Abstract
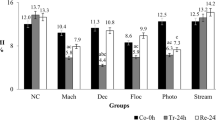
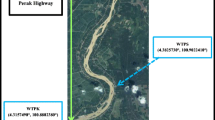
Due to an increase in water consumption in the industrial sector and within the Brazilian population, surface water that receives wastewater from industries, domestic sewage, agricultural industries, and sewage treatment stations can pollute water bodies when not properly treated. The water quality has been linked to catchment characteristics and intensity of agricultural activities. Thus, the aim of this study was to monitor the cytotoxic potential of the water of the Quatorze River, located in the town of Francisco Beltrão, Paraná, Brazil, along its route in the rural area, using the root meristematic cells of Allium cepa L. as a bioindicator. The results showed that the water at points 2, 3, and 4 were not cytotoxic because the rates of A. cepa cell division were unaltered. Point 1 had presented a mitotic index that was statistically larger than the negative control, indicating that this water contained substances with mitogenic capacity, as demonstrated by elevated values in chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). However, the mitotic index values decreased along the route of the river (point 1 to point 4), possibly indicating a mechanism of self-purification, despite having received other sources of pollution. Thus, the results of this study show that the water of the Quatorze River should undergo periodic environmental monitoring at different times of the year, including cytotoxicity analysis, to evaluate the principal sources of contamination to maintain the quality of the river water and, consequently, to maintain human health and equilibrium of the entire ecosystem.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar, W. (2010). Unidades de paisagem da bacia hidrográfica do Rio Quatorze no município de Francisco Beltrão - PR. Perspectiva Geográfica, 6, 153–165.
Amaral, A. M., Barbério, A., Voltolini, J. C., & Barros, L. (2007). Avaliação preliminar da citotoxicidade e genotoxicidade, da água da bacia do rio Tapanhon (SP- Brasil) através do teste Allium (Allium cepa). Revista Brasileira de Toxicologia, 20(1–2), 65–72.
American Public Health Association (APHA), AWWA, WEF. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Barbosa, J. S., Cabral, T. M., Ferreira, D. N., Agnez-Lima, L. F., & Medeiros, S. R. B. (2010). Genotoxicity assessment in aquatic environment impacted by the presence of heavy metals. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73(3), 320–325.
Bianchi, J., Espindola, E. L. G., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2011). Genotoxicity and mutagenicity of water samples from the Monjolinho River (Brazil) after receiving untreated effluents. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 74(4), 826–833.
Cabrera, G. L., & Rodriguez, D. M. G. (1999). Genotoxicity of leachates from a landfill using three bioassays. Mutation Research, 426, 207–210.
Carvalho, F., Ferreira, A. L., & Stapelfeldt, F. (2004). Qualidade das águas do ribeirão Ubá - MG. Revista Escola de Minas, 57(3), 165–172.
Collischonn, W., & Tassi, R. (2008). Introduzindo Hidrologia. Porto Alegre: Instituto de Pesquisas Hidráulicas-UFRGS, 274 pp.
Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (CONAMA). (2005). Resolução número 357, de 17 de março de 2005. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/res/res05/res35705.pdf. Accessed 5 May 2013.
Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (CONAMA). (2011). Resolução número 430, de 13 de maio de 2011. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=646. Accessed 5 May 2013.
Destro, J. (2012). Concentração de infraestrutura prejudica pequenos municípios e freia desenvolvimento social dos grandes. http://www.joaodestro.com.br/blog/parana-desigual.html. Accessed 25 Sep 2012.
Donohue, I., McGarrigle, M., & Mills, P. (2006). Linking catchment characteristics and water chemistry with the ecological status of Irish rivers. Water Research, 40(1), 91–98.
Düsman, E., Faria, J. S., Toledo, F., Mazeti, C. M., Gonçalves, M. E. K., & Vicentini, V. E. P. (2011). Vegetal test-system investigation on cytotoxicity of water from urban streams located in the northeastern region of Maringá, Paraná State, Brazil. Acta Scientiarum. Biological Sciences, 33(1), 71–77.
Düsman, E., Gonçalves, L. A., Reusing, A. F., Martin, P. G., Mariucci, R. G., & Vicentini, V. E. P. (2012). Cytotoxic potential of waters of the streams Mandacaru, Maringá. Miosótis and Nazareth in the urban area of Maringá PR Brazil. Acta Scientiarum. Biological Sciences, 34(3), 311–318.
Egito, L. C. M., Medeiros, M. G., Medeiros, S. R. B., & Agnez-Lima, L. F. (2007). Cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of surface water from the Pitimbu river, northeastern/RN Brazil. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 30(2), 435–441.
Enan, M. R. (2009). Genotoxicity of the herbicide 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D): higher plants as monitoring systems. American-Eurasian Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 3(3), 452–459.
Fabris, B. R., Begnini, K., Tomazoni, J. C., Pokrywiecki, T. S., Bravo, C. E. C., & Tonial, I. B. (2012). Estudo da relação do uso do solo com a qualidade da água da microbacia do Rio Quatorze. Seminário de Iniciação Científica e Tecnológica da UTFPR, 1, 1–8.
Ferreira, C. F., Frueh, A. B., Düsman, E., Heck, M. C., & Vicentini, V. E. P. (2012). Avaliação da citotoxicidade das águas dos Ribeirões Varginha (Califórnia-PR) e Tabatinha (Mandaguari-PR), em Allium cepa L. SaBios Revista de Saúde e Biologia, 7(2), 46–54.
Fiskesjö, G. (1985). The Allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring. Hereditas, 102, 99–112.
Flach, L. M. (2010). A reestruturação produtiva do capital e o trabalho: o sistema de integração da empresa Sadia no município de Francisco Beltrão-Paraná. Dissertação em Geografia, 193 pp.
Genito, D., Gburek, W. J., & Sharpley, A. N. (2002). Response of stream macroinvertebrates to agricultural land cover in a small watershed. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 17(1), 109–119.
Gentile, J. M., Gentile, G. J., Bultman, J., Sechriest, R., Wagner, E. D., & Plewa, M. J. (1982). An evaluation of the genotoxic properties of insecticides following plant and animal activation. Mutation Research, 101(1), 19–29.
Geras’kin, S., Evseeva, T., & Oudalova, A. (2011a). Plants as a tool for the environmental health assessment. In J. Nriagu (Ed.), Encyclopedia of environmental health (pp. 571–579). London: Elsevier.
Geras’kin, S., Oudalova, A., Michalik, B., Dikareva, N., & Dikarev, V. (2011b). Geno-toxicity assay of sediment and water samples from the Upper Silesia post-mining areas, Poland by means of Allium-test. Chemosphere, 83(8), 1133–1146.
Geremias, R., Bortolotto, T., Wilhelm-Filho, D., Pedrosa, R. C., & Fávere, V. T. (2012). Efficacy assessment of acid mine drainage treatment with coal mining waste using Allium cepa L. as a bioindicator. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 79, 116–121.
Gupta, A. K., & Ahmad, M. (2012). Assessment of cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of refinery waste effluent using plant, animal and bacterial systems. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 201–202, 92–99.
Helma, C., Eckl, P., Gottmann, E., Kassie, F., Rodinger, W., Steinkellner, H., et al. (1998). Genotoxic and ecotoxic effects of groundwaters and their relation to routinely measured chemical parameters. Environmental Science and Technology, 32(12), 1799–1805.
Kong, M. S., & Ma, T. H. (1999). Genotoxicity of contaminated soil and shallow well water detected by plant bioassays. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 426(2), 221–228.
Leme, D. M., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2009). Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: a review on its application. Mutation Research, 682, 71–81.
Ma, T. H., Xu, Z., Xu, C., McConnell, H., Rabago, E. V., Arreola, G. A., et al. (1995). The improved Allium/Vicia root tip micronucleus assay for clastogenicity of environmental pollutants. Mutation Research, 334(2), 185–195.
Majer, B. J., Grummt, T., Uhl, M., & Knasmüller, S. (2005). Use of plant bioassays for the detection of genotoxins in the aquatic environment. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 33(1), 45–55.
Mata, J. D. S., Fernández, V., Chordi, A., & Tejedor, C. (2001). Toxicity and mutagenecity of urban wastewater treated with different purifying processes. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 4, 61–71.
Mazzeo, D. E. C., Fernandes, T. C. C., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2011). Cellular damages in the Allium cepa test system, caused by BTEX mixture prior and after biodegradation process. Chemosphere, 85, 13–18.
McMahon, B. J., Anderson, A., Carnus, T., Helden, A. J., Kelly-Quinn, M., Sheridan, H., et al. (2012). Different bioindicators measured at different spatial scales vary in their response to agricultural intensity. Ecological Indicators, 18, 676–683.
Norris, R. H., & Thoms, M. C. (1999). What is river health? Freshwater Biology, 41, 197–209.
Oga, S., Camargo, M. A., & Batistuzzo, J. A. O. (2008). Fundamentos de toxicologia (3rd ed., p. 677). São Paulo: Atheneu.
Ohe, T., Watanabe, T., & Wakabayashi, K. (2004). Mutagens in surface waters: a review. Mutation Research, 567, 109–149.
Oliveira, L. M., Voltolini, J. C., & Barbério, A. (2011). Potencial mutagênico dos poluentes na água do rio Paraíba do Sul em Tremembé, SP, Brasil, utilizando o teste Allium cepa. Ambi-Agua, 6(1), 90–103.
Plewa, M. J., Wagner, E. D., Gentile, G. J., & Gentile, J. M. (1984). An evaluation of the genotoxic properties of herbicides following plant and animal activation. Mutation Research, 136(3), 233–245.
Pontelli, M. E., & Paisani, J. C. (2008). Perspectiva Geográfica – Unioeste Colegiados de geografia, 4, 129–138.
Radić, S., Stipaničev, D., Vujčić, V., Rajčić, M. M., Širac, S., & Pevalek-Kozlina, B. (2010). The evaluation of surface and wastewater genotoxicity using the Allium cepa test. Science of The Total Environment, 408(5), 1228–1233.
Rank, J., & Nielsen, M. H. (1994). Evaluation of the Allium anaphase-telophase test in relation to genotoxicity screening of industrial wastewater. Mutation Research/Environmental Mutagenesis and Related Subjects, 312(1), 17–24.
Rothwell, J. J., Dise, N. B., Allott, T. E. H., Scholefield, P., Davis, H., & Neal, C. (2010). Predicting river water quality across North West England using catchment characteristics. Journal of Hydrology, 395(3–4), 153–162.
Silva, J., Heuser, V., & Andrade, V. (2003). Biomonitoramento Ambiental. In J. Silva, B. Erdtmann, & J. A. P. Henriques (Eds.), Genética Toxicológica (pp. 166–180). Porto Alegre: Alcance.
Skinner, J. A., Lewis, K. A., Bardon, K. A., Tucker, P., Catt, J. A., & Chambers, B. J. (1997). An overview of the environmental impact of agriculture in the U.K. Journal of Environmental Management, 50, 111–128.
Staskoviak, M. (2012). Dezembro de 2011 registrou a 3ª maior seca em 32 anos. http://www.jornaldebeltrao.com.br. Accessed 25 Sep 2012.
Steinkellner, H., Mun-Sik, K., Helma, C., Ecker, S., Ma, T. H., Horak, O., et al. (1998). Genotoxic effects of heavy metals: comparative investigation with plant bioassays. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 31(2), 183–191.
Von Sperling, M. (2005). Princípios do tratamento biológico de águas residuárias. Introdução à qualidade das águas e ao tratamento de esgotos. 3. ed. Belo Horizonte: Departamento de Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental - UFMG, 452 pp.
Vujošević, M., Andelković, S., Savić, G., & Blagojević, J. (2008). Genotoxicity screening of the river Rasina in Serbia using the Allium anaphase-telophase test. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 147(1–3), 75–81.
Wikipedia. (2012). Mapa físico de Francisco Beltrão-PR. http://pt.wikipedia.org/wiki/Francisco_Beltrao. Accessed 25 Sep 2012.
Zagatto, P. A., & Bertoletti, E. (2008). Ecotoxicologia aquática: princípios e aplicações. 2. ed. São Carlos: RiMa, xii, 472 pp.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Laboratory of Mutagenesis and Environmental Monitoring of the State University of Maringá and the Federal Technological University of Paraná—Campus Francisco Beltrão.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Düsman, E., Luzza, M., Savegnago, L. et al. Allium cepa L. as a bioindicator to measure cytotoxicity of surface water of the Quatorze River, located in Francisco Beltrão, Paraná, Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 186, 1793–1800 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3493-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3493-8