Abstract
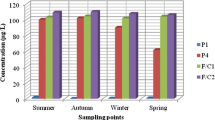
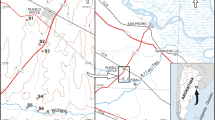
In crop farms, it is common to use animal livestock manure as soil biofertilizer, as well as agricultural defensives that can reach to ground and surface waters. Waterborne microorganisms as Salmonella and Escherichia coli can cause gastroenteritis to consumers, and the presence of chemical compounds can cause DNA mutation damages in exposed organisms. Thus, the present study aimed at quantifying E. coli and Salmonella in surface water from the Suruvi river (located above the Guarani aquifer) and evaluating the water genotoxic potential using Allium cepa as a model. For that, five sampling sites were established, and water samples were collected from March/2013 to June/2014, and submitted to bacteria enumeration, and genotoxicity assay. Moreover, rainfall volume and air temperature were measured. Results indicated the occurrence of Salmonella in 14 % of the samples and high amounts of E. coli (>1875 MPN/100 mL). The amount of E. coli decreased as the rainfall volume increased. The genotoxicity assay results showed that water contains substances, which are able to induce changes in mitotic index on the root meristem cells of A. cepa. In summary, surface water sources are contaminated with fecal material and genotoxic substances, emphasizing the importance of surveillance of surface and groundwater in this region, especially because of the proximity to the Guarani aquifer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albarnaz JD, Toso J, Corrêa AA, Simões CMO, Barardi CRM (2007) Relationship between the contamination of gulls (Larus dominicanus) and oysters (Crassostrea gigas) with Salmonella serovar Typhimurium by PCR-RFLP. Int J Environ Heal R 17(2):1–8
Amaral AM, Barbério A, Voltolini JC, Barros L (2007) Avaliação preliminar da citotoxicidade e genotoxicidade, da água da bacia do rio Tapanhon (SP-Brasil) através do teste Allium (Allium cepa). Ver Bras Toxicol 20(1–2):65–72
Beneli DM (2013) Invertebrados aquáticos e as condições ambientais do rio Suruvi. Monography, Universidade do Contestado, Concórdia
Beyersmann D, Hartwig A (2008) Carcionogenic metal compounds: recent insight into molecular and cellular mechanisms. Arch Toxicol 82:493–512
Bogoni JA, Armiliato N, Araldi-Favassa CT, Techio VH (2014) Genotoxicity in Astyanax bimaculatus (Twospot Astyanax) exposed to the waters of Engano river (Brazil) as determined by micronucleus tests in erythrocytes. Arch Environ Con Tox 66(3):441–449
Brazil (2006) Ministry of Health Surveillance and control of water quality for human consumption/Ministry of Health. Secretariat of Health Surveillance, Brasilia: Ministry of Health, p 212
Debarba L, Amado TJC (1997) Desenvolvimento de sistemas de produção de milho no sul do brasil com características de sustentabilidade. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 21(3):473–480
Düsman E, Luzza M, Savegnago L, Lauxen D, Vicentini VE, Tonial IB, Sauer TP (2014) Allium cepa L. as a bioindicator to measure cytotoxicity of surface water of the Quatorze River, located in Francisco Beltrão, Paraná, Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 186(3):1793–1800
Egito LCM, Medeiros MG, Medeiros SRB, Agnez-Lima LF (2007) Cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of surface water from the Pitimbu river, northeastern/RN Brazil. Genet Mol Biol 30(2):435–441
Fong TT, Lipp EK (2005) Enteric viruses of humans and animals in aquatic environments: health risks, detection, and potential water quality assessment tools. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 69:357–371
Fongaro G, Viancelli A, Magri ME, Elmahdy EM, Biesus LL, Kich JD, Kunz A, Barardi CRM (2014) Utility of specific biomarkers to assess safety of swine manure for biofertilizing purposes. Sci Total Environ 479:277–283
Gadano A, Gurni A, López P, Ferraro G, Carballo M (2002) In vitro genotoxic evaluation of the medicinal plant Chenopodium ambrosioides L. J Ethonopharmacol 81:11–16
Garcia LAT, Viancelli A, Rigotto C, Pilotto MR, Esteves PA, Kunz A, Barardi CRM (2012) Surveillance of human and swine adenovirus, human norovirus and swine circovirus in water samples in Santa Catarina. Brazil. J Water Health 10(3):445–452
Geremias R, Bortolotto T, Wilhelm-Filho D, Pedrosa RC, Fávere VT (2012) Efficacy assessment of acid mine drainage treatment with coal mining waste using Allium cepa L. as a bioindicator. Ecotox Environ Safe 79:116–121
Klerks MM, Franz E, Gent-Pelzer M, Zijlstra C, Bruggen AHC (2007) Differential interaction of Salmonella enterica serovars with lettuce cultivars and plant-microbe factors influencing the colonization efficiency. ISME J 1(7):620–631
Leonard AF, Zhang L, Balfour AJ, Garside R, Gaze WH (2015) Human recreational exposure to antibiotic resistant bacteria in coastal bathing waters. Environ Inter. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2015.02.013
Levantesi C, Bonadonna L, Briancesco R, Grohmann E, Toze S, Tandoi V (2012) Salmonella in surface and drinking water: occurrence and water-mediated transmission. Food Res Int 45(2):587–602
Lodder WJ, Van Den Berg HH, Rutjes SA, De Roda Husman A M (2010) Presence of enteric viruses in source waters for drinking water production in the Netherlands. Appl Environ Microb 76(17):5965–5971
Mazzeo DEC, Fernandes TCC, Marin-Morales MA (2011) Cellular damages in the Allium cepa test system, caused by BTEX mixture prior and after biodegradation process. Chemosphere 85:13–18
Michael GB, Simoneti R, Costa M, Cardoso M (2003) Comparison of different selective enrichment steps to isolate Salmonella sp. from feces of finishing swine. Braz. J Microbiol 34(2):138–142
Morinigo MA, Cornax R, Munoz MA, Romero P, Borrego JJ (1990) Relationships between salmonella spp and indicator microorganisms in polluted natural waters. Water Res 24(1):117–120
Ohe T, Watanabe T, Wakabayashi K (2004) Mutagens in the surface water: a review. Mutat Res 567:109–149
Palhares JCP, Kich JD, Bessa MC, Biesus LL, Berno LG, Triques NJ (2014) Salmonella and antimicrobial resistence in na animal-based agriculture river system. Sci Total Environ 472:654–661
Pillon CN, Miranda CR, Guidoni AL, Cordebella A, Pereira RK (2003) Diagnostico das propriedades suinıcolas da area de abrangencia do Consorcio Lambari, SC. Consorcio Lambari. http://www.consorciolambari.com.br/index.php?option=com_phocadownload&view=category&download=4:diagnosticos-propriedades84&id=1:tac&Itemid=43. Accessed 14 June 2012
Piorkowski GS, Jamieson RC, Hansen LT, Bezanson GS, Yost CK (2014) Characterizing spatial structure of sediment E. coli populations to inform sampling design. Environ Monit Assess 186(1):277–291
Quinn PJ, Carter ME, Markey BK, Carter GR (1994) Clinical veterinary microbiology. Wolfe Publishing, London
Rank J, Nielsen MH (1994) Evaluation of the Allium anaphase-telophase test in relation to genotoxicity screening of industrial wastewater. Mutat Res 312(1):17–24
Ribeiro W (2008) Aquífero Guarani: gestão compartilhada e soberania. Estud Av 22(64):227–238
Scheibe LF, Hirata R (2011) O Sistema Aquífero Integrado Guarani/Serra Geral (SAIG/SG) em Santa Catarina e os Recursos Hídricos da Bacia do Rio do Peixe. In: Joviles Vitório Trevisol; Luiz Fernando Scheibe (eds) Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio do Peixe Natureza e Sociedade. 1ed. UNOESC, Joacaba, pp 55–81
Schneider RN, Nadvorny A, Schmid V (2009) Perfil de resistência antimicrobiana de isolados de Escherichia coli obtidos de águas superficiais e subterrâneas, em área de produção de suínos. Biotemas 22:11–17
Sigua GC, Palhares JCP, Steinmetz RLR, Mulinari MR (2009) Microbiological quality assessment of watershed associated with animal-based agriculture in Santa Catarina, Brazil. Water Air Soil Poll 210:307–316
Silva N, Neto RC, Junqueira VCA, Silveira NFA (2005) Manual de métodos de analise microbiológica da agua. Varela Editora e Livraria, São Paulo
SIRVETA (2013) Sistema de vigilância epidemiológica de enfermidades transmitidas por alimentos. http://www.panalimentos.org/sirveta/e/report_eta01.as. Accessed 3 Nov 2013
Sobsey MD, Khatib LA, Hill VR, Alocilja E, Pillai S (2006) Pathogens in animal wastes and the impacts of waste management practices on their survival, transport and fate. In: Rice JM, Caldwell DF, Humenik FJ (eds) Animal Agriculture and the Environment. ASABE, St. Joseph, pp 609–666
Techio VH, Stolberg J, Kunz A, Zanin E, Perdomo CC (2011) Genotoxicity of swine effluents. Water Sci Technol 63(5):970–976
Topp E, Scott A, Lapen DR, Lyautey E, Duriez P (2009) Livestock waste treatment systems for reducing environmental exposure to hazardous enteric pathogens: some considerations. Bioresour Technol 100(22):5395–5398
Trentini ÉC (2009) Produção Agrícola e Proteção Ambiental: Desafos à gestão dos recursos naturais no meio rural. In: Miranda CR, Miele M (eds) Suinocultura e Meio Ambiente em Santa Catarina: Indicadores de desempenho e avalição sócio-econômica. 1ed. EMBRAPA—Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária, Concórdia, pp 177–201
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2002) Guidance for choosing a sampling design for environmental data collection. http://www.epa.gov/QUALITY/qs-docs/g5s-final.pdf. Accessed 23 June 2014
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2009) Review of zoonotic pathogens in ambient waters. EPA 822-R-09-002. Health and Ecological Criteria Division, Office of Water, Washington, DC
Vanzella TP, Martinez CBR, Cólus IMS (2007) Genotoxic and mutagenic effects of diesel oil water fraction on a neotropical fish species. Mutat Res 631:36–43
Vereen E Jr, Lowrance RR, Jenkins MB, Adams P, Rajeev S, Lipp EK (2013) Landscape and seasonal factors influence Salmonella and Campylobacter prevalence in a rural mixed use watershed. Water Res 47(16):6075–6085
Viancelli A, Kunz A, Steinmetz RLR, Kich JD, Souza CK, Canal CW, Coldebella A, Esteves PA, Barardi CRM (2013) Performance of two swine manure treatment systems on chemical composition and on the reduction of pathogens. Chemosphere 90:1539–1544
Vilariño ML, LeGuyader FS, Polo D, Schaeffer J, Krol J, Romalde JL (2009) Assessment of human enteric viruses in cultured and wild bivalve molluscs. Int Microbiol 12(3):145–151
Acknowledgments
The present study had the financial support from Secretaria de Estado da Educação de SC, art. 170.
Conflict of interest
All authors do not have any actual or potential conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viancelli, A., Deuner, C.W., Rigo, M. et al. Microbiological quality and genotoxic potential of surface water located above the Guarani aquifer. Environ Earth Sci 74, 5517–5523 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4561-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4561-x