Abstract
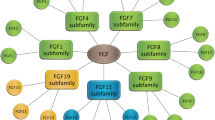
FGFRL1 (fibroblast growth factor receptor like 1) is the most recently discovered member of the FGFR family. It contains three extracellular Ig-like domains similar to the classical FGFRs, but it lacks the protein tyrosine kinase domain and instead contains a short intracellular tail with a peculiar histidine-rich motif. The gene for FGFRL1 is found in all metazoans from sea anemone to mammals. FGFRL1 binds to FGF ligands and heparin with high affinity. It exerts a negative effect on cell proliferation, but a positive effect on cell differentiation. Mice with a targeted deletion of the Fgfrl1 gene die perinatally due to alterations in their diaphragm. These mice also show bilateral kidney agenesis, suggesting an essential role for Fgfrl1 in kidney development. A human patient with a frameshift mutation exhibits craniosynostosis, arguing for an additional role of FGFRL1 during bone formation. FGFRL1 contributes to the complexity of the FGF signaling system.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factor
- FGFR:
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor
- Ig-like:
-
Immunoglobulin-like
- ITIM:
-
Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif
References
Beenken A, Mohammadi M (2009) The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:235–253
Itoh N, Ornitz DM (2004) Evolution of the Fgf and Fgfr gene families. Trends Genet 20:563–569
Eswarakumar VP, Lax I, Schlessinger J (2005) Cellular signaling by fibroblast growth factor receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:139–149
Mohammadi M, Olsen SK, Ibrahimi OA (2005) Structural basis for fibroblast growth factor receptor activation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:107–137
Wilkie AO (2005) Bad bones, absent smell, selfish testes: the pleiotropic consequences of human FGF receptor mutations. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:187–203
Knowles MA (2007) Role of FGFR3 in urothelial cell carcinoma: biomarker and potential therapeutic target. World J Urol 25:581–593
Jackson CC, Medeiros LJ, Miranda RN (2010) 8p11 myeloproliferative syndrome: a review. Hum Pathol 41:461–476
Wiedemann M, Trueb B (2000) Characterization of a novel protein (FGFRL1) from human cartilage related to FGF receptors. Genomics 69:275–279
Kim I, Moon S-O, Yu K-H, Kim U-H, Koh GY (2001) A novel fibroblast growth factor receptor-5 preferentially expressed in the pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta 1518:152–156
Sleeman M, Fraser J, McDonald M, Yuan S, White D, Grandison P, Kumble K, Watson JD, Murison JG (2001) Identification of a new fibroblast growth factor receptor, FGFR5. Gene 271:171–182
Trueb B, Zhuang L, Taeschler S, Wiedemann M (2003) Characterization of FGFRL1, a novel FGF receptor preferentially expressed in skeletal tissues. J Biol Chem 278:33857–33865
Trueb B, Taeschler S (2006) Expression of FGFRL1, a novel fibroblast growth factor receptor, during embryonic development. Int J Mol Med 17:617–620
Wiedemann M, Trueb B (2001) The mouse Fgfrl1 gene coding for a novel FGF receptor-like protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1520:247–250
Hayashi S, Itoh M, Taira S, Agata K, Taira M (2004) Expression patterns of Xenopus FGF receptor-like 1/nou-darake in early Xenopus development resemble those of planarian nou-darake and Xenopus FGF8. Dev Dyn 230:700–707
Beyeler M, Trueb B (2006) Fgfrl1, a fibroblast growth factor receptor-like gene, is found in the cephalochordate Branchiostoma floridae but not in the urochordate Ciona intestinalis. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B 145:43–49
Trueb B, Neuhauss SCF, Baertschi S, Rieckmann T, Schild C, Taeschler S (2005) Fish possess multiple copies of fgfrl1, the gene for a novel FGF receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta 1727:65–74
Zhuang L, Karotki AV, Bruecker P, Trueb B (2009) Comparison of the receptor FGFRL1 from sea urchins and humans illustrates evolution of a zinc binding motif in the intracellular domain. BMC Biochemistry 10:33
Bertrand S, Somorjai I, Garcia-Fernandez J, Lamonerie T, Escriva H (2009) FGFRL1 is a neglected putative actor of the FGF signalling pathway present in all major metazoan phyla. BMC Evol Biol 9:226
Putnam NH, Srivastava M, Hellsten U, Dirks B, Chapman J, Salamov A, Terry A, Shapiro H, Lindquist E, Kapitonov VV, Jurka J, Genikhovich G, Grigoriev IV, Lucas SM, Steele RE, Finnerty JR, Technau U, Martindale MQ, Rokhsar DS (2007) Sea anemone genome reveals ancestral eumetazoan gene repertoire and genomic organization. Science 317:86–94
Steinberg F, Zhuang L, Beyeler M, Kalin RE, Mullis PE, Brandli AW, Trueb B (2010) The FGFRL1 receptor is shed from cell membranes, binds FGFs and antagonizes FGF signaling in Xenopus embryos. J Biol Chem 285:2193–2202
Rieckmann T, Kotevic I, Trueb B (2008) The cell surface receptor FGFRL1 forms constitutive dimers that promote cell adhesion. Exp Cell Res 314:1071–1081
Rieckmann T, Zhuang L, Flück CE, Trueb B (2009) Characterization of the first FGFRL1 mutation identified in a craniosynostosis patient. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:112–121
Zhuang L, Falquet L, Trueb B (2010) Genome-wide comparison of FGFRL1 with structurally related surface receptors. Exp Ther Med 1:161–168
Baertschi S, Zhuang L, Trueb B (2007) Mice with a targeted disruption of the Fgfrl1 gene die at birth due to alterations in the diaphragm. FEBS J 274:6241–6253
Plotnikov AN, Schlessinger J, Hubbard SR, Mohammadi M (1999) Structural basis for FGF receptor dimerization and activation. Cell 98:641–650
Plotnikov AN, Hubbard SR, Schlessinger J, Mohammadi M (2000) Crystal structures of two FGF-FGFR complexes reveal the determinants of ligand-receptor specificity. Cell 101:413–424
Ibrahimi OA, Zhang F, Eliseenkova AV, Itoh N, Linhardt RJ, Mohammadi M (2004) Biochemical analysis of pathogenic ligand-dependent FGFR2 mutations suggests distinct pathophysiological mechanisms for craniofacial and limb abnormalities. Hum Mol Genet 13:2313–2324
Mohammadi M, Olsen SK, Goetz R (2005) A protein canyon in the FGF-FGF receptor dimer selects from an à la carte menu of heparan sulfate motifs. Curr Opin Struct Biol 15:506–516
Kan M, Wang F, Xu J, Crabb JW, Hou J, McKeehan WL (1993) An essential heparin-binding domain in the fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase. Science 259:1918–1921
Powell AK, Fernig DG, Turnbull JE (2002) Fibroblast growth factor receptors 1 and 2 interact differently with heparin/heparan sulfate. Implications for dynamic assembly of a ternary signaling complex. J Biol Chem 277:28554–28563
Loo BM, Kreuger J, Jalkanen M, Lindahl U, Salmivirta M (2001) Binding of heparin/heparan sulfate to fibroblast growth factor receptor 4. J Biol Chem 276:16868–16876
Mantovani A, Locati M, Vecchi A, Sozzani S, Allavena P (2001) Decoy receptors: a strategy to regulate inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Trends Immunol 22:328–336
Davis RS (2007) Fc receptor-like molecules. Annu Rev Immunol 25:525–560
Long EO (2008) Negative signaling by inhibitory receptors: the NK cell paradigm. Immunol Rev 224:70–84
Crocker PR, Redelinghuys P (2008) Siglecs as positive and negative regulators of the immune system. Biochem Soc Trans 36:1467–1471
Daeron M, Jaeger S, Du Pasquier L, Vivier E (2008) Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs: a quest in the past and future. Immunol Rev 224:11–43
Pinheiro da Silva F, Aloulou M, Benhamou M, Monteiro RC (2008) Inhibitory ITAMs: a matter of life and death. Trends Immunol 29:366–373
Steinberg F, Gerber S, Rieckmann T, Trueb B (2010) Rapid fusion and syncytium formation of heterologous cells upon expression of the FGFRL1 receptor. J Biol Chem 285. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.140517
Chen EH, Grote E, Mohler W, Vignery A (2007) Cell-cell fusion. FEBS Lett 581:2181–2193
Oren-Suissa M, Podbilewicz B (2010) Evolution of programmed cell fusion: common mechanisms and distinct functions. Dev Dyn 239:1515–1528
Cebria F, Kobayashi C, Umesono Y, Nakazawa M, Mineta K, Ikeo K, Gojobori T, Itoh M, Taira M, Sanchez Alvarado A, Agata K (2002) FGFR-related gene nou-darake restricts brain tissues to the head region of planarians. Nature 419:620–624
Ogawa K, Kobayashi C, Hayashi T, Orii H, Watanabe K, Agata K (2002) Planarian fibroblast growth factor receptor homologs expressed in stem cells and cephalic ganglions. Dev Growth Differ 44:191–204
Hall C, Flores MV, Murison G, Crosier K, Crosier P (2006) An essential role for zebrafish Fgfrl1 during gill cartilage development. Mech Dev 123:925–940
Hogan BM, Hunter MP, Oates AC, Crowhurst MO, Hall NE, Heath JK, Prince VE, Lieschke GJ (2004) Zebrafish gcm2 is required for gill filament budding from pharyngeal ectoderm. Dev Biol 276:508–522
Hanaoka R, Ohmori Y, Uyemura K, Hosoya T, Hotta Y, Shirao T, Okamoto H (2004) Zebrafish gcmb is required for pharyngeal cartilage formation. Mech Dev 121:1235–1247
Amaya E, Stein PA, Musci TJ, Kirschner MW (1993) FGF signalling in the early specification of mesoderm in Xenopus. Development 118:477–487
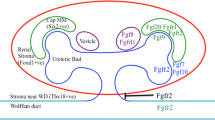
Gerber S, Steinberg F, Beyeler M, Villiger PM, Trueb B (2009) The murine Fgfrl1 receptor is essential for the development of the metanephric kidney. Dev Biol 335:106–119
Saxen L, Sariola H (1987) Early organogenesis of the kidney. Pediatr Nephrol 1:385–392
Potter EL (1962) Pathology of the fetus and infant, 2nd edn. Year Book Medical, Chicago
Gubler MC, Antignac C (2010) Renin-angiotensin system in kidney development: renal tubular dysgenesis. Kidney Int 77:400–406
Anderson SJ, Brennan J, de Sauvage FJ, Ding Z, Edwards J, Fikes NA, Huang W, Ouyang W, Rangel C, Sangha M, Shi Z-Z, Sparks MJ, Trackey J, Vetter M, Wang C-Y, Woodings J (2007) Novel gene disruptions, compositions and methods relating thereto. US Patent 20070292438
Catela C, Bilbao-Cortes D, Slonimsky E, Kratsios P, Rosenthal N, Te Welscher P (2009) Multiple congenital malformations of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome are recapitulated in Fgfrl1 null mice. Dis Model Mech 2:283–294
Lazarus JE, Hegde A, Andrade AC, Nilsson O, Baron J (2007) Fibroblast growth factor expression in the postnatal growth plate. Bone 40:577–586
Battaglia A, Carey JC, Wright TJ (2001) Wolf-Hirschhorn (4p-) syndrome. Adv Pediatr 48:75–113
Engbers H, van der Smagt JJ, van `t Slot R, Vermeesch JR, Hochstenbach R, Poot M (2009) Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome facial dysmorphic features in a patient with a terminal 4p16.3 deletion telomeric to the WHSCR and WHSCR 2 regions. Eur J Hum Genet 17:129–132
Holder AM, Klaassens M, Tibboel D, de Klein A, Lee B, Scott DA (2007) Genetic factors in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Hum Genet 80:825–845
Casaccia G, Mobili L, Braguglia A, Santoro F, Bagolan P (2006) Distal 4p microdeletion in a case of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 76:210–213
Lopez Jiminez N, Gerber S, Popovici V, Mirza S, Copren K, Ta L, Shaw GM, Trueb B, Slavotinek AM (2010) Examination of FGFRL1 as a candidate gene for diaphragmatic defects at chromosome 4p16.3 shows that Fgfrl1 null mice have reduced expression of Tpm3, sarcomere genes and Lrtm1 in the diaphragm. Hum Genet 127:325–336
Schild C, Trueb B (2005) Aberrant expression of FGFRL1, a novel FGF receptor, in ovarian tumors. Int J Mol Med 16:1169–1173
Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Shimada T, Iijima K, Hasegawa H, Okawa K, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2006) Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for FGF23. Nature 444:770–774
Kurosu H, Kuro-O M (2009) The Klotho gene family as a regulator of endocrine fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 299:72–78
Luedi PP, Dietrich FS, Weidman JR, Bosko JM, Jirtle RL, Hartemink AJ (2007) Computational and experimental identification of novel human imprinted genes. Genome Res 17:1723–1730
Falls JG, Pulford DJ, Wylie AA, Jirtle RL (1999) Genomic imprinting: implications for human disease. Am J Pathol 154:635–647
Greber B, Lehrach H, Adjaye J (2007) Silencing of core transcription factors in human EC cells highlights the importance of autocrine FGF signaling for self-renewal. BMC Dev Biol 7:46
Huang X, Ding L, Bennewith KL, Tong RT, Welford SM, Ang KK, Story M, Le QT, Giaccia AJ (2009) Hypoxia-inducible mir-210 regulates normoxic gene expression involved in tumor initiation. Mol Cell 35:856–867
Acknowledgments
Research in the laboratory of the author was supported by grants from the Swiss National Science Foundation (3100A-127046) and from the Swiss Foundation for Research on Muscular Diseases.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trueb, B. Biology of FGFRL1, the fifth fibroblast growth factor receptor. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 951–964 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0576-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0576-3