Abstract
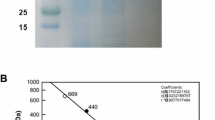
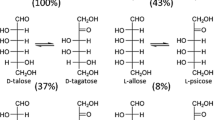
A putative l-rhamnose isomerase (l-RI) gene from Paenibacillus baekrokdamisoli was expressed as a recombinant enzyme in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) and characterized as a producer of d-allose from d-allulose. Recombinant l-RI from P. baekrokdamisoli was homogeneously purified on SDS-PAGE with a 46 kDa molecular mass and specific activity of 1.27 U/mg by His-Trap affinity chromatography. The enzyme was estimated to be a tetramer in enzyme active form because its molecular mass was determined to be approximately 190 kDa by Gelfiltration chromatography. In the isomerization reaction between d-allose and d-allulose, recombinant l-RI exhibited the highest activity at pH 8.0 and 60°C in the presence of 0.5 mM Mn2+. The half-lives of the enzyme at 50, 55, 60, 65, 70, and 75°C were 417, 57, 27, 20, 3.3, and 0.2 h, respectively. The Michaelis-Menten constants (Km), turnover numbers (kcat), and catalytic efficiencies (kcat/Km) of the enzyme for d-allose and d-allulose were 33 mM, 13.79 s−1, and 0.4 mM−1s−1 and 45.24 mM, 6.58 s−1, and 0.14 mM−1s−1, respectively. The enzyme showed isomerization activity for aldoses with right-handed configuration of hydroxyl group at the C-2 and C-3 positions, such as l-mannose, l-lyxose, d-gulose, d-allose, and d-ribose. During production of d-allose from d-allulose, the enzyme produced 125 g/L of d-allose from 500 g/L of d-allulose in 3 h with 41.6 g/L/h productivity with 104 U/mL enzyme. We first reported the l-RI from the Paenibacillus genus, and the results suggested that the P. baekrokdamisoli l-RI could be applied as a d-allose producer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Izumori, K. (2002) Bioproduction strategies for rare hexose sugars. Naturwissenschaften. 89: 120–124.
Zhang, H., M. Jiang, and F. Song (2020) d-Allose is a critical regulator of inducible plant immunity in tomato. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 111: 101507.
Natsume, Y., T. Yamada, T. Iida, N. Ozaki, Y. Gou, Y. Oshida, and T. Koike (2021) Investigation of d-allulose effects on high-sucrose diet-induced insulin resistance via hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps in rats. Heliyon. 7: e08013.
Sui, L., R. Nomura, Y. Dong, F. Yamaguchi, K. Izumori, and M. Tokuda (2007) Cryoprotective effects of d-allose on mammalian cells. Cryobiology. 55: 87–92.
Bu, D., Z. Tu, H. Wang, Y. Hu, Q. Sun, and G. Liu (2022) Insight into the mechanism of d-allose in reducing the allergenicity and digestibility of ultrasound-pretreated α-lactalbumin by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 374: 131616.
Chen, Z., J. Chen, W. Zhang, T. Zhang, C. Guang, and W. Mu (2018) Recent research on the physiological functions, applications, and biotechnological production of d-allose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 102: 4269–4278.
Mooradian, A. D., M. Smith, and M. Tokuda (2017) The role of artificial and natural sweeteners in reducing the consumption of table sugar: a narrative review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN. 18: 1–8.
Nakamura, T., S. Tanaka, K. Hirooka, T. Toyoshima, N. Kawai, T. Tamiya, F. Shiraga, M. Tokuda, R. F. Keep, T. Itano, and O. Miyamoto (2011) Anti-oxidative effects of d-allose, a rare sugar, on ischemia-reperfusion damage following focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Neurosci. Lett. 487: 103–106.
Kano, A., K. Gomi, Y. Yamasaki-Kokudo, M. Satoh, T. Fukumoto, K. Ohtani, S. Tajima, K. Izumori, K. Tanaka, Y. Ishida, Y. Tada, Y. Nishizawa, and K. Akimitsu (2010) A rare sugar, d-allose, confers resistance to rice bacterial blight with upregulation of defense-related genes in Oryza sativa. Phytopathology. 100: 85–90.
Paulino, B. N., A. Sales, L. de Oliveira Felipe, G. M. Pastore, G. Molina, and J. L. Bicas (2021) Biotechnological production of non-volatile flavor compounds. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 41: 26–35.
Choi, M. N., K. C. Shin, D. W. Kim, B. J. Kim, C. S. Park, S. J. Yeom, and Y. S. Kim (2021) Production of d-allose from d-allulose using commercial immobilized glucose isomerase. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9: 681253.
Li, C., L. Gao, K. Du, H. Lin, Y. Ren, J. Lin, and J. Lin (2020) Production of d-allose from d-fructose using immobilized L-rhamnose isomerase and d-psicose 3-epimerase. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 43: 645–653.
Singh, R. S., R. P. Singh, and J. F. Kennedy (2017) Immobilization of yeast inulinase on chitosan beads for the hydrolysis of inulin in a batch system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 95: 87–93.
Dai, Y., J. Zhang, B. Jiang, T. Zhang, and J. Chen (2021) New strategy for rare sugars biosynthesis: aldol reactions using dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)-dependent aldolases. Food Biosci. 44: 101377.
Park, H. Y., C. S. Park, H. J. Kim, and D. K. Oh (2007) Substrate specificity of a galactose 6-phosphate isomerase from Lactococcus lactis that produces d-allose from d-psicose. J. Biotechnol. 132: 88–95.
Kuroishikawa, T., D. Shinmyo, A. Yoshihara, G. Takata, A. Watanabe, M. Ashiuchi, K. Izumori, and Y. Asada (2021) Biochemical synthesis of the medicinal sugar l-gulose using fungal alditol oxidase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 575: 85–89.
Park, C. S., S. J. Yeom, H. J. Kim, S. H. Lee, J. K. Lee, S. W. Kim, and D. K. Oh (2007) Characterization of ribose-5-phosphate isomerase of Clostridium thermocellum producing d-allose from d-psicose. Biotechnol. Lett. 29: 1387–1391.
Wang, R., X. Xu, X. Yao, H. Tang, X. Ju, and L. Li (2021) Enhanced isomerization of rare sugars by ribose-5-phosphate isomerase A from Ochrobactrum sp. CSL1. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 148: 109789.
Bhuiyan, S. H., Y. Itami, and K. Izumori (1997) Isolation of an l-rhamnose isomerase-constitutive mutant of Pseudomonas sp. strain LL172: purification and characterization of the enzyme. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 84: 319–323.
Xu, W., W. Zhang, Y. Tian, T. Zhang, B. Jiang, and W. Mu (2017) Characterization of a novel thermostable l-rhamnose isomerase from Thermobacillus composti KWC4 and its application for production of d-allose. Process Biochem. 53: 153–161.
Mu, W., L. Yu, W. Zhang, T. Zhang, and B. Jiang (2015) Isomerases for biotransformation of d-hexoses. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99: 6571–6584.
Lin, C. J., W. C. Tseng, and T. Y. Fang (2011) Characterization of a thermophilic l-rhamnose isomerase from Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus ATCC 43494. J. Agric. Food Chem. 59: 8702–8708.
Bai, W., J. Shen, Y. Zhu, Y. Men, Y. Sun, and Y. Ma (2015) Characteristics and kinetic properties of l-rhamnose isomerase from Bacillus subtilis by isothermal titration calorimetry for the production of d-allose. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 21: 13–22.
Takata, G., K. Uechi, E. Taniguchi, Y. Kanbara, A. Yoshihara, K. Morimoto, and K. Izumori (2011) Characterization of Mesorhizobium loti L-rhamnose isomerase and its application to L-talose production. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 75: 1006–1009.
Park, C. S., S. J. Yeom, Y. R. Lim, Y. S. Kim, and D. K. Oh (2010) Characterization of a recombinant thermostable l-rhamnose isomerase from Thermotoga maritima ATCC 43589 and its application in the production of L-lyxose and L-mannose. Biotechnol. Lett. 32: 1947–1953.
Seo, M. J., J. H. Choi, S. H. Kang, K. C. Shin, and D. K. Oh (2018) Characterization of L-rhamnose isomerase from Clostridium stercorarium and its application to the production of d-allose from d-allulose (d-psicose). Biotechnol. Lett. 40: 325–334.
Lin, C. J., W. C. Tseng, T. H. Lin, S. M. Liu, W. S. Tzou, and T. Y. Fang (2010) Characterization of a thermophilic L-rhamnose isomerase from Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum NTOU1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58: 10431–10436.
Chen, Z., J. Chen, W. Zhang, T. Zhang, C. Guang, and W. Mu (2018) Improving thermostability and catalytic behavior of l-rhamnose isomerase from Caldicellulosiruptor obsidiansis OB47 toward d-allulose by site-directed mutagenesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66: 12017–12024.
Korndörfer, I. P., W. D. Fessner, and B. W. Matthews (2000) The structure of rhamnose isomerase from Escherichia coli and its relation with xylose isomerase illustrates a change between inter and intra-subunit complementation during evolution. J. Mol. Biol. 300: 917–933.
Prabhu, P., T. T. N. Doan, M. Jeya, L. W. Kang, and J. K. Lee (2010) Cloning and characterization of a rhamnose isomerase from Bacillus halodurans. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 89: 635–644.
Leang, K., G. Takada, Y. Fukai, K. Morimoto, T. B. Granström, and K. Izumori (2004) Novel reactions of L-rhamnose isomerase from Pseudomonas stutzeri and its relation with d-xylose isomerase via substrate specificity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1674: 68–77.
Poonperm, W., G. Takata, H. Okada, K. Morimoto, T. B. Granström, and K. Izumori (2007) Cloning, sequencing, overexpression and characterization of L-rhamnose isomerase from Bacillus pallidus Y25 for rare sugar production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 76: 1297–1307.
Kim, Y. S., K. C. Shin, Y. R. Lim, and D. K. Oh (2013) Characterization of a recombinant L-rhamnose isomerase from Dictyoglomus turgidum and its application for L-rhamnulose production. Biotechnol. Lett. 35: 259–264.
Feng, Z., W. Mu, and B. Jiang (2013) Characterization of ribose-5-phosphate isomerase converting d-psicose to d-allose from Thermotoga lettingae TMO. Biotechnol. Lett. 35: 719–724.
Yeom, S. J., E. S. Seo, Y. S. Kim, and D. K. Oh (2011) Increased D-allose production by the R132E mutant of ribose-5-phosphate isomerase from Clostridium thermocellum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 89: 1859–1866.
Yeom, S. J., B. N. Kim, C. S. Park, and D. K. Oh (2010) Substrate specificity of ribose-5-phosphate isomerases from Clostridium difficile and Thermotoga maritima. Biotechnol. Lett. 32: 829–835.
Yoon, R. Y., S. J. Yeom, C. S. Park, and D. K. Oh (2009) Substrate specificity of a glucose-6-phosphate isomerase from Pyrococcus furiosus for monosaccharides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 83: 295–303.
Park, C.-S. (2014) Characterization of a recombinant L-rhamnose isomerase from Bacillus subtilis and its application on production of L-lyxose and L-mannose. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 19: 18–25.
Menavuvu, B. T., W. Poonperm, K. Leang, N. Noguchi, H. Okada, K. Morimoto, T. B. Granström, G. Takada, and K. Izumori (2006) Efficient biosynthesis of d-allose from d-psicose by cross-linked recombinant L-rhamnose isomerase: separation of product by ethanol crystallization. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 101: 340–345.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2019R1F1A1059906).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.J., Choi, M.S. & Park, CS. Characterization of a Recombinant l-rhamnose Isomerase from Paenibacillus baekrokdamisoli to Produce d-allose from d-allulose. Biotechnol Bioproc E 27, 432–442 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-021-0341-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-021-0341-5