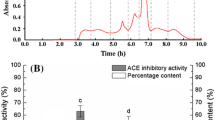
Abstract
Diabetes and hypertension are increasing threats to human health, which could be improved by inhibiting dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), respectively. Herein, we used five different enzymes to hydrolyze silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) muscle protein. Among all treatments, the Neutrase-generated hydrolysate that was purified by a three-step isolation and then was identified using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry resulted in the most potent DPP-IV inhibitory activity and relatively high ACE inhibitory activity. The identified peptide Ala-Ala-Leu-Glu-Gln-Thr-Glu-Arg was the most effective at inhibiting DPP-IV with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of 647.02 ± 4.30 µM. Leu-Leu-Asp-Leu-Gly-Val-Pro showed the highest ACE inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 329.33 ± 15.53 µM. Lys-Ala-Val-Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Leu-Phe exhibited the dual inhibition against both DPP-IV and ACE with IC50 values of 1,317.39 ± 20.93 µM and 726.01 ± 8.69 µM, respectively. Interestingly, it seemed that the majority of peptides which were responsible for inhibiting DPP-IV were different from the ones which caused the inhibition of ACE.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tancredi M, Rosengren A, Svensson AM, Kosiborod M, Pivodic A, Gudbjörnsdottir S, Wedel H, Clements M, Dahlqvist S, Lind M (2015) Excess mortality among persons with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 373(18):1720–1732
Lurbe E, Agabitirosei E, Cruickshank JK, Dominiczak A, Erdine S, Hirth A, Invitti C, Litwin M, Mancia G, Pall D (2016) 2016 European Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. An Esp Pediatr 85(4):167–169
Shaikh A (2017) A practical approach to hypertension management in diabetes. Diabetes Ther 8(5):1–9
Ndisang JF, Vannacci A, Rastogi S (2014) Oxidative stress and inflammation in obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and related cardiometabolic complications. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014:506948
Ferrannini E, Cushman WC (2012) Diabetes and hypertension: the bad companions. Lancet 380(9841):601–610
Gillespie CD, Hurvitz KA (2013) Prevalence of hypertension and controlled hypertension—United States, 2007–2010. MMWR Surveill Summ 62 Suppl 3(3):144–148
World Health Organization (2013) A global brief on hypertension: silent killer, global public health crisis: world health day 2013. World Health Organization, Geneva
Garcés-Rimón M, López-Expósito I, López-Fandiño R, Miguel M (2016) Egg white hydrolysates with in vitro biological multiactivities to control complications associated with the metabolic syndrome. Eur Food Res Technol 242(1):61–69
Hopsuhavu VK, Glenner GG (1966) A new dipeptide naphthylamidase hydrolyzing glycyl-prolyl-beta-naphthylamide. Histochemie 7(3):197–201
Thoma R, Löffler B, Stihle M, Huber W, Ruf A, Hennig M (2003) Structural basis of proline-specific exopeptidase activity as observed in human dipeptidyl peptidase-IV. Structure 11(8):947–959
Tasyurek HM, Altunbas HA, Balci MK, Sanlioglu S (2014) Incretins: their physiology and application in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 30(5):354–371
Fujita H, Yokoyama K, Yoshikawa M (2000) Classification and antihypertensive activity of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins. J Food Sci 65(4):564–569
Lee SY, Sun JH (2017) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory and antioxidant activities of enzymatic hydrolysates of korean native cattle (Hanwoo) myofibrillar protein. Biomed Res Int 2017(5):1–9
Kwok AJ, Mashar M, Khavandi K, Sabir I (2014) DPP-IV inhibitors: beyond glycaemic control? Trends Cardiovasc Med 24(4):157–164
Sanghoon L, Qian ZJ, Sekwon K (2010) A novel angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from tuna frame protein hydrolysate and its antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem 118(1):96–102
Ngo DH, Vo TS, Ryu B, Kim SK (2016) Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Pacific cod skin gelatin using ultrafiltration membranes. Process Biochem 51(10):1622–1628
Zhang C, Zhang Y, Wang ZY, Chen SW, Luo YK (2017) Production and identification of antioxidant and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides from bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) muscle hydrolysate. J Funct Foods 35:224–235
Chai HJ, Chan YL, Li TL, Shiau CY, Wu CJ (2013) Evaluation of lanternfish (Benthosema pterotum) hydrolysates as antioxidants against hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative injury. Food Res Int 54(2):1409–1418
Nielsen PM, Petersen D, Dambmann C, Nielsen PM, Petersen D, Dambmann C (2001) Improved method for determining food protein degree of hydrolysis. J Food Sci 66(5):642–646
Nongonierma AB, Fitzgerald RJ (2013) Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory and antioxidative properties of milk protein-derived dipeptides and hydrolysates. Peptides 39(1):157–163
Lafarga T, Wilm M, Wynne K, Hayes M (2016) Bioactive hydrolysates from bovine blood globulins: generation, characterisation, and in silico prediction of toxicity and allergenicity. J Funct Foods 24:142–155
Bao ZJ, Zhao Y, Wang XY, Chi YJ (2017) Effects of degree of hydrolysis (DH) on the functional properties of egg yolk hydrolysate with alcalase. J Food Sci Technol 54(3):669–678
Neves AC, Harnedy PA, O’Keeffe MB, Alashi MA, Aluko RE, Fitzgerald RJ (2017) Peptide identification in a salmon gelatin hydrolysate with antihypertensive, dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory and antioxidant activities. Food Res Int 100:112–120
Oseguera-Toledo ME, Mejia EGD, Amaya-Llano SL (2015) Hard-to-cook bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) proteins hydrolyzed by alcalase and bromelain produced bioactive peptide fractions that inhibit targets of type-2 diabetes and oxidative stress. Food Res Int 76(Pt 3):839–851
Li-chan ECY, Hunag SL, Jao CL, Ho KP, Hsu KC (2012) Peptides derived from atlantic salmon skin gelatin as dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors. J Agric Food Chem 60(4):973–978
Ji W, Zhang C, Ji H (2017) Two novel bioactive peptides from antarctic krill with dual angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory activities. J Food Sci 82(7):1742–1749
Huang SL, Jao CL, Ho KP, Hsu KC (2012) Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitory activity of peptides derived from tuna cooking juice hydrolysates. Peptides 35(1):114–121
Zhang Y, Chen R, Ma H, Chen S (2015) Isolation and identification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV-inhibitory peptides from trypsin/chymotrypsin-treated goat milk casein hydrolysates by 2D-TLC and LC–MS/MS. J Agric Food Chem 63(40):9543–9549
Lassoued I, Mora L, Nasri R, Aydi M, Toldrá F, Aristoy MC, Barkia A, Nasri M (2015) Characterization, antioxidative and ACE inhibitory properties of hydrolysates obtained from thornback ray (Raja clavata) muscle. J Proteom 128(2):458–468
Yu Y, Fan FJ, Wu D, Yu CP, Wang ZY, Du M (2018) Antioxidant and ACE inhibitory activity of enzymatic hydrolysates from Ruditapes philippinarum. Molecules 23(5):1189–1203
Dai-Hung N, Bomi R, Se-Kwon K (2014) Active peptides from skate (Okamejei kenojei) skin gelatin diminish angiotensin-I converting enzyme activity and intracellular free radical-mediated oxidation. Food Chem 143(1):246–255
Bao C, Chen H, Cao L, Meng J, Jiangpeng (2016) Comparison of ACE inhibitory activity in skimmed goat and cow milk hydrolyzed by alcalase, flavourzyme, neutral protease and proteinase K. Acta Univ Cibiniensis 20(1):77–84
Cao DQ, Lv XJ, Xu XT, Yu H, Sun X, Xu NJ (2017) Purification and identification of a novel ACE inhibitory peptide from marine alga Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis protein hydrolysate. Eur Food Res Technol 243:1829–1837
Natesh R, Schwager SL, Sturrock ED, Acharya KR (2003) Crystal structure of the human angiotensin-converting enzyme–lisinopril complex. Nature 421(6922):551–554
Ji W, Zhang C, Ji H (2017) Purification, identification and molecular mechanism of two dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) protein hydrolysate. J Chromatogr B 1064:56–61
Neves AC, Harnedy PA, O’Keeffe MB, Fitzgerald RJ (2017) Bioactive peptides from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) with angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory, and antioxidant activities. Food Chem 218:396–405
Satake M, Enjoh M, Nakamura Y, Takano T, Kawamura Y, Arai S, Shimizu M (2002) Transepithelial transport of the bioactive tripeptide, Val-Pro-Pro, in human intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayers. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66(2):378–384
Uenishi H, Kabuki T, Seto Y, Serizawa A, Nakajima H (2012) Isolation and identification of casein-derived dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP-4)-inhibitory peptide LPQNIPPL from gouda-type cheese and its effect on plasma glucose in rats. Int Dairy J 22(1):24–30
Tulipano G, Faggi L, Nardone A, Cocchi D, Caroli AM (2015) Characterisation of the potential of β-lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin as sources of bioactive peptides affecting incretin function: in silico and in vitro comparative studies. Int Dairy J 48:66–72
Nongonierma AB, Fitzgerald RJ (2016) Learnings from quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) studies with respect to food protein-derived bioactive peptides: a review. RSC Adv 6(79):75400–75413
Martin RA, Cleary DL, Guido DM, Zurcher-Neely HA, Kubiak TM (1993) Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) from pig kidney cleaves analogs of bovine growth hormone-releasing factor (bGRF) modified at position 2 with Ser, Thr or Val. Extended DPP-IV substrate specificity? BBA Protein Struct M 1164(3):252–260
Wang TY, Hsieh CH, Hung CC, Jao CL, Chen MC, Hsu KC (2015) Fish skin gelatin hydrolysates as dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 stimulators improve glycaemic control in diabetic rats: a comparison between warm- and cold-water fish. J Funct Foods 19:330–340
Liao P, Lan X, Liao D, Sun L, Zhou L, Sun J, Tong Z (2018) Isolation and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from the enzymatic hydrolysate of Carapax trionycis (the shell of the turtle Pelodiscus sinensis). J Agric Food Chem 66:7015–7022
Sun ML, Zhang Q, Ma Q, Fu YH, Jin WG, Zhu BW (2018) Affinity purification of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Volutharpa ampullacea perryi protein hydrolysate using Zn-SBA-15 immobilized ACE. Eur Food Res Technol 244(3):457–468
Salampessy J, Reddy N, Kailasapathy K, Phillips M (2015) Functional and potential therapeutic ACE-inhibitory peptides derived from bromelain hydrolysis of trevally proteins. J Funct Foods 14:716–725
Balti R, Nedjar-Arroume N, Adje EY (2010) Analysis of novel angiotensin l-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) muscle proteins. J Agric Food Chem 58(6):3840–3846
Fitzgerald RJ, Meisel H (2000) Milk protein-derived peptide inhibitors of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme. Br J Nutr 84(1):33–37
Sagardia I, Roa-Ureta RH, Bald C (2013) A new QSAR model, for angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory oligopeptides. Food Chem 136(3–4):1370–1376
Wu J, Aluko RE, Nakai S (2010) Structural requirements of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides: quantitative structure–activity relationship modeling of peptides containing 4-10 amino acid residues. QSAR Comb Sci 25(10):873–880
He N, Lin L, Liu G, Hu SQ (2012) Inhibition mechanism and model of an angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory hexapeptide from yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). Plos One 7(5):e37077
Lacroix IME, Meng G, Cheung IWY, Li-Chan ECY (2016) Do whey protein-derived peptides have dual dipeptidyl-peptidase IV and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activities? J Funct Foods 21:87–96
Gupta S, Kapoor P, Chaudhary K, Gautam A, Kumar R, Raghava GP (2013) In silico approach for predicting toxicity of peptides and proteins. Plos One 8(9):e73957
Høst A, Halken S (2015) Hypoallergenic formulas—when, to whom and how long: after more than 15 years we know the right indication! Allergy 59(s78):45–52
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Science and Technology Ministry of China (Award number 2017YFD0400200) and the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-45).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Compliance with ethics requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Liu, H., Hong, H. et al. Purification and identification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) muscle hydrolysate. Eur Food Res Technol 245, 243–255 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-018-3157-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-018-3157-6