Abstract
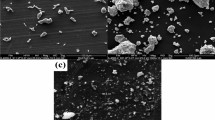
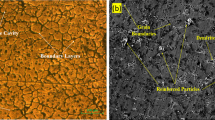
Al–7Si, Al–7Si–4Zn, Al–7Si–4Zn–3Cu alloys were produced by permanent mold casting method to investigate the effects of copper and zinc additions on the machinability properties of Al–7Si alloy. The structural and mechanical properties of the produced alloys were investigated with conventional methods. Machinability properties of these alloys were determined by turning, and they were associated with structural and mechanical properties of the alloys. Machinability experiments were carried out in CNC vertical machining center under dry cutting conditions using uncoated carbide drill and constant cutting speed (120 m/min), feed (0.15 mm/rev) and depth of cut (15 mm) values. The microstructure of Al–7Si binary alloy was observed to be composed of aluminum-rich α phase, primary silicon crystals and eutectic Al–Si phase. The addition of 4% Zn to the Al–7Si alloy did not form a different phase in the microstructure. However, Al2Cu intermetallic phase was formed by addition of 3% Cu. While the hardness and tensile strength of the alloy increased, elongation to fracture significantly reduced. As a result of machinability experiments, it was observed that the minimum thrust force and surface roughness occurred in Al–7Si–4Zn–3Cu alloy, while the maximum built-up edge was observed during drilling of Al–7Si and Al–7Si–4Zn alloys. Microhardness value of machined surface in Al–7Si alloy was found to be the minimum while the maximum Al–7Si–4Zn–3Cu alloy was observed.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gonçalves RA, Silva MB (2015) Influence of copper content on 6351 aluminum alloy machinability. Procedia Manuf 1:683–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2015.09.014
AlSaadi HIA, Tunay RF (2017) The effect of artificial aging on the hardness of aluminum alloy. J Eng Sci Des 5(3):525–532. https://doi.org/10.21923/jesd.287005
Soares RB, De Jesus AMP, Neto RJL, Chinta B, Rosa PAR, Reis A (2017) Comparison between cemented carbide and PCD tools on machinability of a high silicon aluminium alloy. J Mater Eng Perform 26(9):4638–4657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2870-9
Roy P, Sarangi SK, Ghosh A, Chattopadhyay AK (2009) Machinability study of pure aluminium and Al–12%Si alloys against uncoated and coated carbide inserts. Int J Ref Met Hard Mater 27(3):535–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2008.04.008
Uhlman E, Reimers W, Bryne F, Klaus M (2010) Analysis of tool wear and residual stress of CVD diamond coated cemented carbide tools in the machining of aluminium silicon alloys. Prod Eng 4(2–3):203–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-010-0213-x
Wain N, Thomas NR, Hickman S, Wallbank J, Teer DG (2005) Performance of low-friction coatings in the dry drilling of automotive Al–Si alloys. Surf Coat Technol 200(5–6):1885–1892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.08.016
Zedan Y, Samuel FH, Samuel AM, Doty HW (2010) Effects of intermetallics on the machinability of heat-treated Al-(7-11)%Si alloys. J Mater Pro Tech 210(2):245–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imatprotec.2009.09.007
Miracle DB (2005) Metal matrix composites-from science to technological significance. Compos Sci Technol 65(15–16):2526–2540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.05.027
Abdelaziz MH, Samuel AM, Doty HW, Valtierra S, Samuel FH (2019) Effect of additives on the microstructure and tensile properties of Al–Si alloys. J Mater Res Technol 8(2):2255–2268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.03.003
Samuel E, Samuel AM, Doty HW, Valtierra S, Samuel FH (2014) Intermetallic phases in Al–Si based cast alloys: new perspective. Int J Cast Metals Res 27(2):107–114. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743133613Y.0000000083
Basavakumar KG, Mukunda PG, Chakraborty M (2007) Influence of melt treatments and turning inserts on cutting force and surface integrity in turning of Al–7Si and Al–7Si–2.5Cu cast alloys. J Mater Sci 42(20):8714–8724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1754-z
Grum J, Kisin M (2003) Influence of microstructure on surface integrity in turning-part I: the influence of the size of the soft phase in a microstructure on surface-roughness formation. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 43(15):1535–1543. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(03)00199-8
Pan EN, Cherng YC, Lin CA, Chiou HS (1994) Roles of Sr and Sb on Silicon Modification of A356 Aluminium Alloys. AFS Trans 102:609–629
Barzani MM, Sarhan AA, Farahany S, Ramesh S, Maher I (2015) Investigating the machinability of Al–Si–Cu cast alloy containing bismuth and antimony using coated carbide insert. Measurement 62:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2014.10.030
Nishida Y, Arima H, Kim JC, Ando T (2001) Rotary-die equal-channel angular pressing of an Al–7 mass% Si–0.35 mass% Mg alloy. Scr Mater 45(3):261–266
Neishi K, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2001) Achieving superplasticity in a Cu–40% Zn alloy through severe plastic deformation. Scr Mater 45(8):965–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(01)01119-8
Alemdağ Y, Beder M (2014) Microstructural, mechanical and tribological properties of Al–7Si–(0–5)Zn alloys. Mater Des 63:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.06.006
Alemdağ Y, Karabıyık S, Yanar H, Pürçek G (2018) Mechanical properties of multi-directional forged Al–7Si–4Zn–3Cu alloy. Defect Differ Forum 385:250–255. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/DDF.385.250
Basavakumar KG, Mukunda PG, Chakraborty M (2008) Influence of grain refinement and modification on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–7Si and Al–7Si–2.5Cu cast alloys. Mater Charact 59(3):283–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2007.01.011
Hwang YK, Lee CM, Park SH (2009) Evaluation of machinability according to the changes in machine tools and cooling lubrication environments and optimization of cutting conditions using Taguchi method. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 10(3):65–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-009-0049-5
Marani M, Songmene V, Zeinali M, Kouam J, Zedan Y (2019) Neuro-fuzzy predictive model for surface roughness and cutting force of machined Al–20Mg2Si–2Cu metal matrix composite using additives. Neural Comp Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04314-6
Giasin K, Hodzic A, Phadnis V, Ayvar-Soberanis S (2016) Assessment of cutting forces and hole quality in drilling Al2024 aluminium alloy: experimental and finite element study. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(5–8):2041–2061. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8563-y
Basavakumar KG, Mukunda PG, Chakraborty M (2007) Influence of melt treatments and turning inserts on cutting force and surface integrity in turning of Al–12Si and Al–12Si–3Cu cast alloys. Surf Coat Technol 201(8):4757–4766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.10.015
Farid AA, Sharif S, Idris MH (2011) Surface integrity study of high-speed drilling of Al–Si alloy using HSS drill. J Eng Manuf 225(7):1001–1007. https://doi.org/10.1177/2041297510393642
Braga DU, Diniz AE, Miranda GW, Coppini NL (2002) Using a minimum quantity of lubricant (MQL) and a diamond coated tool in the drilling of aluminum–silicon alloys. J Mater Process Technol 122(1):127–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(01)01249-3
Froehlich AR, Jacques RC, Strohaecker TR, Mombru R (2007) The correlation of machinability and microstrutural characteristics of different extruded aluminum alloys. J Mater Eng Perform 16(6):784–791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-007-9097-0
Edwards JD, Frary FC, Jeffries Z (1930) The aluminum industry: aluminum products and their fabrication, vol 2. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
Marani M, Songmene V, Kouam J, Zedan Y (2018) Experimental investigation on microstructure, mechanical properties and dust emission when milling Al–20Mg2 Si–2Cu metal matrix composite with modifier elements. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 99(1–4):789–802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2491-y
Bayraktar Ş, Hekimoğlu AP (2020) Effect of zinc content and cutting tool coating on the machinability of the Al–(5–35) Zn alloys. Met Mater Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00582-y
Hekimoğlu AP, Bayraktar Ş, Turgut Y (2018) Investigation of the effect of cutting speed and feed rate on machining of the Al–35Zn alloy. In: 2nd international symposium on innovative approaches in scientific studies (ISAS 2018-Winter), 30th Nov–2th Dec, Samsun, Turkey
Bayraktar Ş, Hekimoğlu AP, Turgut Y, Hacıosmanoğlu M (2017) Effect of different cutting tools on machinability of the Al–5Zn alloy. In: 2nd international symposium on industrial design engineering (ISIDE), 13th–15th Sep, Nevşehir, Turkey
Bayraktar Ş, Hekimoğlu AP, Turgut Y, Hacıosmanoğlu M (2017) A performance comparison study of uncoated and TiAlN coated carbide end mill on machining of the Al–35Zn alloy. In: 9th international conference on tribology (BalkanTRib’17), 13th–15th Sept, Nevşehir, Turkey
Agustina DB, Saá A, Marcos BM, Rubio EM (2011) Analysis of the machinability of aluminium alloys UNS A97050-T7 and UNS A92024-T3 during short dry turning tests. Adv Mater Res 264:931–936. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.264-265.931
Marcos BM, Sebastián PMA, Contreras SJP, Sánchez CM, Sánchez LM, Sánchez SJM (2005) Study of roundness on cylindrical bars turned of aluminium–copper alloys UNS A92024. J Mater Process Technol 162:644–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.02.061
Vilches F, Hurtado L, Fernández F, Gamboa C (2017) Analysis of the chip geometry in dry machining of aeronautical aluminum alloys. Appl Sci 7(2):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020132
Fatahalla N, Hafiz M, Abdulkhalek M (1999) Effect of microstructure on the mechanical properties and fracture of commercial hypoeutectic Al–Si alloy modified with Na, Sb and Sr. J Mater Sci 34(14):3555–3564
Alemdağ Y, Beder M (2015) Dry sliding wear properties of Al–7Si–4Zn–(0–5)Cu alloys. In: 8th international conference on tribology, 30th Oct–1st Nov, Sinaia, Romania
Özçatalbaş Y, Aydın B (2006) Effect of mechanical properties and cutting geometry on the machinability properties of AA2014 alloy. J Fac Eng Archit Gazi Univ 21(1):21–27. http://dergipark.org.tr/gazimmfd/issue/6667/88807
Pugazhenthi A, Dinaharan I, Kanagaraj G, Selvam JDR (2018) Predicting the effect of machining parameters on turning characteristics of AA7075/TiB2 in situ aluminum matrix composites using empirical relationships. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 40:555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1480-2
Garcia RF, Feix EC, Mendel HT, Gonzalez AR, Souza AJ (2019) Optimization of cutting parameters for finish turning of 6082-T6 aluminum alloy under dry and RQL conditions. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41:317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1826-4
Carrilero MS, Bienvenido R, Sanchez JM, Alvarez A, Gonzalez A, Marcos M (2002) A SEM and EDS insight into the BUL and BUE differences in the turning processes of AA2024 Al–Cu alloy. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42(2):215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(01)00112-2
Gökkaya H (2010) The effect of machining parameters on cutting forces, surface roughness, build-up edge (BUE) and built-up layer (BUL) during machining AA2014(T4) alloy. J Mech Eng 56(9):584–593
Gökkaya H, Nalbant M (2007) Investigating the effects of cutting speeds over the built-up layer and built-up edge formation with SEM. J Fac Eng Archit Gazi Univ 22(3):481–488
Nouari M, List G, Girot F, Gehin D (2005) Effect of machining parameters and coating on wear mechanisms in dry drilling of aluminium alloys. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45(12–13):1436–1442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2005.01.026
List G, Nouari M, Gehin D, Gomez S, Manaud JP, Le Petitcorps Y, Girot F (2005) Wear behaviour of cemented carbide tools in dry machining of aluminium alloy. Wear 259(7–12):1177–1189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2005.02.056
Zeren M, Karakulak E, Gümüş S (2011) Influence of Cu addition on microstructure and hardness of near-eutectic Al–Si–xCu-alloys. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 21(8):1698–1702. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60917-5
Savaşkan T, Bican O, Alemdağ Y (2009) Developing aluminium–zinc-based a new alloy for tribological applications. J Mater Sci 44(8):1969–1976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3297-y
Aurich JC, Sudermann H, Bil H (2005) Characterisation of burr formation in grinding and prospects for modelling. CIRP Ann 54(1):313–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0007-8506(07)60111-5
Pramila Bai BN, Biswas SK (1991) Effect of magnesium addition and heat treatment on mild wear of hypoeutectic aluminium–silicon alloys. Acta Metal Mater 39(5):833–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-7151(91)90283-7
Ramesh A, Melkote SN, Allard LF, Riester L, Watkins TR (2005) Analysis of white layers formed in hard turning of AISI 52100 steel. Mater Sci Eng A 390(1–2):88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.08.052
Osterle W, Li PX (1997) Mechanical and thermal response of a nickel-base superalloy upon grinding with high removal rates. Mater Sci Eng A 238(2):357–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(97)00457-7
Zhou J, Bushlya V, Peng RL, Stahl JE (2012) Identification of subsurface deformation in machining of Inconel 718. Appl Mech Mater 117–119:1681–1688. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.117_119.1681
Dargusch SM, Zhang MX, Palanisamy S, Buddery AJM, StJohn DH (2008) Subsurface deformation after dry machining of grade 2 titanium. Adv Eng Mater 10(1–2):85–88. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200700233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Adriano Fagali de Souza.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayraktar, Ş., Afyon, F. Machinability properties of Al–7Si, Al–7Si–4Zn and Al–7Si–4Zn–3Cu alloys. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 42, 187 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02281-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02281-x