Abstract
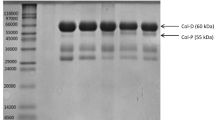
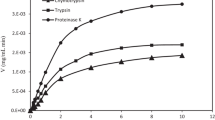
Serine proteinase, purified from the hepatopancreas of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei), was used to hydrolyze acid solubilized collagen (ASC) isolated from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis sp.) skin to produce angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides (ACEIPs). A series of column chromatography assays were used to separate the ACEIPs. A peptide, NPARTCR, was isolated as it exhibited high ACE inhibition potential. Further digestion of this peptide by a proline specific endopeptidase (PSEP), produced a pentapeptide ARTCR with ACE inhibitory activity (IC50) of 77.0 μmol/L. Both NPARTCR and ARTCR inhibited ACE in a non-competitive manner. An in vivo study in rats demonstrated that ARTCR has ACE inhibitory activity via lowering systolic blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). These results suggest that processing by-products from shrimp and tilapia are ideal raw materials for the production of serine proteinase and collagen, respectively. Serine proteinase and collagen are both ideal raw materials that can be used to derive ACE inhibitory active peptides against hypertension.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACEIP:
-
ACE inhibitory peptide
- PSEP:
-
Proline specific endopeptidase
- SHRs:
-
Spontaneously hypertensive rats
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- HBP:
-
High blood pressure
- NPARCTR:
-
Crude peptide isolate
- ARTCR:
-
N-terminal cleavage pentapeptide
References
Anonymous (2018) China Fisheries Yearbook. China Agricultural Press, Beijing, p 25
Aoki H, Ahsan N, Matsuo K, Hagiwara T, Watabe S (2003) Purification and characterization of collagenolytic proteases from the hepatopancreas of Northern shrimp (Pandalus eous). J Agric Food Chem 51:777–783
Balti R, Bougatef A, Sila A, Guillochon D, Dhulster P, Nedjar-Arroume N (2015) Nine novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) muscle protein hydrolysates and antihypertensive effect of the potent active peptide in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem 170:519–525
Barbana C, Boye JI (2011) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory properties of lentil protein hydrolysates: determination of the kinetics of inhibition. Food Chem 127:94–101
Choonpicharn S, Jaturasitha S, Rakariyatham N, Suree N, Niamsup H (2015) Antioxidant and antihypertensive activity of gelatin hydrolysate from Nile tilapia skin. J Food Sci Technol Mysore 52:3134–3139
Eriksson U, Danilczyk U, Penninger JM (2002) Just the beginning: novel functions for angiotensin I-converting enzymes. Curr Biol 12:R745–R752
Forghani B, Zarei M, Ebrahimpour A, Philip R, Bakar J, Hamid AA, Saari N (2016) Purification and characterization of angiotensin converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides derived from Stichopus horrens: stability study against the ACE and inhibition kinetics. J Funct Foods 20:276–290
Fulop V, Bocskei Z, Polgar L (1998) Prolyl oligopeptidase: an unusual beta- propeller domain regulates proteolysis. Cell 94:161–170
Gass J, Khosla C (2007) Prolyl endopeptidases. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:345–355
He R, Malomo SA, Alashi A, Girgih AT, Ju XR, Aluko RE (2013) Purification and hypotensive activity of rapeseed protein-derived renin and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. J Funct Foods 5:781–789
Lassoued I, Mora L, Nasri R, Aydi M, Toldra F, Aristoy MC, Barkia A, Nasri M (2015) Characterization, antioxidative and ACE inhibitory properties of hydrolysates obtained from thomback ray (Raja clavata) muscle. J Proteomics 128:458–468
Law MR, Morris JK, Wald NJ (2009) Use of blood pressure lowing drugs in the prevention of cardiovascular disease: meta-analysis of 147 randomized trials in the context of expectations from prospective epidemiological studies. BMJ 338:b1665
Mäkinen S, Johannson T, Gerd EV, Pihlava JM, Pihlanto A (2012) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory and antioxidant properties of rapeseed hydrolysates. J Funct Foods 4:575–583
Ni H, Li L, Liu G, Hu SQ (2012) Inhibition mechanism and model of an angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory hexapeptide from yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). PLoS ONE 7:e37077
Rao S, Sun J, Liu Y, Zeng H, Su Y, Yang Y (2012) ACE inhibitory peptides and antioxidant peptides derived from in vitro digestion hydrolysate of hen egg white lysozyme. Food Chem 135:1245–1252
Rui X, Boye JI, Simpson BK, Prasher SO (2013) Purification and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides of small red bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) hydrolysates. J Funct Food 5:1116–1124
Sharashova E, Wilsgaard T, Ball J, Morseth B, Gerdts E, Hopstock LA, Mathiesen EB, Schirmen H, Løchen ML (2019) Long-term blood pressure trajectories and incident atrial fibrillation in women and men: the Tromsø Study. Eur Heart J. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz234
Tu M, Wang C, Chen C, Zhang R, Liu H, Lu W, Jiang L, Du M (2018) Identification of a novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from casein and evaluation of the inhibitory mechanisms. Food Chem 256:98–104
Wang MX, Zhong C, Cai QF, Liu GM, Zhang L, Hara K, Su WJ, Cao MJ (2012) Study on prolyl endopeptidase from the skeletal muscle of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Proc Biochem 47:2211–2218
WHO (2013) A global brief on hypertension: Silent killer, global public health crisis. WHO, Geneva, pp 1-39
Wu Q, Cai QF, Tao ZP, Sun LC, Shen JD, Zhang LJ, Liu GM, Cao MJ (2015a) Purification and characterization of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from abalone (Haliotis discus hannai Ino) gonads. Eur Food Res Technol 240:137–145
Wu SG, Feng XZ, Lan XD, Xu YJ, Liao D (2015b) Purification and identification of Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from Lizard fish (Saurida elongata) hydrolysate. J Funct Foods 13:295–299
Yan L, Wang D, Zhu M, Yu Y, Zhang F, Ye X, Linhardt R, Chen S (2019) Highly purified fucosylated chondroitin sulfate oligomers with selective intrinsic factor Xase complex inhibition. Carbohydr Polym 222:115025
Yan LJ, Zhan CL, Cai QF, Weng L, Du CH, Liu GM, Su WJ, Cao MJ (2014) Purification, characterization, cDNA cloning and in vitro expression of a serine proteinase from the intestinal tract of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus) with collagen degradation activity. J Agric Food Chem 62:4769–4777
Yu YK, Hu JN, Miyaguchi YJ, Bai XF, Du YG, Lin BC (2006) Isolation and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from porcine hemoglobin. Peptides 27:2950–2956
Zhang T, Li M, Fu XD, Mou H (2019) Purification and charicterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides with specific structure X-Pro. Eur Food Res Technol 245:1743–1753
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0901004), the National Natural Scientific Foundations of China (31471640, 31702372).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XH contributed to the presented idea and design. LS implemented the computational and statistical analysis and took the lead in writing the manuscript. CZ and AY assisted with data analysis. MC and GL supervised the findings of this work. All authors provided critical feedback and helped to conduct the research, analysis, and preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Animal and human rights statement
This article does not include results from any study involving human subjects performed by any of the authors. All study procedures that involved animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice where the study was conducted.
Additional information
Edited by Xin Yu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, X., Sun, L., Zhong, C. et al. Successive digestion of tilapia collagen by serine proteinase and proline specific endopeptidase to produce novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Mar Life Sci Technol 2, 268–278 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42995-020-00038-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42995-020-00038-y