Abstract
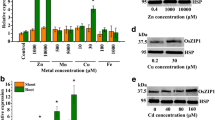
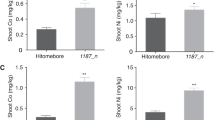
Copper (Cu) is a trace mineral nutrient essential for plant growth; consequently, its uptake, trafficking, and redistribution are precisely controlled. Currently, little is known about the underlying regulatory mechanisms in rice. In this work, we identified OsHIPP24 as a Cu metallochaperone in rice. Heterologous expression of OsHIPP24 in wild-type yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) strain BY4741 increased accumulation of Cu, as well as cadmium (Cd). OsHIPP24 was expressed constitutively in most tissues of rice, including root, stem, leaf, leaf sheath, internode, rachis, and spikelet, and particularly high in root stele along with the vascular bundle of the shoot. Overexpression or knockout of OsHIPP24 in rice led to stunted growth and reduced plant height, regardless of Cu levels in the growth medium. Taken together, these observations indicated that the physiological roles of OsHIPP24 involve the delivery of metal micronutrients via vascular tissues, and that OsHIPP24 plays a crucial role in the growth of rice.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cu:
-
Copper
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
- COPT:
-
COPPER Transporter
- ZIP:
-
Zinc-regulated transporter, Iron-regulated transporter-like Protein family
- YSL:
-
Yellow Stripe-Like family
- NA:
-
Nicotianamine
- HMAs:
-
Heavy metal-transporting ATPases
- Cu/Zn SOD:
-
Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase
- HPPs:
-
HMA plant proteins
- HIPPs:
-
HMA isoprenylated plant proteins
- OE:
-
Overexpression
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- SD-Ura:
-
SD medium without uracil
- SG-Ura:
-
SG medium without uracil
- TF:
-
Trigger factor protein
- IPTG:
-
Isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactopyranoside
- cv:
-
Cultivar
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
References
Abdel-Ghany SE, Müller-Moule P, Niyogi KK, Pilon M, Shikanai T (2005) Two P-type ATPases are required for copper delivery in Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts. Plant Cell 17:1233–1251
Abreu-Neto JB, Turchetto-Zolet AC, Oliveira LFV, Zanettini MHB, Margis-Pinheiro M (2013) Heavy metal-associated isoprenylated plant protein (HIPP): characterization of a family of proteins exclusive to plants. FEBS J 280:1604–1616
Andrés-Colás N, Carrió-Seguí A, Abdel-Ghany SE, Pilon M, Peñarrubia L (2018) Expression of the intracellular COPT3-mediated Cu transport is temporally regulated by the TCP16 transcription factor. Front Plant Sci 9:910
Andrés-Colás N, Sancenón V, Rodríguez-Navarro S, Mayo S, Thiele DJ, Ecker JR, Puig S, Peñarrubia L (2006) The Arabidopsis heavy metal P-type ATPase HMA5 interacts with metallochaperones and functions in copper detoxifification of roots. Plant J 45:225–236
Argüello JM, Eren E, González-Guerrero M (2007) The structure and function of heavy metal transport P1B-ATPases. Biometals 20:233–248
Barth O, Vogt S, Uhlemann R, Zschiesche W, Humbeck K (2009) Stress induced and nuclear localized HIPP26 from Arabidopsis thaliana interacts via its heavy metal associated domain with the drought stress related zinc finger transcription factor ATHB29. Plant Mol Biol 69:213–226
Binder BM, Rodríguez FI, Bleecker AB (2010) The copper transporter RAN1 is essential for biogenesis of ethylene receptors in Arabidopsis. J Biol chem 285:37263–37270
Burkhead JL, Reynolds KAG, Abdel-Ghany SE, Cohu CM, Pilon M (2009) Copper homeostasis. New Phytol 182:799–816
Chen SB, Tao LZ, Zeng LR, Vega-Sanchez ME, Umemura K, Wang GL (2006) A highly efficient transient protoplast system for analyzing defence gene expression and protein-protein interactions in rice. Mol Plant Pathol 7:417–427
Deng FL, Yamaji N, Xia JX, Ma JF (2013) A member of the heavy metal P-type ATPase OsHMA5 is involved in xylem loading of copper in rice. Plant Physiol 163:1353–1362
Garcia-Molina A, Andrés-Colás N, Perea-García A, Neumann U, Dodani SC, Huijser P, Peñarrubia L, Puig S (2013) The Arabidopsis COPT6 transport protein functions in copper distribution under copper-deficient conditions. Plant Cell Physiol 54:1378–1390
Gietz RD, Schiestl RH (2007) High-efficiency yeast transformation using the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method. Nat Protoc 2:31–35
Huang XY, Deng FL, Yamaji N, Pinson SRM, Fujii-Kashino M, Danku J, Douglas A, Guerinot ML, Salt DE, Ma JF (2016) A heavy metal P-type ATPase OsHMA4 prevents copper accumulation in rice grain. Nat Commun 7:12138
Jung HI, Gayomba SR, Rutzke MA, Craft E, Kochian LV, Vatamaniuk OK (2012) COPT6 is a plasma membrane transporter that functions in copper homeostasis in Arabidopsis and is a novel target of SQUAMOSA promoter binding protein-like 7. J Biol chem 287:33252–33267
Khan IU, Rono JK, Zhang BQ, Liu XS, Wang MQ, Wang LL, Wu XC, Chen X, Gao HW, Yang ZM (2019) Identification of novel rice (Oryza sativa) HPP and HIPP genes tolerant to heavy metal toxicity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 175:8–18
Klaumann S, Nickolaus SD, Fürst SH, Starck S, Schneider S, Neuhaus HE, Trentmann O (2011) The tonoplast copper transporter COPT5 acts as an exporter and is required for interorgan allocation of copper in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 192:393–404
Krishna TPA, Maharajan T, Roch GV, Ignacimuthu S, Ceasar SA (2020) Structure, function, regulation and phylogenetic relationship of ZIP family transporters of plants. Front Plant Sci 11:662
Lee S, Kim YY, Lee YS, An G (2007) Rice P1B-type heavy-metal ATPase, OsHMA9, is a metal efflux protein. Plant Physiol 145:831–842
Lin CY, Trinh NN, Fu SF, Hsiung YC, Chia LC, Lin CW, Huang HJ (2013) Comparison of early transcriptome responses to copper and cadmium in rice roots. Plant Mol Bol 81:507–522
Luo JS, Huang J, Zeng DL, Peng JS, Zhang GB, Ma HL, Guan Y, Yi HY, Fu YL, Han B, Lin HX, Qian Q, Gong JM (2018) A defensin-like protein drives cadmium efflux and allocation in rice. Nat Commun 9:645
Ma XL, Zhang QY, Zhu QL, Liu W, Chen Y, Rong Q, Wang B, Yang ZF, Li HY, Lin YR, Xie YY, Shen RX, Chen SF, Wang Z, Chen YL, Guo JX, Chen LT, Zhao XC, Liu YG (2015) A robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants. Mol Plant 8:1274–1284
Nicholas KB, Nicholas HBJ (1997) GeneDoc: A tool for editing and annotating multiple sequence alignments (version2.7). Distributed by the authors (www.psc.edu/biomed/genedoc/)
Shikanai T, Müller-Moulé P, Munekage Y, Niyogi KK, Pilon M (2003) PAA1, a P-Type ATPase of Arabidopsis, functions in copper transport in chloroplasts. Plant Cell 15:1333–1346
Shin LJ, Lo JC, Yeh KC (2012) Copper chaperone antioxidant protein1 is essential for copper homeostasis. Plant Physiol 159:1099–1110
Tan MP, Cheng D, Yang YN, Zhang GQ, Qin MJ, Chen J, Chen YH, Jiang MY (2017) Co-expression network analysis of the transcriptomes of rice roots exposed to various cadmium stresses reveals universal cadmium-responsive genes. BMC Plant Biol 17:194–211
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Zhang BQ, Liu XS, Feng SJ, Zhao YN, Wang LL, Rono JK, Li H, Yang JM (2020) Developing a cadmium resistant rice genotype with OsHIPP29 locus for limiting cadmium accumulation in the paddy crop. Chemosphere 247:125958
Zheng LQ, Yamaji N, Yokosho K, Ma JF (2012) YSL16 is a phloem-localized transporter of the copper-nicotianamine complex that is responsible for copper distribution in rice. Plant Cell 24:3767–3782
Zschiesche W, Barth O, Daniel K, Bohme S, Rausche J, Humbeck K (2015) The zinc-binding nuclear protein HIPP3 acts as an upstream regulator of the salicylate-dependent plant immunity pathway and of flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 207:1084–1096
Acknowledgements
We thank the public technical service center of the Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for help with the metal determination assays.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GC designed the research and wrote the manuscript; GC and SX carried out the experiment and analyzed data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Xiong, S. OsHIPP24 is a Copper Metallochaperone Which Affects Rice Growth. J. Plant Biol. 64, 145–153 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-020-09287-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-020-09287-x