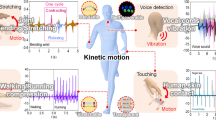
Abstract
Hydrogel-based triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) has a promising applied prospect in wearable electronic devices. However, its low performance, poor stability, insufficient recyclability and inferior self-healing seriously hinder its development. Herein, we report a robust route to a liquid metal (LM)/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogel-based TENG (LP-TENG). Owing to the intrinsically liquid feature of conductive LM within the flexible PVA hydrogel, the as-prepared LP-TENG exhibited comprehensive advantages of adaptability, biocompatibility, outstanding electrical performance, superior stability, recyclability and diverse applications, which were unattainable by traditional systems. Concretely, the LP-TENG delivered appealing open circuit voltage of 250 V, short circuit current of 4 μA and transferred charge of 120 nC with high stability, outperforming most advanced TENG systems. The LP-TENG was successfully employed for versatile applications with multifunctionality, including human motion detection, handwriting recognition, energy collection, message transmission and human–machine interaction. This work presents significant prospects for crafting advanced materials and devices in the fields of wearable electronics, flexible skin and smart robots.
Graphical abstract

摘要
基于水凝胶的TENG在可穿戴电子设备中具有很好的应用前景。然而,其性能低、稳定性差、可回收性不足、自愈性差,严重阻碍了其发展。在此,我们报道了一种基于液态金属(LM)/聚乙烯醇(PVA)水凝胶的TENG(LP-TENG)。由于导电LM在柔性PVA水凝胶中具有固有的液体特性,所以制备的LP-TENG具有传统系统无法实现的适应性、生物相容性、电气性、稳定性、可回收性和多样化应用等综合优势。具体而言,LP-TENG提供了250 V的开路电压、4 μA的短路电流和120 nC的转移电荷以及高稳定性,优于大多数先进的TENG系统。LP-TENG成功应用于多功能的多用途应用,包括人体运动检测、手写识别、能量收集、信息传输和人机交互。这项工作为在可穿戴电子、柔性皮肤和智能机器人领域制造先进材料和设备提供了重要的前景。






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akram W, Chen Q, Xia G, Fang J. A review of single electrode triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy. 2023;106:108043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.108043.
Liu S, Tong W, Gao C, Liu Y, Li X, Zhang Y. Environmentally friendly natural materials for triboelectric nanogenerators: a review. J Mater Chem A. 2023;11(17):9270. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TA10024J.
Zhang H, Zhang DZ, Wang DY, Xu ZY, Yang Y, Zhang B. Flexible single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerator with MWCNT/PDMS composite film for environmental energy harvesting and human motion monitoring. Rare Met. 2022;41(9):3117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02031-z.
Liu Y, Hu C. Triboelectric nanogenerators based on elastic electrodes. Nanoscale. 2020;12(39):20118. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR04868B.
Bagchi B, Datta P, Fernandez CS, Gupta P, Jaufuraully S, David AL, Siassakos D, Desjardins A, Tiwari MK. Flexible triboelectric nanogenerators using transparent copper nanowire electrodes: energy harvesting, sensing human activities and material recognition. Mater Horiz. 2023;10:3124. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MH00404J.
Wang C, Zhang L, He B, Zhou Q, Zhang SH, Kong XL, Chen Z, Pan GB. Three-dimensional CeO2@carbon-quantum-dots scaffold modified with Au nanoparticles on flexible substrates for high performance gas sensing at room temperature. Rare Met. 2023;42(6):1946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02283-3.
Pu X, Guo H, Chen J, Wang X, Xi Y, Hu C, Wang ZL. Eye motion triggered self-powered mechnosensational communication system using triboelectric nanogenerator. Sci Adv. 2017;3(7):e1700694. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700694.
Song Y, Shi Z, Hu GH, Xiong C, Isogai A, Yang Q. Recent advances in cellulose-based piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting: a review. J Mater Chem A. 2021;9(4):1910. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA08642H.
Zhang H, Zhang D, Wang Z, Xi G, Mao R, Ma Y, Wang D, Tang M, Xu Z, Luan H. Ultrastretchable, self-healing conductive hydrogel-based triboelectric nanogenerators for human-computer interaction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(4):5128. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c17904.
Qian SB, Liu G, Yan M, Wu C. Lightweight, self-cleaning and refractory FeCo@MoS2 PVA aerogels: from electromagnetic wave-assisted synthesis to flexible electromagnetic wave absorption. Rare Met. 2022;42(4):1294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02191-y.
Xu Y, Yiu PM, Wang YK, Qin XM, Shibayama T, Watanabe S, Ohnuma M, Chen DZ, Cheng H, Shek CH, Lu ZG, Liu C. Highly flexible, mechanically strengthened metallic glass-based composite electrode with enhanced capacitance and cyclic stability. Rare Met. 2022;41(11):3717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02060-8.
Zhang X, Pan S, Song H, Guo W, Gu F, Yan C, Jin H, Zhang L, Chen Y, Wang S. Photothermal effect enables markedly enhanced oxygen reduction and evolution activities for high-performance Zn–air batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2021;9(35):19734. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ta03652a.
Liu W, Wang X, Song Y, Cao R, Wang L, Yan Z, Shan G. Self-powered forest fire alarm system based on impedance matching effect between triboelectric nanogenerator and thermosensitive sensor. Nano Energy. 2020;73:104843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104843.
Liu W, Wang Z, Wang G, Zeng Q, He W, Liu L, Wang X, Xi Y, Guo H, Hu C, Wang ZL. Switched-capacitor-convertors based on fractal design for output power management of triboelectric nanogenerator. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1883. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15373-y.
Benyoussef M, Zaari H, Belhadi J, Amraoui YE, Ez-Zahraouy H, Lahmar A, Marssi ME. Effect of rare earth on physical properties of Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 system: a density functional theory investigation. J Rare Earths. 2022;40(3):473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2020.12.002.
Wang J, Wu C, Dai Y, Zhao Z, Wang A, Zhang T, Wang ZL. Achieving ultrahigh triboelectric charge density for efficient energy harvesting. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):88. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00131-4.
Wang ZL. Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology for self-powered systems and as active mechanical and chemical sensors. ACS Nano. 2013;7(11):9533. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn404614z.
Lai YC, Wu HM, Lin HC, Chang CL, Chou HH, Hsiao YC, Wu YC. Triboelectric nanogenerators: entirely, intrinsically, and autonomously self-healable, highly transparent, and superstretchable triboelectric nanogenerator for personal power sources and self-powered electronic skins. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(40):1970273. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201970273.
Lai YC, Deng J, Niu S, Peng W, Wu C, Liu R, Wen Z, Wang ZL. Electric eel-skin-inspired mechanically durable and super-stretchable nanogenerator for deformable power source and fully autonomous conformable electronic-skin applications. Adv Mater. 2016;28(45):10024. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201603527.
Li Z, Shen J, Abdalla I, Yu J, Ding B. Nanofibrous membrane constructed wearable triboelectric nanogenerator for high performance biomechanical energy harvesting. Nano Energy. 2017;36:341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.04.035.
Wang X, Wen Z, Guo H, Wu C, He X, Lin L, Cao X, Wang ZL. Fully packaged blue energy harvester by hybridizing a rolling triboelectric nanogenerator and an electromagnetic generator. ACS Nano. 2016;10(12):11369. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.6b06622.
Liu T, Liu M, Dou S, Sun J, Cong Z, Jiang C, Du C, Pu X, Hu W, Wang ZL. Triboelectric-nanogenerator-based soft energy-harvesting skin enabled by toughly bonded elastomer/hydrogel hybrids. ACS Nano. 2018;12(3):2818. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b00108.
Yazdan A, Wang JZ, Hu BK, Xie WS, Zhao LY, Nan CW, Li LL. Boron nitride/agarose hydrogel composites with high thermal conductivities. Rare Met. 2019;39(4):375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01322-2.
Wang L, Liu W, Yan Z, Wang F, Wang X. Stretchable and shape-adaptable triboelectric nanogenerator based on biocompatible liquid electrolyte for biomechanical energy harvesting and wearable human–machine interaction. Adv Func Mater. 2021;31(7):2007221. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202007221.
Liu AP, Chen ZX, Wang ZH. Surface enhanced Raman study of 2D Mxenes-Ag micro nano composite Films. Chin J Rare Met. 2022;46(8):989. https://doi.org/10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.XY22060028.
Li QL, Cao JX, Zhang Q. Study on the regulatory mechanism of reducing graphene oxide content on the electrochemical performance of MXene/reduced graphene oxide based supercapacitors. Chin J Rare Met. 2022;46(9):1133. https://doi.org/10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.XY21040042.
Khan A, Nilam B, Rukhsar C, Sayali G, Mandlekar B, Kadam A. A review article based on composite graphene @tungsten oxide thin films for various applications. Tungsten. 2022;5(4):391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-022-00158-1.
Cheon S, Kang H, Kim H, Son Y, Lee JY, Shin HJ, Kim SW, Cho JH. High-performance triboelectric nanogenerators based on electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride-silver nanowire composite nanofibers. Adv Func Mater. 2017;28(2):1703778. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201703778.
Zhang J, Xu Q, Li H, Zhang S, Hong A, Jiang Y, Hu N, Chen G, Fu H, Yuan M, Dai B, Chu L, Yang D, Xie Y. Self-powered electrodeposition system for sub-10-nm silver nanoparticles with high-efficiency antibacterial activity. J Phys Chem Letters. 2022;13(29):6721. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.2c01737.
Fan YJ, Meng XS, Li HY, Kuang SY, Zhang L, Wu Y, Wang ZL, Zhu G. Stretchable porous carbon nanotube-elastomer hybrid nanocomposite for harvesting mechanical energy. Adv Mater. 2016;29(2):1603115. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201603115.
Li S, Wang J, Peng W, Lin L, Zi Y, Wang S, Zhang G, Wang ZL. Sustainable energy source for wearable electronics based on multilayer elastomeric triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv Energy Mater. 2017;7(13):1602832. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201602832.
Lee KH, Zhang YZ, Jiang Q, Kim H, Alkenawi AA, Alshareef HN. Ultrasound-driven two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene hydrogel generator. ACS Nano. 2020;14(3):3199. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b08462.
Zhou Y, Wan C, Yang Y, Yang H, Wang S, Dai Z, Ji K, Jiang H, Chen X, Long Y. Highly stretchable, elastic, and ionic conductive hydrogel for artificial soft electronics. Adv Func Mater. 2019;29(1):1806220. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201806220.
Ding Y, Zeng M, Fu L. Surface chemistry of gallium-based liquid metals. Matter. 2020;3(5):1477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2020.08.012.
Zheng K, Gu F, Wei H, Zhang L, Chen X, Jin H, Pan S, Chen Y, Wang S. Flexible, permeable, and recyclable liquid-metal-based transient circuit enables contact/noncontact sensing for wearable human-machine interaction. Small Methods. 2023;7(4):e2201534. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202201534.
Luo X, Zhu L, Wang YC, Li J, Nie J, Wang ZL. A flexible multifunctional triboelectric nanogenerator based on MXene/PVA hydrogel. Adv Func Mater. 2021;31(38):2104928. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202104928.
Liao M, Liao H, Ye J, Wan P, Zhang L. Polyvinyl alcohol-stabilized liquid metal hydrogel for wearable transient epidermal sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(50):47358. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b16675.
Cui WJ, Zhang SM, Tian ZY, Chen ZY, Wang YM, Yu BB, Han ZG. Hydrogen bond-mediated polyoxometalate-based metal-organic networks for efficient and selective oxidation of aryl alkenes to aldehydes. Tungsten. 2022;4(2):109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-021-00130-5.
Huang LB, Dai X, Sun Z, Wong MC, Pang SY, Han J, Zheng Q, Zhao C-H, Kong J, Hao J. Environment-resisted flexible high performance triboelectric nanogenerators based on ultrafast self-healing non-drying conductive organohydrogel. Nano Energy. 2021;82:105724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105724.
Yu Z, Zhu Z, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Qin Y, Jiang Q, He H. Wearable cotton fabric-based single-electrode-mode triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered human motion monitoring. Cellulose. 2023;30(8):5355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05194-9.
Lu Y, Xiang H, Jie Y, Cao X, Wang ZL. Antibacterial triboelectric nanogenerator for mite removal and intelligent human monitoring. Adv Mater Technol. 2023;23:2300192. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202300192.
Chan EWC, Sun X, Travas-Sejdic J. Recent progress and future prospects in transient polymer electronics. Macromolecules. 2023;56(11):3755. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.3c00254.
Yu X, Shou W, Mahajan BK, Huang X, Pan H. Materials, processes, and facile manufacturing for bioresorbable electronics: a review. Adv Mater. 2018;30(28):1707624. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201707624.
Yoon J, Han J, Choi B, Lee Y, Kim Y, Park J, Lim M, Kang MH, Kim DH, Kim DM, Kim S, Choi SJ. Three-dimensional printed poly(vinyl alcohol) substrate with controlled on-demand degradation for transient electronics. ACS Nano. 2018;12(6):6006. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b02244.
Li F, Qin Q, Zhou Y, Wu Y, Xue W, Gao S, Shang J, Liu Y, Li RW. Recyclable liquid metal-based circuit on paper. Adv Mater Technol. 2018;3(8):1800131. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.201800131.
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22109120, 62104170 and 82202757) and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. LQ21B030002 and LY23F040001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, HW., Zhao, C., Zhao, ZY. et al. Flexible and multifunctional triboelectric nanogenerator based on liquid metal/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel for energy harvesting and self-powered wearable human–machine interaction. Rare Met. 43, 1186–1196 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02518-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02518-3