Abstract
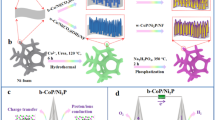
It has been of interest in seeking electrocatalysts that could exercise equally high-efficient and durable hydrogen evolution upon nonselective electrolytes in both acidic and alkaline environments. Herein, we report a facile strategy to fabricate cobalt tungsten phosphides (CoxW2−xP2/C) hollow polyhedrons with tunable composition based on metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) template method. By the deliberate control of W doping, the synthesized catalyst with the composition of Co0.9W1.1P2/C is found to be able to achieve a current density of 10 mA·cm−2 at overpotentials of 35 and 54 mV in acidic and alkaline media, respectively. This combined electrochemical property stands atop the state-of-the-art electrocatalyst counterparts. To unveil the peculiar behavior of the structure, density functional theory (DFT) calculation was implemented and reveals that the surface W-doping facilitates the optimization of hydrogen absorption free energy (ΔGH*) as well as the thermodynamic and kinetics barriers for water dissociation, which is coupled with the hollow structure of Co-W phosphides, leading to the prominent HER catalytic performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, G. Q.; Rui, K.; Dou, S. X.; Sun, W. P. Heterostructures for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803291.
Gong, M.; Wang, D. Y.; Chen, C. C.; Hwang, B. J.; Dai, H. J. A mini review on nickel-based electrocatalysts for alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 28–46.
Xu, Y.; Tu, W. G.; Zhang, B. W.; Yin, S. M.; Huang, Y. Z.; Kraft, M.; Xu, R. Nickel nanoparticles encapsulated in few-layer nitrogen-doped graphene derived from metal-organic frameworks as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605957.
Tu, W. G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J. J.; Zhang, B. W.; Zhou, T. H.; Yin, S. M.; Wu, S. Y.; Li, C. M.; Huang, Y. Z.; Zhou, Y. et al. Investigating the role of tunable nitrogen vacancies in graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for efficient visible-light-driven H2 evolution and CO2 reduction. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7260–7268.
Zhang, Y. Q.; Xia, X. H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, B. W.; Tiep, N. H.; He, H. Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, Y. Z.; Fan, H. J. Ultrafine metal nanoparticles/ N-doped porous carbon hybrids coated on carbon fibers as flexible and binder-free water splitting catalysts. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700220.
Chen, Z. L.; Wu, R. B.; Liu, Y.; Ha, Y.; Guo, Y. H.; Sun, D. L.; Liu, M.; Fang, F. Ultrafine co nanoparticles encapsulated in carbon-nanotubes-grafted graphene sheets as advanced electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802011.
Zhang, X.; Yu, X. L.; Zhang, L. J.; Zhou, F.; Liang, Y. Y.; Wang, R. H. Molybdenum phosphide/carbon nanotube hybrids as pH-universal electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706523.
Wang, R.; Dong, X. Y.; Du, J.; Zhao, J. Y.; Zang, S. Q. MOF-derived bifunctional Cu3P nanoparticles coated by a N, P-codoped carbon shell for hydrogen evolution and oxygen reduction. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703711.
Chen, G. B.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Sun, H. J.; Zhuang, X. D.; Chen, M. W.; Feng, X. L. Accelerated hydrogen evolution kinetics on nife-layered double hydroxide electrocatalysts by tailoring water dissociation active sites. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706279.
Ahn, W.; Park, M. G.; Lee, D. U.; Seo, M. H.; Jiang, G. P.; Cano, Z. P.; Hassan, F. M.; Chen, Z. W. Hollow multivoid nanocuboids derived from ternary Ni-Co-Fe prussian blue analog for dual-electrocatalysis of oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802129.
Zhang, B. W.; Yang, G.; Li, C. J.; Huang, K.; Wu, J. S.; Hao, S. J.; Feng, J. Y.; Peng, D. D.; Huang, Y. Z. Phase controllable fabrication of zinc cobalt sulfide hollow polyhedra as high-performance electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1774–1778.
Xiao, J.; Zhang, Z. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Q. Y.; Jing, F.; Chi, K.; Wang, S. Large-scale printing synthesis of transition metal phosphides encapsulated in N, P co-doped carbon as highly efficient hydrogen evolution cathodes. Nano Energy 2018, 51, 223–230.
Ge, Y. C.; Dong, P.; Craig, S. R.; Ajayan, P. M.; Ye, M. X.; Shen, J. F. Transforming nickel hydroxide into 3D Prussian blue analogue array to obtain Ni2P/Fe2P for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800484.
Shi, Y. M.; Zhang, B. Recent advances in transition metal phosphide nanomaterials: Synthesis and applications in hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1529–1541.
Ouyang, C. B.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Y. Phosphorus-doped CoS2 nanosheet arrays as ultra-efficient electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14160–14163.
Fu, Q.; Wu, T.; Fu, G.; Gao, T. L.; Han, J. C.; Yao, T.; Zhang, Y. M.; Zhong, W. W.; Wang, X. J.; Song, B. Skutterudite-type ternary Co1−xNixP3 nanoneedle array electrocatalysts for enhanced hydrogen and oxygen evolution. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 1744–1752.
Jiang, H.; Gu, J. X.; Zheng, X. S.; Liu, M.; Qiu, X. Q.; Wang, L. B.; Li, W. Z.; Chen, Z. F.; Ji, X. B.; Li, J. Defect-rich and ultrathin N doped carbon nanosheets as advanced trifunctional metal-free electrocatalysts for the ORR, OER and HER. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 322–333.
Gao, K.; Wang, B.; Tao, L.; Cunning, B. V.; Zhang, Z. P.; Wang, S. Y.; Ruoff, R. S.; Qu, L. T. Efficient metal-free electrocatalysts from N-doped carbon nanomaterials: Mono-doping and Co-doping. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805121.
Guan, C.; Xiao, W.; Wu, H. J.; Liu, X. M.; Zang, W. J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, J.; Feng, Y. P.; Pennycook, S. J.; Wang, J. Hollow Mo-doped CoP nanoarrays for efficient overall water splitting. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 73–80.
Wang, T.; Jin, R. M.; Wu, X. Q.; Zheng, J.; Li, X. G.; Ostrikov, K. A highly efficient Ni-Mo bimetallic hydrogen evolution catalyst derived from a molybdate incorporated Ni-MOF. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 9228–9235.
Chen, Y. J.; Dong, C. Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z. H. Hierarchically porous Mo-doped Ni-Fe oxide nanowires efficiently catalyzing oxygen/hydrogen evolution reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 8430–8440.
Guo, Y. P.; Dong, Z. P.; Cui, Z. K.; Zhang, X. J.; Ma, J. T. Promoting effect of W doped in electrodeposited Co-P catalysts for hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 1577–1583.
Jin, Z. Y.; Li, P. P.; Huang, X.; Zeng, G. F.; Jin, Y.; Zheng, B. Z.; Xiao, D. Three-dimensional amorphous tungsten-doped nickel phosphide microsphere as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18593–18599.
Bhat, K. S.; Nagaraja, H. S. Effect of isoelectronic tungsten doping on molybdenum selenide nanostructures and their graphene hybrids for supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 302, 459–471.
Zhang, B.; Zheng, X. L.; Voznyy, O.; Comin, R.; Bajdich, M.; García-Melchor, M.; Han, L. L.; Xu, J. X.; Liu, M.; Zheng, L. R. et al. Homogeneously dispersed multimetal oxygen-evolving catalysts. Science 2016, 352, 333–337.
Ma, Y. Y.; Wu, C. X.; Feng, X. J.; Tan, H. Q.; Yan, L. K.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. H.; Wang, E. B.; Li, Y. G. Highly efficient hydrogen evolution from seawater by a low-cost and stable CoMoP@C electrocatalyst superior to Pt/C. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 788–798.
Wang, X. D.; Chen, H. Y.; Xu, Y. F.; Liao, J. F.; Chen, B. X.; Rao, H. S.; Kuang, D. B.; Su, C. Y. Self-supported NiMoP2 nanowires on carbon cloth as an efficient and durable electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 7191–7199.
Weng, B. C.; Grice, C. R.; Meng, W. W.; Guan, L.; Xu, F. H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C. L.; Zhao, D. W.; Yan, Y. F. Metal-organic framework-derived CoWP@C composite nanowire electrocatalyst for efficient water splitting. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 1434–1442.
Chen, Z. L.; Ha, Y.; Jia, H. X.; Yan, X. X.; Chen, M.; Liu, M.; Wu, R. B. Oriented transformation of Co-LDH into 2D/3D ZIF-67 to achieve Co-N-C hybrids for efficient overall water splitting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803918.
Lu, Q. P.; Wang, A. L.; Cheng, H. F.; Gong, Y.; Yun, Q. B.; Yang, N. L.; Li, B.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Q. H.; Zong, Y. et al. Synthesis of hierarchical 4H/fcc ru nanotubes for highly efficient hydrogen evolution in alkaline media. Small 2018, 14, 1801090.
Lu, X. F.; Yu, L.; Lou, X. W. D. Highly crystalline Ni-doped FeP/carbon hollow nanorods as all-pH efficient and durable hydrogen evolving electrocatalysts. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav6009.
Zhang, B. W.; Hao, S. J.; Xiao, D. R.; Wu, J. S.; Huang, Y. Z. Templated formation of porous Mn2O3 octahedra from Mn-MIL-100 for lithium-ion battery anode materials. Mater. Des. 2016, 98, 319–323.
Zhu, P. P.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, S. J.; Zhang, B. W.; Zhao, P. F.; Yu, J.; Cai, J. X.; Huang, Y. Z.; Yang, Z. Y. Multi-channel FeP@C octahedra anchored on reduced graphene oxide nanosheet with efficient performance for lithium-ion batteries. Carbon 2018, 139, 477–485.
Zhang, B. W.; Li, C. J.; Yang, G.; Huang, K.; Wu, J. S.; Li, Z.; Cao, X.; Peng, D. D.; Hao, S. J.; Huang, Y. Z. Nanostructured CuO/C hollow Shell@3D copper dendrites as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 23807–23812.
Hao, S. J.; Ouyang, B.; Li, C. J.; Zhang, B. W.; Feng, J. Y.; Wu, J. S.; Srinivasan, M.; Huang, Y. Z. Hollow mesoporous Co(PO3)2@carbon polyhedra as high performance anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 8599–8606.
Zhang, H.; Liu, X. M.; Wu, Y.; Guan, C.; Cheetham, A. K.; Wang, J. MOF-derived nanohybrids for electrocatalysis and energy storage: Current status and perspectives. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 5268–5288.
Zhang, M. D.; Dai, Q. B.; Zheng, H. G.; Chen, M. D.; Dai, L. M. Novel MOF-derived Co@N-C bifunctional catalysts for highly efficient Zn-Air batteries and water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705431.
Gao, R. S.; Tang, J.; Yu, X. L.; Tang, S.; Ozawa, K.; Sasaki, T.; Qin, L. C. In situ synthesis of MOF-derived carbon shells for silicon anode with improved lithium-ion storage. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104444.
Yang, Q. J.; Wang, Q. S.; Long, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, L. L.; Pan, J.; Han, J.; Lei, Y.; Shi, W. D.; Song, S. Y. In situ formation of Co9S8 quantum dots in MOF-derived ternary metal layered double hydroxide nanoarrays for high-performance hybrid supercapacitors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1903193.
Li, F.; Wang, C. R.; Han, X. C.; Feng, X. Q.; Qu, Y. Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, W. L.; Zhao, L. P.; Song, X. F.; Zhu, H. et al. Confinement effect of mesopores: In situ synthesis of cationic tungsten-vacancies for a highly ordered mesoporous tungsten phosphide electrocatalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 22741–22750.
Huang, K.; Zhang, B. W.; Wu, J. S.; Zhang, T. Y.; Peng, D. D.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y. Z. Exploring the impact of atomic lattice deformation on oxygen evolution reactions based on a sub-5 nm pure face-centred cubic high-entropy alloy electrocatalyst. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 11938–11947.
Peng, D. D.; Zhang, B. W.; Wu, J. S.; Huang, K.; Cao, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C. J.; Huang, Y. Z. Growth of lattice coherent Co9S8/Co3O4 nanoheterostructure for maximizing the catalysis of Co-based composites. ChemCatChem, 2020, 12, 2431–2435.
Hu, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, W.; Zheng, S. L.; Chen, Z. Mechanistic study of monolayer NiP2 (100) toward solar hydrogen production. Sol. RRL 2020, 4, 1900360.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (No. 51901018), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2019M660456), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51771027 and 21676216), Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by China Association for Science and Technology (YESS, 2019QNRC001), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. FRF-MP-19-001), National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFB0702100) and Singapore MOE AcRF Tier 1 grant M4011528.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Li, C., Hu, J. et al. Cobalt tungsten phosphide with tunable W-doping as highly efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Res. 14, 4073–4078 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3342-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3342-y