Abstract
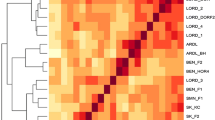
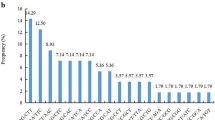
Pumpkin (Cucurbita spp.) is a major vegetable crop grown worldwide. Three species, C. pepo, C. moschata, and C. maxima, are economically important cultivated pumpkins. To develop a core set of markers for DNA profiling and cultivar identification, we used a total of 300 SSRs consisting of 158 CMTp and 142 CMTm that were previously identified in C. pepo and C. moshata, respectively. Polymorphisms in these primers were tested using a subset of 22 cultivars selected from a collection of 160 commercial cultivars. A total of 12 CMTp and 28 CMTm markers were selected based on polymorphism and number of alleles, and these 40 markers were used to genotype all 160 cultivars. Of these, 29 markers (5 CMTp and 24 CMTm) accurately detected a total of 215 alleles with an average of 7.41 alleles per marker in our collection of pumpkin cultivars. Their PIC values ranged from 0.327 to 0.894 with an average of 0.674. Analysis of genetic similarity using the 29 SSR markers revealed that the 160 cultivars were divided into five major clusters representing C. maxima×C. moshata hybrids (cluster I), C. moshata (cluster II), C. maxima (cluster III), C. pepo (cluster IV), and C. ficifolia (cluster V). In clusters I-IV, the cultivars were further separated into 2-3 sub-clusters. In addition, we found that 29 SSR markers were able to differentiate all 160 cultivars. Results from our study will facilitate genetic study and protection of breeders’ intellectual property rights in pumpkins.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Anderson, J.A., G.A. Churchill, J.E. Autrique, S.D. Tanksley, and M.E. Sorrells. 1993. Optimizing parental selection for genetic-linkage maps. Genome 36:181–186.
Bae, K.M., S.C. Sim, J.H. Hong, K.J. Choi, D.H. Kim, and Y.S. Kwon. 2015. Development of genomic SSR markers and genetic diversity analysis in cultivated radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 56:216–224.
Barbazuk, W.B., S.J. Emrich, H.D. Chen, L. Li, and P.S. Schnable. 2007. SNP discovery via 454 transcriptome sequencing. Plant J. 51:910–918.
Blanca, J., J. Canizares, C. Roig, P. Ziarsolo, F. Nuez, and B. Pico. 2011. Transcriptome characterization and high throughput SSRs and SNPs discovery in Cucurbita pepo (Cucurbitaceae). BMC Genomics 12:104.
Bundock, P.C., F.G. Eliott, G. Ablett, A.D. Benson, R.E. Casu, K.S. Aitken, and R.J. Henry. 2009. Targeted single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery in a highly polyploid plant species using 454 sequencing. Plant Biotechnol. J. 7:347–354.
Collard, B.C.Y., M.Z.Z. Jahufer, J.B. Brouwer, and E.C.K. Pang. 2005. An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: The basic concepts. Euphytica 142:169–196.
Esteras, C., P. Gomez, A.J. Monforte, J. Blanca, N. Vicente-Dolera, C. Roig, F. Nuez, and B. Pico. 2012. High-throughput SNP genotyping in Cucurbita pepo for map construction and quantitative trait loci mapping. BMC Genomics 13:80.
FAO. 2015. Food and agriculture organization of the United Nations statistics division. http://faostat3.fao.org/.
Gong, L., H.S. Paris, M.H. Nee, G. Stift, M. Pachner, J. Vollmann, and T. Lelley. 2012. Genetic relationships and evolution in Cucurbita pepo (pumpkin, squash, gourd) as revealed by simple sequence repeat polymorphisms. Theor. Appl. Genet. 124:875–891.
Gong, L., G. Stift, R. Kofler, M. Pachner, and T. Lelley. 2008. Microsatellites for the genus Cucurbita and an SSR-based genetic linkage map of Cucurbita pepo L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 117:37–48.
Hamilton, J.P., C.N. Hansey, B.R. Whitty, K. Stoffel, A.N. Massa, A. Van Deynze, W.S. De Jong, D.S. Douches, and C.R. Buell. 2011a. Single nucleotide polymorphism discovery in elite north american potato germplasm. BMC Genomics 12:302.
Hamilton, J.P., S. Sim, K. Stoffel, A. Van Deynze, C.R. Buell, and D.M. Francis. 2011b. Single nucleotide polymorphism discovery in cultivated tomato via sequencing by synthesis. The Plant Genome 5:17–29.
Hong, J.H., K.J. Choi, and Y.S. Kwon. 2014. Construction of DNA profile data base of strawberry cultivars using microsatellite markers. Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 32:853–863.
Honjo, M., T. Nunome, S. Kataoka, T. Yano, H. Yamazaki, M. Hamano, S. Yui, and M. Morishita. 2011. Strawberry cultivar identification based on hypervariable SSR markers. Breeding Sci. 61:420–425.
Hyten, D.L., S.B. Cannon, Q.J. Song, N. Weeks, E.W. Fickus, R.C. Shoemaker, J.E. Specht, A.D. Farmer, G.D. May, and P.B. Cregan. 2010. High-throughput SNP discovery through deep resequencing of a reduced representation library to anchor and orient scaffolds in the soybean whole genome sequence. BMC Genomics 11:38.
Kwon, Y.S., and K.J. Choi. 2013. Construction of a DNA profile database for commercial cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) cultivars using microsatellite marker. Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 31:344–351.
Kwon, Y.S., and J.H. Hong. 2014. Use of microsatellite markers to identify commercial melon cultivars and for hybrid seed purity testing. Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 32:525–534.
Kwon, Y.S., J.H. Hong, and K.J. Choi. 2013. Construction of a microsatellite marker database of commercial pepper cultivars. Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 31:580–589.
Mcnally, K.L., K.L. Childs, R. Bohnert, R.M. Davidson, K. Zhao, V.J. Ulat, G. Zeller, R.M. Clark, D.R. Hoen, T.E. Bureau, R. Stokowski, D.G. Ballinger, K.A. Frazer, D.R. Cox, B. Padhukasahasram, C.D. Bustamante, D. Weigel, D.J. Mackill, R.M. Bruskiewich, G. Ratsch, C.R. Buell, H. Leung, and J.E. Leach. 2009. Genomewide SNP variation reveals relationships among landraces and modern varieties of rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106:12273–12278.
Paris, H.S. 2000. History of the cultivar-groups of Cucurbita pepo. In: J. Janick (ed) Hortic. Rev. 25. John Wiley, New York, USA.
Paris, H.S., N. Yonash, V. Portnoy, N. Mozees-Daube, G. Tzuri, and N. Katzir. 2003. Assessment of genetic relationships in Cucurbita pepo (Cucurbitaceae) using DNA markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 106:971–978.
Rohlf, F.J., 2008. NTSYSpc: Numerical taxonomy system, ver. 2.20. Exeter Publishing, Ltd, Setauket, USA.
Sim, S.C., M.D. Robbins, A. Van Deynze, A.P. Michel, and D.M. Francis. 2011. Population structure and genetic differentiation associated with breeding history and selection in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Heredity 106:927–935.
Sneath, P.H.A., and R.R. Sokal. 1973. Numerical Taxonomy. W.H. Freeman and Company, San Francisco, USA.
Varshney, R.K., A. Graner, and M.E. Sorrells. 2005. Genic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends Biotechnol. 23:48–55.
Wang, F.G., H.L. Tian, J.R. Zhao, H.M. Yi, L. Wang, and W. Song. 2011. Development and characterization of a core set of SSR markers for fingerprinting analysis of Chinese maize varieties. Maydica 56:7–17.
Whitaker, T.W., and W.P. Bemis. 1964. Evolution in the genus cucurbita. Evolution 18:553–559.
Wu, T.Q., S.B. Luo, R. Wang, Y.J. Zhong, X.M. Xu, Y.E. Lin, X.M. He, B.J. Sun, and H.X. Huang. 2014. The first Illumina-based de novo transcriptome sequencing and analysis of pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duch.) and SSR marker development. Mol. Breeding 34:1437–1447.
Yadav, M., S. Jain, R. Tomar, G.B. Prasad, and H. Yadav. 2010. Medicinal and biological potential of pumpkin: an updated review. Nutr. Res. Rev. 23:184–90.
Yi, S.I., K.M. Bae, Y.S. Kwon, and I.H. Cho. 2006. Development of oriental melon (Cucumis melo L.)-derived SSR markers using a PCR-based method and polymorphic application for the genotyping of commercial lines. Korean J. Genetics 28:317–324.
Zhu, C., M. Gore, E.S. Buckler, and J. Yu. 2008. Status and prospects of association mapping in plants. The Plant Genome 1:5–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sim, SC., Hong, JH. & Kwon, YS. DNA profiling of commercial pumpkin cultivars using simple sequence repeat polymorphisms. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 56, 811–820 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-015-0123-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-015-0123-0