Abstract
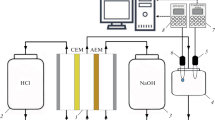
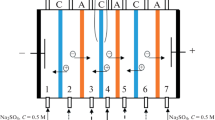
Amino acids that are ampholytes can be effectively separated and purified by the method of neutralization dialysis (ND), whose advantage is the ability to control the pH value of the solution without adding reagents. An important task is to optimize the parameters of the ND process to ensure minimal losses of amino acids during their isolation from mixed solutions. An experimental study of the process of demineralization of the phenylalanine and sodium chloride equimolar mixture by the ND method is carried out. It is established that varying the concentration and flow rate of acid and alkali solutions in the corresponding compartments of the dialysis cell allows for regulating the pH value of the solution being desalted and controlling the amount of amino acid losses. Halving the acid concentration (from 0.10 to 0.05 M) allowes reducing the losses of phenylalanine from 18.3 to 16.4%, and using a lower solution flow rate in the acid compartment (0.75 instead of 1.50 cm s–1) makes it possible to reduce these losses to 14.2%. At the same time, in all experiments, the electrical conductivity of the solution being desalted decreases by 90%, which suggests a high demineralization rate and the effectiveness of the method used to isolate phenylalanine from the mixed solution.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. D’Este, M. Alvarado-Morales, and I. Angelidaki, Biotechnol. Adv. 36, 14 (2018).
M. Ikeda, in Microbial Production of L-Amino Acids (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2002).
K. B. Alia, H. Nadeem, I. Rasul, F. Azeem, S. Hussain, M. H. Siddique, S. Muzammil, M. Riaz, and S. Nasir, in Applications of Ion Exchange Materials in Biomedical Industries (Springer, Cham, 2019).
R. Zadmard, K. Tabar-Heydar, and M. Imani, J. Chromatogr. Sci. 53, 702 (2015).
K. Kupnik, Ž. Knez, M. Primožič, and M. Leitgeb, Sep. Purif. Rev. 52, 58 (2022).
T.-C. Chiu, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 405, 7919 (2013).
A. Giuffrida, G. Maccarrone, V. Cucinotta, S. Orlandini, and A. Contino, J. Chromatogr., A 1363, 41 (2014).
B. B. Vyas and P. Ray, Desalination 362, 104 (2015).
J. Ecker, T. Raab, and M. Harasek, J. Membr. Sci. 389, 389 (2012).
J. M. K. Timmer, M. P. J. Speelmans, and H. C. van der Horst, Sep. Purif. Technol. 14, 133 (1998).
G. Wang, C. Zhang, M. Sun, X. Zhang, C. Wu, and Y. Wu, Sep. Purif. Technol. 188, 539 (2017).
T. Eliseeva and A. Kharina, Membranes 12 (2022).
K. Sato, J. Membr. Sci. 309, 175 (2008).
N. Takai, T. Yamabe, and M. Seno, J. Soc. Chem. Ind. Jpn. 67, 893 (1964).
K. Kikuchi, T. Gotoh, H. Takahashi, S. Higashino, and J. S. Dranoff, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 28, 103 (1995).
M. Kumar, B. P. Tripathi, and V. K. J. Shahi, Chem. Technol. Biotech. 85, 648 (2010).
V. V. Nikonenko, N. D. Pismenskaya, E. I. Belova, Ph. Sistat, P. Huguet, G. Pourcelly, and Ch. Larchet, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 160, 101 (2010).
X. Lin, J. Pan, M. Zhou, Y. Xu, J. Lin, J. Shen, C. Gao, B. van der Bruggen, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 2813 (2016).
A. Merkel, A. M. Ashrafi, and J. Ečer, J. Membr. Sci. 555, 185 (2018).
V. A. Shaposhnik and T. V. Eliseeva, J. Membr. Sci. 161, 223 (1999).
M. Igawa, K. Echizenya, T. Hayashita, and M. Seno, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 60, 381 (1987).
A. Kozmai, M. Chérif, L. Dammak, M. Bdiri, C. Larchet, and V. Nikonenko, J. Membr. Sci. 540, 60 (2017).
M. Chérif, I. Mkacher, L. Dammak, A. Ben Salah, K. Walha, D. Grande, and V. Nikonenko, Desalination 361, 13 (2015).
M. Chérif, I. Mkacher, L. Dammak, A. Ben Salah, K. Walha, V. Nikonenko, S. Korchane, and D. Grande, Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 144033 (2016).
K. Sato, T. Yonemoto, and T. Tadaki, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 26, 68 (1993).
M. Igawa, H. Tanabe, T. Ida, F. Yamamoto, and H. Okochi, Chem. Lett. 22, 1591 (1993).
M. Bleha and G. A. Tishchenko, J. Membr. Sci. 73, 305 (1992).
A. Kozmai, E. Goleva, V. Vasil’eva, V. Nikonenko, and N. Pismenskaya, Membranes 9, 171 (2019).
A. M. Saud, V. I. Vasil’eva, E. A. Goleva, E. M. Akberova, and A. T. Kozlov, Sorbts. Khromatogr. Prots. 20, 749 (2020).
V. I. Vasil’eva, A. M. Saud, and E. M. Akberova, Membr. Membr. Technol. 3, 98 (2021).
M. V. Porozhnyy, A. E. Kozmai, A. A. Mareev, and V. V. Gil, Membr. Membr. Technol. 4, 306 (2022).
A. Durán, J. M. Monteagudo, I. Sanmartín, and P. Gómez, Ultrason. Sonochem. 20, 785 (2013).
D. R. Lide, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2005).
V. I. Vasil’eva and A. M. Saud, Analit. Kontrol 26, 222 (2022).
G. Q. Chen, K. Wei, A. Hassanvand, B. D. Freeman, and S. E. Kentish, Water Res. 175, 115681 (2020).
R. A. Robinson and R. H. Stokes, Electrolyte Solutions, 2nd Revised Ed. (Dover Publications Inc., New York, 2003).
G. A. Denisov, G. Tishchenko, M. Bleha, and L. Shataeva, J. Membr. Sci. 98, 13 (1995).
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, grant no. 21-79-00114, https://rscf.ru/en/project/21-79-00114/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by V. Avdeeva
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porozhnyy, M.V., Gil, V.V. & Kozmai, A.E. Neutralization Dialysis of Phenylalanine and Mineral Salt Mixed Solution: Effect of Concentration and Flow Rate of Acid and Alkali Solutions. Membr. Membr. Technol. 5, 313–322 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751623050086
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751623050086