Abstract
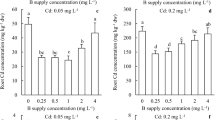
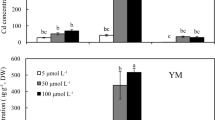
Boron (B) is a microelement and has been demonstrated to alleviate cadmium (Cd) stress and inhibit Cd uptake in wheat. However, the effect of B on accumulation of Cd and mineral elements accumulation in wheat are rarely investigated. A hydroponics experiment was performed with different treatments (CK for without B and Cd application, Cd + B, preB + Cd for B, Cd, and B was added 24 h earlier than Cd added) to explore the effect of B on the growth, subcellular component distribution of Cd, and the mineral distribution. Here, the dry weight of shoot and root were decreased under Cd application compared with CK treatment, while increased under B application, especially under preB + Cd treatment. The root parameters showed a similar trend, including surface area, root length and volume, and tips. The Cd concentrations increased under Cd application in root and shoot, while decreased under B application, especially under preB + Cd treatment in the root. In addition, the B concentration showed a decreasing trend under Cd stress, especially in roots. Subcellular component analysis showed that more than 50% Cd was distributed in soluble fractions in the root, while more than 40% Cd of cell wall (CW) fractions in the shoot, respectively. This suggests that CW fractions and soluble fractions are the main Cd storage sites. The correlation analysis was also discussed among B, Cd, and other elements. Thus, we concluded that Cd toxicity was alleviated under B application in wheat by inhibiting Cd uptake, non-organ distribution, and changing nutrient absorption.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas T, Rizwan M, Ali S, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Qayyum MF, Abbas F, Hannan F, Rinklebed J, Ok YS (2017) Effect of biochar on cadmium bioavailability and uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 140:37–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.02.028
Al-Huqail AA, Nasir Khan M, Ali HM, Siddiqui MH, Al-Huqail AA, AlZuaibr FM, Al-Muwayhi MA, Marraiki N, Al-Humaid LA (2020) Exogenous melatonin mitigates boron toxicity in wheat. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 201:110822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110822
Camacho-Cristobal JJ, Rexach J, Gonzalez-Fontes A (2008) Boron in plants: deficiency and toxicity. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1247–1255. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00742.x
Çatav ŞS, Genç TO, Oktay MK, Küçükakyüz K (2020) Cadmium toxicity in wheat: impacts on element contents, antioxidant enzyme activities, oxidative stress, and genotoxicity. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 104:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02745-4
Chen D, Chen D, Xue R, Long J, Lin X, Lin Y, Jia L, Zeng R, Song Y (2019) Effects of boron, silicon and their interactions on cadmium accumulation and toxicity in rice plants. J Hazard Mater 367:447–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.111
Chen Z, Bai X, Zeng B, Fan C, Li X, Hu B (2023) Physiological and molecular mechanisms of Acacia melanoxylon stem in response to boron deficiency. Front Plant Sci 14:1268835. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1268835
Duan MM, Wang S, Huang DY, Zhu QH, Liu SL, Zhang Q, Zhu HH, Xu C (2018) Effectiveness of simultaneous applications of lime and zinc/iron foliar sprays to minimize cadmium accumulation in rice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:510–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.037
Fahad S, Hussain S, Khan F, Wu C, Saud S, Hassan S, Ahmad N, Gang D, Ullah A, Huang J (2015) Effects of tire rubber ash and zinc sulfate on crop productivity and cadmium accumulation in five rice cultivars under field conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:12424–12434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4518-3
García-Sánchez F, Simón-Grao S, Martínez-Nicolás JJ, Alfosea-Simón M, Liu C, Chatzissavvidis C, Pérez-Péreze JG, Cámara-Zapata JM (2020) Multiple stresses occurring with boron toxicity and deficiency in plants. J Hazard Mater 397:122713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122713
Guo JJ, Tan X, Fu HL, Chen JX, Lin XX, Ma Y, Yang ZY (2018) Selection for cd pollution-safe cultivars of Chinese kale (Brassica alboglabra L. H. Bailey) and biochemical mechanisms of the cultivar-dependent cd accumulation involving in cd subcellular distribution. J Agric Food Chem 66:1923–1934. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05123
Hu Y, Norton GJ, Duan G, Huang Y, Liu Y (2014) Effect of selenium fertilization on the accumulation of cadmium and lead in rice plants. Plant Soil 384:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2189-3
Hua T, Zhang R, Sun H, Liu C (2020) Alleviation of boron toxicity in plants: mechanisms and approaches. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 51:2975–3015. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1807451
Huang L, Bell RW, Dell B (2001) Boron supply into wheat (Triticum aestivum L. Cv. Wilgoyne) ears whilst still enclosed within leaf sheaths. J Exp Bot 52:1731–1738. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/52.361.1731
Huang Y, Huang B, Shen C, Zhou W, Liao Q, Chen Y, Xin J (2022) Boron supplying alters cadmium retention in root cell walls and glutathione content in Capsicum annuum. J Hazard Mater 432:128713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128713
Hussain B, Umer MJ, Li J, Ma Y, Abbas Y, Ashraf MN, Tahir N, Ullah A, Gogoi N, Farooq M (2021) Strategies for reducing cadmium accumulation in rice grains. J Clean Prod 286:125557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125557
Jiang Z, Guo Z, Peng C, Liu X, Zhou Z, Xiao X (2021) Heavy metals in soils around non-ferrous smelteries in China: Status, health risks and control measures. Environ Pollut 282:117038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117038
Klochko K, Kaufman AJ, Yao W, Byrne RH, Tossell JA (2006) Experimental measurement of boron isotope fractionation in seawater. Earth Planet Sci Lett 248:276–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2006.05.034
Kobayashi M, Matoh T, Azuma J (1996) Two chains of rhamnogalacturonan II are cross-linked by borate-diol ester bonds in higher plant cell walls. Plant Physiol 110:1017–1020. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.3.1017
Li XZ, Jia R, Lu XZ, Xu YM, Liang XF, Shen LF, Li BY, Ma C, Wang N, Yao C, Zhang SM (2021) The use of mercapto-modified palygorskite prevents the bioaccumulation of cadmium in wheat. J Hazard Mater 417:125917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125917
Li GZ, Chen SJ, Li NY, Wang YY, Kang GZ (2021a) Exogenous glutathione alleviates cadmium toxicity in wheat by influencing the absorption and translocation of cadmium. Bull Environ Contamin Toxicol 107:320–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03283-8
Loix C, Huybrechts M, Vangronsveld J, Gielen M, Keunen E, Cuypers A (2017) Reciprocal interactions between cadmium-induced cell wall responses and oxidative stress in plants. Front Plant Sci 8:1867. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01867
Long Y, Peng J (2023) Interaction between boron and other elements in plants. Genes 14:130. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010130
Ma J, Cai H, He C, Zhang W, Wang L (2015) A hemicellulose-bound form of silicon inhibits cadmium ion uptake in rice (Oryza sativa) cells. New Phytol 206:1063–1074. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13276
Parks JL, Edwards M (2005) Boron in the environment. Criti Rev Environ Sci Technol 35(2):81–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380590900200
Pommerrenig B, Eggert K, Bienert G (2019) Boron deficiency effects on sugar, ionome, and phytohormone profiles of vascular and non-vascular leaf tissues of common plantain (Plantago major L). Int J Mol Sci 20(16):3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163882
Qin SY, Sun XC, Hu CX, Tan QL, Zhao XH (2017) Uptake, transport and distribution of molybdenum in two oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) cultivars under different nitrate/ammonium ratios. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed Biotechnol) 18(6):512–521. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600249
Qin S, Liu H, Nie Z, Gao W, Li C, Lin Y, Zhao P (2018) AsA-GSH cycle and antioxidant enzymes play important roles in cd tolerance of wheat. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101:684–690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2471-9
Qin SY, Guo WY, Cheng J, Qian YC, Liu HE, Gao W, Nie ZJ, Li C, Zhao P (2019) Effects of different cadmium stress on root system of winter wheat. J Henan Agri Univ 53(4):519–524. https://doi.org/10.16445/j.cnki.1000-2340.2019.04.004
Qin S, Liu H, Nie Z, Rengel Z, Gao W, Li C, Zhao P (2020a) Toxicity of cadmium and its competition with mineral nutrients for uptake by plants: a review. Pedosphere 30(2):168–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(20)60002-9
Qin S, Liu H, Rengel Z, Gao W, Nie Z, Li C, Hou M, Cheng J, Zhao P (2020b) Boron inhibits cadmium uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by regulating gene expression. Plant Sci 297:110522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110522
Qin SY, Liu H, Mei H, Li Y, Gao W, Nie Z, Li C, Wang L, Zhao P (2021) Effect of different cadmium concentrations on growth response of wheat and uptake and subcellular distribution of cd. J Henan Agri Univ 55(6):1029–1035. https://doi.org/10.16445/j.cnki.1000-2340.20210621.001
Qin SY, Xu Y, Nie Z, Liu H, Gao W, Li C, Wang L, Zhao P (2022) Effect of boron on cadmium uptake and expression of cd transport genes at different growth stages of wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 241:113834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113834
Qin S, Xu Y, Liu H, Zhao P (2023) Foliar application of zinc promotes cadmium absorption by increasing expression of cadmium transporter genes and activities of antioxidative enzymes in winter wheat. Pedosphere 33(4):612–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedsph.2022.07.001
Rezapour S, Atashpaz B, Moghaddam SS, Kalavrouziotis IK, Damalas CA (2019) Cadmium accumulation, translocation factor, and health risk potential in a wastewater-irrigated soil-wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) system. Chemosphere 231:579–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.095
Riaz M, Kamran M, Fang Y, Yang G, Rizwan M, Ali S, Zhou Y, Wang Q, Deng L, Wang Y, Wang X (2021a) Boron supply alleviates cadmium toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by enhancing cadmium adsorption on cell wall and triggering antioxidant defense system in roots. Chemosphere 266:128938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128938
Riaz M, Kamran M, Rizwan M, Ali S, Zhou Y, Núñez-Delgado A, Wang X (2021b) Boron application mitigates cd toxicity in leaves of rice by subcellular distribution, cell wall adsorption and antioxidant system. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 222:112540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112540
Rizwan M, Ali S, Abbas T, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Keller C, Al-Wabel MI, Ok YS (2016) Cadmium minimization in wheat: a critical review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 130:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.04.001
Sasaki A, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2014) Overexpression of OsHMA3 enhances cd tolerance and expression of zn transporter genes in rice. J Exp Bot 65(20):6013–6021. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru340
Semane B, Cuypers A, Smeets K, Van Belleghem F, Horemans N, Schat H, Vangronsveld J (2007) Cadmium responses in Arabidopsis thaliana: glutathione metabolism and antioxidative defence system. Physiol Plant 129:519–528. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00822.x
Shi J, Du P, Luo H, Wu H, Zhang Y, Chen J, Wu M, Xu G, Gao H (2022) Soil contamination with cadmium and potential risk around various mines in China during 2000–2020. J Environ Manage 310:114509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114509
Shireen F, Nawaz MA, Chen C, Zhang Q, Zheng Z, Sohail H, Sun JY, Cao HS, Huang Y, Bie Z (2018) Boron: functions and approaches to enhance its availability in plants for sustainable agriculture. Int J Mol Sci 19:1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071856
Singh S, Parihar P, Singh R, Singh VP, Prasad SM (2016) Heavy metal tolerance in plants: role of transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and ionomics. Front Plant Sci 6:1143. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01143
Takano J, Miwa K, Fujiwara T (2008) Boron transport mechanisms: collaboration of channels and transporters. Trends Plant Sci 13(8):451–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.05.007
Tanaka M, Fujiwara T (2008) Physiological roles and transport mechanisms of boron: perspectives from plants. Eur J Physiol 456:671–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0370-8
Thomine S, Lelievre F, Debarbieux E, Schroeder JI, Barbier-Brygoo H (2003) AtNRAMP3, a multispecific vacuolar metal transporter involved in plant responses to iron deficiency. Plant J 34:685–695. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01760.x
Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T (2012) Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation. Rice 5:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1939-8433-5-5
Wang MY, Chen AK, Wong MH, Qiu L, Cheng H, Ye ZH (2011) Cadmium accumulation in and tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties with different rates of radial oxygen loss. Environ Pollut 159:1730–1736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.02.025
Wang S, Wang F, Gao S (2015) Foliar application with nano-silicon alleviates cd toxicity in rice seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:2837–2845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3525-0
Wang M, Chen S, Zheng H, Li S, Chen L, Wang D (2020) The responses of cadmium phytotoxicity in rice and the microbial community in contaminated paddy soils for the application of different long-term N fertilizers. Chemosphere 238:124700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124700
Warington K (1923) The effect of boric acid and borax on the broad bean and certain other plants. Ann Bot 37:629–672. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a089871
Wu F, Dong J, Qian QQ, Zhang GP (2005) Subcellular distribution and chemical form of cd and Cd-Zn interaction in different barley genotypes. Chemosphere 60:1437–1446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.01.071
Wu X, Song H, Guan C, Zhang Z (2020a) Boron alleviates cadmium toxicity in Brassica napus by promoting the chelation of cadmium onto the root cell wall components. Sci Total Environ 728:138833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138833
Wu X, Song H, Guan C, Zhang Z (2020b) Boron mitigates cadmium toxicity to rapeseed (Brassica napus) shoots by relieving oxidative stress and enhancing cadmium chelation onto cell walls. Environ Pollut 263:114546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114546
Xin J, Huang B (2014) Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in two hot pepper cultivars differing in cadmium accumulation. J Agric Food Chem 62:508–515. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4044524
Yan X, Wu P, Ling H, Xu G, Xu F, Zhang Q (2006) Plant nutriomics in China: an overview. Ann Bot 98:473–482. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcl116
Yang S, Wua P, Jeyakumar P, Wang H, Zheng X, Liu W, Wang L, Li X, Ru S (2022) Technical solutions for minimizing wheat grain cadmium: a field study in North China. Sci Total Environ 818:151791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151791
Zhang G, Fukamin M, Sekimoto (2002) Influence of cadmium on mineral concentrations and yield components in wheat genotypes differing in cd tolerance at seedling stage. Field Crops Res 77:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(02)00061-8
Zhang L, Gao C, Chen C, Zhang W, Huang XY, Zhao FJ (2020a) Overexpression of rice OsHMA3 in wheat greatly decreases cadmium accumulation in wheat grains. Environ Sci Technol 54:10100–10108. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c02877
Zhang R, Tao C, Zhang Y, Hou YH, Chang QR (2020b) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils and identification of main influencing factors in a typical industrial park in northwest China. Chemosphere 252:126591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126591
Zhang K, Xu Y, Liu H, Zhao P, Qin S (2022) Difference study of response of different winter wheat seedling growth to cadmium. Shandong Agricul Sic 54(7):104–112. https://doi.org/10.14083/j.issn.1001-4942.2022.07.015
Zhao FJ, Ma Y, Zhu YG, Tang Z, McGrath SP (2015) Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies. Environ Sci Technol 49:750–759. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5047099
Zhao FJ, Tang Z, Song JJ, Huang XY, Wang P (2022) Toxic metals and metalloids: Uptake, transport, detoxification, phytoremediation, and crop improvement for safer food. Mol Plant 15:27–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.09.016
Funding
This work was financed by the Chinese State Natural Science Foundation and the Scientific Technological Key Projects of Henan Province, the contracts No 32002128 and No 212102310979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Y.F., M.X., H.L., P.Z., F.S., S.Q., and G.L. The first draft of the manuscript was written by S.Q., and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Xie, M., Liu, H. et al. Effects of Boron Application on Absorption of Cadmium and Other Mineral Elements of Wheat. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-024-01813-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-024-01813-x