Abstract
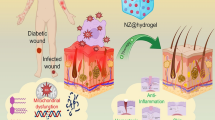
High oxidative stress injury and bacterial infection are the main challenges that impair wound healing in diabetic patients. Therefore, a hydrogel with enhanced antimicrobial and antioxidant properties was developed for rapid healing of diabetic wounds. In this study, chitosan methacrylate-gallic acid (CSMA-GA) polymer with antioxidant activity, antimicrobial activity, and ultraviolet (UV)-triggered gelling properties was developed as a hydrogel precursor. Meanwhile, amphiphilic Pluronic F127 molecules were used to load hydrophobic chlorhexidine drug molecules to obtain F127/chlorhexidine nanoparticle (NP) with strong antibacterial activity. Subsequently, F127/chlorhexidine NPs were encapsulated in CSMA-GA hydrogel to further enhance its antibacterial activity. The hybrid hydrogel platform (CSMA-GA/F127/chlorhexidine (CMGFC)) exhibited high antibacterial efficiency (> 99.9%) and strong reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging ability (> 80.0%), which effectively protected cells from external oxidative stress (upregulated superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione/oxidized glutathione disulfide (GSH/GSSG) levels and downregulated malondialdehyde (MDA) levels). Moreover, in vivo results proved that the CMGFC hydrogel significantly reduced inflammatory responses (downregulated interleukin-6 (IL-6) and upregulated interleukin-10 (IL-10) levels), promoted angiogenesis (upregulated vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD 31) levels), and wound healing (enhanced collagen deposition and tissue remodelling). Overall, the CMGFC hydrogel with enhanced antimicrobial and antioxidant properties demonstrated significant potential to enhance diabetic wound healing.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, Y.; Bao, B. B.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, J. J.; Liu, X. Z.; Gao, T.; Lin, J. Q.; Huang, T. L.; Xu, J.; Chai, Y. M. et al. An FPS-ZM1-encapsulated zeolitic imidazolate framework as a dual proangiogenic drug delivery system for diabetic wound healing. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5216–5229.
Li, W. C.; Jiang, L. B.; Wu, S. J.; Yang, S. W.; Ren, L.; Cheng, B.; Xia, J. A shape-programmable hierarchical fibrous membrane composite system to promote wound healing in diabetic patients. Small 2022, 18, 2107544.
Li, J. Y.; Wei, M. M.; Liu, X.; Xiao, S. N.; Cai, Y.; Li, F.; Tian, J.; Qi, F.; Xu, G. C.; Deng, C. L. The progress, prospects, and challenges of the use of non-coding RNA for diabetic wounds. Mol. Ther. — Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 554–578.
Matoori, S.; Veves, A.; Mooney, D. J. Advanced bandages for diabetic wound healing. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabe4839.
Yang, J. X.; Zeng, W. N.; Xu, P.; Fu, X. X.; Yu, X. J.; Chen, L.; Leng, F.; Yu, C.; Yang, Z. Y. Glucose-responsive multifunctional metal-organic drug-loaded hydrogel for diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 206–218.
Li, G. D.; Ko, C. N.; Li, D.; Yang, C.; Wang, W. H.; Yang, G. J.; Di Primo, C.; Wong, V. K. W.; Xiang, Y. Z.; Lin, L. G. et al. A small molecule HIF-1α stabilizer that accelerates diabetic wound healing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3363.
Wu, Y. B.; Zhou, Z. P.; Luo, L.; Tao, M. X.; Chang, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, X. Y.; Hu, L.; Wu, M. Y. A non-anticoagulant heparin-like snail glycosaminoglycan promotes healing of diabetic wound. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116682.
D. Q.; Liao, Y. Y.; Cornel, E. J.; Lv, M. C.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X. Y.; Fan, L. J.; Sun, M.; Zhu, Y. Q.; Fan, Z. et al. Polymersome wound dressing spray capable of bacterial inhibition and H2S generation for complete diabetic wound healing. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 7972–7985.
Zhao, H.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Lv, X. J.; Zhou, H. T.; Wang, H. R.; Xu, Y. Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. ROS-scavenging hydrogel to promote healing of bacteria infected diabetic wounds. Biomaterials 2020, 258, 120286.
Xian, C. H.; Zhang, Z.; You, X. R.; Fang, Y. F.; Wu, J. Nanosized fat emulsion injection modulating local microenvironment promotes angiogenesis in chronic wound healing. Adv. Funct. Mater., in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202202410.
Wang, H. N.; Xu, Z. J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, G. T.; Wu, J. Advances of hydrogel dressings in diabetic wounds. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 1530–1546.
Shiekh, P. A.; Singh, A.; Kumar, A. Exosome laden oxygen releasing antioxidant and antibacterial cryogel wound dressing OxOBand alleviate diabetic and infectious wound healing. Biomaterials 2020, 249, 120020.
Chen, H. H.; Guo, Y. F.; Zhang, Z. W.; Mao, W. X.; Shen, C. Y.; Xiong, W.; Yao, Y. F.; Zhao, X. Z.; Hu, Y. Q.; Zou, Z. G. et al. Symbiotic algae-bacteria dressing for producing hydrogen to accelerate diabetic wound healing. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 229–237.
Wang, P. Y.; Peng, L. L.; Lin, J. Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, Q.; Jiang, S. H.; Tian, H. N.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. L.; Liu, J. F. Enzyme hybrid viruslike hollow mesoporous CuO adhesive hydrogel spray through glucose-activated cascade reaction to efficiently promote diabetic wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128901.
Lu, Y. F.; Li, H. S.; Wang, J.; Yao, M. Y.; Peng, Y.; Liu, T. F.; Li, Z.; Luo, G. X.; Deng, J. Engineering bacteria-activated multifunctionalized hydrogel for promoting diabetic wound healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105749.
Shen, T.; Dai, K.; Yu, Y. M.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. S. Sulfated chitosan rescues dysfunctional macrophages and accelerates wound healing in diabetic mice. Acta Biomater. 2020, 117, 192–203.
Bao, F.; Pei, G.; Wu, Z. C.; Zhuang, H.; Zhang, Z. W. B.; Huan, Z. G.; Wu, C. T.; Chang, J. Bioactive self-pumping composite wound dressings with micropore array modified Janus membrane for enhanced diabetic wound healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005422.
Ding, Q. Y.; Sun, T. F.; Su, W. J.; Jing, X. R.; Ye, B.; Su, Y. L.; Zeng, L.; Qu, Y. Z.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y. Z. et al. Bioinspired multifunctional black phosphorus hydrogel with antibacterial and antioxidant properties: A stepwise countermeasure for diabetic skin wound healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater., 2022, 11, 2102791.
Liu, B.; Fu, R. Z.; Duan, Z. G.; Zhu, C. H.; Deng, J. J.; Fan, D. D. Ionic liquid-based non-releasing antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, high-transparency hydrogel coupled with electrical stimulation for infected diabetic wound healing. Compos. Part B:Eng. 2022, 236, 109804.
Cheng, S. Y.; Wang, H.; Pan, X. H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, K. X.; Chen, Z. L.; Dong, W.; Xie, A. M.; Qi, X. L. Dendritic hydrogels with robust inherent antibacterial properties for promoting bacteria-infected wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 11144–11155.
Fan, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, X. X.; Zheng, L.; Zou, Y.; Wen, H. Q.; Guan, P. F.; Lu, F.; Luo, Y. A.; Tan, G. X. et al. Exosomes-loaded electroconductive hydrogel synergistically promotes tissue repair after spinal cord injury via immunoregulation and enhancement of myelinated axon growth. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105586.
Jin, X.; Shang, Y. Y.; Zou, Y.; Xiao, M.; Huang, H. L.; Zhu, S. J.; Liu, N. B.; Li, J. N.; Wang, W.; Zhu, P. Injectable hypoxia-induced conductive hydrogel to promote diabetic wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 56681–56691.
Li, N.; Yang, L. Q.; Pan, C. L.; Saw, P. E.; Ren, M.; Lan, B. Y.; Wu, J. F.; Wang, X. Y.; Zeng, T. T.; Zhou, L. Y. et al. Naturally-occurring bacterial cellulose-hyperbranched cationic polysaccharide derivative/MMP-9 siRNA composite dressing for wound healing enhancement in diabetic rats. Acta Biomater. 2020, 102, 298–314.
Lu, J. W.; Chen, Y.; Ding, M.; Fan, X. K.; Hu, J. W.; Chen, Y. H.; Li, J.; Li, Z. H.; Liu, W. Y. A 4arm-PEG macromolecule crosslinked chitosan hydrogels as antibacterial wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118871.
Qin, D.; Zhang, A. D.; Wang, N.; Yao, Y. X.; Chen, X. G.; Liu, Y. Hydroxybutyl chitosan/oxidized glucomannan self-healing hydrogels as BMSCs-derived exosomes carriers for advanced stretchable wounds. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 26, 101342.
Cao, J. F.; Wu, P.; Cheng, Q. Q.; He, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J. P. Ultrafast fabrication of self-healing and injectable carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel dressing for wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 24095–24105.
X.; Liu, X. Z.; Yang, J.; Du, H. B.; Chai, N. W.; Sha, Z.; Geng, M. R.; Zhou, X. J.; He, C. L. Tannic acid-reinforced methacrylated chitosan/methacrylated silk fibroin hydrogels with multifunctionality for accelerating wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116689.
Zou, C. Y.; Lei, X. X.; Hu, J. J.; Jiang, Y. L.; Li, Q. J.; Song, Y. T.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Li-Ling, J.; Xie, H. Q. Multi-crosslinking hydrogels with robust bio-adhesion and pro-coagulant activity for first-aid hemostasis and infected wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 16, 388–402.
Hu, B.; Gao, M. Z.; Boakye-Yiadom, K. O.; Ho, W.; Yu, W.; Xu, X. Y.; Zhang, X. Q. An intrinsically bioactive hydrogel with on-demand drug release behaviors for diabetic wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4592–4606.
Wei, Q. C.; Chen, K. Y.; Zhang, X. Y.; Ma, G. L.; Zhang, W. W.; Hu, Z. G. Facile preparation of polysaccharides-based adhesive hydrogel with antibacterial and antioxidant properties for promoting wound healing. Colloids Surf. B:Biointerfaces 2022, 209, 112208.
Fu, Y.; Zhang, J. H.; Wang, Y. L.; Li, J.; Bao, J. X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, C. Q.; Li, Y. W.; Wu, H. X.; Gu, Z. P. Reduced polydopamine nanoparticles incorporated oxidized dextran/chitosan hybrid hydrogels with enhanced antioxidative and antibacterial properties for accelerated wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117598.
Tu, Z. L.; Chen, M.; Wang, M.; Shao, Z. X.; Jiang, X. Q.; Wang, K. Y.; Yao, Z.; Yang, S. W.; Zhang, X. X.; Gao, W. Y. et al. Engineering bioactive M2 macrophage-polarized anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial scaffolds for rapid angiogenesis and diabetic wound repair. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100924.
K. B.; Yang, C.; Cheng, C. X.; Shi, C. X.; Sun, M. D.; Hu, H. Z.; Shi, T. F.; Chen, X. N.; He, X.; Zheng, X. et al. Bioactive injectable hydrogel dressings for bacteria-infected diabetic wound healing: A “pull—push“ approach. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 26404–26417.
Xu, Z. J.; Liu, G. T.; Huang, J.; Wu, J. Novel glucose-responsive antioxidant hybrid hydrogel for enhanced diabetic wound repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 7680–7689.
Xu, Z. J.; Liu, G. T.; Liu, P.; Hu, Y. Y.; Chen, Y. X.; Fang, Y. F.; Sun, G. G.; Huang, H.; Wu, J. Hyaluronic acid-based glucose-responsive antioxidant hydrogel platform for enhanced diabetic wound repair. Acta Biomater. 2022, 147, 147–157.
Zhang, S. H.; Hou, J. Y.; Yuan, Q. J.; Xin, P. K.; Cheng, H. T.; Gu, Z. P.; Wu, J. Arginine derivatives assist dopamine-hyaluronic acid hybrid hydrogels to have enhanced antioxidant activity for wound healing. Chem. Eng. J 2020, 392, 123775.
Z. J.; Kumar, H.; Tian, Z. L.; Jin, X.; Holzman, J. F.; Menard, F.; Kim, K. Visible light photoinitiation of cell-adhesive gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels for stereolithography 3D bioprinting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 26859–26869.
Zhu, J.; Li, F. X.; Wang, X. L.; Yu, J. Y.; Wu, D. Q. Hyaluronic acid and polyethylene glycol hybrid hydrogel encapsulating nanogel with hemostasis and sustainable antibacterial property for wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13304–13316.
Yuan, Q. J.; Huang, J.; Xian, C. H.; Wu, J. Amino acid-and growth factor-based multifunctional nanocapsules for the modulation of the local microenvironment in tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 2165–2178.
Zhang, S. H.; Ou, Q. M.; Xin, P. K.; Yuan, Q. J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J. Polydopamine/puerarin nanoparticle-incorporated hybrid hydrogels for enhanced wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 4230–4236.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51973243), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 191gzd35), Guangdong Innovative and Entrepreneurial Research Team Program (No. 2016ZT06S029), Shenzhen Basic Research Project (No. JCYJ20190807155801657), and Key international (regional) cooperative research projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 5181001045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_4792_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
A polyphenol-modified chitosan hybrid hydrogel with enhanced antimicrobial and antioxidant activities for rapid healing of diabetic wounds
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Liu, G., Zheng, L. et al. A polyphenol-modified chitosan hybrid hydrogel with enhanced antimicrobial and antioxidant activities for rapid healing of diabetic wounds. Nano Res. 16, 905–916 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4792-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4792-6