Abstract
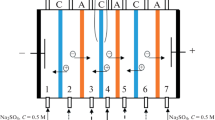
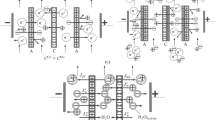
The characteristic features of the mass transport of the components through the ion-exchange membranes during conventional electrodialysis of a ternary aromatic amino acid–disaccharide–mineral salt solution with inert spacers are studied. The mutual influence of the components of the system during the transport through MA-41 and MK-40 heterogeneous membranes is revealed. It is shown that the fluxes of phenylalanine through the membranes reach lower values at a higher concentration of sucrose in the feed solution. Here, lower values of the degree of desalination are observed when compared to the lower concentration of the carbohydrate in the mixture. It is found that most losses of sucrose during desalination are due to its mass transport through the cation-exchange membrane, while phenylalanine, through anion-exchange. The application of an electrodialysis scheme with bipolar and anion-exchange membranes at the next stage provides effective separation of the aromatic amino acid and disaccharide from the preliminary demineralized solution due to the conjugated transport of phenylalanine through the anion-exchange membrane with the hydroxyl ions generated at the inner interface of the bipolar membrane.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
V. G. Doroshenko, V. A. Livshits, L. G. Airich, I. S. Shmagina, E. A. Savrasova, M. V. Ovsienko, and S. V. Mashko, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 51, 733 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683815070017
A. A. Bychkova, O. A. Pakhomova, and Ya. I. Korenman, Vestnik VGUIT 1, 11 (2012).
O. M. Kattan Readi, M. Girones, and K. Nijmeijer, J. Membr. Sci. 429, 338 (2013).
N. Pismenskaya, K. Igritskaya, E. Belova, V. Nikonenko, and G. Pourcelly, Desalination 200, 149 (2006).
E. Belashova, N. Pismenskaya, and G. Pourcelly, Ion transport in Organic and Inorganic Membranes. International Conference Proceedings, Krasnodar, 2016, p. 50.
E. D. Melnikova, N. D. Pismenskaya, L. Bazinet, S. Mikhaylin, and V. V. Nikonenko, Electrochim. Acta 285, 185 (2018).
F. Yuan, Q. Wang, P. Yang, Yu. Tiana, and W. Cong, Sep. Purif. Technol. 153, 51 (2015).
T. V. Eliseeva and A. Yu. Kharina, Russ. J. Electro-chem. 51, 63 (2015).https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193515010048
V. Vasil’eva, E. Goleva, N. Pismenskaya, A. Kozmai, and V. Nikonenko, Sep. Purif. Technol. 210, 48 (2019).
A. M. Saud, V. I. Vasil’eva, E. A. Goleva, E. M. Akberova, and A. T. Kozlov, Sorbts. Khromatogr. Prots. 20, 749 (2020).
O. M. Kattan Readi, H. J. Kuenen, H. J. Zwijnenberg, and K. Nijmeijer, J. Memb. Sci. 443, 219 (2013).
C. Jiang, Y. Zhang, H. Feng, Q. Wang, Ya. Wang, and T. Xu, J. Memb. Sci. 542, 264 (2017).
C. X. Jiang, Q. Y. Wang, Y. L. Zhang, Y. Li, Ya. Wang, and T. Xu, J. Memb. Sci. 498, 48 (2016).
X. Lin, J. Pan, and M. Zhou, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 2813 (2016).
V. A. Shaposhnik, T. V. Eliseeva, A. Yu. Tekuchev, and I. G. Lushchik, Theory and Practice of Sorption Processes: Collection of Scientific Papers (Voronezh. Gos. Univ.), Voronezh, 2000, No. 25, p. 53.
T. V. Eliseeva, A. Yu. Tekuchev, V. A. Shaposhnik, and I. G. Lushchik, Russ. J. Electrochem. 37, 423 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016642510229
I. G. Lushchik, A. S. Arutyunova, and T. V. Eliseeva, in Chemistry. Theory and Technology: Collection of Scientific Articles of Young Scientists, Graduate Students, and Students (Voronezh Gos. Univ.), Voronezh, 2000, No. 3, p. 117.
T. V. Eliseeva, V. A. Shaposhnik, and I. G. Lushik, Desalination 149, 405 (2002).
V. A. Shaposhnik, Kinetics of Electrodialysis (VGU, Voronezh, 1989) [in Russian].
D. L. Kotova, T. A. Krysanova, and T. V. Eliseeva, Spectrophotometric Determination of Amino Acids in Aqueous Solutions: Handbook in Chemistry, Pharmacy, and Bio-logy (Izd-vo Voronezh. un-ta, Voronezh, 2004) [in Russian].
Yu. A. Zolotov, Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry. A Practical Guide (Vysshaya shkola, Moscow, 2003) [in Russian].
I. S. Lur’e, Confectionery Inspection Guide (Pishchevaya promyshlennost', Moscow, 1978) [in Russian].
V. A. Shaposhnik, T. V. Eliseeva, and V. F. Selemenev, Elektrokhimiya 29, 794 (1993).
Chemical Encyclopedia, vol. 4, Ed. by N.S. Zefirova (Bol’shaya rossiiskaya entsiklopediya, Moscow, 1995) [in Russian].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by E. Boltukhina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kharina, A.Y., Charushina, O.E. & Eliseeva, T.V. Specific Features of the Mass Transport of the Components during Electrodialysis of an Aromatic Amino Acid–Mineral Salt–Sucrose Solution. Membr. Membr. Technol. 4, 127–132 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751622020068
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751622020068