Abstract
Background
Lettuce is one of the most extensively farmed vegetables in the world, and it prefers cool growing conditions. High temperatures promote premature bolt formation, reducing quality and yield. The gibberellic acid-stimulated Arabidopsis (GASA) family genes play critical roles in plant growth, development, and stress responses. However, the biological functions of GASA proteins in lettuce have yet to be thoroughly investigated.
Results
Using genome-wide analysis, 20 GASAs were identified in lettuce including, three groups of LsGASA proteins based on the phylogenetic analysis. Except for one, all GASA proteins included a conserved GASA domain with 12 cysteine residues. Cis-element analysis showed that LsGASAs were closely associated with light, phytohormones, and stress resistance. Five segmental and three tandem duplication events were observed in the LsGASA family based on duplication analysis. GASA synteny analysis among lettuce, Arabidopsis, tobacco, and rice revealed that LsGASA5 is highly collinear with all species. Six of the 20 LsGASA showed increased expression patterns at specific time points in the shoot apical meristem when subjected to heat stress. According to gene expression analysis, the majority of GASA were highly expressed in flowers compared to other organs, and six GASA exhibited highly increased expression levels in response to NaCl, abscisic acid, and gibberellin treatment. Furthermore, LsGASA proteins are predominantly found in the plasma membrane and/or the cytosol.
Conclusions
This study provides a comprehensive characterization of LsGASA genes for their diversity and biological functions. Moreover, our results will be useful for further studies on the function of lettuce GASA in abiotic stress- and heat-induced bolting signaling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The GASA/GAST gene family is found in a variety of plant species and includes a signal peptide at the N-terminus and a conserved domain with 12 cysteine residues known as the GASA domain (PF02704) at the C-terminus, [1]. GAST1 (GA-stimulated transcript 1) was first characterized in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) [2]. Other GASAs have been identified in several species, including 19 in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) [3], 15 in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana L.) [1], 9 in rice (Oryza sativa L.) [4], 17 in cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) [5], 37 in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) [6], 14 in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) [7], and 18 in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) [8].
GASA proteins are essential for many biological processes and play a key role in plant development, such as stem elongation [9], flowering [10], root development [11], fruit ripening [12], and seed development [7, 13]. Several studies have reported that GASA is involved in phytohormone responses, including gibberellin (GA), abscisic acid (ABA), auxins (IAA), brassinosteroids (BR), and salicylic acid (SA) [14, 15]. For instance, GASA4 and GASA6 are downregulated by JA, ABA, and SA in Arabidopsis but abundantly expressed by GA, brassinosteroids, auxins, and cytokinins [15]. GASA1 expression analysis in wheat revealed that ACC, ABA, and MeJA were responsible for its induction [16]. Several interactions between GASA and DELLAs, which are negative regulators of GA signaling, have been discovered which imply that GASA significantly contributes to GA signaling [17]. GsGASA1 is involved in suppressing root development through the accumulation of DELLA proteins under cold stress [18]. Other studies have reported that GASA influences resistance to abiotic stress [19, 20]. For instance, it has been demonstrated that Arabidopsis specimens that overexpress FsGASA4 (Fagus sylvatica) and TaGASR1 are more resistant to oxidation, and salt during seed germination and seedling growth [21] and heat stress resistance, respectively [16].
Lettuce is a cool season crop with an optimal growth temperature range of 15–25 °C that is mostly used in salads. In recent years, the consumption of lettuce has increased significantly owing to its health benefits, such as allelopathic activity and a variety of bioactive phytochemical nutrients including anthocyanins, phenolic acids, and carotenoids [22, 23]. Harsh environmental conditions typically decrease lettuce production [24].
Environmental factors such as heat stress restrict plant growth and productivity [25]. The transition from the vegetative to the reproductive stage is accelerated under heat stress, which directly results in bolting and flowering [26]. FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) and SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS1 (SOC1), which play important roles in the flowering molecular pathway, were upregulated by heat treatment and delayed bolting and flowering were observed after the knockdown of soc1 and ft by RNAi from lettuce [27, 28]. Bolting lettuce results in a decreased leaf nutrient content, texture, and productivity. Therefore, studies related to delayed bolting and flowering are required to maintain suitable yield and quality.
Elucidation of the molecular regulatory network of heat-induced bolting in lettuce might be crucial for the development of heat-resistant lettuce since lettuce bolting time affects yield, quality, and consumer preference. Although GASAs are important regulators of plant development, heat-induced bolting with GASA expression has not yet been studied in lettuce. In this study, we identified a novel GASA family in the lettuce genome and examined their gene structure, conserved protein motifs, cis-acting elements, chromosomal localization, and synteny. The expression of LsGASA in the apical meristem tissues in response to heat stress was investigated. In addition, transcript levels of heat induced GASA were analyzed in response to abiotic stress and hormones, and subcellular localization was observed.
Results
Identification and characterization of the GASA family in Lactuca sativa
The identified 20 GASAs were renamed LsGASA1 to LsGASA20 according to their chromosomal locations and distributed across lettuce genome loci 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, and 9 (Additional file 1: Table S1).
The amino acid sequences of the 20 LsGASAs were analyzed, revealing that the sequences ranged from 78 to 662 amino acids in length, 8.34 to 67.73 kDa in molecular weight, 6.77 to 9.52 in isoelectric point, and − 0.33 to 0.21 in grand average of hydropathicity values (Additional file 1: Table S1). Prediction of subcellular localization indicated that most LsGASAs were found in the extracellular matrix, except for LsGASA4, LsGASA17, LsGASA19, LsGASA20, and LsGASA16, which are located in the chloroplast and cytoplasm, respectively (Additional file 2: Fig. S1).
A phylogenetic tree was constructed for the LsGASA (Fig. 1A), dividing it into three subclades. The exon-intron structure of the LsGASA contained no more than three introns (Fig. 1C). Most of the predicted motifs were distributed at the C-terminus of LsGASA proteins. One motif was present in the N-terminus of the LsGASA proteins; one motif was present except for LsGASA4 (Fig. 1B).
Phylogenetic analysis and multiple sequence alignment
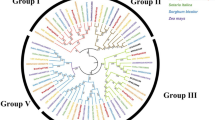
Based on the phylogenetic analysis of LsGASAs with GASA families of other plant species, GASA protein families can be classified into three groups: Groups I, II, and III. In lettuce, Groups I, II, and III contained fifteen, four, and one LsGASA proteins, respectively (Fig. 2A). The amino acid sequence of the LsGASA proteins was compared to the GASA amino acid sequences of other species (Fig. 2B). Multiple alignments of the LsGASA amino acid sequences revealed the presence of a conserved GASA domain that included 12 cysteines in the C-terminal domain, except for LsGASA17.
Phylogenetic analysis and amino acid sequence alignment from five plant species. A Phylogenetic tree of 77 GASA from lettuce (Ls: Lactuca sativa L.), Arabidopsis (At: Arabidopsis thaliana L.), grape (Vv: Vitis vinifera L.), rice (Oz: Oryza sativa L.), tobacco (Nt: Nicotiana tabacum L.). The different colors indicate different subfamily. B Sequence alignment of GASA proteins from LsGASA1–20, OsGASA1, NtGASA1, AtGASA1, and VvGASA1. Black asterisk represents their conserved cysteine region. Red background represented identical amino acids. Red text indicates similar sequences
Chromosomal location, evolutionary relationships, and synteny analysis
Twenty LsGASAs were distributed on lettuce chromosomes 1 to 9, except for chromosomes 5, 6, and 7 (Fig. 3). Chromosomes 2, 4, and 8 contained more than three genes, whereas chromosomes 1, 3, and 9 contained fewer than three.
To deduce the evolutionary relationship of GASA among different species, syntenic analysis was performed for lettuce, tobacco, Arabidopsis, and rice (Fig. 4). Numerous syntenic blocks have been observed between lettuce and tobacco, Arabidopsis, and rice. Among the synteny blocks, three LsGASA genes (LsGASA4, LsGASA5, and LsGASA12) and four genes (LsGASA5, LsGASA6, LsGASA8, and LsGASA19) showed pairwise synteny with NtGASA and AtGASA, respectively. Furthermore, LsGASA5, LsGASA12, and LsGASA14 showed pairwise synteny with the OsGASA family, with LsGASA5 being syntenic with the both OsGASA.
In duplication analysis, six genes were tandemly duplicated and clustered by three duplication events on chromosomes 2, 4, and 8 (LsGASA3/4, LsGASA12/13, and LsGASA15/16). On the other hand, segmental duplications were detected on three gene pairs, including LsGASA1/11, LsGASA6/8, and LsGASA9/10 (Additional file 3: Table S2). The Ka/Ks ratio was determined using tandem-and segmentally duplicated gene pairs. Tandem and segmentally duplicated gene pairs showed Ka/Ks < 0.6, and events were estimated to be between 5.4 and 39.3 Mya (Additional file 3: Table S2).
Determination of cis-regulatory elements in the promoters of LsGASA
To investigate the potential roles of cis-acting elements in LsGASAs, we analyzed the sequences 1.5 kb upstream of each LsGASA. The promoter region of the LsGASA genes contained hormone-responsive, stress-related regulatory, growth-, developmental-, and light-responsive elements (Fig. 5). The cis-elements that responded to hormones included abscisic acid response elements (ABREs), auxin-responsive elements (TGAelement and AuxRR-core), gibberellin-responsive elements (TATC-box, P-box, and GARE-motif), and MeJA response elements (TGACG-motif and CGTCA-motif). Except for GASA19, all other GASAs contained at least one sequence of hormone-responsive cis-acting elements. LsGASAs contain various stress-related elements, including ARE, DRE core, GC motif, LTR, MBS, MYB, MYC, and TC-rich repeats. Most GASA contains 35 MYB, 70 MYC, and 48 ARE elements in their promoters. All GASA contained ARE elements. In the promoter of LsGASAs, light-responsive elements (ACE, AE-box, AT1-motif, ATCT-motif, Box 4, Box II, G-box, chs-CMA1a, GA-motif, GT1-motif, GATA-motif, I-box, LAMP-element, MRE, TCCC-motif, and TCT-motif) showed the largest number compared to hormone-responsive and stress-responsive elements. Among the various elements, all GASA contained Box 4 elements that were associated with light-responsive elements (Fig. 5).
Number of each cis-acting element of the LsGASA promoter regions (1.5 kb upstream of the start codon). ABRE, ABRE3a, ABRE4: abscisic acid responsiveness. AuxRR-core: auxin responsiveness. CGTCA-motif, TGACG-motif: MeJA responsiveness. TATC-box, GARE-motif, P-box: gibberellin-responsive elements. TCA-element: salicylic acid responsiveness elements. LTR: involved in low-temperature responsiveness. W box: involved in both biotic and abiotic stress responses. MBS: drought inducibility. TC-rich repeats: involved in defense and stress responsiveness. MYB, MYC: ABA- and drought-responsive elements. DRE core: dehydration-responsiveness. ARE: essential for anaerobic induction. GC-motif: hypoxia-induced response element. CAT-box: related to meristem expression. G-box, GT1-motif, ACE: involved in light responsiveness. AE-box: part of the module for light response. MRE: MYB-binding site involved in light responsiveness. ATCT-motif, Box 4: part of a light responsive module. Box 2, chs-CMA1a, GATA-motif, I-box, LAMP-element, TCCC-motif, TCT-motif, GA-motif: part of a light-responsive element. AT1-motif: part of a light-responsive module
Expression profiling of LsGASA in responses to heat stress in lettuce SAM
To examine the effect of heat stress on lettuce SAM development, the morphological features of lettuce SAM were observed (Fig. 6A). There was no noticeable difference between days 0 and 1 in the control or heat stress treatments. On day 2, the heat-stressed plants had a larger dome size than the control plants. On day 3 of the heat stress treatment, the shoot apical meristem became sharper. These results suggest that lettuce bolting is promoted by high temperatures.
Paraffin sections and semi qRT-PCR analysis in shoot apical meristem (SAM) under heat stress conditions. A paraffin sections of SAM under high temperature conditions of 35/25 °C for 3 days.(a–e) control, (g–h) heat treatment. Toluidine Blue O stained tissues (Sections = 8 μm, Bars = 100 μm). DAP; Days after treatment. B Semi qRT-PCR analysis of 20 LsGASA in SAM under high temperature conditions of 35/25 °C for 72 h (uncropped full length gel image is provided in the Supplementary Information file Fig. S1)
To investigate the response of LsGASA in the SAM of lettuce under heat stress, we performed semi-qRT-PCR at seven different time points: 0, 2, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h of heat treatment (Fig. 6B). The band pixel intensities of LsGASAs and LsUBQ21 were quantified using ImageJ, presenting a computerized method to express the degree of gene expression (Additional file 4: Fig. S2). Similar expression patterns were observed for LsGASA1 and LsGASA18, which peaked at 6 h and subsequently gradually decreased after 24 h of heat treatment (Fig. 6B). The expression levels of LsGASA2, LsGASA9, and LsGASA12 gradually increased until 6 h and then decreased. However, LsGASA2, LsGASA9, and LsGASA12 expression increased again from 48 h to 72 h of heat treatment. Transcripts of LsGASA6 were highly increased until 6 h and then decreased but increased again after 48 h of heat treatment (Fig. 6B). Transcripts of LsGASA2, LsGASA6, LsGASA9, and LsGASA12 exhibited similar expression patterns in qRT-PCR, peaking at 12 h and then decreasing (Fig. 7). LsGASA1 expression increased from 12 to 48 h. LaGASA18 was highly expressed after 12 h of heat treatment.
For further study, we selected six LsGASA (1, 2, 6, 9, 12, and 18) that displayed increased expression in the SAM of lettuce under heat treatment. These results suggest that the six LsGASAs may be involved in heat-induced bolting mechanisms.
Expression analysis of six LsGASA in response to abiotic stresses and hormone treatments
To evaluate the expression levels of the six selected LsGASAs across an array of lettuce tissue samples, we analyzed the expression of the six GASAs in leaves, roots, stems, seeds, and flowers (Additional file 5: Fig. S3). LsGASA2, LsGASA6, LsGASA9, and LsGASA12 were more highly expressed in flower buds than in other tissues. LsGASA18 transcripts were highly expressed in seeds. LsGASA1 was highly expressed in the stems and roots compared to other tissues.
To investigate the effects of abiotic stresses and hormones on the expression of the six LsGASA, different stimuli, including PEG, NaCl, low temperatures, GA, PAC, and ABA, were applied (Fig. 8). Under PEG treatment, LsGASA1, LsGASA6, and LsGASA9 showed similar expression patterns, increasing at 6 h and decreasing at 12 h of heat treatment. The transcript levels of LsGASA12 increased until 12 h and then decreased at 24 h. The expression of LsGASA2 and LsGASA18 decreased after treatment. In the NaCl treatment, all GASA genes showed increased expression levels. In particular, LsGASA6 was highly expressed after NaCl treatment compared to other GASAs. Under cold treatment, LsGASA1 and LsGASA12 showed increased expression. By contrast, the expression levels of LsGASA2, LsGASA6, LsGASA9, and LsGASA18 were not significantly different. Following GA treatment, all GASAs showed upregulated expression. The transcript of LsGASA1 gradually increased from 6 h to 48 h. LsGASA6 showed maximum expression levels at 6 h, whereas LsGASA2, LsGASA9, and LsGASA12 showed high expression levels at 12 h. Under ABA treatment, all GASA genes showed upregulated expression, and LsGASA6 showed the highest expression under ABA treatment. Following PAC treatment, the expression levels of all LsGASA showed upregulation patterns, which increased at 6 h, except for LsGASA9.
Expression analysis of 20 LsGASA in response to stress and hormone treatments. 20% polyethylene glycol (PEG), 250 mM sodium chloride (NaCl), Cold (4 °C), 100 μM abscisic acid (ABA), 150 μΜ gibberellin acid (GA3), 150 μΜ paclobutrazol (PAC). All treatments were conducted for 72 h. Error bars are the standard error of the mean
Subcellular localization of LsGASA
To examine the subcellular localization of the six LsGASAs, cassettes of LsGASA-GFP were transfected into lettuce protoplasts. Most LsGASA-GFP fusion proteins have been detected in the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, or both. LsGASA1-GFP, LsGASA9-GFP, and LsGASA18-GFP were localized to the cytoplasm. LsGASA6-GFP and LsGASA12-GFP are located in the plasma membrane and cytoplasm, respectively. However, only the LsGASA2-GFP fusion protein was detected in the nucleus (Fig. 9).
Discussions
GASA proteins are essential for hormone signaling, abiotic and biotic stress responses, and many aspects of plant growth and development [9, 18, 29, 30]. However, studies on the role of GASA in high-temperature-induced lettuce bolting are lacking. In this study, we identified 20 GASA in the lettuce genome, and six GASA that were highly expressed in SAM under heat stress were chosen and further characterized. Most of the amino acid sequences of the LsGASA proteins ranged in length from 78 to 116 amino acids (Additional file 1: Table S1). However, the lengths of the amino acid sequences of LsGASA4 and LsGASA20 were 460 aa and 662 aa, respectively. The cDNA lengths of the LsGASAs were also similar, except for those of LsGASA4 and LsGASA20 (Additional file 1: Fig. S1 and Fig. 1C). Protein domain analysis revealed that they contained a signal peptide, except for LsGASA16 and LsGASA17 (Fig. 1B). Furthermore, the number of exons and introns in the gene structure analysis varied from one to three (Fig. 1C). These results indicate that LsGASA may gain or lose exons or introns because of chromosomal rearrangements [31].
Phylogenetic analysis of LsGASA along with other GASA revealed a closer relationship with dicotyledonous species than with monocotyledonous species (Fig. 2A). Gene duplication analysis of the LsGASA family revealed three tandem duplications and five segmental duplication gene pairs (Additional file 3: Table S2). These findings are consistent with a previous report indicating that segmental duplications occur more frequently than tandem duplications [7]. Evolutionary events related to duplication can affect the structure of the genome. Gene structure analysis revealed that the LsGASA family varied in terms of exons (Fig. 1C). However, there was no significant difference in the number of exons among the three subgroups (Fig. 2). The number of exons can influence post-transcriptional processes such as alternative splicing. The number of exons can also affect the expression patterns of genes, specifically resulting in genes with fewer exons being quickly induced [32]. Gene expression analysis revealed that LsGASAs exhibited a variety of expression patterns in response to abiotic stress and phytohormones (Fig. 8). The VvGASA family is mainly distributed on one chromosome; on the other hand, the LsGASA family is widely distributed on three chromosomes (Fig. 3). These results suggest that duplication of GASA occurs on multiple chromosomes during the expansion of the lettuce GASA family. From the synteny analysis, it was shown that less collinearity was observed between lettuce and rice compared to the other two dicot species (Fig. 4), which is thought to be because lettuce and rice separated earlier in the past. Furthermore, different types of LsGASA were collinear with GASAs in other species, whereas only LsGASA5 homologs were found in all species. This suggests that GASA5 is extensively conserved across plant species and is important for plant growth.
Cis-element analysis of the LsGASA showed that most LsGASAs contained various hormone-responsive elements in their promoters (Fig. 5). In the promoters of LsGASAs, ABA-responsive ABRE elements, auxin-responsive CGTCA, and MeJA-responsive TGACG motifs were abundant (Fig. 5). Previous studies have revealed that the transcript of GASA from Populus euphratica is downregulated in leaves under MeJA treatment [33]. In Prunus mume, six GASA were upregulated after ABA treatment, and five GASA were upregulated at different time points after IAA treatment [34]. In the present study, all the LsGASAs contained at least four regulatory elements related to light-responsive elements in their promoters (Fig. 5). Light has also been reported to affect AtGASA expression [13]. AtGASA4 transcripts are downregulated by far-red light signaling regulators under light conditions, resulting in early flowering [35]. Additionally, LsGASA contained several MYB and MYC elements (Fig. 5). The XsMYB44 transcription factor plays a positive regulatory role in response to combined stresses by inducing stomatal closure and regulating ROS homeostasis [36]. The presence of multiple regulatory elements in LsGASA promoters indicates that GASA may participate in various hormone-signaling pathways.
In general, high temperatures promote bolting in lettuce plants. In a previous study, transcripts of LsGA3ox1 were not only upregulated by high temperatures but also increased by GA, leading to bolting [37]. In our study, the development process of SAM revealed that high-temperature-treated plants increased the number of bolts faster than control plants (Fig. 6A). Furthermore, the transcript levels of LsGASAs (LsGASA1, LsGASA2, LsGASA6, LsGASA9, LsGASA12, and LsGASA18) in SAM were highly increased under heat treatment (Fig. 7). These findings imply that these six GASAs may be involved in the heat-induced bolting pathway.
The GASA family has been reported to be differentially expressed in different organs as well as in diverse abiotic stresses and hormones [4, 38, 39]. Expression analysis of lettuce organs showed that six LsGASA were expressed in the leaves, roots, seeds, stems, and flowers (Additional file 5: Fig. S3). Most of these genes were upregulated in roots, seeds, and flowers. In particular, LsGASA6 was most strongly expressed in the flowers (Additional file 5: Fig. S3). Previous studies have reported that NtGASAs and MdGASAs are more highly expressed in flowers and buds than in other organs [8, 38]. In addition, the transcripts of six LsGASAs showed an increasing pattern in the cold, PEG, and NaCl treatments (Fig. 8). Previous studies have reported that GASA is involved in various abiotic stressors and hormones. Overexpression of GASR1 increases salt stress tolerance in transgenic rice [40]. SmGASA4-overexpression in Arabidopsis promotes drought resistance [41]. AtGASA4 and AtGASA6 are upregulated by growth hormones and downregulated by stress hormones [15]. In this study, six LsGASA were highly expressed in response to ABA and GA. After PAC treatment, the expression levels of LsGASAs increased, except for LsGASA9 (Fig. 8). Based on the above evidence, our results suggest that the six GASA may play diverse roles related to abiotic stresses as well as hormone-induced bolting and flowering pathways.
According to subcellular localization analyses in various crops, GASA proteins are mostly located in the extracellular region and plasma membrane [14, 16, 42]. In the present study, the subcellular location of most LsGASA proteins was predicted to be in the extracellular regions (Additional file 2: Fig. S1). However, the six selected LsGASA proteins were mostly localized in the plasma membrane or cytoplasm of lettuce protoplasts, or both (Fig. 9). A previous study showed that CcGASA4, which is highly expressed in hormone-treated flowers, is localized in the plasma membrane and nucleus in Arabidopsis protoplasts [42]. GhGASA10–1 from cotton, which is localized in the cell membrane of tobacco epidermal cells, is highly expressed by IAA during the fiber elongation stages [14]. LsGASA6 and LsGASA12 proteins were localized in the plasma membrane and cytoplasm, and LsGASA2 was localized in the nucleus (Fig. 9). They were highly expressed in flowers as well as in the hormone treatments (Additional file 5: Fig. S3 and Fig. 8). These results suggest that LsGASAs may participate in various hormonal signaling pathways and plant developmental processes.
Conclusions
In this study, we identified 20 LsGASA families in the lettuce genome. Sequence analysis revealed that LsGASA contains a conserved GASA domain, and the distributions of exons and introns were different among the different subgroups. The LsGASAs were located on six chromosomes and were distributed into three groups according to phylogenetic analysis. In the analysis of cis-regulatory elements, LsGASAs contain various stress-, light-, and hormone-related elements. We analyzed the expression patterns of 20 GASA genes in SAM under heat stress and found six genes predicted to be related to heat-induced bolting. Six LsGASA (LsGASA1, LsGASA2, LsGASA6, LsGASA9, LsGASA12, and LsGASA18), which are heat-induced genes in SAM, were investigated for their expression patterns in different organs and response to abiotic stress and hormones. Tissue-specific expression revealed that LsGASAs were highly expressed in the roots and flowers. Six LsGASAs exhibited diverse expression patterns in response to different abiotic stressors and hormone treatments. In addition, the subcellular localization of the six LsGASAs was mostly in the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, or both. Overall, this study provides fundamental information on the LsGASA family and its responses to various abiotic stresses. This study will allow for a comprehensive investigation into the functional roles of each LsGASA; these findings will then allow for future studies into the characterization of mechanisms that underlie heat-induced bolting in lettuce.
Materials and methods
Identification of the LsGASA family in lettuce
To identify LsGASA, the hidden Markov model (HMM) profiles of the GASA domain (PF02704) from the Pfam database (https://pfam.xfam.org/) were used as a query, and the putative GASA protein sequences were identified using HMMER v 3.0 [43] searching against the lettuce genome (https://plants.ensembl.org/index.html) with a predefined threshold of E < 1e-5. The selected proteins containing GASA domains were confirmed using InterProScan (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/sequence-search). The ExPASy ProtParam (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/) tool was used to estimate the physical and chemical characteristics of all identified GASA proteins, including their isoelectric point, molecular weight, and grand average of hydropathy.
Chromosome distribution and evolutionary analysis of LsGASA
The chromosomal localization of LsGASAs was determined using the lettuce genome database. The MapChart program was used to graphically map lettuce chromosomes [44]. The CDSs of LsGASA were aligned using ClustalW and KaKs_calculator 3.0 [45] was used to determine the rates of non-synonymous (Ka) and synonymous (Ks) substitutions for duplicate LsGASA pairs. The divergence time (T) was calculated using the following eq. [46]:
where x = 6.56 × 10− 9.
TBtools [47] was used to identify syntenic relationships between lettuce and the tobacco/Arabidopsis genome. GFF files were obtained from EnsemblPlants (https://plants.ensembl.org/index.html) for lettuce and Arabidopsis, and from the Sol Genomics Network (https://solgenomics.net/organism/Nicotiana_tabacum/genome) for tobacco. The genome sequences and GFF files of lettuce and other species were used as input files for the One-Step MCScanX tool in TBtools. Consequently, the output files, Ctl, simplified GFF, and collinearity file were used for the dual synteny plot in TBtools for synteny visualization.
Phylogenetic tree, multiple alignments, and gene structure analysis
A phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method with 1000 bootstrap replicates using MEGA X software [48]. Multiple sequence alignment of GASA proteins was performed using ESPript 3.0 [49]. The Gene Structure Display Server 2.0 (https://gsds.gao-lab.org/) was used to display the exon-intron structures of the LsGASA.
Conserved motif and cis-acting regulatory elements analysis
The conserved motifs of LsGASA proteins were predicted using MEME Suite (http://meme-suite.org/), and the subcellular localization of LsGASA proteins was predicted using WoLF PSORT (https://wolfpsort.hgc.jp/) and Plant-mPLoc server (https://rostlab.org/services/nlsdb/). Furthermore, the cis-acting elements of the promoters up to 1500 bp upstream of the start codon of all LsGASAs were predicted using PlantCARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/).
Subcellular localization analysis
To examine the subcellular localization of LsGASAs, the CDS of LsGASA were cloned into the pCR/GW/TOPO cloning vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and then cloned into the pMDC43 vector using LR Clonase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Recombinant vectors containing the GFP expression cassette were examined for transient expression using lettuce protoplast transfection. The subcellular localization of LsGASAs was observed using a confocal laser scanning microscope (LSM 700, Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
Plant material, growth, and abiotic stress conditions
The lettuce cultivar D. atrakce (accession no. IT275492; National Agrobiodiversity Center, Korea) was used in this study. Germplasm was provided by the National Agrobiodiversity Center, Korea, with permission for use in this experiment. D. atrakce was grown in 32 cell trays and placed in a growth chamber (HB-301 L-3, Hanbaek science, Korea) set at 22/20 °C (16 h/8 h), 60% relative humidity, and 18,000 lx light intensity. Plants were exposed to abiotic stress and hormone treatment 25 d after planting. To examine the responses of the LsGASAs to abiotic stresses and phytohormone applications, 25-day-old seedlings were subjected to diverse treatments such as heat stress (35/25 °C, 16 h/8 h), 20% polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000), 250 mM sodium chloride (NaCl), low temperature (4 °C), 150 μΜ of GA3, 150 μΜ of paclobutrazol (PAC) and 100 μM of ABA, and the treated lettuce seedling shoot apical meristem (SAM) and leaves were harvested at time intervals of 2, 6, 12, 24, 48 and 72 h. All the obtained samples were immediately stored at − 80 °C until further use.
Paraffin sections
SAM of heat-stressed ‘Detenicka atrakce’ was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, followed by vacuum for 20 min. An ethanol series of 30, 50, 70, 95, and 100% was used to dehydrate the fixed samples. The dehydrated samples were cleaned with tert-butyl alcohol (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) series (35, 50, 70, and 100%). The cleaned samples were infiltrated and embedded in Paraplast Plus (Sigma-Aldrich) at 58 °C. Embedded samples were cut into 8-μm thick sections using a microtome (Leica RM2255). For observation, sectioned samples were stained with 0.05% toluidine blue O (Sigma-Aldrich) in citrate buffer (pH 4) and coverslips were applied using Canada balsam (Duksan Science, Korea). Finally, slides were observed under an upright microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
Gene expression analysis
Total RNA was extracted from organ tissues (leaves, roots, stems, seeds, and flowers) and the extract was treated with TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). A Power cDNA synthesis kit (iNtRON Biotechnology, Korea) was used to synthesize first-strand circular DNA (cDNA) from 1 μg total RNA according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to confirm the specificity of gene-specific primers designed using Primer-BLAST (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/index.cgi? LINK_LOC=BlastHome) (Additional file 6: Table S3). Diluted cDNAs were used as templates for semi-quantitative real-time (RT)-PCR analysis. Semi-qRT-PCR was performed as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of 1 min at 95 °C, 30 s at 58 °C, 1 min at 72 °C, and a final elongation step at 72 °C for 5 min. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed using EvaGreen 2X qPCR Mastermix (ABM, Vancouver, BC, Canada) on a CFX-96 RT-PCR systems (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) with three independent replicates. Gene expression was calculated as the fold change using the 2−ΔΔCT method [50].
Availability of data and materials
The genome sequences of Lactuca Sativa L. were downloaded from the Phytozome database (https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/info/Lsativa_V8) and the datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included in the article and its Additional files.
References
Herzog M, Dorne AM, Grellet F. GASA, a gibberellin-regulated gene family from Arabidopsis thaliana related to the tomato GAST1 gene. Plant Mol Biol. 1995;27(4):743–52.
Shi L, Gast RT, Gopalraj M, Olszewski NE. Characterization of a shoot-specific, GA3-and ABA-regulated gene from tomato. Plant J. 1992;2(2):153–9.
Su D, Liu K, Yu Z, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Wu Y, et al. Genome-wide characterization of the tomato GASA family identifies SlGASA1 as a repressor of fruit ripening. Hort Res. 2023;10(1):uhac222.
Rezaee S, Ahmadizadeh M, Heidaru P. Genome-wide characterization, expression profiling, and post-transcriptional study of GASA gene family. Gene Rep. 2020;20:100795.
Faraji S, Mehmood F, Malik HMT, Ahmed I, Heidari P, Poczai P. The GASA gene family in cacao (Theobroma cacao, Malvaceae): genome wide identification and expression analysis. Agron. 2021;11(7):1425.
Cheng X, Wang S, Xu D, Liu X, Li X, Xiao W, et al. Identification and analysis of the GASR gene family in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and characterization of TaGASR34, a gene associated with seed dormancy and germination. Front Genet. 2019;10:980.
Ahmad B, Yao J, Zhang S, Li X, Zhang X, Yadav V, et al. Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of GASA genes during different stages of seed development in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) predict their involvement in seed development. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):1088.
Li Z, Gao J, Wang G, Wang S, Chen K, Pu W, et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of GASA gene family in Nicotiana tabacum. Front Genet. 2021;12:768942.
Zhang S, Yang C, Peng J, Sun S, Wang X. GASA5, a regulator of flowering time and stem growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol. 2009;69(6):745–59.
Ben-Nissan G, Lee JY, Borohov A, Weiss D. GIP, a Petunia hybrida GA-induced cysteine-rich protein: a possible role in shoot elongation and transition to flowering. Plant J. 2004;37(2):229–38.
Zimmermann R, Sakai H, Hochholdinger F. The gibberellic acid stimulated-like gene family in maize and its role in lateral root development. Plant Physiol. 2010;152(1):356–65.
Moyano-Canete E, Bellido ML, Garcia-Caparros N, Medina-Puche L, Amil-Ruiz F, González-Reyes JA, et al. FaGAST2, a strawberry ripening-related gene, acts together with FaGAST1 to determine cell size of the fruit receptacle. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013;54(2):218–36.
Roxrud I, Lid SE, Fletcher JC, Schmidt ED, Opsahl-Sorteberg HG. GASA4, one of the 14-member Arabidopsis GASA family of small polypeptides, regulates flowering and seed development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007;48(3):471–83.
Chen B, Sun Y, Tian Z, Fu G, Pei X, Pan Z, et al. GhGASA10–1 promotes the cell elongation in fiber development through the phytohormones IAA-induced. BMC Plant Biol. 2021;21(1):448.
Qu J, Kang SG, Hah C, Jang JC. Molecular and cellular characterization of GA-stimulated transcripts GASA4 and GASA6 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci. 2016;246:1–10.
Zhang L, Geng X, Zhang H, Zhou C, Zhao A, Wang F, et al. Isolation and characterization of heat-responsive gene TaGASR1 from wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Plant Biol. 2017;60:57–65.
GsGASA1 mediated root growth inhibition in response to chronic cold stress is marked by the accumulation of DELLAs.
Sun S, Wang H, Yu H, Zhong C, Zhang X, Peng J, et al. GASA14 regulates leaf expansion and abiotic stress resistance by modulating reactive oxygen species accumulation. J Exp Bot. 2013;64(6):1637–47.
Alonso-Ramírez A, Rodríguez D, Reyes D, Jiménez JA, Nicolás G, López-Climent M, et al. Evidence for a role of gibberellins in salicylic acid-modulated early plant responses to abiotic stress in Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Physiol. 2009;150:1335–44.
Zhang S, Wang X. Overexpression of GASA5 increases the sensitivity of Arabidopsis to heat stress. J Plant Physiol. 2011;168(17):2093–101.
Ko CB, Woo YM, Lee DJ, Lee MC, Kim CS. Enhanced tolerance to heat stress in transgenic plants expressing the GASA4 gene. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2007;45(9):722–8.
Mou B. Nutritional quality of lettuce. Curr Nutr Food Sci. 2012;8:177–87.
Mulabagal V, Ngouajio M, Nair A, Zhang Y, Gottumukkala AL, Nair MG. In vitro evaluation of red and green lettuce (Lactuca sativa) for functional food properties. Food Chem. 2010;118(2):300–6.
Sgherri C, Pérez-López U, Micaelli F, Miranda-Apodaca J, Mena-Petite A, Muñoz-Rueda A, et al. Elevated CO2 and salinity are responsible for phenolics-enrichment in two differently pigmented lettuces. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2017;115:269–78.
Wahid A, Gelani S, Ashraf M, Foolad MR. Heat tolerance in plants: an overview. Environ Exp Bot. 2007;61(3):199–223.
Thompson HC, Knott JE. The effect of termperature and photoperiod on the growth of lettuce. Proc Amer Soc Hort Sci. 1933;30:507–9.
Chen Z, Han Y, Ning K, Ding Y, Zhao W, Yan S, et al. Inflorescence development and the role of LsFT in regulating bolting in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). front. Plant Sci. 2018;8:2248.
Chen Z, Zhao W, Ge D, Han Y, Ning K, Luo C, et al. LCM-seq reveals the crucial role of LsSOC1 in heat-promoted bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Plant J. 2018;95(3):516–28.
Darqui FS, Radonic LM, Trotz PM, López N, Rovere CV, Hopp HE, et al. Potato snakin-1 gene enhances tolerance to Rhizoctonia solani and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in transgenic lettuce plants. J Biotechnol. 2018;283:62–9.
Wang L, Wang Z, Xu Y, Joo SH, Kim SK, Xue Z, et al. OsGSR1 is involved in crosstalk between gibberellins and brassinosteroids in rice. The Plant J. 2009;57(3):498–510.
Xu G, Guo C, Shan H, Kong H. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon–intron structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(4):1187–92.
Heidari P, Puresmaeli F, Mora-Poblete F. Genome-wide identification and molecular evolution of the magnesium transporter (MGT) gene family in Citrullus lanatus and Cucumis sativus. Agronomy. 2022;12:2253.
Han S, Jiao Z, Niu MX, Yu X, Huang M, Liu C, et al. Genome-wide comprehensive analysis of the GASA gene family in Populus. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12336.
Zhang M, Cheng W, Wang J, Cheng T, Zhang Q. Genome-wide identification, evolution, and expression analysis of GASA gene family in Prunus mume. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10923.
Chen C, Lee SC, Pan SM, Hsieh HL. GASA4, a GA-stimulated gene, participates in light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2007;172(6):1062–71.
Li J, Zhao S, Yu X, Du W, Li H, Sun Y, et al. Role of Xanthoceras sorbifolium MYB44 in tolerance to combined drought and heat stress via modulation of stomatal closure and ROS homeostasis. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021;162:410–20.
Fukuda M, Matsuo S, Kikuchi K, Mitsuhashi W, Toyomasu T, Honda I. The endogenous level of GA1 is upregulated by high temperature during stem elongation in lettuce through LsGA3ox1 expression. J Plant Physiol. 2009;166(18):2077–84.
Fan S, Zhang D, Zhang L, Gao C, Xin M, Tahir MM, et al. Comprehensive analysis of GASA family members in the Malus domestica genome: identification, characterization, and their expressions in response to apple flower induction. BMC Genomics. 2017;18(1):827.
Zhang K, Hu Y, Yang D, Yan C, Li N, Li Z, et al. Genome-wide identification of GASA gene family in ten cucurbitaceae species and expression analysis in cucumber. Agronomy. 2022;12(8):1978.
Lee SC, Han SK, Kim SR. Salt-and ABA-inducible OsGASR1 is involved in salt tolerance. J Plant Biol. 2015;58:96–101.
Wang H, Wei T, Wang X, Zhang L, Yang M, Chen L, et al. Transcriptome analyses from mutant salvia miltiorrhiza reveals important roles for SmGASA4 during plant development. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):2088.
Wu T, Cheng C, Zhong Y, Lv Y, Ma Y, Zhong G. Molecular characterization of the gibberellin-stimulated transcript of GASA4 in citrus. Plant Growth Regul. 2020;91:89–99.
Finn RD, Clements J, Eddy SR. HMMER web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:W29–37.
Voorrips R. MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered. 2002;93(1):77–8.
Zhang Z. KaKs_Calculator 3.0: calculating selective pressure on coding and non-coding sequences. Genom Proteom Bioinform. 2022:S1672-0229(21)00259-X.
Yuan S, Xu B, Zhang J, Xie Z, Cheng Q, Yang Z, et al. Comprehensive analysis of CCCH-type zinc finger family genes facilitates functional gene discovery and reflects recent allopolyploidization event in tetraploid switchgrass. BMC Genomics. 2015;16(1):129.
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant. 2020;13(8):1194–202.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol. 2018;35(6):1547–9.
Robert X, Gouet P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:W320–4.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the plant materials provided by the National Agrobiodiversity Center, Korea.
Funding
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2021R1I1A1A01048945) and partly by a grant from the Ojeong Plant Breeding Research Center of Korea University, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JSY, SHL and YWS conceived and designed the study. JSY, SHL, WJJ, and DYK performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript with support from YWS. All the authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publications
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All methods and materials complied with the relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and legislation.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Characteristics of LsGASAs from lettuce.
Additional file 2: Fig. S1.
A heat map of predicted subcellular localization of 20 LsGASA family. Nucl: nucleus, Cyto: cytoplasm, Mito: mitochondria, Cysk: cytoskeleton, Chlo: chloroplast, E.R: endoplasmic reticulum, Plas: plasma membrane, Golg: golgi apparatus, Pero: peroxisome, and Extra: extracellular.
Additional file 3: Table S2.
Ks, Ka, and Ka/Ks calculation and divergent time of the duplicated LsGASA pairs.
Additional file 4: Fig. S2.
Semi qRT-PCR analysis of 20 LsGASA in shoot apical meristem (SAM) under heat stress conditions using ImageJ program.
Additional file 5: Fig. S3.
Expression analysis of six LsGASA in different tissues (leaf, root, seed, stem and flower). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.
Additional file 6: Table S3.
List of specific primers used in the study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.H., Yoon, J.S., Jung, W.J. et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the lettuce GASA family in response to abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol 23, 106 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04101-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04101-5