Abstract
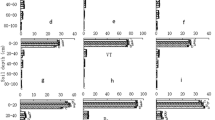
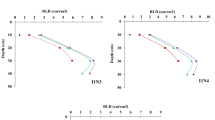
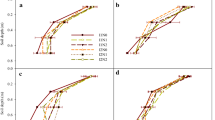
Root growth and its adaptation are quite important for efficient use of water and nutrients. The present study investigated the effects of alternate partial root-zone irrigation (APRI) coupled with nitrogen application on root growth and nitrogen-use efficiency (NUE) of maize (Zea mays L.). Treatments (conducted at Wuwei City, northwest China) included APRI with controlled irrigation at 45%, 65%, and 80% of field capacity (FC) (W1, W2, and W3, respectively) coupled with nitrogen application rate of 100, 200, and 300 kg N ha−1 (N1, N2, and N3, respectively). The study found a significant interaction effect of irrigation regimes and nitrogen application rates on maize root growth and NUE. Compared with N2, N3 did not increase the length, surface area, weight, and volume of roots at the filling and maturity stages under W2, while it did under W3, which suggests that increasing nitrogen application rates did not compensate for the adverse effect of drought on root growth. In addition, NUE positively correlated with these root morphological parameters but negatively with the root-to-shoot ratio at the filling and maturity stages. The W2N2 treatment with moderate soil moisture and relatively high soil nitrate-nitrogen promoted total root growth and deeper roots and optimized vertical root distribution, with a low root-to-shoot ratio, resulting in the greatest NUE. These results suggest that moderately controlled irrigation (W2) combined with a reasonable nitrogen rate (N2) improves root growth and optimizes root distribution, resulting in a high NUE in maize under alternate partial root-zone irrigation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Waheda MH, Ali EA (2013) Effect of irrigation systems, amounts of irrigation water and mulching on corn yield, water use efficiency and net profit. Agric Water Manage 120:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2012.06.017
Buckley TN, Sack L, Farquhar GD (2017) Optimal plant water economy. Plant Cell Environ 40:881–896. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12823
Du TS, Kang SZ, Zhang JH, Davis WJ (2015) Deficit irrigation and sustainable water-resource strategies in agriculture for China’s food security. J Exp Bot 66:2253–2269. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv034
FAO STAT (2020) Prod Stat. Core production data base. Electronic resource. http://faostat.fao.org/. Accessed 2020.09.08
Giunta F, Motzo R, Pruneddu G (2008) Has long-term selection for yield in durum wheat also induced changes in leaf and canopy traits? Field Crops Res 106:68–76
Guo JJ, Fan JL, Xiang YZ, Zhang FC, Yan SC, Zhang XY, Zheng J, Li YP, Tang ZJ, Li ZJ (2022) Coupling effects of irrigation amount and nitrogen fertilizer type on grain yield, water productivity and nitrogen use efficiency of drip-irrigated maize. Agric Water Manage 255:107008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107389
Hu TT, Kang SZ, Li FS, Zhang JH (2009) Effects of partial root-zone irrigation on the nitrogen absorption and utilization of maize. Agric Water Manage 96:208–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2008.07.011
Jha SK, Gao Y, Liu H, Huang ZD, Wang GS, Liang YP, Duan AW (2017) Root development and water uptake in winter wheat under different irrigation methods and scheduling for North China. Agric Water Manage 182:139–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.12.015
Ju XT, Xing GX, Chen XP, Zhang S, Zhang L, Liu X, Cui ZL, Yin B, Christie P, Zhu Z, Zhang FS (2009) Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. PANS 106:3041–3046. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0813417106
Ju CX, Buresh RJ, Wang ZQ, Zhang H, Liu LJ, Yang JC, Zhang JH (2015) Root and shoot traits for rice varieties with higher grain yield and higher nitrogen use efficiency at lower nitrogen rates application. Field Crops Res 175:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2015.02.007
Kang J, Hao XM, Zhou HP, Ding RS (2021) An integrated strategy for improving water use efficiency by understanding physiological mechanisms of crops responding to water deficit: present and prospect. Agric Water Manage 255:107008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107008
Kant S (2018) Understanding nitrate uptake, signaling and remobilization for improving plant nitrogen use efficiency. Semin Cell Dev Biol 74:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.08.034
Kirda C, Topcu S, Kaman H, Ulger AC, Yazici A, Cetin M, Derici MR (2005) Grain yield response and N-fertilizer recovery of maize under deficit irrigation. Field Crops Res 93:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2004.09.015
Li SX, Wang ZH, Malhi S, Li SQ, Gao YJ, Tian XH (2009) Nutrient and water management effects on crop production, and nutrient and water use efficiency in dryland areas of China. Adv Agronomy 102:223–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(09)01007-4
Li QQ, Dong BD, Qiao YZ, Liu MY, Zhang J (2010) Root growth, available soil water, and water-use efficiency of winter wheat under different irrigation regimes applied at different growth stages in North China. Agric Water Manage 97:1676–1682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2010.05.025
Li GH, Zhao B, Dong ST, Zhang JW, Liu P, Lu WP (2020) Controlled-release urea combining with optimal irrigation improved grain yield, nitrogen uptake, and growth of maize. Agric Water Manage 227:105834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105834
Mi GH, Chen FJ, Wu QP, Lai NW, Yuan LX, Zhang FS (2010) Ideotype root architecture for efficient nitrogen acquisition by maize in intensive cropping systems. Sci China Life Sci 53:1369–1373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-010-4097-y
Mu XH, Chen FJ, Wu QP, Chen QW, Wang JF, Yuan LX, Mi GH (2015) Genetic improvement of root growth increases maize yield via enhanced post-silking nitrogen uptake. Eur J Agronomy 63:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2014.11.009
Ogawa A, Kawashima C, Yamauchi A (2005) Sugar accumulation along the seminar root axis as affected by osmotic stress in maize: a possible physiological basis for plastic lateral root development. Plant Prod Sci 8:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1626/pps.8.173
Passioura J (1983) Roots and drought resistance. Agric Water Manage 7:265–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-3774(83)90089-6
Peng YF, Li XX, Li CJ (2012) Temporal and spatial profiling of root growth revealed novel response of maize roots under various nitrogen supplies in the field. PLoS ONE 7:e3326. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037726
Pikul JL, Hammack L, Riedell WE (2005) Corn yield, nitrogen use, and corn rootworm infestation of rotations in the Northern Corn Belt. Agronomy J 97:854–863. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2004.0263
Prince SJ, Murphy M, Mutava RN, Durnell LA, Valliyodan B, Shannon JG, Nguyen HT (2017) Root xylem plasticity to improve water use and yield in water-stressed soybean. J Exp Bot 68:2027–2036. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw472
Qi DL, Hu TT (2017) Effects of varied nitrogen supply and irrigation methods on distribution and dynamics of soil NO3 -N during maize season. J Agric Sci 9:1–14. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v9n1p1
Qi DL, Pan C (2022) Responses of shoot biomass accumulation, distribution, and nitrogen use efficiency of maize to nitrogen application rates under waterlogging. Agric Water Manage 261:107352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107352
Qi DL, Hu TT, Niu XL (2017) Responses of root growth and distribution of maize to nitrogen application patterns under partial root-zone irrigation. Int J Plant Prod 11:209–224
Qi DL, Hu TT, Song X, Zhang ML (2019) Effect of nitrogen supply method on root growth and grain yield of maize under alternate partial root-zone irrigation. Sci Rep 9:8191
Qi DL, Hu TT, Liu TT (2020) Biomass accumulation and distribution, yield formation and water use efficiency responses of maize (Zea mays L.) to nitrogen supply methods under partial root-zone irrigation. Agric. Water Manage. 230:105981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105981
Qi DL, LiX PC, Li JF, Xu Y, Zhu JQ (2021) Effect of nitrogen supply methods on the gas exchange, antioxidant enzymatic activities, and osmoregulation of maize (Zea mays L.) under alternate partial root-zone Irrigation. J Soil Sci Plant Nutri 21:2083–2095. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00504-1
Qi DL, Hu TT, Song X (2020b) Effects of nitrogen application rates and irrigation regimes on grain yield and water use efficiency of maize under alternate partial root-zone irrigation. J Inter Agric 19: 2792–2806. http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
Ran H, Kang SZ, Li FS, Tong L, Du TS (2016) Effects of irrigation and nitrogen management on hybrid maize seed production in north-west China. Front Agric Sci Engin 3:55–64. https://doi.org/10.15302/J-FASE-2016091
Ran H, Kang SZ, Li FS, Du TS, Ding RS, Tong L (2017) Responses of water productivity to irrigation and N supply for hybrid maize seed production in an arid region of Northwest China. J Arid Land 9:504–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-017-0017-3
Rasmussen IS, Dresbøll DB, Thorup-Kristensen K (2015) Winter wheat cultivars and nitrogen (N) fertilization—effects on root growth, N uptake efficiency and N use efficiency. Eur J Agronomy 68:38–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2015.04.003
Sadras VO (2009) Does partial root-zone drying improve irrigation water productivity in the field? A meta-analysis. Irri Sci 27:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-008-0141-0
Sarker KK, Hossain A, Timsina J, Biswas SK, Malone SL, Alam MK, Loescher HW, Bazzaz M (2020) Alternate furrow irrigation can maintain grain yield and nutrient content, and increase crop water productivity in dry season maize in sub-tropical climate of South Asia. Agric Water Manage 238:106229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106229
Sattelmacher B, Gerendas J, Toms K, Brück H, Bagdady NH (1993) Interaction between root growth and mineral nutrition. Environ Exp Bot 33:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/0098-8472(93)90056-L
Sepaskhah AR, Ahaadi SH (2010) A review on partial root-zone drying irrigation. Int J Plant Prod 4:241–258
Tian ZW, Liu XX, Yu JH, Gu SL, Zhang L, Jiang D, Cao WX, Dai TB (2019) Early nitrogen deficiency favors high nitrogen recovery efficiency by improving deeper soil root growth and reducing nitrogen loss in wheat. Arch Agronomy Soil Sci 66:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2019.1671972
Trachsel S, Kaeppler SM, Browm KM, Lynch JP (2013) Maize root growth angles become steeper under low N conditions. Field Crops Res 140:18–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2012.09.010
Wang CY, Liu W, Li QX, Ma DY, Lu HF, Feng W, Xie YX, Zhu YJ, Guo TC (2014) Effects of different irrigation and nitrogen regimes on root growth and its correlation with above-ground plant parts in high-yielding wheat under field conditions. Field Crops Res 165:138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2014.04.011
Wang ZQ, Zhang WY, Beebout SS, Zhang H, Liu LJ, Yang JC, Zhang JH (2016) Grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice as influenced by irrigation regimes and their interaction with nitrogen rates. Field Crops Res 193:54–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2016.03.006
Wang YS, Janz B, Engedal T, Neergaard A (2017a) Effect of irrigation regimes and nitrogen rates on water use efficiency and nitrogen uptake in maize. Agric Water Manage 179:271–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.06.007
Wang YS, Jensen CR, Liu FL (2017b) Nutritional responses to soil drying and rewetting cycles under partial root-zone drying irrigation. Agric Water Manage 179:254–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.04.015
Wang Y, Zhang XY, Chen J, Chen AJ, Wang LY, Guo XY, Niu YL, Liu SR, Mi GH, Gao Q (2018) Reducing basal nitrogen rate to improve maize seedling growth, water and nitrogen use efficiencies under drought stress by optimizing root morphology and distribution. Agric Water Manage 212:328–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.09.010
Xing HL, Zhou WB, Wang C, Li L, Li XN, Cui NB, Hao WP, Liu FL, Wang YS (2021) Excessive nitrogen application under moderate soil water deficit decreases photosynthesis, respiration, carbon gain and water use efficiency of maize. Plant Physi Biochem 66:1065–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.07.014
Xu GW, Lu DK, Wang HZ, Li YJ (2018) Morphological and physiological traits of rice roots and their relationships to yield and nitrogen utilization as influenced by irrigation regime and nitrogen rate. Agric Water Manage 203:385–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.02.033
Xu GW, Song KJ, Lu DK, Wang HZ, Chen MC (2019) Influence of water management and nitrogen application on rice root and shoot traits. Agronomy J 111:2232–2244. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2019.02.0096
Xu J, Guo ZY, Li ZM, Li FJ, Xue XK, Wu XR, Zhang XM, Li H, Zhang XD, Han QF (2021) Stable oxygen isotope analysis of the water uptake mechanism via the roots in spring maize under the ridge–furrow rainwater harvesting system in a semi-arid region. Agric Water Manage 252:106879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106879
Yang R, Su YZ (2009) Effects of nitrogen fertilization and irrigation rate on grain yield, nitrate accumulation and nitrogen balance on sandy farmland in the marginal oasis in the middle of Heihe River basin. Acta Ecolo Sinica 28:1460–1469 ((in Chinese). CNKI:SUN:STXB.0.2009-03-048)
Yang JC, Zhang JH (2010) Crop management techniques to enhance harvest index in rice. J Exp Bot 61:3177–3189. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq112
Yang JC, Zhang H, Zhang JH (2012) Root morphology and physiology in relation to the yield formation of rice. J Inter Agric 11:920–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(12)60082-3
Yu LY, Zhao XN, Gao XD, Siddique KHM (2020) Improving/maintaining water-use efficiency and yield of wheat by deficit irrigation: a global meta-analysis. Agric Water Manage 228:105906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105906
Zhang XY, Chen SY, Sun HY, Wang YM, Shao LW (2009) Root size, distribution and soil water depletion as affected by cultivars and environmental factors. Field Crops Res 114:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2009.07.006
Zhang J, Liu HX, Pang XP, Yu C, Wang Q, Zhou YP, Lin LG, Guo ZG (2019) Effect of partial root-zone irrigation (PRD) on the gas exchange and antioxidant enzymatic activities in Alfalfa. J Soil Sci Plant Nutri 19:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-0018-8
Zhou QY, Kang SZ, Zhang L, Li FS (2007) Comparison of APRI and Hydrus-2D models to simulate soil water dynamics in a vineyard under alternate partial root zone drip irrigation. Plant Soil 291:211–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-9187-z
Zou HY, Fan JL, Zhang FC, Xiang YZ, Wu LF, Yan SC (2020) Optimization of drip irrigation and fertilization regimes for high grain yield, crop water productivity and economic benefits of spring maize in Northwest China. Agric Water Manage 230:105986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105986
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the research grants from the National Natural Science Fund of China (51809006; 51079124). The authors would like to thank all the reviewers who participated in the review, as well as MJ Editor (www.mjeditor.com) for providing English editing services during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, D., Hu, T. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rates and Irrigation Regimes on Root Growth and Nitrogen-Use Efficiency of Maize under Alternate Partial Root-Zone Irrigation. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22, 2793–2804 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-00846-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-00846-4