Abstract
Gibel carp (Carassius gibelio) is a cyprinid fish that originated in eastern Eurasia and is considered as invasive in European freshwater ecosystems. The populations of gibel carp in Europe are mostly composed of asexually reproducing triploid females (i.e., reproducing by gynogenesis) and sexually reproducing diploid females and males. Although some cases of coexisting sexual and asexual reproductive forms are known in vertebrates, the molecular mechanisms maintaining such coexistence are still in question. Both reproduction modes are supposed to exhibit evolutionary and ecological advantages and disadvantages. To better understand the coexistence of these two reproduction strategies, we performed transcriptome profile analysis of gonad tissues (ovaries) and studied the differentially expressed reproduction-associated genes in sexual and asexual females. We used high-throughput RNA sequencing to generate transcriptomic profiles of gonadal tissues of triploid asexual females and males, diploid sexual males and females of gibel carp, as well as diploid individuals from two closely-related species, C. auratus and Cyprinus carpio. Using SNP clustering, we showed the close similarity of C. gibelio and C. auratus with a basal position of C. carpio to both Carassius species. Using transcriptome profile analyses, we showed that many genes and pathways are involved in both gynogenetic and sexual reproduction in C. gibelio; however, we also found that 1500 genes, including 100 genes involved in cell cycle control, meiosis, oogenesis, embryogenesis, fertilization, steroid hormone signaling, and biosynthesis were differently expressed in the ovaries of asexual and sexual females. We suggest that the overall downregulation of reproduction-associated pathways in asexual females, and their maintenance in sexual ones, allows the populations of C. gibelio to combine the evolutionary and ecological advantages of the two reproductive strategies. However, we showed that many sexual-reproduction-related genes are maintained and expressed in asexual females, suggesting that gynogenetic gibel carp retains the genetic toolkits for meiosis and sexual reproduction. These findings shed new light on the evolution of this asexual and sexual complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The establishment of sexual reproduction has been a major event in the evolution of eukaryotes [1]. However, asexual reproduction has evolved independently in dozens of eukaryotic lineages, and is documented in approximately 80 vertebrate species, all representing reptiles, amphibians [2], and teleost fish [3]. Asexual species often originate from hybridization events and/or ploidy alteration [4,5,6,7]. These processes usually affect meiosis and generate new species with asexual females only [8,9,10,11]. Both sexual and asexual reproduction exhibit various evolutionary and ecological advantages and disadvantages. The main disadvantage of sexual reproduction is the two-fold cost of meiosis and the production of male offspring [12]. Consequently, sexual individuals can be outnumbered by parthenogenetic females that exhibit twice the egg production rate. On the other hand, parthenogenetic forms suffer from the accumulation of deleterious mutations and reduced adaptive abilities, including lower ecological tolerance and higher susceptibility to parasites, following the principle of Muller`s ratchet [13]. Hence, asexually reproducing species are usually considered a short-term evolutionary dead-end, and this explains the maintenance of sexual reproduction in the vast majority of eukaryotic lineages [14]. Still, asexual reproduction persists in nature, and for some vertebrates, sexual and asexual complexes of closely-related species often coexist with sexual forms in the same habitats (e.g., the teleosts Poecilia and Cobitis, and the lizard Aspidoscelis) [6, 15, 16].
Interspecific hybridization played an important role in the formation of polyploid asexual species. In amphibians and teleosts, all-female asexual species reproduce by gynogenesis [17], a process where females use the sperm from males of the same species or a closely-related species to induce embryogenesis, without the contribution of paternal genetic material to the offspring. Regarding fish, several asexual-sexual complexes have been reported. The asexual North American leuciscid Phoxinus eos-neogaeus is the result of interspecific hybridization between the sexual species P. eos and P. neogaeus [18]. In the European Cobitis complex, hybridization between sexual species generated sterile males and asexual triploid females that produce eggs through premeiotic endoreplication [6, 19]. The asexual Poecilia formosa from the Amazon basin, which forms eggs through achiasmatic meiosis without recombination [15], results from hybridization between two sexual species, P. mexicana and P. latipinna [20]. The Iberian minnow Leuciscus alburnoides represents another case of a species resulting from hybridization, this with a complex genetic constitution and exhibiting the coexistence of diploid and triploid forms, as well as gynogenesis and sexual reproduction [21, 22].
The gibel carp (Carassius gibelio), also known as Prussian carp, considered as a member of the C. auratus complex or with a species status [23, 24], is a cyprinid fish originating from eastern Eurasia that became invasive in European freshwater ecosystems during the 20th century, due to its high ecological tolerance and adaptive abilities [25, 26]. Gibel carp exhibits a dual mode of reproduction - sexual reproduction and gynogenesis [23, 27,28,29]. The emergence of asexual reproduction in this species is concomitant with a triploidization event [30]. The first populations invading the freshwaters of the Czech Republic around 1975 [31] included only triploid asexual females. Fifteen years later, mixed populations composed of triploid asexual females and diploid females and males reproducing sexually appeared. A low proportion of triploid and tetraploid males was also reported [31, 32]. In Asian populations of C. auratus gibelio (following the taxonomy used by Asian authors), this phenomenon was explained by allogynogenesis, where heterologous sperm sometimes contribute to the phenotype of the offspring [33]. Zhou et al. (2000) [32] even reported molecular evidence of sexual reproduction in the asexual females of Chinese populations of C. auratus gibelio. They suggest that homologous sperm insemination of the eggs of asexual females is similar to classical sexual reproduction (the fused nucleus of the zygote undergoes recombination and removes extra maternal chromosomes). However, there is no empirical evidence of the capacity of sexual reproduction in the asexual form of C. gibelio distributed across Europe.
The coexistence of the two reproduction forms in C. gibelio might be a unique case of the switch from a unisexual species to a partly sexual species. Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the coexistence of asexual and sexual individuals (summarized by Knytl et al. [23]). The Red Queen hypothesis predicts evolution towards equilibrium in the populations of sexual and asexual forms coexisting together and co-evolving with parasites. As asexual reproduction is associated with reduced genetic diversity, parasitism is supposed to play an important role in the maintenance of sexual reproduction [28, 34]. Clonally reproducing females of C. gibelio suffer from higher parasite loads when compared to the genetically variable sexual form which is expected to escape the parasite infection. Sexual selection also increases the variability of immune genes, therefore sexual diploids show higher genetic diversity in immune genes than asexual triploids, in accordance with the Red Queen hypothesis [28]. The coexistence of the two reproduction forms in fish may also be facilitated by other ecological processes, such as male discrimination against asexual females [35], the generation of sexual individuals from asexual females [36], the differential competitive abilities of asexuals and sexuals [37], and the occupation of different ecological niches [38]. While asexual reproduction allows for a quick clonal multiplication of individuals in stable environments [39], sexual reproduction favors genetic diversity [40], heterozygosity, and DNA repair, and hence adaptation to changing environments. Moreover, the necessity of asexual forms to coexist with sexual forms is directly related to gynogenesis, which requires males of conspecifics or close species in the same habitats for egg activation.
Carassius gibelio represents a unique example of a species where sexual and asexual forms coexist [34]. Hence, this species constitutes an object of study to elucidate the evolution of sexuality and asexuality in animals, and the mechanisms responsible for the stable coexistence of sexual and asexual individuals. Furthermore, the origin of C. gibelio is still in question. The widely accepted hypothesis is that C. gibelio arose from autotriploidization within the evolutionary branch of the C. auratus complex, leading to triploid asexual females [41,42,43,44]. However, Yuan et al. (2010) [45], focusing on hox genes, suggested the potential hybrid origin of triploid asexual C. gibelio from C. auratus and C. carpio. Understanding the role of polyploidization in the origin of C. gibelio, and the extent of the genomic contribution of C. carpio and C. auratus to C. gibelio, could provide a better understanding of the evolution of asexual and sexual reproduction in C. gibelio.
Here, the molecular mechanisms associated with reproduction in C. gibelio were analysed to study the coexistence of asexual and sexual forms. In particular, the expression of reproduction-related genes was expected to differ between asexual and sexual females, since meiosis-related genes are not important for asexually reproducing individuals. To test this hypothesis, transcriptome profile analyses of gonadal tissues (ovaries) from asexual females and sexual females of C. gibelio were performed. In addition, the transcriptomes of the closely-associated species C. carpio and C. auratus were also analysed, with a particular emphasis on the genes contributing to sexual reproduction.
Materials and methods
Fish tissue sampling
Asexual and sexual C. gibelio were obtained from artificial breeding of the parental fish collected in their natural habitats. Parental C. gibelio were sampled in the locality (Dyje River, Czech Republic) and genotyped following the approach of Pakosta et al. [46], Papoušek et al. [47] and Šimková et al. [48]. Asexual female offspring was obtained by induced embryogenesis using sperm of C. carpio. The sexual offspring was obtained from the artificial interbreeding of sexual specimens. The ploidy of parental asexual females used for gynogenesis (i.e. induced embryogenesis by C. carpio) and parental sexual specimens used for interbreeding was analysed by flow cytometry following Šimková et al. (2015). From each fish, fin clip about 1 cm2 was sampled for ploidy detection. Before analysis this tissue was homogenised with scissors on Petri dish in 2 ml solution of CyStain DNA 1 step PARTEC and relative DNA content was estimated using Partec CCA I flow cytometer (Partec GmbH; www.sysmex-par tec.com). Diploid C. auratus was used as a reference standard. All parental C. gibelio were also genotyped for mtDNA (D-loop) and microsatellite loci were amplified following Papoušek et al. (2008), Šimková et al. (2013) and Pakosta et al. (2018).
The fish offspring was reared in aquarium conditions until the age of four years and subsequently their gonadal tissues were sampled (the age of the examined fish corresponded to 4+). Cyprinus carpio and Carassius auratus were obtained from external breeding facilities. Fish were euthanized using physical stunning through a blow to the skull with a blunt wooden instrument immediately followed by exsanguination.
Four or five biological samples per fish group from a total of 8 fish groups were analysed (females and males of C. gibelio resulting from sexual reproduction, females and temperature-induced males of C. gibelio resulting from gynogenesis, females and males of sexual C. auratus, and females and males of sexual C. carpio). Gonadal tissues of each fish specimen were individually submerged in Ambion RNAlater stabilization solution (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Tubes with tissues were stored at -80ºC until the isolation of total RNA. Prior to sampling, ploidy of each C. gibelio specimen was checked using the same methodology as described above.
RNA extraction and library preparation
Total RNA was isolated from the gonad tissue of each fish specimen. For extraction, PureLink® RNA Mini Kit (Ambion) with Trizol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and on-column PureLink DNase treatment were used according to the manufacturer´s protocol. Reagent and buffer volumes were adjusted according to the weight of tissue entering the isolation process (30 mg on average). The final elution was performed using 100 µl of RNAse-free water in the first step and the primal eluate in the second step. The yield and concentration of RNA isolates were checked using a QubitTM 4 fluorometer (Invitrogen by Thermo Fisher Scientific) and Qubit RNA HS Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The quality and integrity of RNA were analysed using RNA 6000 Nano Kit on a 2100 Bioanalyser instrument (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). All RNA isolates were normalized by dilution at a uniform concentration of 20 ng/µl with RNase-free water. They served as templates for DNA library preparation in twice the reaction volume recommended by the manufacturer.
All samples (RNA integrity number – RIN > 7) were used for DNA library preparation. 500ng of total RNA was used for mRNA enrichment using the Poly(A) mRNA Magnetic Isolation Module (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA). Subsequently, NEBNext® Ultra™ Directional RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina®, and NEBNext® Multiplex Oligos for Illumina® (Dual Index Primers Set 2, New England Biolabs) were used for library preparation, with 11 PCR cycles utilized for PCR enrichment. RNA fragmentation (13 min at 94 °C) and the size selection conditions (a bead volume of 30 µl and 15 µl for the first and second bead selections, respectively) were further modified in the protocol. The quantification of DNA libraries was performed on a QubitTM 4 fluorometer (Invitrogen by Thermo Fisher Scientific) using Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit, and quality and size control were performed on a 2100 Bioanalyser with DNA 1000 Kit (Agilent Technologies). Finally, amplicons were pooled in equimolar amounts. The final concentration of each library in the pool was 10 nM in the pool. Subsequently, NEBNext® Ultra™ Directional RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® and NEBNext® Multiplex Oligos for Illumina® (Dual Index Primers Set 2, New England Biolabs) together with spike-in RNA were used for cDNA library preparation from total RNA. The quality of prepared cDNA libraries was evaluated using a Qubit fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The quality of cDNA libraries was visualized by a 2100 Bioanalyser (Agilent Technologies), and the libraries were finally sequenced by Macrogen Korea on Illumina HiSeq X (one lane) in a paired-end configuration producing 150 bp long reads. Quality and quantity control steps were carried out by a service company.
NGS data analyses
A quality check of raw paired-end fastq reads was carried out by FastQC [49] and their origin was categorized using BioBloomTools v2.3.4 [15]. The Illumina adapters clipping and quality trimming of raw fastq reads were performed using Trimmomatic v0.39 [50] with settings CROP:250 LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:5 MINLEN:35. Trimmed RNAseq reads were mapped to the Carassius auratus genome (ASM336829v1) with Ensembl annotation (release 104) using STAR v2.7.3a [51] as a splice-aware short read aligner and default parameters except for --outFilterMismatchNoverLmax 0.1 and --twopassMode Basic. Quality control after alignment concerning the number and percentage of uniquely- and multi-mapped reads, rRNA contamination, mapped regions, read coverage distribution, strand specificity, gene biotypes, and PCR duplication was performed using several tools – namely, RSeQC v4.0.0 [52], Picard toolkit v2.25.6 [53], and Qualimap v.2.2.2 [54]. All statistics were processed by MultiQC v1.10.1 [55].
SNP clustering analysis
The genomic sequences of all collected samples were aligned to the Carassius auratus reference genome (ASM336829v1-104) utilizing the Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (BWA) software [56]. Post alignment and germline variants were called using Strelka2 variant calling software [57], generating variant calls in VCF format which were further filtered to retain only high-confidence variants. These variants were then annotated using the reference Gene Transfer Format (GTF) file for Carassius auratus (ASM336829v1-104). Subsequent data processing was carried out in R, where the variant tables were further refined and merged with sample information. A series of filtering steps were performed to ensure only variants with sufficient coverage and sample counts were retained for analysis. The filtered variant table was then reorganized and formatted for subsequent comparative analyses. Variants located on sex chromosomes were excluded for certain analyses to ensure accurate cross-species comparisons. The data were then restructured to compare SNP identity across species, generating similarity matrices and Venn diagrams to visualize the overlap of SNPs by species and ploidy levels.
Differential expression analysis and pathway enrichment analysis
Appropriate bioinformatics tools were used for the processing of raw sequencing data. The genome of C. auratus was used as reference. The differential gene expression was calculated on the basis of the gene counts produced using featureCounts from the Subread package v2.0 [58] and further analysed by Bioconductor package DESeq2 v1.34.0 [59]. Data generated by DESeq2 with independent filtering were selected for differential gene expression analysis to avoid potential false positive results. Differences in gene expression were considered significant on the basis of a cut-off of the adjusted p-value ≤ 0.05. GO term enrichment was analysed using David [60] to retrieve Gene Ontology terms in the Biological process, Cellular Component and Molecular function categories, as well as KEGG pathways [61, 62]. Graphical representations of the GO enrichment were realized using R [63] and Revigo [64]. Reproduction-associated candidate genes were retrieved using the BlastKoala tool of KEGG [61], the BioMart tool of Ensembl [65], and published studies [20, 66,67,68]. GO terms enrichment was tested using Fisher’s exact test (α = 0.05) with false discovery rate (FDR) correction of the p-value. To interpret the biological functions of the DEGs, their mapping to the Gene Ontology (GO) [62] and KEGG [61] databases was performed to analyse pathway enrichment. In each of six fish groups associated with sexual reproduction and asexual males, significantly differently-expressed genes (DEGs) compared to the triploid asexual females of C. gibelio were selected on the basis of the following criteria: Basemean > 10, and a padj value < 0.05. For KEGG pathway analysis, no filtering based on log2 fold change was applied. Gene functions were investigated using the biological databases Uniprot [69], KEGG [61], Zfin [70] and GeneCards [71]. Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed using the DESeq2 R package [59]. For PCA based on reproduction-associated genes, a set of 208 reproduction genes was selected using the BioMart tool of Ensembl [65].
Gene selection and real-time quantitative PCR
Based on the results of an NGS approach and published studies [20, 66,67,68], as well as the presence of appropriate GO and KEGG terms, candidate reproduction-associated genes were selected for the further analyses of gene expression. A-tubulin (A-tub) was used as a housekeeping gene to normalize variation in the gene expression, this gene was previously reported to be stable in fish ovary [72]. The Reference Gene Selection Tool from Bio-Rad CFX Maestro software (Bio-Rad), based on geNorm software principles [73] with an algorithm to normalize the Cq of each gene against the Cq values of the reference gene, was used. A total of 20 biologically-relevant genes were selected from transcriptomic outputs using published studies, and the expressions of 17 of them were validated by real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR). Three genes were excluded because of the amplification of unspecific products. Primers were designed using Primer Blast [74] at the exon-exon junction. A summary of the genes analysed, and their primer sequences are presented in Table 1.
Reverse transcription following total RNA extraction from preserved samples of gonadal tissues stored in RNAlater was performed using High-Capacity RNA-to-cDNA Kit (Applied Biosystems by Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The suitability of primers, their optimal annealing temperatures and amplicon lengths, and the specificity of the amplification of all selected genes were verified by classical PCR for representative samples of all fish groups. The PCR reaction mix (10 ul) contained 5 µl of prepared cDNA, 1 x Taq Buffer with (NH4)2SO4, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 200 µM of each dNTP, 0.4 µM of forward and reverse primers (Table 1), 1 U of Taq DNA polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and nuclease-free water. PCR was run under the following conditions: initial denaturation at 95˚C for 4 min; 30 cycles of 95˚C for 30 s, an optimization gradient of 40–65˚C for 30 s, 72˚C for 45 s; and a final amplification at 72˚C for 10 min. At least 5 samples from each fish group were used for the test. Three replicates for each sample were included in the qPCR analysis.
Real-time qPCR was performed using the LightCycler 480 II Real-Time PCR System (Roche Diagnostics) and LightCycler 480 SYBR Green I Master chemistry (Roche). The reaction mixture (final volume 20 µl) consisted of 10 µl of 2x SYBR Green I Master, 1 µl of each primer, 3 µl of dd H2O, and 5 µl of cDNA template. To test the reaction efficiency and to obtain the standard amplification curve, templates were prepared by means of six serial decimal dilutions of the cDNA of representatives of each fish group. Reactions were run on a LightCycler 480 Instrument II under the following conditions: 95˚C for 5 min; 45 cycles of 95˚C for 10 s, 55˚C for 10 s, and 72˚C for 10 s; melt curve 55˚C → 95˚C (increment 0.5˚C)/5 s. In each run plate, together with samples run in triplicates, one negative control, in which RNase/DNase-free water was used instead of the cDNA and A-tub as the reference gene, was analysed. LightCycler 480 software 1.5.1 was used for analyses of qPCR outputs. The relative expression value of the differentially expressed target gene – the normalized expression – was computed using the ΔΔCq method. Differences in gene expression between sexual and asexual females were statistically evaluated. The sequences of the primers used in this analysis are listed in Table 1.
Results
Next generation sequencing and assembly and SNPs analysis of C. gibelio
The sequencing of four to five diploid males and females from C. gibelio, C. auratus and C. carpio, and triploid females and males of C. gibelio yielded from 8 M to 17 M raw reads per individual (Additional file 1). The number of mapped reads varied between 5 M and 12 M. Across individual samples, from 51 to 83% of reads were uniquely mapped, and from 12% to 22% of reads were multimapped. A total of 857,874 SNPs were identified in the transcriptomes of the eight fish groups (males and females of the three species including both triploid and diploid forms of gibel carp). Clustering analysis based on SNP numbers showed that C. gibelio and C. auratus are closely related and that asexual C. gibelio and sexual C. gibelio are conspecific (Fig. 1A). Specifically, the proportion of SNPs shared between C. gibelio and C. auratus was 2.35 times higher than the proportion of SNPs shared by C. gibelio and C. carpio (Fig. 1B). However, C. carpio and C. auratus shared only 3555 SNPs. The sexual diploid and asexual triploid individuals of C. gibelio were more similar to each other than to C. auratus or C. carpio and both forms shared a similar number of SNPs with C. auratus (Fig. 1C).
Differential gene expression analysis
The transcriptome profiles of the females and males of C. gibelio, C. auratus and C. carpio were analysed (Fig. 2). Both reproductive forms – asexual and sexual – were included for C. gibelio. In all cases, the biological replicates of same sex, ploidy level, and species tend to be more similar to each other. PCA based on transcriptome-wide gene expression (Fig. 2A) showed differences in transcriptome profiles between sexes of the same species, these separated by PC1, and a similarity between the transcriptome profiles of the asexual females of C. gibelio and the sexual females of C. gibelio and C. auratus. However, even the females of C. auratus were separated from C. gibelio by PC1. Likewise, the transcriptomes of the diploid and triploid males of C. gibelio and C. auratus also tended to be similar to each other. According to the transcriptome profiles, the males and females of C. carpio were separated from the other fish groups by PC2. To compare the expression levels of reproduction-related genes among fish groups, a total of 208 genes related to reproduction were selected. This set of reproductive genes led to a similar grouping of species and sexes, as revealed by all of the transcriptomic data; however, the asexual triploid females C. gibelio were more separated from the sexual ones of by PC2 (Fig. 2B).
Principal component analysis (PCA) of normalized RNAseq read counts between the diploid males and females of C. gibelio, C. auratus and C. carpio and the triploid females and males of C. gibelio for all genes (A) and a set of 208 randomly selected reproductive genes (B), on the first two principal components
The numbers of non-differentially and differentially expressed genes are shown in Table 2. For all comparisons, the number of upregulated genes in C. gibelio asexual females was higher than the number of downregulated genes or similar to the number of downregulated genes. Comparison of the asexual and sexual females of C. gibelio revealed 1728 differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The numbers of upregulated and downregulated genes are shown in Table 2. The number of DEGs in asexual C. gibelio females was lower compared to sexual females in every species than compared to males of the same species. The number of DEGs between asexual C. gibelio females and C. auratus females and males and the number of DEGs between asexual C. gibelio females and C. carpio females and males was higher when compared to the number of DEGs between asexual C. gibelio females and sexual C. gibelio females and males (Table 2).
GO enrichment analysis
The full transcriptomes of the three species were functionally annotated to 3747 GO terms for females and 3755 GO terms for males. A total of 3635 were shared by all female lines, and 3721 were shared by all male lines. 30 GO terms identified in asexual females of C. gibelio were not identified in the sexual females of C. gibelio, and 30 GO terms identified in the sexual females were not present in the asexual females of C. gibelio. Furthermore, 3 GO terms were identified in diploid males of C. gibelio but not in triploid males, and 3 GO terms were identified in triploid males of C. gibelio but not in diploid males (Fig. 3).
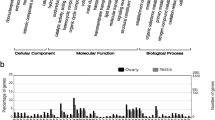
Transcriptomes of sexual and asexual females were compared and investigated for pathway enrichment using overrepresentation analysis. Of the total of 1728 DEGs, 1471 were successfully annotated to the Gene Ontology (GO) and KEGG databases. A total of 809 were upregulated in asexual females in comparison to sexual females, and 662 downregulated. The significantly enriched GO terms are presented in Fig. 4. In the biological process category, we identified GO terms associated with gametogenesis and cell cycle control, including egg coat formation (GO:0035803), the binding of sperm to zona pellucida (GO:0007339), the positive regulation of acrosome reaction (GO:2,000,344), synaptonemal complex assembly (GO:0007130), the negative regulation of nuclear division (GO:0051784), and the negative regulation of cell cycle process (GO:0010948). In the cellular component category, the most enriched terms included egg coat (GO:0035805). In the molecular function category, they included the structural constituent of egg coat (GO:0035804) and calcium ion binding (GO:0005509). The significantly enriched KEGG pathways included oocyte meiosis (caua04114), and cell cycle (caua04110).
Dot plot of GO terms enrichment analysis in the biological process (A), cellular component (B), molecular function (C), and KEGG pathway (D) categories. The x-axis represents the fold enrichment (the number of DEGs in the GO term / the number of all DEGs)/(the number of genes annotated in this pathway/ the number of the genes annotated in all pathways). The y-axis corresponds to the enriched GO terms. The magnitude of dots represents the number of DEGs in the GO term, and the color corresponds to the -log10 of the p-value
Meiosis-associated genes
To determine whether meiotic pathways are disrupted in asexual females of C. gibelio, we first analysed the differences in expression levels of the meiosis-associated genes between sexual and asexual females following refs [66,67,68, 75, 76]. Of the set of 40 meiosis-associated genes, almost all were detected in both asexual and sexual females; however, pms1 was not detected in most sexual and asexual females, and hormad2 was not detected in any sexual or asexual individual. Hence, the meiotic pathways did not appear to be disrupted in asexual females. Seven genes were significantly differently regulated. Spo11, msh2, pds5b and stag1a displayed higher expression levels in sexual females when compared to asexual females, as well as rec114, which was close to significance (padj = 0.07). In contrast, rad1, one rad51b homologue and slc39a1 were significantly more expressed in asexual females. The other meiosis-associated genes, including meiotic nuclear division 1 (mnd1), dmc1, the double strand break repair rad1 and several rad51 homologues, did not show significant gene expression differences (Table 3).
Identification of differentially expressed genes in sexual and asexual females ofC. gibelio
Among the 1728 differentially expressed genes revealed by transcriptome profile analysis, we specifically focussed on the genes related to reproduction pathways revealed by GO and KEGG enrichment analyses and published studies [20, 66, 68]. We identified genes that were involved in reproduction pathways including cell cycle control, oocyte meiosis and maturation, and signalling pathways related to reproduction and sex differentiation (Fig. 5, see Table 4 for the list of the genes and their biological function).
Asexual females retained detectable expressions of all the reproduction-associated genes identified. However, several genes involved in cell cycle control were differently expressed between asexual and sexual females. Asexual females upregulated genes of the Cyclin family, such as ccna2, ccnb2, ccnd2a and ccnf as well as cdk14, a member of the cyclin dependant kinase family (Additional file 2). They also upregulated growth arrest and DNA damage protein 45 alpha B (gadd45ab), the activator e2f1, mitotic arrest deficient 2 like 2 (mad2l2), ring finger 212 (rnf212), aurora kinase a (aurora a), cell division cycle protein 20 (cdc20), the apoptosis regulator bcl2, serine threonine kinase 1 (akt1), and cdk5rap1, which encodes the CDK5 regulatory-subunit-associated protein 1 (see Table 4 for their functions). Members of the formin family, fmnl1a and fmnl2a, were also upregulated in asexual females, as well as the spindlin spinb, while spinw was downregulated. Sexual females also upregulated two genes encoding ATP-dependant RNA helicases, ddx20 and ddx52; as well as nqo1, which encodes the NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1; rassf7b, which encodes the ras-associated domain-containing protein 7b; and stag1a, which encodes a cohesin subunit.
Sexual females upregulated genes involved in oocyte meiosis such as shugoshin 1 (sgo1); serine/threonine kinase 10 (plkk1); phosphatase 1 (pp1); serine/threonine-protein kinase 32 C (stk32c); cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binging (cpeb); syce1, which encodes a protein of the synaptonemal complex that forms between homologous chromosomes during meiosis; and several gene copies of early mitotic inhibitor 1 (emi1, also known as fbxo5) (Additional file 3, Table 4). They also upregulated genes involved in DNA mismatch repair, including rfc4 (replication factor C subunit 4) and genes that encode components of the minichromosome maintenance protein complex, mcm5 and mcm9. Inversely, asexual females upregulated c1orf146, involved in synaptonemal complex assembly.
Concerning oocyte maturation pathways (Additional file 4), sexual females upregulated bucky ball (buc), cell division cycle protein 25 (cdc25), fizzy-related protein homolog 1b (fzr1b), phospholipases cb4 and cd4 (plcb4 and plcd4), and several gene copies of zona-pellucida sperm-binding protein 3 (zp3el) (Table 4). On the other hand, asexual females upregulated h2af1, which encodes an oocyte-specific histone, and uhrf1, which encodes the oocyte specific cell cycle regulator E3 ubiquitin ligase. Members of the fibroblast growth factor (fgf) family were also upregulated. Several egg fertilization-related genes were differently regulated. Calmodulin 3a (calm3a), spag1a (sperm-associated antigen 1a-like), and clec, which encodes a C-type lectin, were upregulated in sexual females (Additional file 3). Camk1gb, which encodes a calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, and calmodulin-regulated spectrin-associated protein 2 (camsap2a) were upregulated in asexual females (Table 4).
Genes involved in signalling pathways were also differentially regulated. Sexual females upregulated genes involved in the gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) signalling pathway, which is important for female sexual differentiation (Additional file 5), such as creb, heparin-binding egf-like growth factor (hbegf), growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (grb2), rbpms2b, involved in ovarian development, and members of the Ras/MAPK family, specifically, hrasa, hrasb and rasa1b, as well as limb bud-heart (lbh), bmp8 and bambia (Table 4). Asexual females upregulated pkc; phospholipase d4b (pld4b); mapk8ip3, involved in the FSH signalling pathway; the protein-kinase encoding gene clk4; plexin b1a; bmp2b; and members of the wnt family (wnt5 and wnt7); as well as fbxo15 and fbxo28, two members of the fbxo family (F-box with uncharacterized domains). Furthermore, components of the TGF-β (transforming growth factor) signalling pathway were differently regulated. Tgf-β 1a was upregulated in sexual females, while the activin receptors acvr1 and acvr2ba, bmp and activin membrane bound inhibitor activin receptor 2 (bambia), the receptor regulated mothers against decapentaplegic homolog (smad2) and the inhibitory smad6 were downregulated (Additional file 6).
KEGG analysis identified DEGs involved in hormonal systems. Asexual females upregulated cyp19a1a, the doublesex and mab3 related transcription factors dmrta2 and dmrt2a, the sry-box transcription factor sox8a, inhibin alpha (inha), and oxtr, encoding the oxytocin receptor (Table 4). Sexual females upregulated piwil2, c-x-c motif chemokine 12 (cxcl12), nuclear receptor coactivator 2 (ncoa2), and luteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin receptor (lhcgr). Several genes related to steroid biosynthesis were also found to be differently regulated between asexual and sexual females (Additional file 7). Asexual females upregulated delta14-sterol reductase (fk); lathosterol oxidase-like (ste1); 17beta-estradiol 17-dehydrogenase (hsd17b1, 1.1.1.62); β-hydroxy-δ5-steroid dehydrogenase (Hsd3b); and genes encoding a glucuronosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.17), a squalene synthase (EC 2.5.1.21), a delta14-sterol reductase (1.3.1.70), a sterol desaturase (erg3), and a lathosterol oxidase (EC 1.14.19.20). They downregulated hyd1, which encodes a cholestenol delta isomerase; the cytochrome P450 family member cyp27b1 (EC 1.14.15.18); and genes encoding a cholestenone-5-alpha-reductase (EC 1.3.1.22), a cholestenol delta-isomerase (EC 5.3.3.5), and a cholesterase (EC 3.1.1.13) (Additional file 7).
Validation of gene expression resulting from RNAseq by RT-qPCR
To validate the DEGs revealed by RNAseq, we performed RT-qPCR for 17 selected genes involved in reproduction that were significantly up- or downregulated in asexual females of C. gibelio compared to sexual females (Table 1). The RT-qPCR analysis confirmed the downregulation of 10 and upregulation of 7 reproduction-associated genes (Fig. 6). There was a positive correlation between the log2 fold change of RNAseq and the log2 fold change of qPCR (r = 0.89, p < 0.001) (Additional file 8).
Validation of gene expression resulting from RNAseq by the RT-qPCR approach using 17 reproduction-related genes. The x-axis displays the gene names. The y-axis displays the log2 fold change of the gene expression between sexual females and asexual females of C. gibelio. A positive log2 fold change of the gene expression indicates that the gene was upregulated in asexual females when compared to sexual females. A negative log2 fold change indicates that the gene was downregulated in asexual females when compared to sexual females. The data represent the means of five independent biological replicates, and bars represent standard deviation. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in the log2 fold change of qPCR data between sexual and asexual females of C. gibelio based on Student’s t-test: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001
Discussion
The present study analysed the transcriptome profiles of gonadal tissues from C. gibelio using RNAseq, specifically to identify DEGs in ovaries associated with reproduction in triploid gynogenetic females and diploid sexual females. We also analysed the transcriptome profiles of gonads in male C. gibelio, and males and females of the two closely-related species C. auratus and C. carpio. A total of 1728 genes were significantly upregulated or downregulated in asexual females of C. gibelio compared to sexual females. The transcriptome profiles based on normalized RNAseq read counts showed a sex-dependant difference for both - all transcribed genes or reproduction-associated genes, with an overall similarity between gynogenetic and sexual females of C. gibelio and females of C. auratus, and an overall similarity between the males of the two Carassius species.
GO term overrepresentation analyses and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses indicated an overall overexpression of genes involved in meiosis and cell cycle control (cell cycle, negative regulation of nuclear division, negative regulation of cell cycle process, oocyte meiosis, and synaptonemal complex assembly), oocyte maturation (egg coat formation, structural constituent of egg coat, and calcium ion binding) and fertilization (binding of sperm to zona pellucida, positive regulation of acrosome reaction). Calcium ion binding, which plays critical roles in fertilization and early development (for review, see Whitaker [77]), was also overrepresented in sexual females. This suggests that the regulation of oogenesis, as well as the response of oocytes to sperm cell binding, differ between sexual reproduction and gynogenesis, where the eggs are only activated by the sperm cell (for review, see Schlupp [78]). An overall downregulation of meiotic and reproduction-associated genes was also reported in Poecilia formosa, a gynogenetic fish species of the Amazon basin, compared to its sexual parental ancestors, P. mexicana and P. latipinna [20]. Similar results were reported in invertebrates that use cyclical parthenogenesis, such as the planktonic crustacean Daphnia, rotifers, and aphids, where the sexual forms upregulate genes involved in cell cycle control, meiosis, oogenesis, and oocyte maturation [79,80,81,82].
On the basis of ovarian transcriptome profiles, we identified around 100 reproduction-associated genes related to oocyte meiosis, oogenesis, embryogenesis, hormone signalling, and fertilization that were differently expressed between sexual and gynogenetic females; the expression pattern of a set of 17 selected genes based on the basis of RNAseq was validated by RT-qPCR. We also specifically analysed 40 meiosis-related genes inferred by previous studies [66,67,68, 75, 76]. We showed that sexual females upregulated several meiosis-associated genes involved in recombination and crossover and in DNA double-strand break formation during meiosis, including spo11, msh2, pds5b, sbk3, stag1a, and rec114. Two components of the minichromosome complex (mcm4 and mcm9), involved in crossover inhibition during meiosis [83], as well as syce1, a component of the synaptonemal complex that forms between homologous chromosomes during recombination, were also upregulated in sexual females [84,85,86]. Sexual females also upregulated genes involved in oocyte maturation, such as emi1 (also named fbxo5), a major F-box constituent of the E3 ubiquitin ligase protein that regulates the anaphase promoting complex (APC) during meiosis and mitosis [87,88,89,90]; and spinw, a major maternal transcript expressed in oocytes during early development. The importance of spindlin in oocytes to embryo transition in C. gibelio has been established [91]. Furthermore, several genes involved in cell cycle regulation, including three members of the Ras/MAPK family, hrasa, hrasb and rasa1b, which encode GTPases controlling cell growth, division, and differentiation [92,93,94,95] through the action of mitogen activated protein kinases [96], were also more expressed in sexual females. This suggests that cell cycle control regulation differs between sexual and gynogenetic females of C. gibelio.
In accordance with our results, gynogenetic P. formosa was shown to underexpress meiosis-related genes, including sbk3, setd7 and stk32c, compared to its supposed sexual ancestors [20]. Similarly, in cyclically parthenogenetic Daphnia, meiosis-related genes, including genes related to the spindle assembly checkpoint, the APC, and meiosis chromosome segregation, were upregulated during sexual reproduction [81]. In particular, spo11, which encodes a topoisomerase involved in chromosomal recombination during the meiotic prophase, was also described as an important player in the meiosis-to-parthenogenesis transition in pea aphid [97], although it was not reported in asexual P. formosa [20].
However, our study also revealed that meiosis pathways were not fully disrupted in gynogenetic females of C. gibelio. They retained detectable expressions of all reproduction-associated genes identified, including meiosis-specific genes, in contrast to P. formosa, where some meiosis-related genes were not expressed [20]. According to our analyses, several of the core meiosis specific genes, such as dmc1, mlh1, mnd1, mre11 and genes of the msh family [67, 68, 75, 76], did not show significant differences in expression between sexual and gynogenetic females of gibel carp. Gynogenetic females even upregulated rad1, a member of the cell cycle checkpoint, also involved in the recombination process during meiosis; rnf212, involved in meiotic recombination; and mad2l2, involved in the spindle assembly checkpoint; as well as meiosis-specific genes that were previously found to be downregulated in gynogenetic P. formosa, such as b4galt, clk4, dmrta2, grapb, and rasl11b [20]. However, these results are in accordance with a study suggesting that meiosis is retained even in gynogenetic strains of C. gibelio in North-east Asia [98]. Furthermore, meiosis genes were reported not to be necessarily associated with sexual reproduction, since asexual amoeba constitutively expressed meiosis-associated genes [66]. Similar results were reported also in rotifers, where no meiosis-specific genes were differently expressed between parthenogenetic and sexual forms [80], and cyclically-parthenogenetic Daphnia, which was shown to express meiosis-specific genes during the parthenogenetic phase [99]. In the pea aphid, several oogenesis and cell cycle-related genes were also upregulated during the asexual reproduction phase [79].
Our results reveal an overall upregulation of pathways related to oocyte maturation in sexual females. They upregulated buc, involved in the formation of Balbiani bodies in the oocytes and germ plasm assembly, including follicular epithelium morphogenesis [100]. This gene plays a key role in the specification of oocyte anterior/posterior polarity through interactions with the RNA-binding proteins, such as rbpms2, a coactivator of transcriptional activity involved in meiosis and oogenesis [101]. Sexual females of C. gibelio also upregulate genes involved in progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation, such as members of the plexin and Wnt families. The Wnt pathway regulator lbh, previously reported to be upregulated in females during oocyte maturation in C. gibelio, was also more expressed in sexual females in our study. Similarly, in aphids, genes involved in oocyte axis formation were found to be upregulated during the sexual phase [82]. Furthermore, our analyses support an overall upregulation of sperm-egg recognition and fertilization pathways in sexual females. They upregulated calm3a, a member of the calmodulin family responsible for calcium-dependant signal transduction following sperm binding, as well as plcb4, a phospholipase involved in oocyte fertilization [102]. In addition, sexual females upregulated components of the zona pellucida, the extracellular matrix surrounding the oocyte involved in sperm-egg recognition [103]. A gene encoding a Ca2+-dependant C-type lectin, which was shown to be translocated in cortical granules during oocyte maturation and involved in sperm-egg recognition and fertilization in C. gibelio [104], was also significantly upregulated in sexual females. These findings highlight the importance of oocyte maturation, sperm-egg recognition, and fertilization pathways in the coexistence of sexual and asexual females.
Inversely, some genes involved in oocyte development, such as DAZ-like genes, were not differentially expressed between gynogenetic and sexual females of gibel carp in our study, while others, including bcl2; the oocyte specific histone h2af1o, which plays a key role in fish embryogenesis [105]; and several members of the FGF family, which promote meiosis and maturation of the oocytes [106], were even more expressed in asexual females than in sexual ones. Oocyte maturation and sperm cell binding pathways are not expected to be disrupted in asexual females, since they produce oocytes. Furthermore, gynogenetic C. gibelio females still require sperm cell binding to activate the eggs [78, 107]. The overexpression of some oogenesis-related genes was also reported in aphids during the parthenogenetic phase of their life cycle [79]. Furthermore, the downregulation of uhrf1, an oocyte-specific epigenetic regulator [108] in sexual females of C. gibelio, also reported in aphids [79], suggests a difference in the epigenetic regulation of oogenesis between sexual and asexual forms. Hence, these results suggest that many genes and pathways are involved in both parthenogenetic oogenesis and sexual oogenesis in C. gibelio. However, gene expression differs between the two reproduction forms. It is noteworthy that members of the same gene family can be up- or downregulated, such as members of the zona pellucida and F-box families. Such divergent expression, also reported in Daphnia [81], may suggest functional divergence among members of the same multigenic families.
Our analyses also suggest differences in hormonal signalling and sex differentiation processes between sexual and gynogenetic reproduction. Components of the GnRH signalling pathway, and genes linked to ovarian fertility, such as the gene encoding the luteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin receptor (lhcgr), were more expressed in sexual females. The TGF-β signalling pathway, involved in many physiological processes including sexual differentiation in fish [109,110,111], was also differently regulated between gynogenetic and sexual females of C. gibelio. Sexual females upregulated smad genes, involved in oogenesis, ovarian function, and folliculogenesis via the negative regulation of TGF-β signalling [108, 112,113,114]. Regarding gynogenetic females, they upregulated two dmrt genes. These genes were shown to promote male differentiation and repress female-specific differentiation of the gonads, and they are also involved in brain sexual differentiation [114,115,116,117,118] as well as in XY reversal in sex-alternating fish species [115]. Gynogenetic females of C. gibelio also upregulated ncoa2, a transcriptional coactivator of steroid receptors and nuclear receptor, as well as sox8, involved in female sex determination [119], meiotic progression, and embryonic development [120], and inhibin alpha (inha), involved in steroid hormone biosynthesis. Ovarian aromatase or estrogen synthetase (cyp19a1a), a member of the cytochrome P450 subfamily involved in steroidogenesis [121] and female folliculogenesis and gonadal differentiation, was also upregulated in gynogenetic females of C. gibelio, as was oxtr, a gene encoding the oxytocin receptor, a component of the oxytocin signalling system that modulates reproductive behaviour. Our results also suggest that sexual females upregulated some genes associated with the steroid hormone synthesis pathway. The hydroxysteroid 17-β-dehydrogenase gene hsd17b1, which is both estrogenic [122] and androgenic [123], was more expressed in gynogenetic females. Furthermore, sexual females also upregulated the germ cell maintenance gene piwil2, a member of the Argonaute family involved in male fertility [124].
In this study, we also investigated the evolutionary history of C. gibelio. Ploidy changes shaped the evolution of cyprinids, particularly that of the Carassius auratus complex. This complex was formed by allotetraploidization [42, 125] and further polyploidization events have been reported in diverse lineages of the complex, including C. auratus and C. gibelio [42, 126]. The evolutionary origin of C. gibelio is still in question. A study based on dmrt genes suggested a recent autopolyploidization event within the C. auratus complex that generated the triploid gynogenetic C. gibelio [41]. However, an origin of C. gibelio by hybridization between C. auratus and C. carpio has also been proposed [45]. Our SNP clustering, based on gonadal transcriptomes, using C. gibelio, C. auratus and C. carpio, suggests a close evolutionary relationship between sexual and gynogenetic C. gibelio, as well as a close relatedness between C. gibelio and C. auratus, even though we identified SNPs shared only by C. gibelio and C. carpio, suggesting some genetic contribution of C. carpio to the genome of C. gibelio. The study of Yuan et al. [118] proposed that triploid gynogenetic C. gibelio (3n = 150) resulted from interspecific hybridization between diploid C. auratus (2n = 100) and C. carpio (2n = 100), contributing with two sets and one set of chromosomes, respectively. Specifically, their study showed that two gene copies of four different Hox genes in the genome of gynogenetic C. gibelio are orthologous to the Hox genes of C. auratus and that one is orthologous to the Hox gene of C. carpio [45]. However, the diploid form of C. gibelio was not included in that study. Other studies using mtDNA and hoxa2b gene sequences even suggested a more complex relationship between C. gibelio and C. auratus, where the monophyly of C. gibelio was not supported [127, 128]. In addition, gene flow was highlighted between the two species [98, 127], suggesting that C. gibelio and C. auratus were conspecific and interfertile.
Ploidy changes often affect meiosis, and parthenogenetic species usually result from interspecific hybridization [8] with some exceptions [129]. Polyploidy can lead to the formation of unreduced eggs whose cell cycle is arrested at the metaphase of meiosis II [130]. This results in asexually reproducing species, where the offspring are clones of the mother. Unisexual fish reproduce through gynogenesis, where the sperm from males of the same or closely-related species is still required to activate the egg. Still, because meiosis pathways were not disrupted, a later genetic contribution from a sperm donor such as C. auratus and C. carpio cannot be excluded. Such a case of a complex evolutionary history was reported in the unisexual salamander Ambystoma. However, in this case, the haploid genome of the sperm donor replaced the nuclear genome, a phenomenon known as kleptogenesis [131, 132].
Our results suggest that all along their evolutionary history, asexual lines of C. gibelio did not lose the genetic toolkit for meiosis, and that the sexual reproduction genetic toolkit is not under relaxed selection, a condition also reported in asexual P. formosa [20] and snails [133]. The re-acquisition of sexual reproduction in asexual species is very rare and very few cases have been reported. Either some gynogenetic C. gibelio females were able to secondarily regain sexual reproduction and to produce both diploid and triploid males, or a minority of sexual individuals still persisted within the already formed gynogenetic form and became more abundant later [68]. In all cases, this led to the current sympatric coexistence of sexual and gynogenetic individuals [27, 32]. Polyploidy in general, and triploidy in the case of gynogenetic C. gibelio could possibly compensate the deleterious effects of Muller’s ratchet or the accumulation of deleterious mutations by increasing the number of gene copies and favouring heterozygosity [66]. The genomic incorporation of sperm-derived fragments from an exogenous species, which was reported in gynogenetic C. gibelio from aquaculture in China [33], can also favor genetic diversity in asexual lines. In C. gibelio, the combination of the advantages of gynogenetic reproduction, which allows for faster population growth [26], and sexual reproduction, which provides higher resistance to parasites and higher immune gene variability [28], higher aerobic performance and better immunity [134], lower metabolic rate, and lower energy intake [135], might explain the coexistence of sexual and asexual forms, and the high adaptive abilities of this species and its invasiveness in European water ecosystems.
Data availability
The data used in this study have been deposited in NCBI´s Gene Expression Omnibus and are accessible through GEO Series accession number GSE254010 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE254010).
References
Cavalier-smith T. Origins of the machinery of recombination and sex. Heredity. 2002;88(2):125–41.
Neaves WB, Baumann P. Unisexual reproduction among vertebrates. Trends Genet. 2011;27(3):81–8.
Tobler M, Schlupp I. Parasites in sexual and asexual mollies (Poecilia, Poeciliidae, Teleostei): a case for the Red Queen? Biol Lett. 2005;1(2):166–8.
Dufresne F, Hebert PDN. Hybridization and origins of Polyploidy. Proc R Soc Lond. 1994;258(1):141–6.
Hartfield M. On the origin of asexual species by means of hybridization and drift. Mol Ecol. 2016;25(14):3264–5.
Janko K, Kotlik P, Rab P. Evolutionary history of asexual hybrid loaches (Cobitis: Teleostei) inferred from phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial DNA variation. J Evol Biol. 2003;16(6):1280–7.
Xu S, Innes DJ, Lynch M, Cristescu ME. The role of hybridization in the origin and spread of asexuality in Daphnia. Mol Ecol. 2013;22(17):4549–61.
Lamatsch DK, Stöck M. Sperm-Dependent Parthenogenesis and Hybridogenesis in Teleost Fishes. In: Schön I, Martens K, Dijk P, editors. Lost Sex [Internet]. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands; 2009 [cited 2023 Jul 30]. pp. 399–432. http://link.springer.com/https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2770-2_19.
Rothfels CJ, Otto SP. Polyploid Speciation. In: Encyclopedia of Evolutionary Biology [Internet]. Elsevier; 2016 [cited 2023 Dec 4]. pp. 317–26. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780128000496000731.
Stenberg P, Saura A. Meiosis and its deviations in Polyploid animals. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2013;140(2–4):185–203.
Van de Peer Y, Mizrachi E, Marchal K. The evolutionary significance of polyploidy. Nat Rev Genet. 2017;18(7):411–24.
Maynard Smith J. The origin and maintenance of sex. 1971.
Muller HJ. The relation of recombination to mutational advance. Mutat Res Mol Mech Mutagen. 1964;1(1):2–9.
Otto SP. The Evolutionary Enigma of Sex. Am Nat. 2009;174(S1):S1–14.
Dedukh D, Da Cruz I, Kneitz S, Marta A, Ormanns J, Tichopád T, et al. Achiasmatic meiosis in the unisexual Amazon Molly, Poecilia formosa. Chromosome Res. 2022;30(4):443–57.
Walker JM, Cordes JE, Paulissen MA. Rare syntopy of the diploid parthenogenetic lizard (Aspidoscelis laredoensis) and both gonochoristic progenitors (A. Gularis and A. sexlineata) in Texas, USA. Herpetol Conserv Biol. 2016;11(1):29–39.
JianFang G, Li Z. Genetic basis and breeding application of clonal diversity and dual reproduction modes in polyploid Carassius auratus Gibelio. Sci China Life Sci. 2010;53(4):409–15.
Angers B, Schlosser IJ. The origin of Phoxinus eos-neogaeus unisexual hybrids: hybridization in Phoxinus. Mol Ecol. 2007;16(21):4562–71.
Tichopád T, Franěk R, Doležálková-Kaštánková M, Dedukh D, Marta A, Halačka K, et al. Clonal gametogenesis is triggered by intrinsic stimuli in the hybrid’s germ cells but is dependent on sex differentiation. Biol Reprod. 2022;107(2):446–57.
Schedina IM, Groth D, Schlupp I, Tiedemann R. The gonadal transcriptome of the unisexual Amazon Molly Poecilia formosa in comparison to its sexual ancestors, Poecilia mexicana and Poecilia latipinna. BMC Genomics. 2018;19(1):12.
Alves MJ, Coelho MM, Collares-Pereira MJ. Evolution in action through hybridisation and polyploidy in an Iberian freshwater fish: a genetic review. Genetica. 2001;111:375–85.
Collares-Pereira MJ, Coelho MM. Reconfirming the hybrid origin and generic status of the Iberian cyprinid complex Squalius alburnoides. J Fish Biol. 2010;76(3):707–15.
Knytl M, Forsythe A, Kalous L. A fish of multiple faces, which show us enigmatic and incredible phenomena in Nature: Biology and Cytogenetics of the Genus Carassius. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8095.
Kalous L, Bohlen J, Rylková K, Petrtýl M. Hidden diversity within the prussian carp and designation of a neotype for Carassius gibelio (Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Ichthyol Explor Freshw. 2012;23(1):11–8.
Hanfling B, Bolton P, Harley M, Carvalho GR. A molecular approach to detect hybridisation between crucian carp (Carassius carassius) and non-indigenous carp species (Carassius spp and Cyprinus carpio). Freshw Biol. 2005;50(3):403–17.
Fuad MMH, Vetešník L, Šimková A. Is gynogenetic reproduction in gibel carp (Carassius gibelio) a major trait responsible for invasiveness? J Vertebr Biol [Internet]. 2021 Nov 18 [cited 2023 Aug 5];70(4). https://bioone.org/journals/journal-of-vertebrate-biology/volume-70/issue-4/jvb.21049/Is-gynogenetic-reproduction-in-gibel-carp-Carassius-gibelio-a-major/https://doi.org/10.25225/jvb.21049.full.
Gui J, Zhou L. Genetic basis and breeding application of clonal diversity and dual reproduction modes in polyploid Carassius auratus Gibelio. Sci China Life Sci. 2010;53(4):409–15.
Šimková A, Košař M, Vetešník L, Vyskočilová M. MHC genes and parasitism in Carassius gibelio, a diploid-triploid fish species with dual reproduction strategies. BMC Evol Biol. 2013;13(1):122.
Šimková A, Hyršl P, Halačka K, Vetešník L. Physiological and condition-related traits in the gynogenetic-sexual Carassius auratus complex: different investments promoting the coexistence of two reproductive forms? BMC Evol Biol. 2015;15(1):154.
Zhu HP, Ma DM, Gui JF. Triploid origin of the gibel carp as revealed by 5S rDNA localization and chromosome painting. Chromosome Res. 2006;14(7):767–76.
Lusková V, Lusk S, Halačka K, Vetešník L. Carassius auratus Gibelio—the most successful invasive fish in waters of the Czech Republic. Russ J Biol Invasions. 2010;1(3):176–80.
Zhou L, Wang Y, Gui JF. Genetic evidence for Gonochoristic Reproduction in Gynogenetic Silver Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus Gibelio Bloch) as revealed by RAPD assays. J Mol Evol. 2000;51(5):498–506.
Chen F, Li XY, Zhou L, Yu P, Wang ZW, Li Z, et al. Stable genome incorporation of sperm-derived DNA fragments in gynogenetic clone of Gibel Carp. Mar Biotechnol. 2020;22(1):54–66.
Hakoyama H, Nishimura T, Matsubara N, Iguchi K. Difference in parasite load and nonspecific immune reaction between sexual and gynogenetic forms of Carassius auratus. Biol J Linn Soc. 2001;72(3):401–7.
Moore WS, McKay FE. Coexistence in Unisexual-Bisexual species complexes of Poeciliopsis (Pisces: Poeciliidae). Ecology. 1971;52(5):791–9.
Barron JN, Lawson TJ, Jensen PA. Analysis of potential factors allowing coexistence in a sexual/asexual minnow complex. Oecologia. 2016;180(3):707–15.
Schley D, Doncaster CP, Sluckin T. Population models of sperm-dependent parthenogenesis. J Theor Biol. 2004;229(4):559–72.
Vrijenhoek RC. UNISEXUAL FISH: Model systems for studying Ecology and Evolution. Annu Rev Ecol Syst. 1994;94(25):71–96.
Barbuti R, Mautner S, Carnevale G, Milazzo P, Rama A, Sturmbauer C. Population dynamics with a mixed type of sexual and asexual reproduction in a fluctuating environment. BMC Evol Biol. 2012;12(1):49.
Zhao X, Li Z, Ding M, Wang T, Wang MT, Miao C, et al. Genotypic males play an important role in the creation of genetic diversity in Gynogenetic Gibel Carp. Front Genet. 2021;12:691923.
Li XY, Zhang XJ, Li Z, Hong W, Liu W, Zhang J, et al. Evolutionary history of two divergent Dmrt1 genes reveals two rounds of polyploidy origins in gibel carp. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2014;78:96–104.
Luo J, Gao Y, Ma W, Bi X y, Wang S y, Wang J et al. Tempo and mode of recurrent polyploidization in the Carassius auratus species complex (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae). Heredity. 2014;112(4):415–27.
Kuhl H, Du K, Schartl M, Kalous L, Stöck M, Lamatsch DK. Equilibrated evolution of the mixed auto-/allopolyploid haplotype-resolved genome of the invasive hexaploid prussian carp. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):4092.
Wang Y, Li XY, Xu WJ, Wang K, Wu B, Xu M, et al. Comparative genome anatomy reveals evolutionary insights into a unique amphitriploid fish. Nat Ecol Evol. 2022;6(9):1354–66.
Yuan J, He Z, Yuan X, Jiang X, Sun X, Zou S. Speciation of polyploid Cyprinidae fish of common carp, crucian carp, and silver crucian carp derived from duplicated hox genes. J Exp Zoolog B Mol Dev Evol. 2010;314B(6):445–56.
Pakosta T, Vetešník L, Šimková A. A long temporal study of Parasitism in Asexual-Sexual populations of Carassius gibelio: does the parasite infection support coevolutionary red Queen dynamics? BioMed Res Int. 2018;2018:1–10.
Papoušek I, Vetešník L, Halačka K, Lusková V, Humpl M, Mendel J. Identification of natural hybrids of gibel carp Carassius auratus Gibelio (Bloch) and crucian carp Carassius carassius (L.) from lower Dyje River floodplain (Czech Republic). J Fish Biol. 2008;72(5):1230–5.
Šimková A, Dávidová M, Papoušek I, Vetešník L. Does interspecies hybridization affect the host specificity of parasites in cyprinid fish? Parasit Vectors. 2013;6(1):95.
Andrews S. FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. 2010.
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(15):2114–20.
Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(1):15–21.
Wang L, Wang S, Li W. RSeQC: quality control of RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(16):2184–5.
Picard Toolkit. [Internet]. Broad Institute. 2018. Available from: GitHub Repository. http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/; Broad Institute.
Okonechnikov K, Conesa A, García-Alcalde F. Qualimap 2: advanced multi-sample quality control for high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2016;32(2):292–4.
Ewels P, Magnusson M, Lundin S, Käller M. MultiQC: summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics. 2016;32(19):3047–8.
Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(14):1754–60.
Kim S, Scheffler K, Halpern AL, Bekritsky MA, Noh E, Källberg M, et al. Strelka2: fast and accurate calling of germline and somatic variants. Nat Methods. 2018;15(8):591–4.
Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W. featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(7):923–30.
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of Fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15(12):550.
Sherman BT, Hao M, Qiu J, Jiao X, Baseler MW, Lane HC, et al. DAVID: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(W1):W216–21.
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Ishiguro-Watanabe M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D587–92.
The Gene Ontology Consortium, Carbon S, Douglass E, Good BM, Unni DR, Harris NL, et al. The Gene Ontology resource: enriching a GOld mine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D325–34.
Bonnot T, Gillard M, Nagel D. A simple protocol for informative visualization of enriched gene ontology terms. BIO-Protoc. 2019;9(22):1–9.
Supek F, Bošnjak M, Škunca N, Šmuc T. C Gibas editor 2011 REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of Gene Ontology terms. PLoS ONE 6 7 e21800.
Kinsella RJ, Kahari A, Haider S, Zamora J, Proctor G, Spudich G, et al. Ensembl BioMarts: a hub for data retrieval across taxonomic space. Database. 2011;2011(0):bar030–030.
Maciver SK. Asexual amoebae escape Muller’s Ratchet through Polyploidy. Trends Parasitol. 2016;32(11):855–62.
Patil S, Moeys S, Von Dassow P, Huysman MJJ, Mapleson D, De Veylder L, et al. Identification of the meiotic toolkit in diatoms and exploration of meiosis-specific SPO11 and RAD51 homologs in the sexual species Pseudo-nitzschia multistriata and Seminavis robusta. BMC Genomics. 2015;16(1):930.
Schurko AM, Logsdon JM. Using a meiosis detection toolkit to investigate ancient asexual scandals and the evolution of sex. BioEssays. 2008;30(6):579–89.
Bairoch A. The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt). Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;33(Database issue):D154–9.
Bradford YM, Van Slyke CE, Ruzicka L, Singer A, Eagle A, Fashena D et al. Zebrafish information network, the knowledgebase for Danio rerio research. Wood V, editor. Genetics. 2022;220(4):iyac016.
Safran M, Dalah I, Alexander J, Rosen N, Iny Stein T, Shmoish M, et al. GeneCards Version 3: the human gene integrator. Database. 2010;2010(0):baq020–020.
Mahanty A, Purohit GK, Mohanty S, Nayak NR, Mohanty BP. Suitable reference gene for quantitative real-time PCR analysis of gene expression in gonadal tissues of minnow Puntius sophore under high-temperature stress. BMC Genomics. 2017;18(1):617.
Vandesompele J, Preter KD, Roy NV, Paepe AD. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002;3(7):research00341–003411.
Ye J, Coulouris G, Zaretskaya I, Cutcutache I, Rozen S, Madden TL. Primer-BLAST: a tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012;13(1):134.
Hillers KJ, Villeneuve AM. Chromosome-Wide Control of Meiotic Crossing over in C. Elegans. Curr Biol. 2003;13(18):1641–7.
Ramesh M, Malik S, Logsdon J. A phylogenomic inventory of meiotic GenesEvidence for sex in Giardia and an early eukaryotic origin of meiosis. Curr Biol. 2005;15(2):185–91.
Whitaker M. Calcium at fertilization and in Early Development. Physiol Rev. 2006;86(1):25–88.
Schlupp I. The Evolutionary Ecology of Gynogenesis. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst. 2005;36(1):399–417.
Gallot A, Shigenobu S, Hashiyama T, Jaubert-Possamai S, Tagu D. Sexual and asexual oogenesis require the expression of unique and shared sets of genes in the insect Acyrthosiphon pisum. BMC Genomics. 2012;13(1):76.
Hanson SJ, Stelzer CP, Welch DBM, Logsdon JM. Comparative transcriptome analysis of obligately asexual and cyclically sexual rotifers reveals genes with putative functions in sexual reproduction, dormancy, and asexual egg production. BMC Genomics. 2013;14(1):412.
Huynh TV, Hall AS, Xu S. The Transcriptomic signature of cyclical parthenogenesis. Genome Biol Evol. 2023;15(7):1–12.
Le Trionnaire G, Wucher V, Tagu D. Genome expression control during the photoperiodic response of aphids: Seasonal photoperodism in aphids. Physiol Entomol. 2013;38(2):117–25.
Hartmann M, Kohl KP, Sekelsky J, Hatkevich T. Meiotic MCM proteins promote and inhibit crossovers during meiotic recombination. Genetics. 2019;212:461–8.
Costa Y, Speed R, Öllinger R, Alsheimer M, Semple CA, Gautier P, et al. Two novel proteins recruited by synaptonemal complex protein 1 (SYCP1) are at the centre of meiosis. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(12):2755–62.
Page SL, Hawley RS. The genetics and molecular biology of the synaptonemal complex. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20(1):525–58.
Takemoto K, Imai Y, Saito K, Kawasaki T, Carlton PM, Ishiguro K, ichiro et al. Sycp2 is essential for synaptonemal complex assembly, early meiotic recombination and homologous pairing in zebrafish spermatocytes. Cohen PE, editor. PLOS Genet. 2020;16(2):e1008640.
Miller JJ, Summers MK, Hansen DV, Nachury MV, Lehman NL, Loktev A, et al. Emi1 stably binds and inhibits the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome as a pseudosubstrate inhibitor. Genes Dev. 2006;20(17):2410–20.
Anitha A, Gupta YR, Deepa S, Ningappa M, Rajanna KB, Senthilkumaran B. Gonadal transcriptome analysis of the common carp, Cyprinus carpio: identification of differentially expressed genes and SSRs. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2019;279:67–77.
Iwai T, Yoshii A, Yokota T, Sakai C, Hori H, Kanamori A, et al. Structural components of the synaptonemal complex, SYCP1 and SYCP3, in the medaka fish Oryzias latipes. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(13):2528–37.
Page J, Viera A, Parra MT, Fuente RDL, Suja JÁ, Prieto I et al. Involvement of Synaptonemal Complex Proteins in Sex Chromosome Segregation during Marsupial Male Meiosis. Hawley RS, editor. PLoS Genet. 2006;2(8):e136.
Sun M, Li Z, Gui J. Dynamic distribution of spindlin in nucleoli, nucleoplasm and spindle from primary oocytes to mature eggs and its critical function for oocyte-to‐embryo transition in gibel carp. J Exp Zool Part Ecol Genet Physiol. 2010;313A(8):461–73.
Kipreos ET, Pagano M. The F-box protein family. Genome Biol. 2000;1(5):reviews30021.
Molina JR, Adjei AA. The Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway. J Thorac Oncol. 2006;1(1):7–9.
Stacey DW. Cyclin D1 serves as a cell cycle regulatory switch in actively proliferating cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15(2):158–63.
Tidyman WE, Rauen KA. The RASopathies: developmental syndromes of Ras/MAPK pathway dysregulation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009;19(3):230–6.
Goriely A, Wilkie AOM. Paternal age effect mutations and selfish Spermatogonial Selection: Causes and consequences for Human Disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90(2):175–200.
Srinivasan DG, Abdelhady A, Stern DL. Gene Expression Analysis of Parthenogenetic Embryonic Development of the Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum, Suggests That Aphid Parthenogenesis Evolved from Meiotic Oogenesis. Zhang M, editor. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(12):e115099.
Zhang J, Sun M, Zhou L, Li Z, Liu Z, Li XY, et al. Meiosis completion and various sperm responses lead to unisexual and sexual reproduction modes in one clone of polyploid Carassius gibelio. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):10898.
Zhang YN, Zhu XY, Wang WP, Wang Y, Wang L, Xu XX, et al. Reproductive switching analysis of Daphnia similoides between sexual female and parthenogenetic female by transcriptome comparison. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):34241.
Marlow FL, Mullins MC. Bucky ball functions in Balbiani body assembly and animal–vegetal polarity in the oocyte and follicle cell layer in zebrafish. Dev Biol. 2008;321(1):40–50.
Aguero T, Zhou Y, Kloc M, Chang P, Houliston E, King M. Hermes (Rbpms) is a critical component of RNP complexes that sequester germline RNAs during Oogenesis. J Dev Biol. 2016;4(1):2.
Coward K, Ponting CP, Zhang N, Young C, Huang CJ, Chou CM, et al. Identification and functional analysis of an ovarian form of the egg activation factor phospholipase C zeta (PLCζ) in pufferfish: analysis of an ovarian form of PLC Zeta. Mol Reprod Dev. 2011;78(1):48–56.
Familiari G. Structural changes of the zona pellucida during fertilization and embryo development. Front Biosci. 2008;Volume(13):6730.
Dong CH, Yang ST, Yang ZA, Zhang L, Gui JF. A C-type lectin associated and translocated with cortical granules during oocyte maturation and egg fertilization in fish. Dev Biol. 2004;265(2):341–54.
Yue HM, Li Z, Wu N, Liu Z, Wang Y, Gui JF, Oocyte-Specific. H2A Variant H2af1o Is Required for Cell Synchrony Before Midblastula Transition in Early Zebrafish Embryos1. Biol Reprod [Internet]. 2013 Oct 1 [cited 2023 Nov 3];89(4). https://academic.oup.com/biolreprod/article-lookup/doi/https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.113.108043.
Du C, Davis JS, Chen C, Li Z, Cao Y, Sun H, et al. FGF2/FGFR signaling promotes cumulus–oocyte complex maturation in vitro. Reproduction. 2021;161(2):205–14.
Beukeboom LW, Vrijenhoek RC. Evolutionary genetics and ecology of sperm-dependent parthenogenesis. J Evol Biol. 1998;11(6):755–82.
Maenohara S, Unoki M, Toh H, Ohishi H, Sharif J, Koseki H et al. P Cohen editor 2017 Role of UHRF1 in de novo DNA methylation in oocytes and maintenance methylation in preimplantation embryos. PLOS Genet 13 10 e1007042.
Amberg JJ, Goforth RR, Sepúlveda MS. Antagonists to the wnt Cascade exhibit sex-specific expression in gonads of sexually mature Shovelnose Sturgeon. Sex Dev. 2013;7(6):308–15.
Liu Y, Zhang W, Du X, Zhao J, Liu X, Li X, et al. Sexually dimorphic expression in developing and adult gonads shows an important role of gonadal soma-derived factor during sex differentiation in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;210:1–8.
Prathibha Y, Senthilkumaran B. Expression of wnt4/5 during reproductive cycle of catfish and wnt5 promoter analysis. J Endocrinol. 2017;232(1):1–13.
Li Q. Inhibitory SMADs: potential regulators of ovarian Function1. Biol Reprod. 2015;92(2):1–6.
Kaivo-oja N, Jeffery LA, Ritvos O, Mottershead DG. Smad signalling in the ovary. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2006;4(1):21.
Bayer EA, Stecky RC, Neal L, Katsamba PS, Ahlsen G, Balaji V, et al. Ubiquitin-dependent regulation of a conserved DMRT protein controls sexually dimorphic synaptic connectivity and behavior. eLife. 2020;9:e59614.
Casado-Navarro R, Serrano-Saiz E. DMRT Transcription Factors in the control of nervous system sexual differentiation. Front Neuroanat. 2022;16:937596.
Kopp A. Dmrt genes in the development and evolution of sexual dimorphism. Trends Genet. 2012;28(4):175–84.
Peng W, Xu J, Zhang Y, Feng J, Dong C, Jiang L, et al. An ultra-high density linkage map and QTL mapping for sex and growth-related traits of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):26693.
Johnsen H, Andersen Ø. Sex dimorphic expression of five dmrt genes identified in the Atlantic cod genome. The fish-specific dmrt2b diverged from dmrt2a before the fish whole-genome duplication. Gene. 2012;505(2):221–32.
Yang B, Sun W, Jin L, Li P, Zhou Y, Qian G, et al. SOX8 is essential for male sexual differentiation in the Chinese soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis. Biol Reprod. 2023;108(6):988–96.
Takada S, Koopman P. Origin and possible roles of the Sox8 transcription factor gene during sexual development. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2003;101(3–4):212–8.
Ahmed S. Review of the molecular modelling studies of the cytochrome P-450 estrogen synthetase enzyme, aromatase. Drug Des Discov. 1998;15(4):239–52.
He W, Gauri M, Li T, Wang R, Lin SX. Current knowledge of the multifunctional 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (HSD17B1). Gene. 2016;588(1):54–61.
Saloniemi T, Welsh M, Lamminen T, Saunders P, Mäkelä S, Streng T, et al. Human HSD17B1 expression masculinizes transgenic female mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009;301(1–2):163–8.
Gomes Fernandes M, He N, Wang F, Van Iperen L, Eguizabal C, Matorras R, et al. Human-specific subcellular compartmentalization of P-element induced wimpy testis-like (PIWIL) granules during germ cell development and spermatogenesis. Hum Reprod. 2018;33(2):258–69.
Risinger C, Larhammar D. Multiple loci for synapse protein SNAP-25 in the tetraploid goldfish. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1993;90(22):10598–602.
Luo J, Zhang YP, Huang SY. Genetic diversity in Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus). 1999;37(9/10):267–79.
Gu Q, Wang S, Zhong H, Yuan H, Yang J, Yang C, et al. Phylogeographic relationships and the evolutionary history of the Carassius auratus complex with a newly born homodiploid raw fish (2nNCRC). BMC Genomics. 2022;23(1):242.
Podlesnykh AV, Apalikova OV, Brykov VA. Phylogenetic relationships of silver crucian carp in Carassius auratus complex based on mtDNA analysis. Russ J Genet. 2012;48(12):1207–17.
Sinclair EA, Pramuk JB, Bezy RL, Crandall KA, Sites JW Jr. DNA evidence for nonhybrid origins of parthenogenesis in natural populations of vertebrates. Evolution. 2009;64(5):1346–57.
Tunquist BJ, Eyers PA, Chen LG, Lewellyn AL, Maller JL. Spindle checkpoint proteins Mad1 and Mad2 are required for cytostatic factor–mediated metaphase arrest. J Cell Biol. 2003;163(6):1231–42.
Bi K, Bogart JP. Probing the meiotic mechanism of intergenomic exchanges by genomic in situ hybridization on lampbrush chromosomes of unisexual Ambystoma (Amphibia: Caudata). Chromosome Res. 2010;18(3):371–82.
Bogart JP, Bartoszek J, Noble DWA, Bi K. Sex in unisexual salamanders: discovery of a new sperm donor with ancient affinities. Heredity. 2009;103(6):483–93.
Rice CS. Evolution of meiosis genes in sexual vs. asexual Potamopyrgus antipodarum [Internet] [Master of Science]. [Iowa City, IA, United States]: University of Iowa; 2015 [cited 2023 Jul 30]. https://iro.uiowa.edu/esploro/outputs/graduate/9983776608402771.
Šimková A, Vojtek L, Halačka K, Hyršl P, Vetešník L. The effect of hybridization on fish physiology, immunity and blood biochemistry: a case study in hybridizing Cyprinus carpio and Carassius gibelio (Cyprinidae). Aquaculture. 2015;435:381–9.
Vetešník L, Halačka K, Šimková A. The effect of ploidy and temporal changes in the biochemical profile of gibel carp (Carassius gibelio): a cyprinid fish species with dual reproductive strategies. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2013;39(2):171–80.
Edgar R. Gene expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(1):207–10.
Kalous J, Kubelka M, Šolc P, Šušor A, Motlík J. AKT (protein kinase B) is implicated in meiotic maturation of porcine oocytes. Reproduction. 2009;138(4):645–54.
Mouillet JF, Yan X, Ou Q, Jin L, Muglia LJ, Crawford PA, et al. DEAD-Box Protein-103 (DP103, Ddx20) is essential for early embryonic development and modulates ovarian morphology and function. Endocrinology. 2008;149(5):2168–75.
Steinfeld JS, Ameyaw KK, Wood CG, Johnston RM, Escauriza AJJ, Torija EG et al. The zebrafish dmrt family genes have cooperative and antagonistic roles in sex determination and oogenesis [Internet]. Developmental Biology; 2022 Aug [cited 2023 Sep 27]. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.28.505603.
Sun H, Sun G, Zhang H, An H, Guo Y, Ge J, et al. Proteomic profiling reveals the Molecular Control of Oocyte Maturation. Mol Cell Proteom. 2023;22(1):100481.
Silva ESD, Amaral C, Barreta M, Antoniazzi A, Andrade LGD, Ferreira R, et al. FGF18 modulates CTGF mRNA expression in cumulus–oocyte complexes and early bovine embryos: preliminary data. Zygote. 2022;30(2):239–43.
Pandey A, Gupta N, Gupta SC. Improvement of in vitro oocyte maturation with lectin supplementation and expression analysis of Cx43, GDF-9, FGF-4 and fibronectin mRNA transcripts in Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). J Assist Reprod Genet. 2009;26(6):365–71.
Jin S, Tong T, Fan W, Fan F, Antinore MJ, Zhu X, et al. GADD45-induced cell cycle G2-M arrest associates with altered subcellular distribution of cyclin B1 and is independent of p38 kinase activity. Oncogene. 2002;21(57):8696–704.
Suzumori N, Pangas S, Rajkovic A. Candidate genes for premature ovarian failure. Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(3):353–7.
Oh ET, Kim HG, Kim CH, Lee J, Kim C, Lee JS, et al. NQO1 regulates cell cycle progression at the G2/M phase. Theranostics. 2023;13(3):873–95.
Braden TD, Bervig T, Conn PM. Protein Kinase-C activation stimulates synthesis of Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptors, but does not mediate GnRH-Stimulated receptor synthesis. Endocrinology. 1991;129(5):2486–90.
Bill CA, Vines CM, Phospholipase C. In: Islam MdS, editor. Calcium Signaling [Internet]. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2020 [cited 2023 Sep 27]. pp. 215–42. (Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; vol. 1131). http://link.springer.com/https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12457-1_9.
Regev A, Goldman S, Shalev E. Expression of plexin-B1 in the mouse ovary and its possible role in follicular development. Fertil Steril. 2005;84:1210–9.
Kaufman OH, Lee K, Martin M, Rothhämel S, Marlow FL. rbpms2 functions in Balbiani body architecture and ovary fate. Pelegri F, editor. PLOS Genet. 2018;14(7):e1007489.
Chae HD, Mitton B, Lacayo NJ, Sakamoto KM. Replication factor C3 is a CREB target gene that regulates cell cycle progression through the modulation of chromatin loading of PCNA. Leukemia. 2015;29(6):1379–89.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the Bioinformatics Core Facility of CEITEC Masaryk University for providing the transcriptomic data presented in this paper. We also kindly thank Matthew Nicholls for English revision of the final draft.
Funding
The study was funded by the Czech Science Foundation, Project No. 22–27023 S. We declare that the contributions of Kristína Civáňová Křížová and Kristýna Voříšková to this study were strictly associated only with their part-time commitment to project No. 22–27023 S and that no additional institutional resources were provided by the Parasitology Group, Department of Botany and Zoology, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University Brno.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FJ processed data analyses with the assistance of TT, performed a part of qPCR, and wrote the manuscript. MD performed basic bioinformatics analyses. VB performed SNP analyses. KV performed library preparation. KCK and MS performed a part of qPCR. MHF and FJ performed RNA extraction and quantification. LV performed experimental breeding and fish sampling. AŠ designed and supervised the study and contributed to the interpretation of results and the writing of the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The research was undertaken in line with the ethical requirements of the Czech Republic. The maintenance and care of experimental fish, as well as method of fish killing complied with legal requirements in the Czech Republic § 6, 7, 9 and 10 regulation No. 419/2012 about the care, breeding and using experimental animals. The experiment was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee at the Faculty of Science, Masaryk University in Brno, Czech Republic. The experiment was conducted under the experimental project approved by the Ministry of Education, Sports and Youth under document n. MSMT-30071/2022-5.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Jacques, F., Tichopád, T., Demko, M. et al. Reproduction-associated pathways in females of gibel carp (Carassius gibelio) shed light on the molecular mechanisms of the coexistence of asexual and sexual reproduction. BMC Genomics 25, 548 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-024-10462-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-024-10462-4