Abstract
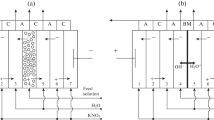
The research established patterns of the separation of phenylalanine aqueous salt solutions by electrodialysis. It also determined the conditions for the effective and selective separation of the target component by selecting a membrane with the desired properties. The composition of the model solution simulating industrial water in the technology of microbiological synthesis included an aromatic amino acid, phenylalanine (0.05 M), and sodium chloride (0.01 M). Experimental membranes with different mass fractions of sulfonated cation-exchange resin were used. The experiments were carried out in galvanostatic mode using a seven-section electrodialyzer. It was established that the content of the ion-exchanger in the membrane influences the features of the transport of mineral salt and amino acid ions, the value of the separation factor, and the degree of solution demineralization. It was shown that the change in the content of the sulfonated cation-exchanger in the membranes from 45 to 70 wt % makes it possible to increase the rate of mass transfer of a mineral ion by 1.5 times during the electrodialysis of a mixed solution of an amino acid and a mineral salt. For all experimental membranes, the separation factor dependencies on the current density are characterized by the point of extremum corresponding to the interval exceeding the limiting diffusion current ilim by 2–3 times. The maximum separation efficiency was found for a membrane with a cation-exchanger content of 70 wt %. When the value of the limiting diffusion current was exceeded by 2 times, with an increase in the resin content in the membrane, the separation factor increased by 1.5 times. Additionally, the degree of demineralization of the mixed solution in the case of the membrane with the maximum content of the ion-exchanger was 40–60%. The possibility of almost complete demineralization of the solution in the case of the membrane with a resin content of 70 wt % was established when the limiting current density was exceeded by 6 times. The study revealed the role of electroconvection in increasing the loss of an amino acid (the target product) at overlimiting current modes of electrodialysis. It was shown that the main reason for the increase in the amino acid transport through the sulfonated cation-exchange membrane in intense current modes is electroconvection. The occurrence of electroconvection negatively affects the process of water splitting. The electroconvective mixing of the solution at the membrane/solution interface destroys the barrier effect of the depleted diffusion layer with a high pH value. The possibility of deep demineralization of phenylalanine mineral salt solution with a minimal loss of the target product using a membrane with 70 wt % fraction of a sulfonated cation-exchange resin in intense current modes of electrodialysis was established.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bykov, V.A., Krylov, I.A., Manakov, M.N., Markvichev, N.S., Orlova, L.M., and Tarasova, N.V., Biotechnology, book 6: Microbiological Production of Biologically Active Substances and Preparation, Moscow: Vysshaya shkola, 1987.
Vasil’eva, V., Goleva, E., Pismenskaya, N., Kozmai, A., and Nikonenko, V., Effect of surface profiling of a cation-exchange membrane on the phenylalanine and NaCl separation performances in diffusion dialysis, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2019, vol. 210, p. 48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.07.065
Kozmai, A., Goleva, E., Vasil’eva, V., Nikonenko, V., and Pismenskaya, N., Neutralization dialysis for phenylalanine and mineral salt separation. Simple theory and experiment, Membranes, 2019, vol. 9, p. 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9120171
Vasil’eva, V.I., Saud, A.M., and Akberova, E.M., Effect of the mass fraction of ion-exchange resin in a Ralex CM cation-exchange membrane on demineralization of phenylalanine aqueous salt solutions by neutralization dialysis, Membr. Membr. Technol., 2021, vol. 3, p. 98. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751621020074
Grib, H., Belhocine, D., Lounici, H., Pauss, A., and Mameri, N., Desalting of phenylalanine solutions by electrodialysis with ion-exchange membranes, J. Appl. Electrochem., 2000, vol. 30, p. 259. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003990031853
Choi, J., Oh, S., and Moon, S., Structural effects of ion-exchange membrane on the separation of l-phenylalanine (l-Phe) from fermentation broth using electrodialysis, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2002, vol. 77, p. 785. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.638
Aghajanyan, A.E., Hambardzumyan, A.A., Vardanyan, A.A., and Saghiyan, A.S., Desalting of neutral amino acids fermentative solutions by electrodialysis with ion-exchange membranes, Desalination, 2008, vol. 228, p. 237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.10.012
Eliseeva, T.V., Kharina, A.Y., Voronyuk, I.V., Kabanova, V.I., and Bui, T.P.H., Demineralization of tyrosine and phenylalanine solutions during electrodialysis using homogeneous and heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes, Sorbtsionnye Khromatogr. Protsessy, 2013, vol. 13, no. 5, p. 647.
Sun, Z., Gao, X., Zhang, Y., and Gao, C., Separation and purification of L-phenylalanine from the fermentation broth by electrodialysis, Desalin. Water Treat., 2016, vol. 57, p. 22304. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1137082
Kharina, A.Y. and Eliseeva, T.V., Desalination of phenylalanine solution by electro membrane methods, Kondens. Sredy Mezhfaznye Granitsy, 2017, vol. 19, no. 1, p. 126.
Pismenskaya, N., Rybalkina, O., Moroz, I., Mareev, S., and Nikonenko, V., Influence of electroconvection on chronopotentiograms of an anion-exchange membrane in solutions of weak polybasic acid salts, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, vol. 22, p. 13518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413518
Mondal, S., Griffiths, I.M., and Ramon, G.Z., Forefronts in structure-performance models of separation membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 2019, vol. 588, p. 117166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.06.006
Stenina, I., Golubenko, D., Nikonenko, V., and Yaroslavtsev, A., Selectivity of transport processes in ion-exchange membranes: relationship with the structure and methods for its improvement, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, vol. 21, p. 5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155517
Kovalev, N.V., Karpenko, T.V., Shel’deshov, N.V., and Zabolotskiy, V.I., Ion transport through a modified heterogeneous bipolar membrane and electromembrane recovery of sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide from a sodium sulfate solution, Membr. Membr. Technol., 2020, vol. 2, no. 6, p. 391. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751620060050
Ahmad, M., Qaiser, A.A., Huda, N.U., and Saeed, A., Heterogeneous ion exchange membranes based on thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU): effect of PSS/DVB resin on morphology and electrodialysis, RSC Adv., 2020, vol. 56010, p. 3029. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA06178A
Zabolotskiy, V.I., But, A.Yu., Vasil’eva, V.I., Akberova, E.M., and Melnikov, S.S., Ion transport and electrochemical stability of strongly basic anion-exchange membranes under high current electrodialysis conditions, J. Membr. Sci., 2017, vol. 526, p. 60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.12.028
Vasil’eva, V.I., Zhiltsova, A.V., Akberova, E.M., and Fataeva, A.I., Influence of surface inhomogeneity on current–voltage characteristics of heterogeneous ion exchange membranes, Kondens. Sredy Mezhfaznye Granitsy, 2014, vol. 16, no. 3, p. 257.
Porozhnyy, M.V., Shkirskaya, S.A., Butylskii, D.Y., Dotsenko, V.V., Safronova, E.Y., Yaroslavtsev, A.B., and Nikonenko, V.V., Physicochemical and electrochemical characterization of Nafion-type membranes with embedded silica nanoparticles: effect of functionalization, Electrochim. Acta, 2021, vol. 370, p. 137689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.137689
Vasil’eva, V.I., Akberova, E.M., and Zabolotskii, V.I., Electroconvection in systems with heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes after thermal modification, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2017, vol. 53, no. 4, p. 398. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193517040127
Akberova, E.M., Vasil’eva, V.I., Zabolotsky, V.I., and Novak, L., Effect of the sulfocation-exchanger dispersity on the surface morphology, microrelief of heterogeneous membranes and development of electroconvection in intense current modes, J. Membr. Sci., 2018, vol. 566, p. 317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.08.042
Hale, D.K. and McCauley, D.J., Structure and properties of heterogeneous cation-exchange membranes, Trans. Faraday Soc., 1961, vol. 57, p. 135. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA06178A
Vyas, P.V., Shah, B.G., Trivedi, G.S., Ray, P., Adhikary, S.K., and Rangarajan, R., Studies on heterogeneous cation-exchange membranes, React. Funct. Polym., 2000, vol. 44, p. 101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-5148(99)00084-X
Vyas, P.V., Shah, B.G., Trivedi, G.S., Ray, P., Adhikary, S.K., and Rangarajan, R., Characterization of heterogeneous anion-exchange membrane, J. Membr. Sci., 2001, vol. 187, p. 39. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(00)00613-X
Oren, Y., Freger, V., and Linder, C., Highly conductive ordered heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 2004, vol. 239, p. 17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2003.12.031
Hosseini, S.M., Madaeni, S.S., and Khodabakhshi, A.R., Heterogeneous cation exchange membrane: preparation, characterization and comparison of transport properties of mono and bivalent cations, Sep. Sci. Techn., 2010, vol. 45, p. 2308. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2010.497792
Křivčík, J., Vladařová, J., Hadrava, J., Černín, A., and Brožová, L., The effect of an organic ion-exchange resin on properties of heterogeneous ion-exchange membrane, Desalin. Water Treat., 2010, vol. 14, p. 179. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2010.1025
Meshcheryakova, E.E., Brovkina, M.A., Falina, I.V., Vasil’eva, V.I., and Akberova, E.M., The effect of the concentration of ion-exchange resin on the electrotransport properties of heterogeneous membranes, Sorbtsionnye Khromatogr. Protsessy, 2022, vol. 22, p. 523. https://doi.org/10.17308/sorpchrom.2022.22/10607
Vyas, P.V., Ray, P., Adhikary, S.K., Shah, B.G., and Rangarajan, R., Studies of the effect of variation of blend ratio on permselectivity and heterogeneity of ion-exchange membranes, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2003, vol. 257, p. 127. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9797(02)00025-5
Pivovarov, N.Y., Greben’, V.P., Kustov, V.N., Golikov, A.P., and Rodzik, I.G., Influence of heterogeneity of ion-exchange membranes on the limiting current and current-voltage curves, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2001, vol. 37, p. 808. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016782919030
Akberova, E.M. and Vasil’eva, V.I., Effect of the resin content in cation-exchange membranes on development of electroconvection, Electrochem. Commun., 2020, vol. 111, p. 106659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2020.106659
Isaev, N.I. and Shaposhnik, V.A., Synthesis and Properties of Ion Exchange Materials, Moscow: Nauka, 1968.
Badessa, T.S. and Shaposhnik, V.A., Electrical conductance studies on ion exchange membrane using contact-difference method, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, vol. 231, p. 453.
Vasil’eva, V.I. and Saud, A.M., Spectrophotometric determination of phenylalanine in aqueous solutions with different acidity, Anal. Kontrol’, 2022, vol. 26, p. 222. https://doi.org/10.15826/analitika.2022.26.3.003
Saud, A.M., Smagin, M.A., and Vasil’eva, V.I., Features of sodium determination in dilute mixed solutions with phenylalanine by flame photometry, Zavod. Lab. Diagn. Mater., 2020, vol. 86, p. 13.
Hwang, S.-T. and Kammermeyer, K., Membranes in Separations, New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1975.
Shaposhnik, V.A., Eliseeva, T.V., and Selemenev, V.F., Transport of glycine through the ion-exchange membranes during the electrodialysis, Elektrohimiya, 1993, vol. 29, p. 794.
Elisseeva, T.V., Shaposhnik, V.A., and Luschik, I.G., Demineralization and separation of amino acids by electrodialysis with ion-exchange membranes, Desalination, 2002, vol. 149, p. 405. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(02)00763-4
Zabolotskii, V.I., Gnusin, N.P., Yel’nikova, L.F., and Blednich, V.M., The investigation of the process of the deep desalination of amino acids from mineral impurities by electrodialysis with ion exchange membranes, Zh. Prikl. Khim., 1986, vol. 59, p. 140.
Eliseeva, T. and Shaposhnik, V., Effects of circulation and facilitated electromigration of amino acids in electrodialysis with ion-exchange membranes, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2000, vol. 36, p. 64. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02757798
Eliseeva, T.V., Kharina, A.Y., Chernikova, E.N., and Charushina, O.E., Demineralization of heterocyclic amino acid solutions by an electromembrane method, Sorbtsionnye Khromatogr. Protsessy, 2021, vol. 21, p. 492. https://doi.org/10.17308/sorpchrom.2021.21/3633
Vasil’eva, V.I. and Eliseeva, T.V., Laser-interferometry study of the barrier effect in the electrodialysis of amino acid solutions, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2000, vol. 36, p. 30. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02757792
Zagorodnykh, L.A., Bobreshova, O.V., Kulintsov, P.I., and Aristov, I.V., Kinetics of the electrical mass transfer of sodium and glycine cations with allowance for the protonation of zwitterions in conditions of limiting concentration polarization of electromembrane systems with cation-exchange membranes, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2005, vol. 41, p. 275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11175-005-0062-7
Eliseeva, T. and Kharina, A., Desalination of neutral amino acid solutions in an electromembrane system, Membranes, 2022, vol. 12, p. 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070665
Shaposhnik, V.A., Vasil’eva, V.I., and Grigorchuk, O.V., Transfer Phenomena in Ion-Exchange Membranes, Moscow: Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, 2001.
Zabolotskii, V.I., Shel’deshov, N.V., and Gnusin, N.P., Dissociation of water molecules in systems with ion-exchange membranes, Usp. Khim., 1988, vol. 57, no. 8, p. 1403.
Zabolotskii, V.I., Bugakov, V.V., Sharafan, M.V., and Chermit, R.K., Transfer of electrolyte ions and water dissociation in anion-exchange membranes under intense current conditions, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2012, vol. 48, no. 6, p. 650. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193512060158
Vasil’eva, V., Zabolotsky, V., Shaposhnik, V., Zhiltsova, A., and Grigorchuk, O., The oscillation of concentration field at the membrane-solution interface and transport mechanisms under overlimiting current density, Desalin. Water Treat., 2010, vol. 14, p. 214.
Shaposhnik, V.A., Vasil’eva, V.I., and Reshetnikova, E.V., Concentration polarization of ion-exchange membranes in electrodialysis: an interferometric study, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2000, vol. 36, p. 773. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02757679
Nikonenko, V.V., Vasil’eva, V.I., Akberova, E.M., Uzdenova, A.M., Urtenov, M.K., Kovalenko, A.V., Pismenskaya, N.P., Mareev, S.A., and Pourcelly, G., Competition between diffusion and electroconvection at an ion-selective surface in intensive current regimes, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2016, vol. 235, p. 233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2016.06.014
Vasil’eva, V.I., Saud, A.M., and Akberova, E.M., Direct evidences of the electroconvective mechanism of neutral amino acid transport during electrodialysis, Mendeleev Commun., 2023, vol. 33, p. 275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mencom.2023.02.041
Belova, E., Lopatkova, G., Pismenskaya, N., Nikonenko, V., and Larchet, C., Role of water splitting in development of electroconvection in ion-exchange membrane systems, Desalination, 2006, vol. 199, p. 59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.03.142
Zyryanova, S., Mareev, S., Gil, V., Korzhova, E., Pismenskaya, N., Sarapulova, V., Rybalkina, O., Boyko, E., Larchet, C., Dammak, L., and Nikonenko, V., How electrical heterogeneity parameters of ion-exchange membrane surface affect the mass transfer and water splitting rate in electrodialysis, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, vol. 21, p. 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030973
Nikonenko, V.V., Mareev, S.A., Pis’menskaya, N.D., Uzdenova, A.M., Kovalenko, A.V., Urtenov, M.Kh., and Pourcelly, G., Effect of electroconvection and its use in intensifying the mass transfer in electrodialysis, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2017, vol. 53, p. 1122. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193517090099
Funding
The study was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation no. 21-19-00397, https://rscf.ru/en/ project/21-19-00397/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasil’eva, V.I., Saud, A.M. & Akberova, E.M. Separation of Phenylalanine Aqueous Salt Solutions by Electrodialysis Using Membranes with Different Mass Fractions of Sulfonated Cation-Exchange Resin. Russ J Electrochem 59, 988–997 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193523110149
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193523110149