). This analysis showed terminal deletions in both arms of chromosome 4. In 4p16.3, the array showed a 1,710,458 bp deletion, losing one copy of the 34 genes located in that region (from 68,345 bp to 1,778,803 bp). The analysis also exhibited an additional segment of 342,143 bp (from 1,784,441 bp to 2,126,584 bp). Thus, gaining three copies of the nine genes. In 4q35.2, the array showed a 3,056,579 bp deletion (from 187,900,881 to 190,957,460 bp), losing one copy of the seven genes (Table 1).
Discussion and conclusions
Ring chromosome formation has been described by different mechanisms [1,2,3,4,5]. The ring chromosome 4 in our patient presents a terminal deletion with duplication resulting from inv dup del rearrangement [52]. This deletion and duplication is caused by homologous recombination between duplicated segments near the breakpoints, allowing telomere healing and telomere capture with the formation of an intermediate dicentric chromosome [2, 52].
The influence of deletions has been described in cases of ring chromosome 4. Deletions and duplication could influence the physical characteristics in our patient. To increase our understanding of the effect of deletion, we compared the phenotype of the patient with that of each of the 49 cases previously reported: 20 female and 29 male infants, diagnosed between 21 weeks of gestation and 27 years (Additional file 1).
From all reported physical features, we analysed 53 that are present in at least two patients. Three characteristics were identified to be more common in the 49 cases with ring chromosome 4: low birth weight with 78% appearance frequency, growth retardation (94%), and microcephaly (80%). The less frequent appearance traits include malformed ears (43%), mental retardation (41%), micrognathia (37%), clinodactyly (37%), hypospadias (36% of boys), heart defects (35%), retarded bone age (35%), skeletal abnormalities (33%), hypoplasia postaxial and thumbs alterations (31%), cryptorchidism (29%), short stature (27%), hypertelorism (27%), cleft palate (24%), broad nose (22%), transverse palmar crease (22%), changes in skin (22%), down-turned mouth (20%), seizures (20%), low set ears (18%), epicanthal folds (18%), abnormal phalanges (18%), renal malformation (18%), beaked nose (16%), hypotonia (16%), genitalia abnormalities (16%), low ridge count (16%), clubbed feet (16%), short philtrum (14%), high arched palate (14%), toes alterations (14%), and sacral dimple (12%), ptosis palpebrae (12%), cleft lip +/− palate (12%), prominent glabella (10%), brachycephaly (8%), antimongoloid slant of the palpebral fissures (8%), overlapping toes (8%), intestinal malformation (8%), high forehead (6%), exophthalmos (6%), coloboma (6%), preauricular pit (6%), flat nasal bridge (6%), prominent bridge (6%), teeth deficient in enamel (6%), short neck (6%), other visceral alterations (6%), prominent occiput (4%), strabismus (4%) and hyperactivity (4%).
Our case presented only 8 of these 53 features: microcephaly, mental retardation, micrognathia, clinodactyly, short stature, low set ears, beaked nose and sacral dimple (Additional file 1).
Analysing closely the reported cases with ring chromosome 4, it is noticeable that increases in the clinical features are present according to the breakpoint. On short arm 4p15, the median number of present traits is 16 (range, 11–19). On short arm 4p16, the median is 11 (range, 3–21), and on 4p16.3, the median is eight characteristics (range, 1–28). On the long arm, the median numbers of characteristics are as follows: on 4q22.3–34, eight (range, 6–10), on 4q35, 12 (range, 3–28), and nine characteristics (range, 1–14) were identified when the breakpoint was on 4q35.2 (Fig. 4).
The association between clinical features and alterations of chromosome 4 was discussed by Parker et al., who described physical findings for the deletion of the short and long arms and ring chromosome 4. Some characteristics were not exhibited in all cases with rings, possibly because they had different breakpoints [13]. In addition, with the exception of 3 characteristics, 18 coincide with Finley’s analysis in relation to deletions of 4p15 and p16 [22], and with the exception of 2 features, 22 coincide with Halal and Vekemans’s clinical and cytogenetic comparison [28].
In our case, duplication of 4p16.3 was found. Several cases have been reported on microduplications with shared clinical features, some of which are associated with microdeletion syndromes [53,54,55,56]. Roselló et al. reported a de novo case with a 1.3 Mb deletion and a 1.1 Mb duplication of the terminal 4p region; the patient presented hypertelorism, epicanthal folds, broad nasal bridge, low set ears, and absence of seizures. On the other hand, our case exhibited a 1.7 Mb deletion and a 0.3 Mb duplication, the individual only shows low set ears. Even though our case presented a microdeletion and a microduplication with ring formation which showed less clinical features than the case of Roselló et al. without ring formation, the phenotype may be due to the amount of genetic material altered.
Both cases showed a duplication of WHSC1, WHSC2, and LETM1 that can be the cause of clinical features different from Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome (WHS) and 4p trisomy syndrome [57]. As remarked by other authors, microdeletions or microduplications on LETM1 may suggest a cause for the clinical signs of seizures [57]; our case presents microduplications, and seizures remain absent. Microduplication syndrome also describes clinical features, such as psychomotor and language delay, seizures, high forehead with frontal bossing, hypertelorism, prominent glabella, long narrow palpebral fissures, short neck and low set ears [56], where only the latest characteristic is present in our case.
The cytogenetic results of our patient showed 79% of cells with rings in different presentations: cells with 46 chromosomes with monocentric ring, dicentric ring, polyploid cells with monocentric ring, and interlocked ring. The rest of the cells had a normal karyotype, cells with loss of chromosome 4 and cells polyploid with an absent ring. Karyotype comparison with 49 reported cases is presented in Additional file 2, where 37 cases detailed the ring chromosome 4 in mosaic state. Twelve cases described the presence of a ring without any specificity regarding whether it was in a mosaic state.
Of the 49 cases reported, only 17 made reference to the use of FISH analysis [3, 5, 31, 33, 34, 36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44, 46, 48, 51]. Although four cases presented normal results, this does not exclude the possibility that the ring chromosomes may have lost material in one or two arms. In the other fourteen cases, including our patient, losses were found in 4p16. Ten cases with terminal deletions (one in telomere and nine in subtelomeres), three cases with deletions at 4p16.3 (one with a breakpoint distal to RP11-20I20 and two with deletion of the Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome critical region) and one case with deletion at 4p16 (with a breakpoint distal to D4S1511 at 4p15). Six cases showed losses in 4q, one case in 4q34 (with a breakpoint distal to D4S575) and five cases with terminal deletions (one in a telomere and four, including our patient, in subtelomeres). The results of FISH analysis have allowed us to define or confirm the breakpoints of the ring chromosomes identified by cytogenetic analysis. Cases with ring chromosome 4 show frequent loss of subtelomeric segments (Fig. 5).
To refine the length of the losses of chromosome 4 in our patient, we used a mapping array. A deletion in 4p between 68,345 bp and 1,778,803 bp and a deletion in 4q between 187,900,881 bp and 190,957,460 bp were detected, refining the original information of losses by FISH between 492,870 bp and 793,358 bp, and 190,183,811 bp and 190,408,149 bp, respectively. Additionally, a gain of 342,143 bp of 4p16.3 between 1.78 and 2.12 Mb was found to contain 9 genes. The loss of some of these genes has been associated with WHS. However, as in our case, the gain of these genes as has already been explained can show different clinical features.
In our case and six other cases with ring chromosome 4 [3, 40, 42, 44, 48, 51], array-CGH was used to delimit the loss. However, only in our case and the other four cases [3, 42, 44, 48] has the loss been identified in 4p with an average size of 975,315 bp (range, 130,153-1,710,458 bp), and in this and two other cases [40, 48], the loss in 4q has an average size of 3,531,973 bp (range, 2,449,000-5,090,342 bp) (Fig. 6).
Review of deletions of chromosome 4 by Arrays. a The mapping array plot is shown as copy number (Y-axis) versus cytogenetics co-ordinates (X-axis). The deletions were identified (red dashed boxes) in 4p16.3 (1.71 Mb) and 4q35.2 (3.06 Mb) and the gain (green dashed box) in 4p16.3 (342 kb). b The first line represents 4p16.3 from 0 to 2,000,000 bp, the following lines show the loss location in our case and in other cases reported in the literature (each number on the left corresponds to the bibliographic reference), the solid line represents the deletion and the dotted line indicates the region that may or may not be deleted. c The first line represents 4q35.2 from 186,000,000 to 191,273,070 bp, the following lines show the loss location in our case and in other cases reported in the literature (each number on the left corresponds to the bibliographic reference)
The difference in whether detecting deletions and variations in the deletion limits could be due to the type of array platform used and its resolution degree. The arrays utilized in this study and in other cases with ring chromosome 4 have a range of coverage between 44 K and 750 K.
The deleted region of 1,710,458 bp of 4p16.3 contained 34 genes. Of these genes, the following should be highlighted: phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class G (PIGG). Allelic variants of this gene have been associated with intellectual disability, hypotonia, and early-onset seizures. Complexin 1 (CPLX1) gene positively regulates a late step in exocytosis of various cytoplasmic vesicles, such as synaptic vesicles and other secretory vesicles [58]. Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 (FGFRL1) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family. Mice with a targeted deletion of the FGFRL1 gene die perinatally due to alterations in their diaphragm. These mice also show bilateral kidney agenesis, suggesting an essential role for FGFRL1 in kidney development. A human patient with a frameshift mutation exhibits craniosynostosis, suggesting an additional role of FGFRL1 during bone formation [59]. The C-terminal binding protein 1 (CTBP1) gene encodes a phosphoprotein that is a transcriptional repressor and may play a role during cellular proliferation. Diseases associated with CTBP1 include hypotonia, ataxia, developmental delay and tooth enamel defect syndrome [58].
In the other cases studied by array, the number of genes involved in the deletion was according to the size of the loss: six genes in the 130,153 bp deletion [48], 14 genes in the 759,758 bp deletion [42], 16 genes at the deletion of 897,434 bp [44] and 31 genes at the deletion of 1,378,772 bp [3].
In our study, the loss of 3,056,579 bp of 4q35.2 contained seven genes. These genes do not seem to be associated with the patient’s phenotype [58]. Previously, an interstitial deletion of 5.75 Mb has been described in the genomic region 4q35.1-q35.2 between 184,717,878 and 190,469,337 bp without discernible clinical effects [60]. In other cases, proportional to the size of the loss in 4q35, four genes were in the deletion of 2,449,000 bp [48], and 19 genes were in the deletion of 5,090,342 bp [40].
The clinical variability observed in our case and all the cases reported could respond to the size of chromosome 4 deletion involved in the ring as described for rings in other chromosomes [61, 62] and, for our case, the coexistence of the deletion and duplication of chromosome 4, which have rarely been reported in the literature.
Availability of data and materials
All data used in this study are available from the corresponding authors for request.
Abbreviations
- ABCA11P :
-
ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily A Member 11, Pseudogene
- APGAR:
-
Appearance, Pulse, Grimace, Activity, and Respiration
- ATP5I :
-
ATP Synthase Membrane Subunit E
- C4orf42 :
-
Chromosome 4 Open Reading Frame 42
- C4orf48 :
-
Chromosome 4 Open Reading Frame 48
- CRIPAK :
-
Cysteine Rich PAK1 Inhibitor
- DGKQ :
-
Diacylglycerol Kinase Theta
- FAM53A :
-
Family With Sequence Similarity 53 Member A
- FRG1 :
-
FSHD Region Gene 1
- FRG2 :
-
FSHD Region Gene 2
- GAK :
-
Cyclin G Associated Kinase
- IDUA :
-
Alpha-L-Iduronidase
- KIAA1530 :
-
UV Stimulated Scaffold Protein A
- LETM1 :
-
Leucine Zipper And EF-Hand Containing Transmembrane Protein 1
- LOC100129917 :
-
Uncharacterized LOC100129917
- LOC100130872 :
-
Uncharacterized LOC100130872
- LOC401164 :
-
Uncharacterized LOC401164
- MAEA :
-
Macrophage Erythroblast Attacher
- MFSD7 :
-
Major Facilitator Superfamily Domain-Containing Protein 7
- MIR943 :
-
MicroRNA 943
- MYL5 :
-
Myosin Light Chain 5
- NAT8L :
-
N-Acetyltransferase 8 Like
- PCGF3 :
-
Polycomb Group Ring Finger 3
- PDE6B :
-
Phosphodiesterase 6B
- POLN :
-
DNA Polymerase Nu
- RNF212 :
-
Ring Finger Protein 212
- SCARNA22 :
-
Small Cajal Body-Specific RNA 22
- SLBP :
-
Stem-Loop Binding Protein
- SLC26A1 :
-
Solute Carrier Family 26 Member 1
- SPON2 :
-
Spondin 2
- TACC3 :
-
Transforming Acidic Coiled-Coil Containing Protein 3
- TMED11P :
-
Transmembrane P24 Trafficking Protein 11, Pseudogene
- TMEM129 :
-
Transmembrane Protein 129
- TMEM175 :
-
Transmembrane Protein 175
- TRIML1 :
-
Tripartite Motif Family Like 1
- TRIML2 :
-
Tripartite Motif Family Like 2
- TUBB4Q :
-
Tubulin, Beta Polypeptide 4, Member Q, Pseudogene
- ZFP42 :
-
ZFP42 Zinc Finger Protein
- ZNF141 :
-
Zinc Finger Protein 141
- ZNF595 :
-
Zinc Finger Protein 595
- ZNF718 :
-
Zinc Finger Protein 718
- ZNF721 :
-
Zinc Finger Protein 721
- ZNF732 :
-
Zinc Finger Protein 732
- ZNF876P :
-
Zinc Finger Protein 876, Pseudogene
References
Knijnenburg J, van Haeringen A, Hansson KB, Lankester A, Smit MJ, Belfroid RD, Bakker E, Rosenberg C, Tanke HJ, Szuhai K. Ring chromosome formation as a novel escape mechanism in patients with inverted duplication and terminal deletion. Eur J Hum Genet. 2007;15:548–55.
Rossi E, Riegel M, Messa J, Gimelli S, Maraschio P, Ciccone R, Stroppi M, Riva P, Perrota CS, Mattina T, Memo L, Baumer A, Kucinskas V, Castellan C, Schinzel A, Zuffardi O. Duplications in addition to terminal deletions are present in a proportion of ring chromosomes: clues to the mechanisms of formation. J Med Genet. 2008;45:147–54.
Guilherme RS, Meloni VFA, Kim CA, Pellegrino R, Takeno SS, Spinner NB, Conlin LK, Christofolini DM, Kulikowski LD, Melaragno MI. Mechanisms of ring chromosome formation, ring instability and clinical consequences. BMC Med Genet. 2011;12:171–7.
Côté GB, Katsantoni A, Deligeorgis D. The cytogenetic and clinical implications of a ring chromosome 2. Ann Genet. 1981;24:231–5.
Sigurdardottir S, Goodman BK, Rutberg J, Thomas GH, Jabs EW, Geraghty MT. Clinical, cytogenetic and fluorescence in situ hybridization findings in two cases of “complete ring” syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1999;87:384–90.
Carter R, Baker E, Hayman D. Congenital malformations associated with a ring 4 chromosome. J Med Genet. 1969;6:224–7.
Faed M, Stewart A, Keay AJ. Chromosome abnormalities in two cases with bilateral radial elements defects. J Med Genet. 1969;6:342–6.
Hecht F. Ring - 4 chromosome: Ring autosomes, Lorelei of clinical-karyotype correlation and deletion mapping. Birth Defects: Original Article Series. New York: The National Foundation-March of Dimes; 1969;5(5):106–13.
Dallaire L. A ring B chromosome in a female with multiple skeletal abnormalities. Birth Defects: Original Article Series. New York: The National Foundation-March of Dimes; 1969;5(5):114–6.
Bobrow M, Jones LF, Clarke G. A complex chromosomal rearrangement with formation of a ring 4. J Med Genet. 1971;8:235–9.
Surana RB, Bailey JD, Conen PE. A Ring-4 chromosome in a patient with normal intelligence and short stature. J Med Genet. 1971;8:517–21.
Bofinger MK, Dignan PSJ, Schmidt RE, Warkany J. Reduction malformations and chromosome anomalies. Am J Dis Child. 1973;125:135–43.
Parker CE, Alfi OS, Derencsenyl A, Mavalwala J, Donnell G. A child with a ring-4 chromosome (46,XX/46,XX,r4). Am J Dis Child. 1974;128(3):371–374.
Niss R, Passarge E. Derivative chromosomal structures from a ring chromosome 4. Hum Genet. 1975;28:9–23.
Fraisse J, Lauras B, Couturier J, Freycon F. Ring of the chromosome 4. I – with 4p- phenotype. Ann Genet. 1977;20(2):101–4.
Chavin-Colin F, Turleau C, Limal JM, de Grouchy J. Ring of the chromosome 4. II. Without facial dysmorphism. Ann Genet. 1977;20(2):105–9.
McDermott A, Voyce MA, Romain D. Ring chromosome 4. J Med Genet. 1977;14:228–32.
Pérez-Castillo A, Abrisqueta JA. Ring chromosome 4 and wolf syndrome. Hum Genet. 1977;37:87–91.
Bernstein R, Milne AT, Jenkins T. Translocation of chromosome 4 and 9 with ring formation of chromosome 4 short arm. J Med Genet. 1978;15:310–4.
del Mazo J, Abrisqueta JA, Pérez-Castillo A, Aller V, Martín Lucas MA, de Torres ML, Martín MJ. Partial deletion of 4p16 band in a ring chromosome and wolf syndrome. Hum Genet. 1978;44:105–8.
Young RS, Zalneraitis EL. Neurological and neuropathological findings in ring chromosome 4. J Med Genet. 1980;17:487–90.
Finley WH, Finley SC, Chonmaitree T, Koors JE, Chandler WC. Ring 4 chromosome with terminal p and q deletions. Am J Dis Child. 1981;135(8):729–31.
Grace E. Two cases of ring chromosome 4 showing variability of both ring structure and phenotype. J Med Genet. 1984;21:55.
Kosztolányi G. Ring chromosome 4: wolf syndrome and unspecific developmental anomalies. Acta Paediatr Hung. 1985;26(2):157–65.
Gutkowska A, Krajewska-Walasek M, Wiśniewski L. Ring chromosome 4: 46,XY,r(4)(p16q35) in a boy. Klin Padiatr 1985;197(4):294–296.
Giuffrè L, Cammarata M, Corsello G, Benigno V, Graziano L, Roccella F, Balsamo V. Ring chromosome 4 in twins [in Italian]. Pediatr Med Chir. 1987;9(3):349–50.
Fryns JP, Kleczkowska A, Jaeken J, Van den Berghe H. Ring chromosome 4 mosaicism and potter sequence. Ann Genet. 1988;31(2):120–2.
Halal F, Vekemans M. Ring chromosome 4 in a child with duodenal atresia. Am J Med Genet. 1990;37(1):79–82.
Sherer DM, Shah YG, Wang N, Metlay LA, Woods JR Jr. Prenatal diagnosis and subsequent management of a fetus with a 46XY r(4)(p15-q35) karyotype. Am J Perinatol. 1991;8(1):53–5.
Freyberger G, Wamsler C, Schmid M. Ring chromosome 4 in a child with mild dysmorphic signs. Clin Genet. 1991;39(2):151–5.
Pezzolo A, Gimelli G, Cohen A, Lavaggetto A, Romano C, Fogu G, Zuffardi O. Presence of telomeric and subtelomeric sequences at the fusion points of ring chromosomes indicates that the ring syndrome is caused by ring instability. Hum Genet. 1993;92:23–7.
Hou JW, Wang TR. Amelia, dextrocardia, asplenia, and congenital short bowel in deleted ring chromosome 4. J Med Genet. 1996;33:879–81.
Calabrese G, Giannotti A, Mingarelli R, Di Gilio MC, Piemontese MR, Palka G. Two newborns with chromosome 4 imbalances: deletion 4q33-q35 and ring r(4) (pterq35.2-qter). Clin Genet. 1997;51:264–7.
Anderson CE, Wallerstein R, Zamerowski ST, Witzleben C, Hoyer JR, Gibas L, Jackson LG. Ring chromosome 4 mosaicism coincidence of oligomeganephronia and signs of Seckel syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1997;72:281–5.
Pinto-Escalante D, Ceballos-Quintal JM, Castillo-Zapata I, Canto-Herrera J. Ring syndrome in a patient with a mosaic ring chromosome 4 [in Spanish]. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2001;58:532–6.
Kocks A, Endele S, Heller R, Schröder B, Schäfer HJ, Städtler C, Makrigeorgi-Butera M, Winterpacht A. Partial deletion of 4p and 4q in a fetus with ring chromosome 4: phenotype and molecular mapping of the breakpoints. J Med Genet. 2002;39:e23–6.
Blackett PR, Li S, Mulvihill JJ. Ring chromosome 4 in a patient with early onset type 2 diabetes, deafness, and developmental delay. Am J Med Genet. 2005;137A:213–6.
Lee MH, Park SY, Kim YM, Kim JM, Yoo KJ, Lee HH, Ryu HM. Molecular cytogenetic characterization of ring chromosome 4 in a female having a chromosomally normal child. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2005;111:175–8.
Balci S, Engiz Ö, Aktas D, Vargel I, Beksaç MS, Mrasek K, Vermeesch J, Liehr T. Ring chromosome 4 and wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS) in a child with multiple anomalies. Am J Med Genet. 2006;140A:628–32.
Chen CP, Hsu CY, Tzen CY, Lee CC, Chen WL, Chen LF, Wang W. Prenatal diagnosis of mosaic ring chromosome 4. Prenat Diagn. 2007;27:485–7.
South ST, Bleyl SB, Carey JC. Two unique patients with novel microdeletions in 4p16.3 that exclude the WHS critical regions: Implications for critical region designation. Am J Med Genet. 2007;143A:2137–42.
Concolino D, Rossi E, Strisciuglio P, Iembo MA, Giorda R, Ciccone R, Tenconi R, Zuffardi O. Deletion of a 760 kb region at 4p16 determines the prenatal and postnatal growth retardation characteristic of wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. J Med Genet. 2007;44:647–50.
Kim JH, Oh PS, Na HY, Kim SH, Cho HC. A case of mosaic ring chromosome 4 with subtelomeric 4p deletion. Korean J Lab Med. 2009;29:77–81.
Soysal Y, Balci S, Hekimler K, Liehr T, Ewers E, Schoumans J, Bui TH, Içduygu FM, Kosyakova N, Imirzalioğlu N. Characterization of double ring chromosome 4 mosaicism associated with bilateral hip dislocation, cortical dysgenesis, and epilepsy. Am J Med Genet. 2009:2782–7.
Sodré CP, Guilherme RS, Meloni VFA, Brunoni D, Juliano Y, Andrade JAD, Belangero SIN, Christofolini DM, Kulikowski LD, Melaragno MI. Ring chromosome instability evaluation in six patients with autosomal rings. Genet Mol Res. 2010;9(1):134–43.
Domínguez MG, Barros-Núñez P, González-Ramos IA, Rivera H. Variegated-like mosaicism and ring syndrome in a r(4) boy. Appraisal of 38 patients with a fairly complete ring 4. Genet Couns. 2010;21(4):411–22.
Chen BP, Lin SP, Su YN, Chern SR, Tsai FJ, Wu PC, Lee CC, Wang W. Mosaic ring chromosome 4 in a child with mild dysmorphisms, congenital heart defects and developmental delay. Genet Couns. 2011;22(3):321–6.
Akbas H, Cine N, Erdemoglu M, Atay AE, Simsek S, Turkyilmaz A, Fidanboy M. Prenatal diagnosis of 4p and 4q subtelomeric microdeletion in de novo ring chromosome 4. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2013;2013:248050.
Aparicio Rodríguez JM, Barrientos Pérez M, Chatelain MS. Chromosome aberrations in a Mexican pediatric hospital. Ring chromosomes 4, 13 and 18. J Asian Sci Res. 2014;4(6):280–91.
Paththinige CS, Sirisena ND, Kariyawasam UGIU, Saman Kumura LPC, Dissanayake VHW. Ring chromosome 4 in a child with multiple congenital abnormalities: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Genet. 2016;2016:4645716.
Burgemeister AL, Daumiller E, Dietze-Armana I, Klett C, Freiberg C, Stark W, Lingen M, Centonze I, Rettenberger G, Mehnert K, Zirn B. Continuing role for classical cytogenetics: case report of a boy with ring syndrome caused by complete ring chromosome 4 and review of literature. Am J Med Genet A. 2017;173(3):727–32.
Pristyazhnyuk IE, Menzorov AG. Ring chromosomes: from formation to clinical potential. Protoplasma. 2018;255(2):439–49.
Yobb TM, Somerville MJ, Willatt I, Firth HV, Harrison K, MacKenzie J, Gallo N, Morrow BE, Shaffer LG, Babcock M, Chernos J, Bernier F, Sprysak K, Christiansen J, Haase S, Elyas B, Lilley M, Bamforth S, McDermid HE. Microduplication and triplication of 22q11.2: a highly variable syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;76(5):865–76.
Torniero C, Dalla Bernardina B, Novara F, Cerini R, Bonaglia C, Pramparo T, Ciccone R, Guerrini R, Zuffardi O. Dysmorphic features, simplied gyral pattern and 7q11.23 duplication reciprocal to the Williams-Beuren deletion. Eur J Hum Genet. 2008;16(8):880–7.
Hannes F, Drozniewska M, Vermeesch JR, Haus O. Duplication of the wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome critical region causes neurodevelopmental delay. Eur J Med Genet. 2010;53:136–40.
Cyr AB, Nimmakayalu M, Longmuir SQ, Patil SR, Keppler-Noreuil KM, Shchelochkov OA. A novel 4p16.3 microduplication distal to WHSC1 and WHSC2 characterized by oligonucleotide array with new phenotypic features. Am J Med Genet. 2011;155:2224–8.
Roselló M, Monfort S, Orellana C, Ferrer-Bolufer I, Quiroga R, Oltra S, Martínez F. Submicroscopic duplication of the wolf-Hirschhorn critical region with a 4p terminal deletion. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2009;125(2):103–8.
GeneCards®: The Human Gene Database. https://www.genecards.org/
Trueb B. Biology of FGFRL1, the fifth fibroblast growth factor receptor. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(6):951–64.
Yakut S, Clarck OA, Sanhal C, Nur BG, Mendilcioglu I, Karauzum SB, Cetin Z. A familial interstitial 4q35 deletion with no discernible clinical effects. Am J Med Genet. 2015;167A:1836–41.
Paz-y-Miño C, Benítez J, Ayuso C, Cascos-Sánchez A. Ring chromosome 6: clinical and cytogenetic behaviour. Am J Med Genet. 1990;35:481–3.
Paz-y-Miño C, Guevara-Aguirre J, Paz-y-Miño A, Velarde F, Armendáriz-Castillo I, Yumiceba V, Hernández JM, García JL, Leone PE. Ring chromosome 15 – cytogenetics and mapping arrays: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2018;12(1):340.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by Centro de Investigación Genética y Genómica-Universidad UTE (CIGG-UTE). These researchers of CIGG-UTE had a role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CP-y-M and PEL designed and wrote the paper, CP-y-M diagnosed the patient and provided genetic counselling, AP and SDV collected the sample and performed the cytogenetic and FISH studies, JLG and JMHR performed the mapping array, and PEL and AP analysed the array results. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present work was approved by the Ethics and Bioethics Committee from “Universidad de las Américas” with approval number 2015–0702. Written informed consents were obtained from the patient’s parents for their cytogenetic analysis.
Consent for publication
The parents signed the informed consent on behalf of the patient, authorizing her cytogenetic analysis, molecular studies and any accompanying images for publication of this case report. Written consents are available for review by the editor-in-chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1.
Comparison of clinical characteristics between the proposita and the reported cases with ring chromosome 4.
Additional file 2.
Comparison of cytogenetic results between the proposita and the reported cases with ring chromosome 4.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Paz-y-Miño, C., Proaño, A., Verdezoto, S.D. et al. Clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular findings in a patient with ring chromosome 4: case report and literature review. BMC Med Genomics 12, 167 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-019-0614-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-019-0614-4