Abstract
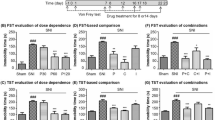
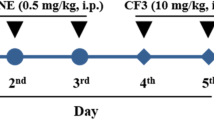
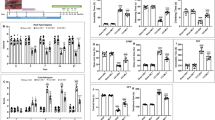
Neuroinflammation is critical to the comorbidity of chronic pain and depression. Pyroptosis is an inflammatory cell death that is different from apoptosis. Activation of the P2X4 receptor leads to inflammation and is involved in chronic pain and depression. Pinocembrin (5,7-dihydroxyflavanone) is a natural flavonoid compound with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and neuroprotective effects. In this study, an animal model of chronic pain and depression comorbidity was used to explore the therapeutic effect of pinocembrin in P2X4-mediated pyroptosis. The results showed that nociceptive behaviours and depression-like behaviours were obvious in the model rats induced by chronic constrictive injury (CCI) and chronic unpredictable mild stimulus (CUMS). In the model rats, the mRNA and protein levels of the P2X4 receptor in the hippocampus were increased, and the coexpression of P2X4 and the astrocyte marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the hippocampus was increased. The protein content of connexion 43 (Cx43), NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain (ASC) and caspase-1 was increased. The serum content of IL-1β and the mRNA and protein expression of IL-1β were increased. The protein content of p-P38MAPK was increased. After treatment with pinocembrin in the model rats, these behavioural changes were improved, and the mRNA and protein levels of the above indicators were decreased. The results of molecular docking confirmed that the affinity of pinocembrin and the P2X4 receptor was − 7.8 (kcal/mol). At the same time, pinocembrin inhibited the ATP release and Ca2+ signal release in primary astrocytes and ATP-activated current of HEK293 cells transfected with the pcDNA3.0-EGFP-hP2X4 plasmid. Therefore, pinocembrin relieved nociceptive and depression-like behaviours in rats with chronic pain and depression comorbidity by inhibiting P2X4 receptor–mediated pyroptosis in the hippocampus.
Graphical abstract
The mechanism of pinocembrin in treating rats with chronic pain and depression comorbidity. GJ stands for gap junction, and Cx43 is mainly expressed in astrocytes.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be provided by the authors without any retention.
References
Raja SN, Carr DB, Cohen M, Finnerup NB, Flor H, Gibson S, Keefe FJ, Mogil JS, et al (2020) The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain 161(9):1976–1982. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001939
Bouali-Benazzouz R, Landry M, Benazzouz A, Fossat P (2021) Neuropathic pain modeling: focus on synaptic and ion channel mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol:102030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2021.102030
Yin N, Yan E, Duan W, Mao C, Fei Q, Yang C, Hu Y, Xu X (2021) The role of microglia in chronic pain and depression: innocent bystander or culprit? Psychopharmacology 238(4):949–958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05780-4
Cookson BT, Brennan MA (2001) Pro-inflammatory programmed cell death. Trends Microbiol 9(3):113–114
Humphries F, Shmuel-Galia L, Ketelut-Carneiro N, Li S, Wang B, Nemmara VV, Wilson R, Jiang Z, et al (2020) Succination inactivates gasdermin D and blocks pyroptosis. Science 369(6511):1633–1637. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb9818
Asih PR, Prikas E, Stefanoska K, Tan ARP, Ahel HI, Ittner A (2020) Functions of p38 MAP kinases in the central nervous system. Front Mol Neurosci 13:570586. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2020.570586
Li L, Zou Y, Liu B, Yang R, Yang J, Sun M, Li Z, Xu X, et al (2020) Contribution of the P2X4 receptor in rat hippocampus to the comorbidity of chronic pain and depression. ACS Chem Neurosci 11(24):4387–4397. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00623
Xing L, Yang T, Cui S, Chen G (2019) Connexin hemichannels in astrocytes: role in CNS disorders. Front Mol Neurosci 12:23. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2019.00023
Suurvali J, Boudinot P, Kanellopoulos J, RuutelBoudinot S (2017) P2X4: a fast and sensitive purinergic receptor. Biomed J 40(5):245–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bj.2017.06.010
Jurga AM, Piotrowska A, Makuch W, Przewlocka B, Mika J (2017) Blockade of P2X4 receptors inhibits neuropathic pain-related behavior by preventing MMP-9 activation and consequently, pronociceptive interleukin release in a rat model. Front Pharmacol 8:48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00048
Ribeiro DE, Casarotto PC, Staquini L, Pinto ESMA, Biojone C, Wegener G, Joca S (2019) Reduced P2X receptor levels are associated with antidepressant effect in the learned helplessness model. PeerJ 7:e7834. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7834
Campos ACP, Antunes GF, Matsumoto M, Pagano RL, Martinez RCR (2020) Neuroinflammation, pain and depression: an overview of the main findings. Front Psychol 11:1825. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01825
Sun YB, Zhao H, Mu DL, Zhang W, Cui J, Wu L, Alam A, Wang DX, Ma D (2019) Dexmedetomidine inhibits astrocyte pyroptosis and subsequently protects the brain in in vitro and in vivo models of sepsis. Cell Death Dis 10(3):167. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1416-5
Cai M, Zhuang W, Lv E, Liu Z, Wang Y, Zhang W, Fu W (2022) Kaemperfol alleviates pyroptosis and microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease via inhibiting p38MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Neurochem Int 152:105221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105221
Li S, Sun Y, Song M, Song Y, Fang Y, Zhang Q, Li X, Song N, Ding J, Lu M, Hu G (2021) NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis exerts a crucial role in astrocyte pathological injury in mouse model of depression. JCI Insight 6 (23). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.146852
Kang ZC, Wang HG, Yang YL, Zhao XY, Zhou QM, Yang YL, Yang JY, Du GH (2020) Pinocembrin ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by vascular dementia: contribution of Reelin-dab1 signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther 14:3577–3587. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S249176
Ye T, Zhang C, Wu G, Wan W, Guo Y, Fo Y, Chen X, Liu X et al (2020) Pinocembrin decreases ventricular fibrillation susceptibility in a rat model of depression. Front Pharmacol 11:547966. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.547966
Guan S, Shen Y, Ge H, Xiong W, He L, Liu L, Yin C, Wei X, Gao Y (2019) Dihydromyricetin alleviates diabetic neuropathic pain and depression comorbidity symptoms by inhibiting P2X7 receptor. Front Psych 10:770. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00770
Yang R, Li Z, Zou Y, Yang J, Li L, Xu X, Schmalzing G, Nie H et al (2021) Gallic acid alleviates neuropathic pain behaviors in rats by inhibiting P2X7 receptor-mediated NF-kappaB/STAT3 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 12:680139. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.680139
Yang R, Li L, Yuan H, Liu H, Gong Y, Zou L, Li S, Wang Z et al (2019) Quercetin relieved diabetic neuropathic pain by inhibiting upregulated P2X4 receptor in dorsal root ganglia. J Cell Physiol 234(3):2756–2764. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27091
Ge H, Sun M, Wei X, Zhang M, Tu H, Hao Y, Chen R, Ye M, Gao Y (2020) Protective effects of dihydromyricetin on primary hippocampal astrocytes from cytotoxicity induced by comorbid diabetic neuropathic pain and depression. Purinergic Signal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-020-09752-9
Ge H, Guan S, Shen Y, Sun M, Hao Y, He L, Liu L, Yin C et al (2019) Dihydromyricetin affects BDNF levels in the nervous system in rats with comorbid diabetic neuropathic pain and depression. Sci Rep 9(1):14619. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51124-w
Ivetic M, Bhattacharyya A, Zemkova H (2019) P2X2 receptor expression and function is upregulated in the rat supraoptic nucleus stimulated through refeeding after fasting. Front Cell Neurosci 13:284. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00284
Sangweni NF, Moremane M, Riedel S, van Vuuren D, Huisamen B, Mabasa L, Barry R, Johnson R (2020) The prophylactic effect of pinocembrin against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in an in vitro H9c2 cell model. Front Pharmacol 11:1172. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.01172
Jurga AM, Paleczna M, Kadluczka J, Kuter KZ (2021) Beyond the GFAP-Astrocyte Protein Markers in the Brain. Biomolecules 11 (9). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091361
Roughan WH, Campos AI, Garcia-Marin LM, Cuellar-Partida G, Lupton MK, Hickie IB, Medland SE, Wray NR et al (2021) Comorbid chronic pain and depression: shared risk factors and differential antidepressant effectiveness. Front Psychiatry 12:643609. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.643609
IsHak WW, Wen RY, Naghdechi L, Vanle B, Dang J, Knosp M, Dascal J, Marcia L et al (2018) Pain and depression: a systematic review. Harv Rev Psychiatry 26(6):352–363. https://doi.org/10.1097/HRP.0000000000000198
Yang X, Wang X, Chen XY, Ji HY, Zhang Y, Liu AJ (2018) Pinocembrin(-)lecithin complex: characterization, solubilization, and antioxidant activities. Biomolecules 8 (2). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8020041
Saraiva M, Vieira P, O'Garra A (2020) Biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin-10. J Exp Med 217 (1). https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20190418
Xia CY, Wang ZZ, Wang HQ, Ren SY, Lou YX, Jin C, Qu TG, Feng ST et al (2020) Connexin 43: a novel ginsenoside Rg1-sensitive target in a rat model of depression. Neuropharmacology 170:108041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108041
Zhu G, Chen Z, Dai B, Zheng C, Jiang H, Xu Y, Sheng X, Guo J, Dan Y, Liang S, Li G (2018) Chronic lead exposure enhances the sympathoexcitatory response associated with P2X4 receptor in rat stellate ganglia. Environ Toxicol 33(6):631–639. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22547
Layhadi JA, Fountain SJ (2017) P2X4 receptor-dependent Ca(2+) influx in model human monocytes and macrophages. International journal of molecular sciences 18 (11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112261
Rathinam VAK, Zhao Y, Shao F (2019) Innate immunity to intracellular LPS. Nat Immunol 20(5):527–533. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-019-0368-3
Arioz BI, Tastan B, Tarakcioglu E, Tufekci KU, Olcum M, Ersoy N, Bagriyanik A, Genc K, et al (2019) Melatonin attenuates LPS-induced acute depressive-like behaviors and microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation through the SIRT1/Nrf2 pathway. Front Immunol 10:1511. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01511
Yuan H, Ouyang S, Yang R, Li S, Gong Y, Zou L, Jia T, Zhao S, Wu B et al (2018) Osthole alleviated diabetic neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X4 receptor in dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res Bull 142:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.08.008
Zhao YW, Pan YQ, Tang MM, Lin WJ (2018) Blocking p38 signaling reduces the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the phosphorylation of p38 in the habenula and reverses depressive-like behaviors induced by neuroinflammation. Front Pharmacol 9:511. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00511
Zhao S, Zhou Y, Fan Y, Gong Y, Yang J, Yang R, Li L, Zou L et al (2019) Involvement of purinergic 2X4 receptor in glycoprotein 120-induced pyroptosis in dorsal root ganglia. J Neurochem 151(5):584–594. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14850
Ma H, Li C, Wang J, Zhang X, Li M, Zhang R, Huang Z, Zhang Y (2021) Amygdala-hippocampal innervation modulates stress-induced depressive-like behaviors through AMPA receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118 (6). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2019409118
Gu J, Huang H, Liu C, Jiang B, Li M, Liu L, Zhang S (2021) Pinocembrin inhibited cardiomyocyte pyroptosis against doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction via regulating Nrf2/Sirt3 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 95:107533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107533
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China for funding and the corresponding author for his contribution to this study.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81861138042, 81870574, 82060247, 81660199, 82160163, 81570735, 31560276, 81701114, and 81860217), the Science and Technology Key Program Founded by the Education Department of Jiangxi Province (GJJ190015) and the Key Research and Development programs of Jiangxi Province (20192BBH80017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.S.X, S.D.L, and R.N.Y contributed to the design of experiments and composition of the manuscript. R.N.Y was for analysis of data. R.N.Y, J.J.Y, Z.J.L, R.C.S., L.F.Z, L.L, X.M.X, G.L.L, and S.M.L performed the experiments.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Nanchang University. All the experiments were in accordance with the relevant rules and regulations of Nanchang University and the regulations of China and national guidelines.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
The animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Nanchang University. Ethic Committee Name: Animal Ethic Committee of Nanchang University, China. Approval Code: SYKX2015-0001.Approval Date:12 October 2015.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, R., Yang, J., Li, Z. et al. Pinocembrin Inhibits P2X4 Receptor–Mediated Pyroptosis in Hippocampus to Alleviate the Behaviours of Chronic Pain and Depression Comorbidity in Rats. Mol Neurobiol 59, 7119–7133 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-03023-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-03023-x