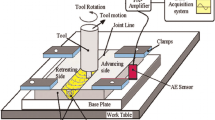
Abstract
Finishing is an essential process after manufacturing of miniature products. The conventional finishing processes can be used to produce good surface in micro domain but effectiveness of these processes is very poor for polishing of ductile, hard and brittle materials. Considering aforementioned, rotary abrasive float polishing set-up has been developed and utilized for polishing of aluminium matrix composite specimens. The effect of abrasive particle size, abrasive concentration, lap rotation and polishing time on surface finish were analysed. Taguchi L18 mixed orthogonal array was engaged for the experimental design and optimization. The surface roughness height (Ra, µm) of the polished specimens were enhanced from 0.437 to 0.049 µm i.e. 88.79%, when experiments were performed at optimal parametric setting. Abrasive particle size, lap rotation and polishing time was found significant factors in deciding surface roughness. Scanning electrode microscopic and optical images confirm the absence of any scratch and roughness peaks on polished surface specimens.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeon, C. H., Jeong, Y. H., Seo, J. J., Tien, H. N., Hong, S. T., Yum, Y. J., Hur, S. H., & Lee, K. J. (2014). Material properties of graphene/aluminum metal matrix composites fabricated by friction stir processing. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 15, 1235–1239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0462-2
Dwivedi, S. P., Sharma, S., & Mishra, R. K. (2016). Mechanical and metallurgical characterizations of AA2014/eggshells waste particulate metal matrix composite. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 3, 281–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-016-0036-0
Li, C., Liu, X., Xu, M., Chen, J., Li, S., Li, P., & Ko, T. J. (2023). Formation Mechanism and Adhesion Evaluation of Debris in Ti–6Al–4V Alloy Turning. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 10(5), 1189–1205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-022-00487-z
Ho, K. H., Newman, S. T., Rahimifard, S., & Allen, R. D. (2004). State of the art in wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM). International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 44(12–13), 1247–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.04.017
Brinksmeier, E., Riemer, O., & Gessenharter, A. (2006). Finishing of structured surfaces by abrasive polishing. Precision Engineering, 30(3), 325–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/jprecisioneng.2005.11.012
Feng, K., Lyu, B., Zhao, T., Yin, T., & Zhou, Z. (2022). Fabrication and application of gel-forming CeO2 fixed abrasive tools for quartz glass polishing. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 23(9), 985–1002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-022-00687-2
Greitemeier, D., Dalle Donne, C., Syassen, F., Eufinger, J., & Melz, T. (2016). Effect of surface roughness on fatigue performance of additive manufactured Ti–6Al–4V. Materials Science and Technology, 32(7), 629–634. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743284715Y.0000000053
Pradhan, D., Mahobia, G. S., Chattopadhyay, K., & Singh, V. (2018). Effect of surface roughness on corrosion behaviour of the super alloy IN718 in simulated marine environment. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 740, 250–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.042
Rahaman, M. L., Zhang, L., Liu, M., & Liu, W. (2015). Surface roughness effect on the friction and wear of bulk metallic glasses. Wear, 332, 1231–1237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2014.11.030
Wei, S., Zhang, T., Wei, H., Wang, W., Wang, H., & Liu, Y. (2023). Simulation study on removal mechanism of Si3N4 ceramic in rotary ultrasonic grinding. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 24(6), 945–965. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-023-00808-5
Kishore, K., Sinha, M.K., Singh, A., Archana, Gupta, M. K. & Korkmaz, M. E. (2022). A comprehensive review on the grinding process: Advancements, applications and challenges. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 236(22), 10923–10952. https://doi.org/10.1177/09544062221110782
Rahi, D. K., & Dubey, A. K. (2022). Evaluation of machining performance for electrochemical surface grinding of aluminium based hybrid MMC. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 23(9), 1039–1047. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-022-00670-x
Lerra, F., Candido, A., Liverani, E., & Fortunato, A. (2022). Prediction of micro-scale forces in dry grinding process through a FEM—ML hybrid approach. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 23, 15–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-021-00601-2
Dixit, N., Sharma, V., & Kumar, P. (2021). Research trends in abrasive flow machining: A systematic review. Journal of manufacturing Processes, 64, 1434–1461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.03.009
Jain, V. K., & Adsul, S. G. (2000). Experimental investigations into abrasive flow machining (AFM). International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 40(7), 1003–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(99)00114-5
Gorana, V. K., Jain, V. K., & Lal, G. K. (2006). Prediction of surface roughness during abrasive flow machining. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 31(3), 258–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-005-0197-4
Zhu, Y. S., Wu, J., Lu, W. Z., Zuo, D. W., Xiao, H. P., Cao, D. W., & Ko, T. J. (2022). Surface formation mechanics and its microstructural characteristics of AAJP of aluminum alloy by using amino thermosetting plastic abrasive. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 9, 59–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00284-6
Wang, A. C., Liu, C. H., Liang, K. Z., & Pai, S. H. (2007). Study of the rheological properties and the finishing behaviour of abrasive gels in abrasive flow machining. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 21(10), 1593–1598. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03177380
Zhao, J., Huang, J., Wang, R., Peng, H., Hang, W., & Ji, S. (2020). Investigation of the optimal parameters for the surface finish of K9 optical glass using a soft abrasive rotary flow polishing process. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 49, 26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.11.011
Chih-Hua, W., Chun Wai, K., Stephen Yee Ming, W., & Adri Muhammad, A. B. (2020). Numerical and experimental investigation of abrasive flow machining of branching channels. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 108, 2945–2966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05589-z
Zhu, Y. S., Lu, W. Z., Zuo, D. W., Xiao, H. P., Cao, D. W., & Ko, J. T. (2019). Development of abrasive jet polishing by using amino thermosetting plastic abrasive for aluminium alloy. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 43, 218–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.05.016
Misra, A., Pandey, P. M., Dixit, U. S., Roy, A., & Silberschmidt, V. V. (2019). Multi-objective optimization of ultrasonic-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing process. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 101(5), 1661–1670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3060-0
Poudel, B., Lee, P. H., Song, G., Nguyen, H., Kim, K., Jung, K., Shao, C., Kwon, P., & Chung, H. (2021). Innovative magnetic-field assisted finishing (MAF) using nano-scale solid lubricant: A case study on mold steel. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 9, 1411–1426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-021-00404-w
Yadav, R. D., Singh, A. K., & Arora, K. (2020). Parametric analysis of magnetorheological finishing process for improved performance of gear profile. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 57, 254–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.06.024
Sharma, V. K. (2021). Modeling and analysis of a novel rotational magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing process. International Journal of Lightweight Materials and Manufacture., 4(3), 290–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijlmm.2021.02.001
Umehara, N., Kirtane, T., Gerlick, R., Jain, V. K., & Komanduri, R. (2006). A new apparatus for finishing large size/large batch silicon nitride (Si3N4) balls for hybrid bearing applications by magnetic float polishing (MFP). International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 46, 151–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2005.04.015
Singh, D. K., Jain, V. K., & Raghuram, V. (2006). Experimental investigations into forces acting during magnetic abrasive finishing. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 30, 652–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-005-0118-6
Liang, H., Yan, Q., Pan, J., Luo, B., Lu, J., & Zhang, X. (2021). Characteristics of forces in plane polishing based on the magnetorheological effect with dynamic magnetic fields formed by rotating magnetic poles. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 49(1), 255–269. https://doi.org/10.1520/JTE20180769
Hirata, T., Takei, Y., & Mimura, H. (2014). Machining property in smoothing of steeply curved surfaces by elastic emission machining’. Procedia CIRP, 13, 198–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.04.034
Lee, H., Kim, H., & Jeong, H. (2022). Approaches to sustainability in chemical mechanical polishing (CMP): A review. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 9, 349–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-021-00406-8
Ahn, Y., Youn, J., Back, C. W., & Kim, Y. K. (2004). Chemical mechanical polishing by colloidal silica-based slurry for micro-scratch reduction. Wear, 257, 785–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2004.03.020
Soares, S. F., Baselt, D. R., Black, J. P., Jungling, K. C., & Stowell, W. K. (1994). Float-polishing process and analysis of float-polished quartz. Applied optics, 33(1), 89–95. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.33.000089
Chi, X., & Suo, X. H. (2011). Study on float polishing of metal nanometer surface. In Advanced Materials Research (Trans Tech Publications Ltd.), (vol. 154, pp. 1757–1760). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.154-155.1757
Chechi, P., Maurya, S. K., Prasad, R., & Manna, A. (2023). Influence on microstructural and mechanical properties of al2o3/graphite/flyash-reinforced hybrid composite using scrap aluminum alloy. International Journal of Metalcasting. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-023-01069-8
ASTM E8 (2001). Standard test methods for tension testing of metallic materials. Annual book of ASTM standards, ASTM international.
Hetzner, D. W. (2003). Micro-indentation hardness testing of materials using ASTM E384. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 9(S02), 708–709. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1431927603443547
Maurya, S. K., Susheel, C. K., & Manna, A. (2022). Experimental investigation of wire EDM parameters during machining of fabricated hybrid Al/(SiC+ZrO2+NiTi)-MMC. Advances in Materials and Processing Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2022.2109684
Manna, A., & Bhattacharyya, B. (2006). Taguchi and Gauss elimination method: A dual response approach for parametric optimization of CNC wire cut EDM of PRAlSiCMMC. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 28, 67–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-004-2331-0
Namba, Y., Tsuwa, H., Wada, R., & Ikawa, N. (1987). Ultra-precision float polishing machine. CIRP Annals, 36(1), 211–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)62588-8
Tsai, F. C., Yan, B. H., Kuan, C. Y., & Huang, F. Y. (2008). A Taguchi and experimental investigation into the optimal processing conditions for the abrasive jet polishing of SKD61 mold steel. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 48, 932–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2007.08.019
Krishnaiah, K., & Shahabudeen, P. (2012). Applied design of experiments and Taguchi methods. PHI Learning Pvt Ltd.
Acknowledgements
The authors highly acknowledge the Department of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering PEC Chandigarh, SAIF-Panjab University and NITTTR Chandigarh for allowing usage of testing facilities.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Saurabh Kumar Maurya, Chander Kant Susheel designed the research, performed experiments and analysed data. Saurabh Kumar Maurya conducted the calculations and drafted the original research article. Alakesh Manna provided technical guidance and reviewed the manuscript. All authors contributed to the scientific discussions and reviewed the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interests/competing interests related to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maurya, S.K., Susheel, C.K. & Manna, A. Experimental Analysis of Polishing of Hybrid Aluminium Metal Matrix Composite Reinforced with SiC, ZrO2, and NiTi Particles Using a Developed Rotary Abrasive Float Polishing System. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-024-01024-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-024-01024-5