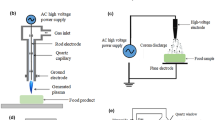
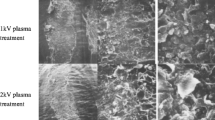
Abstract
In the last decade, the contribution of non-thermal technology for providing safe and nutritious food has increased. Therefore, food scientists have put effort into developing and applying non-thermal technology to meet the ever-increasing demand for healthy food. The cold plasma is an emerging non-thermal technology for food processing that uses electrons, radicals, and ions generated at ambient temperature for inactivating microorganisms and enzymes. This technology encompasses various process parameters, such as power or potential difference, frequency, feed gas, and treatment time. The choice of feed gas can significantly influence the effectiveness of plasma exposure and its effect on different food constituents. For instance, the plasma using noble gas as feed gas preserved the physicochemical attributes (pH, TSS, TA, and color) and bioactive compounds of food but required a longer duration for enzyme and microbial inactivation. On the contrary, the oxygen and nitrogen-rich feed gas plasma generate an abundant amount of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species that alter the important physicochemical attributes and the functional components like vitamin C and phenolic compounds but are very efficient in inactivating the enzymes and microorganisms. This review briefs the readers about cold plasma, different equipment associated with its generation, reactive species generated specific to feed gas and feed gas interaction with other process parameters. Additionally, it elucidates the impact of different feed gases utilized in plasma formation on physicochemical characteristics, microbial eradication, enzyme inactivation, and bioactive compounds.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The data and materials will be made available on request.
References
Abdel-Naeem, H. H. S., Ebaid, E. M. S. M., Khalel, K. H. M., Imre, K., Morar, A., Herman, V., & EL-Nawawi, F. A. M. (2022). Decontamination of chicken meat using dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma technology: The effect on microbial quality, physicochemical properties, topographical structure, and sensory attributes. LWT, 165, 113739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113739
Ahangari, M., Ramezan, Y., & Khani, M. R. (2021). Effect of low pressure cold plasma treatment on microbial decontamination and physicochemical properties of dried walnut kernels (Juglans regia L.). Journal of Food Process Engineering, 44(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.13593
Akarca, G., Atik, A., Atik, İ, & Denizkara, A. J. (2023). The use of cold plasma technology in solving the mold problem in Kashar cheese. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 60(2), 752–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13197-022-05661-4/TABLES/5
Al-Hilphy, A. R., Abdulstar, A. R., & Gavahian, M. (2021). Moderate electric field pasteurization of milk in a continuous flow unit: Effects of process parameters, energy consumption, and shelf-life determination. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 67, 102568. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2020.102568
Ali, M., Cheng, J., & Sun, D. (2021). Effects of dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma treatments on degradation of anilazine fungicide and quality of tomato ( Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) juice. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 56(1), 69–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14600
Almeida, F. D. L., Cavalcante, R. S., Cullen, P. J., Frias, J. M., Bourke, P., Fernandes, F. A., & Rodrigues, S. (2015). Effects of atmospheric cold plasma and ozone on prebiotic orange juice. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 32, 127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2015.09.001
Alsaedi, A. W. M., Al-Mousawi, A. J., Al-Hilphy, A. R., & Gavahian, M. (2023). Non-thermal pasteurization of milk by an innovative energy-saving moderate electrical field equipped with elongated electrodes and process optimization. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 88, 103445. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2023.103445
Alves Filho, E. G., Silva, L. M. A., de Brito, E. S., Castro, D. R. G., Bezerra, J. A., Sanches, E. A., Rodrigues, S., Fernandes, F. A. N., & Campelo, P. H. (2021). Effect of glow and dielectric barrier discharges plasma on volatile and non-volatile chemical profiling of camu-camu juice. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14(7), 1275–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-021-02639-6/TABLES/4
Amanpour, A., Vandamme, J., Polat, S., Kelebek, H., Van Durme, J., & Selli, S. (2019). Non-thermal plasma effects on the lipoxygenase enzyme activity, aroma and phenolic profiles of olive oil. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 54(April), 123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2019.04.004
Andreou, V., Giannoglou, M., Xanthou, M. Z., Passaras, D., Kokkoris, G., Gogolides, Ε, & Katsaros, G. (2023). Inactivation of pectinmethylesterase in fresh orange juice by cold atmospheric plasma technology: A kinetic study. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 86, 103361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2023.103361
Ashtiani, S. H. M., Aghkhani, M. H., Feizy, J., & Martynenko, A. (2023). Effect of cold plasma pretreatment coupled with osmotic dehydration on drying kinetics and quality of mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-023-03096-Z/TABLES/4
Attri, P., & Choi, E. H. (2013). Influence of reactive oxygen species on the enzyme stability and activity in the presence of ionic liquids. PLoS ONE, 8(9). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075096
Attri, P., Venkatesu, P., Kaushik, N., Han, Y. G., Nam, C. J., Choi, E. H., & Kim, K. S. (2012). Effects of atmospheric-pressure non-thermal plasma jets on enzyme solutions. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 60(6), 959–964. https://doi.org/10.3938/JKPS.60.959/METRICS
Bagheri, H., Abbaszadeh, S., & Sepandi, M. (2021). Simultaneous effect of cold plasma and MAP on the quality properties of mixed nuts snack during storage. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 45(4), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.15381
Baier, M., Foerster, J., Schnabel, U., Knorr, D., Ehlbeck, J., Herppich, W. B., & Schlüter, O. (2013). Direct non-thermal plasma treatment for the sanitation of fresh corn salad leaves: Evaluation of physical and physiological effects and antimicrobial efficacy. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 84, 81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2013.03.022
Baier, M., Janßen, T., Wieler, L. H., Ehlbeck, J., Knorr, D., & Schlüter, O. (2015). Inactivation of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O104: H4 using cold atmospheric pressure plasma. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 120(3), 275–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2015.01.003
Bang, I. H., Kim, Y. E., Lee, S. Y., & Min, S. C. (2020). Microbial decontamination of black peppercorns by simultaneous treatment with cold plasma and ultraviolet C. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 63(May), 102392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2020.102392
Bang, I. H., Lee, E. S., Lee, H. S., & Min, S. C. (2020). Microbial decontamination system combining antimicrobial solution washing and atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma treatment for preservation of mandarins. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 162(2019), 111102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.111102
Bao, Y., Reddivari, L., & Huang, J. Y. (2020a). Development of cold plasma pretreatment for improving phenolics extractability from tomato pomace. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 65(July), 102445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2020.102445
Bao, Y., Reddivari, L., & Huang, J. Y. (2020b). Enhancement of phenolic compounds extraction from grape pomace by high voltage atmospheric cold plasma. Lwt, 133(July), 109970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109970
Basak, S., & Annapure, U. S. (2022). Recent trends in the application of cold plasma for the modification of plant proteins - A review. Future Foods, 5, 100119. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUFO.2022.100119
Belgacem, Z. B., Carre, G., Charpentier, E., Le-Bras, F., Maho, T., Robert, E., Pouvesle, J. M., Polidor, F., Gangloff, S. C., Boudifa, M., & Gelle, M. P. (2017). Innovative non-thermal plasma disinfection process inside sealed bags: Assessment of bactericidal and sporicidal effectiveness in regard to current sterilization norms. PLoS ONE, 12(6), e0180183. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0180183
Benredjem, D., Pain, J. C., Calisti, A., & Ferri, S. (2022). Ionization by electron impacts and ionization potential depression. Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 55(10), 105001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6455/AC68B9
Bermúdez-Aguirre, D., Wemlinger, E., Pedrow, P., Barbosa-Cánovas, G., & Garcia-Perez, M. (2013). Effect of atmospheric pressure cold plasma (APCP) on the inactivation of Escherichia coli in fresh produce. Food Control, 34(1), 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.04.022
Bezerra, J. de A., Lamarão, C. V., Sanches, E. A., Rodrigues, S., Fernandes, F. A. N., Ramos, G. L. P. A., Esmerino, E. A., Cruz, A. G., & Campelo, P. H. (2023). Cold plasma as a pre-treatment for processing improvement in food: A review. In Food Research International (Vol. 167, p. 112663). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112663
Bharti, B., Li, H., Ren, Z., Zhu, R., & Zhu, Z. (2022). Recent advances in sterilization and disinfection technology: A review. Chemosphere, 308, 136404. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2022.136404
Birania, S., Attkan, A. K., Kumar, S., Kumar, N., & Singh, V. K. (2022). Cold plasma in food processing and preservation: A review. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 45(9), e14110. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFPE.14110
Boulos, M. I., Fauchais, P. L., & Pfender, E. (2023). Basic concepts of plasma generation. Handbook of Thermal Plasmas, 473–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84936-8_11
Brochier, B., Mercali, G. D., & Marczak, L. D. F. (2019). Effect of moderate electric field on peroxidase activity, phenolic compounds and color during ohmic heating of sugarcane juice. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 43(12), e14254. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFPP.14254
Bruggeman, P. J., Kushner, M. J., Locke, B. R., Gardeniers, J. G. E., Graham, W. G., Graves, D. B., Hofman-Caris, R. C. H. M., Maric, D., Reid, J. P., Ceriani, E., Fernandez Rivas, D., Foster, J. E., Garrick, S. C., Gorbanev, Y., Hamaguchi, S., Iza, F., Jablonowski, H., Klimova, E., Kolb, J., … Zvereva, G. (2016). Plasma–liquid interactions: A review and roadmap. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 25(5), 053002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/25/5/053002
Bruno, G., Heusler, T., Lackmann, J. W., von Woedtke, T., Weltmann, K. D., & Wende, K. (2019). Cold physical plasma-induced oxidation of cysteine yields reactive sulfur species (RSS). Clinical Plasma Medicine, 14, 100083. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CPME.2019.100083
Burducea, I., Burducea, C., Mereuta, P. E., Sirbu, S. R., Iancu, D. A., Istrati, M. B., Straticiuc, M., Lungoci, C., Stoleru, V., Teliban, G. C., Robu, T., Burducea, M., & Nastuta, A. V. (2023). Helium atmospheric pressure plasma jet effects on two cultivars of Triticum aestivum L. Foods, 12(1), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/FOODS12010208
Bursać Kovačević, D., Gajdoš Kljusurić, J., Putnik, P., Vukušić, T., Herceg, Z., & Dragović-Uzelac, V. (2016). Stability of polyphenols in chokeberry juice treated with gas phase plasma. Food Chemistry, 212, 323–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.192
Bursać Kovačević, D., Putnik, P., Dragović-Uzelac, V., Pedisić, S., Režek Jambrak, A., & Herceg, Z. (2016). Effects of cold atmospheric gas phase plasma on anthocyanins and color in pomegranate juice. Food Chemistry, 190, 317–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.099
Castro, D. R. G., Mar, J. M., da Silva, L. S., da Silva, K. A., Sanches, E. A., de Araújo Bezerra, J., Rodrigues, S., Fernandes, F. A. N., & Campelo, P. H. (2020). Improvement of the bioavailability of amazonian juices rich in bioactive compounds using glow plasma technique. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(4), 670–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02427-8
Cheignon, C., Tomas, M., Bonnefont-Rousselot, D., Faller, P., Hureau, C., & Collin, F. (2018). Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Redox Biology, 14, 450–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.REDOX.2017.10.014
Chen, F. F. (2018). Erratum to: Introduction to plasma physics and controlled fusion. In Introduction to Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-22309-4_11
Chen, S., Wang, H., & Dong, F. (2022). Activation and characterization of environmental catalysts in plasma-catalysis: Status and challenges. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 427, 128150. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2021.128150
Cheng, J. H., Chen, Y. Q., & Sun, D. W. (2021). Effects of plasma activated solution on the colour and structure of metmyoglobin and oxymyoglobin. Food Chemistry, 353, 129433. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2021.129433
Cheng, J. H., Li, J., & Sun, D. W. (2023). Effects of dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma on structure, surface hydrophobicity and allergenic properties of shrimp tropomyosin. Food Chemistry, 409, 135316. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2022.135316
Cheng, J. H., Sun, D. W., Han, Z., & Zeng, X. A. (2014). Texture and structure measurements and analyses for evaluation of fish and fillet freshness quality: A review. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 13(1), 52–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12043
Cheng, J. H., Wang, H., & Sun, D. W. (2023). Insight into the IgE-binding sites of allergenic peptides of tropomyosin in shrimp (Penaeus chinensis) induced by cold plasma active particles. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 234, 123690. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2023.123690
Choi, S., Attri, P., Lee, I., Oh, J., Yun, J. H., Park, J. H., Choi, E. H., & Lee, W. (2017). Structural and functional analysis of lysozyme after treatment with dielectric barrier discharge plasma and atmospheric pressure plasma jet. Scientific Reports, 17(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01030-w
Choi, S., Puligundla, P., & Mok, C. (2017). Effect of corona discharge plasma on microbial decontamination of dried squid shreds including physico-chemical and sensory evaluation. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 75, 323–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.08.063
Chutia, H., Kalita, D., Mahanta, C. L., Ojah, N., & Choudhury, A. J. (2019). Kinetics of inactivation of peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase in tender coconut water by dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Lwt, 101(October 2018), 625–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.11.071
Chutia, H., & Mahanta, C. L. (2021). Influence of cold plasma voltage and time on quality attributes of tender coconut water (Cocos nucifera L.) and degradation kinetics of its blended beverage. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 45(4), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.15372
Cong, L., Huang, M., Zhang, J., & Yan, W. (2021). Effect of dielectric barrier discharge plasma on the degradation of malathion and chlorpyrifos on lettuce. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 101(2), 424–432. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10651
Conrads, H., Schmidt, M., & Conrads, H. (2000). Plasma generation and plasma sources. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 9(4), 441–454. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/9/4/301
Csadek, I., Vankat, U., Schrei, J., Graf, M., Bauer, S., Pilz, B., Schwaiger, K., Smulders, F. J. M., & Paulsen, P. (2023). Treatment of ready-to-eat cooked meat products with cold atmospheric plasma to inactivate Listeria and Escherichia coli. Foods, 12(4), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040685
Cserhalmi, Z., Sass-Kiss, Á., Tóth-Markus, M., & Lechner, N. (2006). Study of pulsed electric field treated citrus juices. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 7(1–2), 49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2005.07.001
Cullen, P. J., Lalor, J., Scally, L., Boehm, D., Milosavljević, V., Bourke, P., & Keener, K. (2018). Translation of plasma technology from the lab to the food industry. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 15(2), 1700085. https://doi.org/10.1002/PPAP.201700085
da Costa Pinto, C., Sanches, E. A., Clerici, M. T. P. S., Rodrigues, S., Fernandes, F. A. N., de Souza, S. M., Teixeira-Costa, B. E., de Araújo Bezerra, J., Lamarão, C. V., & Campelo, P. H. (2023). Modulation of the physicochemical properties of Aria (Goeppertia allouia) starch by cold plasma: Effect of excitation frequency. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 16(4), 768–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-022-02970-6/TABLES/3
Darvish, H., Ramezan, Y., Khani, M. R., & Kamkari, A. (2022). Effect of low-pressure cold plasma processing on decontamination and quality attributes of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Food Science & Nutrition, 10(6), 2082–2090. https://doi.org/10.1002/FSN3.2824
Darvishi, H., Mohammadi, P., Fadavi, A., Koushesh Saba, M., & Behroozi-Khazaei, N. (2019). Quality preservation of orange concentrate by using hybrid ohmic – Vacuum heating. Food Chemistry, 289, 292–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2019.03.043
Dasan, B. G., & Boyaci, I. H. (2018). Effect of cold atmospheric plasma on inactivation of Escherichia coli and physicochemical properties of apple, orange, tomato juices, and sour cherry nectar. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11(2), 334–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-2014-0
De Baerdemaeker, K., Van der Linden, I., Nikiforov, A., Zuber, S., De Geyter, N., & Devlieghere, F. (2022). Non-thermal plasma inactivation of Salmonella Typhimurium on different matrices and the effect of selected food components on its bactericidal efficacy. Food Research International, 151, 110866. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2021.110866
De Baerdemaeker, K., Van Reepingen, A., Nikiforov, A., De Meulenaer, B., De Geyter, N., & Devlieghere, F. (2023). Non-thermal plasma decontamination using a multi-hollow surface dielectric barrier discharge: Impact of food matrix composition on bactericidal efficacy. Foods, 12(2), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020386
de Castro, D. R. G., Mar, J. M., da Silva, L. S., da Silva, K. A., Sanches, E. A., de Araújo Bezerra, J., Rodrigues, S., Fernandes, F. A. N., & Campelo, P. H. (2020). Dielectric barrier atmospheric cold plasma applied on camu-camu juice processing: Effect of the excitation frequency. Food Research International, 131, 109044. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2020.109044
Deng, S., Ruan, R., Mok, C. K., Huang, G., & Chen, P. (2005). Non-thermal plasma disinfection of Escherichia coli on almond. ASAE Annual International Meeting, 1. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.19589
Denoya, G. I., Polenta, G. A., Apóstolo, N. M., Cejas, E., Fina, B., Chamorro, J. C., Ferreyra, M., Prevosto, L., & Vaudagna, S. R. (2023). Effect of in-package cold plasma treatments on the quality of minimally processed apples. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 58(5), 2465–2475. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.16387
Ding, H., Wang, T., Sun, Y., Zhang, Y., Wei, J., Cai, R., Guo, C., Yuan, Y., & Yue, T. (2023). Role and mechanism of cold plasma in inactivating Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris in apple juice. Foods, 12(7), 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/FOODS12071531
Dong, X. Y., & Yang, Y. L. (2019). A novel approach to enhance blueberry quality during storage using cold plasma at atmospheric air pressure. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12, 1409–1421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02305-y
Dong, S., Fan, L., Ma, Y., Du, J., & Xiang, Q. (2021). Inactivation of polyphenol oxidase by dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma: Kinetics and mechanisms. Lwt, 145(136), 111322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111322
Durek, J., Fröhling, A., Bußler, S., Hase, A., Ehlbeck, J., & Schlüter, O. K. (2022). Pilot-scale generation of plasma processed air and its influence on microbial count, microbial diversity, and selected quality parameters of dried herbs. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 75, 102890. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2021.102890
Dzimitrowicz, A., Jamroz, P., Cyganowski, P., Bielawska-Pohl, A., Klimczak, A., & Pohl, P. (2021). Application of cold atmospheric pressure plasmas for high-throughput production of safe-to-consume beetroot juice with improved nutritional quality. Food Chemistry, 336(2020), 127635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127635
Dzimitrowicz, A., Pohl, P., Caban, M., Jamroz, P., Cyganowski, P., Bykowski, M., Klimczak, A., & Bielawska-Pohl, A. (2022). How does direct current atmospheric pressure glow discharge application influence on physicochemical, nutritional, microbiological, and cytotoxic properties of orange juice? Food Chemistry, 377, 131903. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2021.131903
Eazhumalai, G., Ranjitha Gracy, T. K., Mishra, A., & Annapure, U. S. (2022). Atmospheric pressure nonthermal pin to plate plasma system for the microbial decontamination of oat milk. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 46(10), e16181. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFPP.16181
Ehlbeck, J., Schnabel, U., Polak, M., Winter, J., Von Woedtke, T., Brandenburg, R., Von Dem Hagen, T., & Weltmann, K. D. (2011). Low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma sources for microbial decontamination. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 44(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/44/1/013002
Elez Garofulić, I., Režek Jambrak, A., Milošević, S., Dragović-Uzelac, V., Zorić, Z., & Herceg, Z. (2015). The effect of gas phase plasma treatment on the anthocyanin and phenolic acid content of sour cherry Marasca (Prunus cerasus var. Marasca) juice. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 62(1), 894–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.08.036
Esmaeili, Z., Hosseinzadeh Samani, B., Nazari, F., Rostami, S., & Nemati, A. (2023). The green technology of cold plasma jet on the inactivation of Aspergillus flavus and the total aflatoxin level in pistachio and its quality properties. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 46(1), e14189. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.14189
Feizollahi, E., & Roopesh, M. S. (2021). Degradation of zearalenone by atmospheric cold plasma: Effect of selected process and product factors. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14(11), 2107–2119. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-021-02692-1/TABLES/5
Fernandes, F. A., Santos, V. O., & Rodrigues, S. (2019). Effects of glow plasma technology on some bioactive compounds of acerola juice. Food Research International, 115, 16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.07.042
Fridman, A. (2008). Plasma Chemistry. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511546075
Fröhling, A., Baier, M., Ehlbeck, J., Knorr, D., & Schlüter, O. (2012). Atmospheric pressure plasma treatment of Listeria innocua and Escherichia coli at polysaccharide surfaces: Inactivation kinetics and flow cytometric characterization. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 13, 142–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2011.11.002
Fu, T., Liu, Y., & Wang, J. (2022). Salmonella enteritidis and Listeria monocytogenes: Inactivation effect and aerobic respiratory limitation of cold plasma treatment. Journal Fur Verbraucherschutz Und Lebensmittelsicherheit, 17(3), 243–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00003-022-01376-Y/TABLES/3
Gan, Z., Feng, X., Hou, Y., Sun, A., & Wang, R. (2021). Cold plasma jet with dielectric barrier configuration: Investigating its effect on the cell membrane of E. coli and S. cerevisiae and its impact on the quality of chokeberry juice. Lwt, 136(P1), 110223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110223
Ganesan, A. R., Tiwari, U., Ezhilarasi, P. N., & Rajauria, G. (2021). Application of cold plasma on food matrices: A review on current and future prospects. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 45(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.15070
Gao, Y., Francis, K., & Zhang, X. (2022). Review on formation of cold plasma activated water (PAW) and the applications in food and agriculture. Food Research International, 157, 111246. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2022.111246
Garofulić, I. E., Jambrak, A. R., Milošević, S., Dragović-Uzelac, V., Zorić, Z., & Herceg, Z. (2015). The effect of gas phase plasma treatment on the anthocyanin and phenolic acid content of sour cherry Marasca (Prunus cerasus var. Marasca) juice. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 62(1), 894–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.08.036
Giannoglou, M., Stergiou, P., Dimitrakellis, P., Gogolides, E., Stoforos, N. G., & Katsaros, G. (2020). Effect of cold atmospheric plasma processing on quality and shelf-life of ready-to-eat rocket leafy salad. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 66(August), 102502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2020.102502
Giannoglou, M., Xanthou, Z. M., Chanioti, S., Stergiou, P., Christopoulos, M., Dimitrakellis, P., Efthimiadou, Α., Gogolides, Ε., & Katsaros, G. (2021). Effect of cold atmospheric plasma and pulsed electromagnetic fields on strawberry quality and shelf-life. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 68(January). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2021.102631
Gilmore, B. F., Flynn, P. B., O’Brien, S., Hickok, N., Freeman, T., & Bourke, P. (2018). Cold plasmas for biofilm control: Opportunities and challenges. Trends in Biotechnology, 36(6), 627–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.03.007
Gu, Y., Shi, W., Liu, R., Xing, Y., Yu, X., & Jiang, H. (2021). Cold plasma enzyme inactivation on dielectric properties and freshness quality in bananas. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 69(February), 102649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2021.102649
Guiyun, C., Yushan, W., Mingyue, Z., Wanxing, M., Xixian, X., & Ye, C. (2022). Cold atmospheric plasma treatment improves the γ-aminobutyric acid content of buckwheat seeds providing a new anti-hypertensive functional ingredient. Food Chemistry, 388, 133064. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2022.133064
Guo, L., Zhao, P., Yao, Z., Li, T., Zhu, M., Wang, Z., Huang, L., Niyazi, G., Liu, D., & Rong, M. (2023). Inactivation of Salmonella enteritidis on the surface of eggs by air activated with gliding arc discharge plasma. Food Control, 148, 109662. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCONT.2023.109662
Han, L., Ziuzina, D., Heslin, C., Boehm, D., Patange, A., Sango, D. M., Valdramidis, V. P., Cullen, P. J., & Bourke, P. (2016). Controlling microbial safety challenges of meat using high voltage atmospheric cold plasma. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7(JUN), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00977
Hatzisymeon, M., Tataraki, D., Tsakiroglou, C., Rassias, G., & Aggelopoulos, C. A. (2021). Highly energy-efficient degradation of antibiotics in soil: Extensive cold plasma discharges generation in soil pores driven by high voltage nanopulses. Science of the Total Environment, 786, 147420. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.147420
Hayyan, M., Hashim, M. A., & Alnashef, I. M. (2016). Superoxide ion: Generation and chemical implications. Chemical Reviews, 116(5), 3029–3085. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.CHEMREV.5B00407/ASSET/IMAGES/CR-2015-004079_M052.GIF
Herceg, Z., Kovačević, D. B., Kljusurić, J. G., Jambrak, A. R., Zorić, Z., & Dragović-Uzelac, V. (2016). Gas phase plasma impact on phenolic compounds in pomegranate juice. Food Chemistry, 190, 665–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.135
Hosseini, S. M., Rostami, S., Hosseinzadeh Samani, B., & Lorigooini, Z. (2020). The effect of atmospheric pressure cold plasma on the inactivation of Escherichia coli in sour cherry juice and its qualitative properties. Food Science and Nutrition, 8(2), 870–883. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.1364
Hou, Y., Wang, R., Gan, Z., Shao, T., Zhang, X., He, M., & Sun, A. (2019). Effect of cold plasma on blueberry juice quality. Food Chemistry, 290(October 2018), 79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.123
Houée-Lévin, C., Bobrowski, K., Horakova, L., Karademir, B., Schöneich, C., Davies, M. J., & Spickett, C. M. (2015). Exploring oxidative modifications of tyrosine: An update on mechanisms of formation, advances in analysis and biological consequences, 49(4), 347–373. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2015.1007968
Hozák, P., Jirešová, J., Khun, J., Scholtz, V., & Julák, J. (2022). Shelf life prolongation of fresh strawberries by nonthermal plasma treatment. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 46(9), e16150. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFPP.16150
Huang, Y., Wang, H., Liu, Q., Zhou, J., Gao, S., Yu, J., Zhang, X., & Wang, M. (2022). Comparing impacts of dielectric barrier discharge plasma and electron beam irradiation processing on characteristics of Tartary buckwheat whole flour. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 77, 102986. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2022.102986
Illera, A. E., Chaple, S., Sanz, M. T., Ng, S., Lu, P., Jones, J., Carey, E., & Bourke, P. (2019). Effect of cold plasma on polyphenol oxidase inactivation in cloudy apple juice and on the quality parameters of the juice during storage. Food Chemistry: X, 3(March). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2019.100049
Illera, A. E., Souza, V. R., Nikmaram, N., Tang, L., & Keener, K. M. (2022). High voltage atmospheric cold plasma decontamination of Salmonella enteritidis on chicken eggs. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 82, 103210. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2022.103210
Inguglia, E. S., Oliveira, M., Burgess, C. M., Kerry, J. P., & Tiwari, B. K. (2020). Plasma-activated water as an alternative nitrite source for the curing of beef jerky: Influence on quality and inactivation of Listeria innocua. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 59, 102276. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2019.102276
Iqbal, A., Murtaza, A., Muhammad, Z., Elkhedir, A. E., Tao, M., & Xu, X. (2018). Inactivation, aggregation and conformational changes of polyphenol oxidase from quince (Cydonia oblonga Miller) juice subjected to thermal and high-pressure carbon dioxide treatment. Molecules 2018, Vol. 23, Page 1743, 23(7), 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES23071743
Jamróz, P., Gręda, K., Pohl, P., & Żyrnicki, W. (2014). Atmospheric pressure glow discharges generated in contact with flowing liquid cathode: Production of active species and application in wastewater purification processes. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 34(1), 25–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11090-013-9503-3/FIGURES/7
Jayasena, D. D., Kim, H. J., Yong, H. I., Park, S., Kim, K., Choe, W., & Jo, C. (2015). Flexible thin-layer dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment of pork butt and beef loin: Effects on pathogen inactivation and meat-quality attributes. Food Microbiology, 46, 51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2014.07.009
Ji, Y., Hu, W., Liao, J., Jiang, A., Xiu, Z., Gaowa, S., Guan, Y., Yang, X., Feng, K., & Liu, C. (2020). Effect of atmospheric cold plasma treatment on antioxidant activities and reactive oxygen species production in postharvest blueberries during storage. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 100(15), 5586–5595. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10611
Jurov, A., Škoro, N., Spasić, K., Modic, M., Hojnik, N., Vujošević, D., Đurović, M., Petrović, Z. L., & Cvelbar, U. (2022). Helium atmospheric pressure plasma jet parameters and their influence on bacteria deactivation in a medium. The European Physical Journal D 2022 76:2, 76(2), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1140/EPJD/S10053-022-00357-Y
Joy, K., & J., Kalaivendan, R. G. T., Eazhumalai, G., Kahar, S. P., & Annapure, U. S. (2022). Effect of pin-to-plate atmospheric cold plasma on jackfruit seed flour functionality modification. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 78, 103009. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2022.103009
Kalaivendan, R. G. T., Eazhumalai, G., & Annapure, U. S. (2023). Impact of novel atmospheric pin-to-plate cold plasma on a seed galactomannan: Physical and chemical characteristics and its application in orange juice stabilization. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2023(1), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-023-03129-7
Kang, C., Xiang, Q., Zhao, D., Wang, W., Niu, L., & Bai, Y. (2019). Inactivation of Pseudomonas deceptionensis CM2 on chicken breasts using plasma-activated water. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 56(11), 4938–4945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03964-7
Karunanithi, S., Guha, P., & Srivastav, P. P. (2022). Cold plasma-assisted microwave pretreatment on essential oil extraction from betel leaves: process optimization and its quality. Food and Bioprocess Technology 2022 16:3, 16(3), 603–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-022-02957-3
Katsigiannis, A. S., Hojnik, N., Modic, M., Bayliss, D. L., Kovač, J., & Walsh, J. L. (2022). Continuous in-line decontamination of food-processing surfaces using cold atmospheric pressure air plasma. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 81, 103150. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2022.103150
Kaur, M., Kumar, S., Samota, M. K., & Lalremmawii. (2023). Ohmic heating technology systems, factors governing efficiency and its application to inactivation of pathogenic microbial, enzyme inactivation, and extraction of juice, oil, and bioactive compounds in the food sector. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1, 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-023-03126-W/TABLES/8
Kaushik, N. K., Ghimire, B., Li, Y., Adhikari, M., Veerana, M., Kaushik, N., Jha, N., Adhikari, B., Lee, S. J., Masur, K., Von Woedtke, T., Weltmann, K. D., & Choi, E. H. (2018). Biological and medical applications of plasmaactivated. Biological Chemistry, 400(1), 39–62. https://doi.org/10.1515/HSZ-2018-0226/XML
Ke, Z., Bai, Y., Zhu, H., Xiang, X., Liu, S., Zhou, X., & Ding, Y. (2022). Characteristics of myoglobin degradation by cold plasma and its pro-oxidative activity on lipid in washed fish muscle. Food Chemistry, 389, 132972. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2022.132972
Ke, Z., & Huang, Q. (2013). Inactivation and heme degradation of horseradish peroxidase induced by discharge plasma. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 10(8), 731–739. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppap.201300035
Khani, M. R., Shokri, B., & Khajeh, K. (2017). Studying the performance of dielectric barrier discharge and gliding arc plasma reactors in tomato peroxidase inactivation. Journal of Food Engineering, 197, 107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.11.012
Kheto, A., Mallik, A., Sehrawat, R., Gul, K., & Routray, W. (2023). Atmospheric cold plasma induced nutritional & anti-nutritional, molecular modifications and in-vitro protein digestibility of guar seed (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.) flour. Food Research International, 168, 112790. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2023.112790
Khodabandeh, M., Azizi, M., Shokri, B., Bahreini, M., Rezadoost, H., & Salehi, M. (2023). Optimization of the radiofrequency low-pressure cold plasma conditions for decontamination of saffrons. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1, 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-023-03112-2/FIGURES/6
Khoshkalam Pour, A., Khorram, S., Ehsani, A., Ostadrahimi, A., & Ghasempour, Z. (2022). Atmospheric cold plasma effect on quality attributes of banana slices: Its potential use in blanching process. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 76(December 2021), 102945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2022.102945
Kim, B., Yun, H., Jung, S., Jung, Y., Jung, H., Choe, W., & Jo, C. (2011). Effect of atmospheric pressure plasma on inactivation of pathogens inoculated onto bacon using two different gas compositions. Food Microbiology, 28(1), 9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2010.07.022
Kim, H. J., Yong, H. I., Park, S., Choe, W., & Jo, C. (2013). Effects of dielectric barrier discharge plasma on pathogen inactivation and the physicochemical and sensory characteristics of pork loin. Current Applied Physics, 13(7), 1420–1425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2013.04.021
Kim, J. E., Oh, Y. J., Won, M. Y., Lee, K. S., & Min, S. C. (2017). Microbial decontamination of onion powder using microwave-powered cold plasma treatments. Food Microbiology, 62, 112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2016.10.006
Kim, J. H., & Min, S. C. (2018). Moisture vaporization-combined helium dielectric barrier discharge-cold plasma treatment for microbial decontamination of onion flakes. Food Control, 84, 321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCONT.2017.08.018
Kim, S. Y., Lee, S. Y., & Min, S. C. (2019). Improvement of the antioxidant activity, water solubility, and dispersion stability of prickly pear cactus fruit extracts using argon cold plasma treatment. Journal of Food Science, 84(10), 2876–2882. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14791
Klämpfl, T. G., Isbary, G., Shimizu, T., Li, Y. F., Zimmermann, J. L., Stolz, W., Schlegel, J., Morfill, G. E., & Schmidt, H. U. (2012). Cold atmospheric air plasma sterilization against spores and other microorganisms of clinical interest. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78(15), 5077–5082. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00583-12/ASSET/20A88143-323B-4E4D-83A0-94A42462CD63/ASSETS/GRAPHIC/ZAM9991034400005.JPEG
Kogelschatz, U. (2003). Dielectric-barrier discharges: Their history, discharge physics, and industrial applications. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 23(1), 1–46. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022470901385/METRICS
Kumar, S., Pipliya, S., & Srivastav, P. P. (2023a). Effect of cold plasma on different polyphenol compounds: A review. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 46(1), e14203. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFPE.14203
Kumar, S., Pipliya, S., & Srivastav, P. P. (2023b). Effect of cold plasma processing on physicochemical and nutritional quality attributes of kiwifruit juice. Journal of Food Science. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.16494
Kumar, S., Pipliya, S., & Srivastav, P. P. (2023c). nth order kinetic modelling of peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase inactivation in kiwifruit juice during cold plasma and thermal treatment. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 103475. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2023.103475
Laroussi, M. (2023). The dielectric barrier discharge and the start of a beautiful friendship: Personal remembrance of Dr. Ulrich Kogelschatz. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 2023, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11090-023-10313-2
Lee, H.-J., Jung, S., Jung, H.-S., Park, S.-H., Choe, W.-H., Ham, J.-S., & Jo, C. (2012). Evaluation of a dielectric barrier discharge plasma system for inactivating pathogens on cheese slices. Journal of Animal Science and Technology, 54(3), 191–198. https://doi.org/10.5187/jast.2012.54.3.191
Lee, H., Kim, J. E., Chung, M. S., & Min, S. C. (2015). Cold plasma treatment for the microbiological safety of cabbage, lettuce, and dried figs. Food Microbiology, 51, 74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2015.05.004
Lee, H. S., Kim, N., & Min, S. C. (2022a). Inactivation of Salmonella in steamed fish cake using an in-package combined treatment of cold plasma and ultraviolet-activated zinc oxide. Food Control, 135, 108772. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCONT.2021.108772
Lee, H. S., Lee, H., Ryu, S., Eom, S., & Min, S. C. (2023). In-package cold plasma treatment for microbial inactivation in plastic-pouch packaged steamed rice cakes. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 389, 110108. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJFOODMICRO.2023.110108
Lee, H. S., Park, H. H., & Min, S. C. (2020). Microbial decontamination of red pepper powder using pulsed light plasma. Journal of Food Engineering, 284(January), 110075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.110075
Lee, M. J., Lee, H. J., Lee, Y., Yang, J. Y., Song, J. S., Woo, S. Y., Kim, H. Y., Song, S. Y., Seo, W. D., Son, Y. J., & Park, S. I. (2022b). Cold plasma treatment increases bioactive metabolites in oat (Avena sativa L.) sprouts and enhances in vitro osteogenic activity of their extracts. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 1, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11130-022-01029-3/FIGURES/3
Lee, S. H. I., Fröhling, A., Schlüter, O., Corassin, C. H., De Martinis, E. C. P., Alves, V. F., Pimentel, T. C., & Oliveira, C. A. F. (2021). Cold atmospheric pressure plasma inactivation of dairy associated planktonic cells of Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus. Lwt, 146(April). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111452
Lee, S. Y., In, J., Chung, M. S., & Min, S. C. (2021). Microbial decontamination of particulate food using a pilot-scale atmospheric plasma jet treatment system. Journal of Food Engineering, 294(December 2020), 110436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.110436
Lee, K. H., Kim, H. J., Woo, K. S., Jo, C., Kim, J. K., Kim, S. H., & Kim, W. H. (2016). Evaluation of cold plasma treatments for improved microbial and physicochemical qualities of brown rice. Lwt, 73, 442–447.
Lee, S. Y., Lee, W. K., Lee, J. W., Chung, M. S., Oh, S. W., Shin, J. K., & Min, S. C. (2021). Microbial decontamination of rice germ using a large-scale plasma jet-pulsed light-ultraviolet-c integrated treatment system. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14(3), 542–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02590-6
Leins, M., Kopecki, J., Gaiser, S., Schulz, A., Walker, M., Schumacher, U., Stroth, U., & Hirth, T. (2014). Microwave plasmas at atmospheric pressure. Contributions to Plasma Physics, 54(1), 14–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctpp.201300033
Li, X., Li, M., Ji, N., Jin, P., Zhang, J., Zheng, Y., & Li, F. (2019). Cold plasma treatment induces phenolic accumulation and enhances antioxidant activity in fresh-cut pitaya (Hylocereus undatus) fruit. Lwt, 115, 108447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108447
Li, S., Zhang, R., Lei, D., Huang, Y., Cheng, S., Zhu, Z., Wu, Z., & Cravotto, G. (2021). Impact of ultrasound, microwaves and high-pressure processing on food components and their interactions. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 109, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIFS.2021.01.017
Li, R., Zhu, H., Chen, Y., Zhou, G., Li, C., & Ye, K. (2022). Cold plasmas combined with Ar-based MAP for meatball products: Influence on microbiological shelflife and quality attributes. LWT, 159, 113137. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LWT.2022.113137
Li, J., Zhou, Y., & Lu, W. (2023). Enhancement of haskap vacuum freeze-drying efficiency and quality attributes using cold plasma pretreatment. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-023-03186-Y/FIGURES/7
Liao, X., Li, J., Muhammad, A. I., Suo, Y., Chen, S., Ye, X., Liu, D., & Ding, T. (2018). Application of a dielectric barrier discharge atmospheric cold plasma (Dbd-Acp) for Eshcerichia Coli inactivation in apple juice. Journal of Food Science, 83(2), 401–408. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14045
Liao, X., Liu, D., Xiang, Q., Ahn, J., Chen, S., Ye, X., & Ding, T. (2017). Inactivation mechanisms of non-thermal plasma on microbes: A review. Food Control, 75, 83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.12.021
Lin, C. M., Patel, A. K., Chiu, Y. C., Hou, C. Y., Kuo, C. H., Dong, C. D., & Chen, H. L. (2022). The application of novel rotary plasma jets to inhibit the aflatoxin-producing Aspergillus flavus and the spoilage fungus, Aspergillus niger on peanuts. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 78, 102994. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2022.102994
Liu, Y., Sun, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., Duan, M., Wang, H., Dai, R., Liu, Y., Li, X., & Jia, F. (2023). Inactivation mechanisms of atmospheric pressure plasma jet on Bacillus cereus spores and its application on low-water activity foods. Food Research International, 169, 112867. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2023.112867
Liu, Z., Zhao, W., Zhang, Q., Gao, G., & Meng, Y. (2021). Effect of cold plasma treatment on sterilizing rate and quality of kiwi turbid juice. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 44(6). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.13711
Lu, X., Naidis, G. V., Laroussi, M., Reuter, S., Graves, D. B., & Ostrikov, K. (2016). Reactive species in non-equilibrium atmospheric-pressure plasmas: Generation, transport, and biological effects. Physics Reports, 630, 1–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYSREP.2016.03.003
Luo, J., Xu, W., Liu, Q., Zou, Y., Wang, D., & Zhang, J. (2022). Dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma treatment of pork loin: Effects on muscle physicochemical properties and emulsifying properties of pork myofibrillar protein. LWT, 162, 113484. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LWT.2022.113484
Malinowski, S., Herbert, P. A. F., Rogalski, J., & Jaroszyńska-Wolińska, J. (2018). Laccase enzyme polymerization by soft plasma jet for durable bioactive coatings. Polymers, 10(5), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM10050532
Mandal, R., Singh, A., & Pratap Singh, A. (2018). Recent developments in cold plasma decontamination technology in the food industry. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 80(July), 93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.07.014
Mehta, D., Sharma, N., Bansal, V., Sangwan, R. S., & Yadav, S. K. (2019). Impact of ultrasonication, ultraviolet and atmospheric cold plasma processing on quality parameters of tomato-based beverage in comparison with thermal processing. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 52(January), 343–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2019.01.015
Mehta, D., Yadav, K., Chaturvedi, K., Shivhare, U. S., & Yadav, S. K. (2022). Impact of cold plasma on extraction of polyphenol from de-oiled rice and corn bran: Improvement in extraction efficiency, in vitro digestibility, antioxidant activity, cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory responses. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(5), 1142–1156. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-022-02801-8/FIGURES/6
Mehta, D., & Yadav, S. K. (2020). Impact of atmospheric non-thermal plasma and hydrothermal treatment on bioactive compounds and microbial inactivation of strawberry juice: A hurdle technology approach. Food Science and Technology International, 26(1), 3–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/1082013219865360
Mehta, D., & Yadav, S. K. (2022). Recent advances in cold plasma technology for food processing. Food Engineering Reviews, 14(4), 555–578. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12393-022-09317-Z
Miguel, T. B. A. R., Porto, E. C. M., de Paiva Pinheiro, S. K., de Castro Miguel, E., Fernandes, F. A. N., & Rodrigues, S. (2021). Protective effect of natural and processed coconut water by non-thermal technologies against oxidative stress in brine shrimp (Artemia salina). Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14(4), 702–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-021-02600-7/FIGURES/9
Min, S. C., Roh, S. H., Niemira, B. A., Sites, J. E., Boyd, G., & Lacombe, A. (2016). Dielectric barrier discharge atmospheric cold plasma inhibits Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, and Tulane virus in Romaine lettuce. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 237, 114–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJFOODMICRO.2016.08.025
Misra, N. N., Kaur, S., Tiwari, B. K., Kaur, A., Singh, N., & Cullen, P. J. (2015). Atmospheric pressure cold plasma (ACP) treatment of wheat flour. Food Hydrocolloids, 44, 115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.08.019
Misra, N. N., Pankaj, S. K., Segat, A., & Ishikawa, K. (2016). Cold plasma interactions with enzymes in foods and model systems. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 55(April 2018), 39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2016.07.001
Misra, N. N., Patil, S., Moiseev, T., Bourke, P., Mosnier, J. P., Keener, K. M., & Cullen, P. J. (2014). In-package atmospheric pressure cold plasma treatment of strawberries. Journal of Food Engineering, 125(1), 131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.10.023
Misra, N. N., Schlüter, O., & Cullen, P. J. (2016). Plasma in Food and Agriculture. In Cold Plasma in Food and Agriculture, 1–16. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801365-6.00001-9
Misra, N. N., Tiwari, B. K., Raghavarao, K. S. M. S., & Cullen, P. J. (2011). Nonthermal plasma inactivation of food-borne pathogens. Food Engineering Reviews, 3(3–4), 159–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-011-9041-9
Misra, N. N., Yadav, B., Roopesh, M. S., & Jo, C. (2018). Cold plasma for effective fungal and mycotoxin control in foods: Mechanisms, inactivation effects, and applications. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 18, 106–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12398
Mohamed, E. E., Younis, E. R., & Mohamed, E. A. (2021). Impact of atmospheric cold plasma (ACP) on maintaining bolti fish (Tilapia nilotica) freshness and quality criteria during cold storing. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 45(5), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.15442
Mol, S., Akan, T., Kartal, S., Coşansu, S., Tosun, ŞY., Alakavuk, D. Ü., Ulusoy, Ş, Doğruyol, H., & Bostan, K. (2022). Effects of air and helium cold plasma on sensory acceptability and quality of fresh sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Food and Bioprocess Technology, 16(3), 537–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-022-02950-W/FIGURES/8
Molina-Hernandez, J. B., Laika, J., Peralta-Ruiz, Y., Palivala, V. K., Tappi, S., Cappelli, F., Ricci, A., Neri, L., & Chaves-López, C. (2022). Influence of atmospheric cold plasma exposure on naturally present fungal spores and physicochemical characteristics of sundried tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Foods, 11(2), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/FOODS11020210/S1
Mousavi, M., Hosseini, S. M., Hosseini, H., Abedi, A. S., Khani, M., Heshmati, A., Abhari, K., Shahraz, F., Taghizadeh, M., & Akhavan, A. (2022). Gliding arc plasma discharge conditions on microbial, physicochemical, and sensory properties of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei): In vivo and in vitro studies. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(10), 2327–2343. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-022-02886-1/FIGURES/7
Namini, Y. N., Heidarzadeh, S., Khaledi, A., Abbasi, E., Abbasi, A., & Esmaeili, D. (2019). Study on the killing effect of cold atmospheric pressure plasma on MRSA Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo infection model. Malaysian Journal of Microbiology, 15(5), 394–399. https://doi.org/10.21161/mjm.180295
Namjoo, M., Moradi, M., Dibagar, N., & Niakousari, M. (2022). Cold plasma pretreatment prior to ultrasound-assisted air drying of cumin seeds. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(9), 2065–2083. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-022-02863-8/FIGURES/9
Nasiru, M. M., Boateng, E. F., Alnadari, F., Umair, M., Wang, Z., Senan, A. M., Yan, W., Zhuang, H., & Zhang, J. (2023). Dielectric barrier discharge cold atmospheric plasma treatment of egg white protein: Insights into the functional, rheological, and structural properties. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2023(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-023-03159-1
Niedźwiedź, I., Płotka-Wasylka, J., Kapusta, I., Simeonov, V., Stój, A., Waśko, A., Pawłat, J., & Polak-Berecka, M. (2022). The impact of cold plasma on the phenolic composition and biogenic amine content of red wine. Food Chemistry, 381, 132257. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2022.132257
Niemira, B. A. (2012). Cold plasma decontamination of foods. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 3(1), 125–142. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-food-022811-101132
Ocaña de Jesus, R. L., Ibanez, A. T. G., Puebla, I. R., Diaz, A. G., Romero, P. G. R., Sanchez, J. V., Segundo, C. T., & Valencia, H. M. (2022). Microbiological study of the effect of a dielectric barrier discharge interaction on processed orange juices exposed to the environment. Food Science and Technology, 42. https://doi.org/10.1590/fst.02622
Oh, Y. J., Song, A. Y., & Min, S. C. (2017). Inhibition of Salmonella typhimurium on radish sprouts using nitrogen-cold plasma. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 249, 66–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.03.005
Okyere, A. Y., Rajendran, S., & Annor, G. A. (2022). Cold plasma technologies: Their effect on starch properties and industrial scale-up for starch modification. Current Research in Food Science, 5, 451–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CRFS.2022.02.007
Olatunde, O. O., & Benjakul, S. (2018). Nonthermal processes for shelf-life extension of seafoods: A revisit. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 17(4), 892–904. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12354
Oner, M. E., Gultekin Subasi, B., Ozkan, G., Esatbeyoglu, T., & Capanoglu, E. (2023). Efficacy of cold plasma technology on the constituents of plant-based food products: Principles, current applications, and future potentials. Food Research International, 172, 113079. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2023.113079
Ott, L. C., Jochum, J., Burrough, L., Clark, S., Keener, K., & Mellata, M. (2022). High voltage atmospheric cold plasma inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes in fresh digitatum cheese. Food Microbiology, 105, 104007. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FM.2022.104007
Ozen, E., Kumar, G. D., Mishra, A., & Singh, R. K. (2022). Inactivation of Escherichia coli in apple cider using atmospheric cold plasma. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 382, 109913. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJFOODMICRO.2022.109913
Ozen, E., & Singh, R. K. (2020). Atmospheric cold plasma treatment of fruit juices: A review. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 103(July), 144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.07.020
Paixão, L. M. N., Fonteles, T. V., Oliveira, V. S., Fernandes, F. A. N., & Rodrigues, S. (2019). Cold plasma effects on functional compounds of siriguela juice. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(1), 110–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2197-z
Pan, Y., Li, T., Wu, C., Guo, S., Fan, G., Li, X., Zhou, D., & Hua, X. (2023). Subcellular damages of pathogenic fungi combined with gene expression analysis reveals mechanisms that cold plasma controlling apricot disease. Food Bioscience, 53, 102728. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FBIO.2023.102728
Pankaj, S. K., Bueno-Ferrer, C., O’Neill, L., Tiwari, B. K., Bourke, P., & Cullen, P. J. (2017). Characterization of dielectric barrier discharge atmospheric air plasma treated chitosan films. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 41(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.12889
Pankaj, S. K., Wan, Z., Colonna, W., & Keener, K. M. (2017b). Effect of high voltage atmospheric cold plasma on white grape juice quality. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 97(12), 4016–4021. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8268
Pankaj, S. K., Wan, Z., & Keener, K. M. (2018). Effects of cold plasma on food quality: A review. Foods, 7(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7010004
Park, H., Puligundla, P., & Mok, C. (2020). Cold plasma decontamination of brown rice grains: Impact on biochemical and sensory qualities of their corresponding seedlings and aqueous tea infusions. Lwt, 131(June), 109508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109508
Park, Y. jae, Puligundla, P., & Mok, C. (2021). Decontamination of chokeberries (Aronia melanocarpa L.) by cold plasma treatment and its effects on biochemical composition and storage quality of their corresponding juices. Food Science and Biotechnology, 30(3), 405–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-020-00867-8
Pathak, N., Grossi Bovi, G., Limnaios, A., Fröhling, A., Brincat, J. P., Taoukis, P., Valdramidis, V. P., & Schlüter, O. (2020). Impact of cold atmospheric pressure plasma processing on storage of blueberries. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 44(February), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.14581
Phaniendra, A., Jestadi, D. B., & Periyasamy, L. (2015). Free radicals: Properties, sources, targets, and their implication in various diseases. Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry, 30(1), 11–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-014-0446-0
Pipliya, S., Kumar, S., Babar, N., & Srivastav, P. P. (2023). Recent trends in non-thermal plasma and plasma activated water: Effect on quality attributes, mechanism of interaction and potential application in food & agriculture. Food Chemistry Advances, 2, 100249. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOCHA.2023.100249
Pipliya, S., Kumar, S., & Srivastav, P. P. (2022). Inactivation kinetics of polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase in pineapple juice by dielectric barrier discharge plasma technology. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 80(February), 103081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2022.103081
Pipliya, S., Kumar, S., & Srivastav, P. P. (2023a). Effect of dielectric barrier discharge nonthermal plasma treatment on physicochemical, nutritional, and phytochemical quality attributes of pineapple [Ananas comosus (L.)] juice. Journal of Food Science, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.16767
Pipliya, S., Kumar, S., & Srivastav, P. P. (2023b). Modeling of the inactivation kinetics of aerobic mesophiles and yeasts and molds natural microbiota in nonthermal plasma-treated pineapple (Ananas comosus) juice. Journal of Food Science. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.16721
Porto, E., Alves Filho, E. G., Silva, L. M. A., Fonteles, T. V., do Nascimento, R. B. R., Fernandes, F. A. N., de Brito, E. S., & Rodrigues, S. (2020). Ozone and plasma processing effect on green coconut water. Food Research International, 131(December 2019), 109000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109000
Pourbagher, R., Abbaspour-Fard, M. H., Khomeiri, M., Sohbatzadeh, F., & Rohani, A. (2022). Effects of gas type and cold plasma treatment time on Lecanicillium fungicola spores reduction and changes in qualitative, chemical, and physiological characteristics of button mushroom during postharvest storage. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 46(10), e16901. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFPP.16901
Privat-Maldonado, A., Schmidt, A., Lin, A., Weltmann, K. D., Wende, K., Bogaerts, A., & Bekeschus, S. (2019). ROS from physical plasmas: redox chemistry for biomedical therapy. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9062098
Ramazzina, I., Berardinelli, A., Rizzi, F., Tappi, S., Ragni, L., Sacchetti, G., & Rocculi, P. (2015). Effect of cold plasma treatment on physico-chemical parameters and antioxidant activity of minimally processed kiwifruit. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 107, 55–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.04.008
Ranjha, M. M. A. N., Shafique, B., Aadil, R. M., Manzoor, M. F., & Cheng, J. H. (2023). Modification in cellulose films through ascent cold plasma treatment and polymerization for food products packaging. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 134, 162–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIFS.2023.03.011
Rao, W., Li, Y., Dhaliwal, H., Feng, M., Xiang, Q., Roopesh, M. S., Pan, D., & Du, L. (2023). The application of cold plasma technology in low-moisture foods. Food Engineering Reviews, 15(1), 86–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12393-022-09329-9
Rashvand, M., Altieri, G., Abbaszadeh, R., Matera, A., Genovese, F., Feyissa, A. H., & Di Renzo, G. C. (2023). Prediction of CO2 and ethylene produced in-packaged apricot under cold plasma treatment by machine learning approach. Journal of Food Process Engineering, e14418. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFPE.14418
Ravash, N., Hesari, J., Feizollahi, E., Dhaliwal, H. K., & Roopesh, M. S. (2023). Valorization of cold plasma technologies for eliminating biological and chemical food hazards. Food Engineering Reviews, 2023(1), 1–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12393-023-09348-0
Ricciardi, E. F., Del Nobile, M. A., Conte, A., Fracassi, F., & Sardella, E. (2022). Effects of plasma treatments applied to fresh ricotta cheese. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 76, 102935. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2022.102935
Rød, S. K., Hansen, F., Leipold, F., & Knøchel, S. (2012). Cold atmospheric pressure plasma treatment of ready-to-eat meat: Inactivation of Listeria innocua and changes in product quality. Food Microbiology, 30(1), 233–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2011.12.018
Rodacka, A., Gerszon, J., Puchala, M., & Bartosz, G. (2016). Radiation-induced inactivation of enzymes – Molecular mechanism based on inactivation of dehydrogenases. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 128, 112–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RADPHYSCHEM.2016.05.022
Rodacka, A., Serafin, E., & Puchala, M. (2010). Efficiency of superoxide anions in the inactivation of selected dehydrogenases. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 79(9), 960–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RADPHYSCHEM.2010.04.001
Rodrigues, S., & Fernandes, F. A. N. (2022a). Effect of dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment in pasteurized orange juice: Changes in volatile composition, aroma, and mitigation of off-flavors. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 16(4), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-022-02976-0/FIGURES/4
Rodrigues, S., & Fernandes, F. A. N. (2022b). Glow discharge plasma processing for the improvement of pasteurized orange juice’s aroma and off-flavor. Processes, 10(9), 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/PR10091812
Rodriguez-Aguilera, R., Oliveira, J. C., Montanez, J. C., & Mahajan, P. V. (2011). Effect of modified atmosphere packaging on quality factors and shelf-life of surface mould ripened cheese: Part I constant temperature. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 44(1), 330–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LWT.2010.06.015
Rodríguez, Ó., Gomes, W. F., Rodrigues, S., & Fernandes, F. A. N. (2017). Effect of indirect cold plasma treatment on cashew apple juice (Anacardium occidentale L.). LWT - Food Science and Technology, 84, 457–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.06.010
Rodriguez, Ó., Rodrigues, S., & Fernandes, F. A. N. (2022). Effect of glow discharge plasma technology on the phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of four tropical juices with different phenolic composition. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 46(1), e16110. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFPP.16110
Roshanak, S., Maleki, M., Sani, M. A., Tavassoli, M., Pirkhezranian, Z., & Shahidi, F. (2023). The impact of cold plasma innovative technology on quality and safety of refrigerated hamburger: Analysis of microbial safety and physicochemical properties. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 388, 110066. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJFOODMICRO.2022.110066
Sabanci, S., Cevik, M., Cokgezme, O. F., Yildiz, H., & Icier, F. (2019). Quality characteristics of pomegranate juice concentrates produced by ohmic heating assisted vacuum evaporation. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 99(5), 2589–2595. https://doi.org/10.1002/JSFA.9474
Salleh, S. Z., Yusoff, A. H., Zakaria, S. K., Taib, M. A. A., Abu Seman, A., Masri, M. N., Mohamad, M., Mamat, S., Ahmad Sobri, S., Ali, A., & Teo, P. T. (2021). Plant extracts as green corrosion inhibitor for ferrous metal alloys: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 304, 127030. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2021.127030
Sani, I. K., Aminoleslami, L., Mirtalebi, S. S., Sani, M. A., Mansouri, E., Eghbaljoo, H., Jalil, A. T., Thanoon, R. D., Khodaei, S. M., Mohammadi, F., & Kazemzadeh, B. (2023). Cold plasma technology: Applications in improving edible films and food packaging. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 37, 101087. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FPSL.2023.101087
Sarangapani, C., O’Toole, G., Cullen, P. J., & Bourke, P. (2017). Atmospheric cold plasma dissipation efficiency of agrochemicals on blueberries. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 44, 235–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2017.02.012
Saremnezhad, S., Soltani, M., Faraji, A., & Hayaloglu, A. A. (2021). Chemical changes of food constituents during cold plasma processing: A review. Food Research International, 147(December 2020), 110552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110552
Sarkar, A., Niranjan, T., Patel, G., Kheto, A., Tiwari, B. K., & Dwivedi, M. (2023). Impact of cold plasma treatment on nutritional, antinutritional, functional, thermal, rheological, and structural properties of pearl millet flour. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 46(5), e14317. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFPE.14317
Schmidt, M., Schneider, R., & Wagner, H. (2013). Physics of nonthermal plasmas. In Nonthermal Plasma Chemistry and Physics. https://doi.org/10.1201/b12956-8
Setsuhara, Y., Cho, K., Shiratani, M., Sekine, M., & Hori, M. (2013). Plasma interactions with aminoacid (l-alanine) as a basis of fundamental processes in plasma medicine. Current Applied Physics, 13(SUPPL.1), S59–S63. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CAP.2013.01.030
Shao, L., Zhao, Y., Zou, B., Li, X., & Dai, R. (2021). Ohmic heating in fruit and vegetable processing: Quality characteristics, enzyme inactivation, challenges and prospective. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 118, 601–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIFS.2021.10.009
Sharma, S., Prabhakar, H., & Singh, R. K. (2022). Atmospheric cold plasma-induced changes in milk proteins. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(12), 2737–2748. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-022-02915-Z/TABLES/5
Sharma, S., & Singh, R. K. (2022). Effect of atmospheric pressure cold plasma treatment time and composition of feed gas on properties of skim milk. LWT, 154, 112747. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LWT.2021.112747
Shelar, A., Singh, A. V., Dietrich, P., Maharjan, R. S., Thissen, A., Didwal, P. N., Shinde, M., Laux, P., Luch, A., Mathe, V., Jahnke, T., Chaskar, M., & Patil, R. (2022). Emerging cold plasma treatment and machine learning prospects for seed priming: A step towards sustainable food production. RSC Advances, 12(17), 10467–10488. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA00809B
Shen, J., Sun, Q., Zhang, Z., Cheng, C., Lan, Y., Zhang, H., Xu, Z., Zhao, Y., Xia, W., & Chu, P. K. (2015). Characteristics of DC gas-liquid phase atmospheric-pressure plasma and bacteria inactivation mechanism. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 12(3), 252–259. https://doi.org/10.1002/PPAP.201400129
Shintani, H., Sakudo, A., Burke, P., & McDonnell, G. (2010). Gas plasma sterilization of microorganisms and mechanisms of action. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 1(5), 731–738. https://doi.org/10.3892/ETM.2010.136/HTML
Shirani, K., Shahidi, F., & Mortazavi, S. A. (2020). Investigation of decontamination effect of argon cold plasma on physicochemical and sensory properties of almond slices. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 335(September), 108892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108892
Silva, R. M., Filho, E. G. A., Campelo, P. H., Silva, F. E. F., Zampieri, D. S., Gramosa, N. V., Fernandes, F. A. N., & Rodrigues, S. (2022). NMR spectroscopy and chemometrics to evaluate the effect of different non-thermal plasma processing on sapota-do-solimões (Quararibea cordata Vischer) juice quality and composition. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(4), 875–890. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-022-02792-6/TABLES/4
Situ, H., Li, Y., Gao, J., Zhang, C., Qin, X., Cao, W., Lin, H., & Chen, Z. (2023). Effects of cold atmospheric plasma on endogenous enzyme activity and muscle protein oxidation in Trachinotus ovatus. Food Chemistry, 407, 135119. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2022.135119
Song, A. Y., Oh, Y. J., Kim, J. E., Song, K. B., Oh, D. H., & Min, S. C. (2015). Cold plasma treatment for microbial safety and preservation of fresh lettuce. Food Science and Biotechnology, 24(5), 1717–1724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0223-8
Sriraksha, M. S., Ayenampudi, S. B., Noor, M., Raghavendra, S. N., & Chakka, A. K. (2022). Cold plasma technology: An insight on its disinfection efficiency of various food systems, 29(4), 428–441. https://doi.org/10.1177/10820132221089169
Starek, A., Pawłat, J., Chudzik, B., Kwiatkowski, M., Terebun, P., Sagan, A., & Andrejko, D. (2019). Evaluation of selected microbial and physicochemical parameters of fresh tomato juice after cold atmospheric pressure plasma treatment during refrigerated storage. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44946-1
Stoica, M., Alexe, P., & Mihalcea, L. (2014). Atmospheric cold plasma as new strategy for foods processing -An overview. Innovative Romanian Food Biotechnology, 15(February 2020). https://www.bioaliment.ugal.ro/revista/15/paper%2015.1.pdf
Subrahmanyam, K., Gul, K., Sehrawat, R., & Allai, F. M. (2023). Impact of in-package cold plasma treatment on the physicochemical properties and shelf life of button mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus). Food Bioscience, 52, 102425. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FBIO.2023.102425
Sudarsan, A., & Keener, K. (2022). Inactivation of spoilage organisms on baby spinach leaves using high voltage atmospheric cold plasma (HVACP) and assessment of quality. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 79, 103023. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2022.103023
Surowsky, B., Fischer, A., Schlueter, O., & Knorr, D. (2013). Cold plasma effects on enzyme activity in a model food system. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 19, 146–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2013.04.002
Surowsky, B., Fröhling, A., Gottschalk, N., Schlüter, O., & Knorr, D. (2014). Impact of cold plasma on Citrobacter freundii in apple juice: Inactivation kinetics and mechanisms. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 174, 63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.12.031
Takai, E., Kitamura, T., Kuwabara, J., Ikawa, S., Yoshizawa, S., Shiraki, K., Kawasaki, H., Arakawa, R., & Kitano, K. (2014). Chemical modification of amino acids by atmospheric-pressure cold plasma in aqueous solution. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 47(28). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/47/28/285403
Takai, E., Kitano, K., Kuwabara, J., & Shiraki, K. (2012). Protein inactivation by low-temperature atmospheric pressure plasma in aqueous solution. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 9(1), 77–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppap.201100063
Takamatsu, T., Uehara, K., Sasaki, Y., Miyahara, H., Matsumura, Y., Iwasawa, A., Ito, N., Azuma, T., Kohno, M., & Okino, A. (2014). Investigation of reactive species using various gas plasmas. RSC Advances, 4(75), 39901–39905. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA05936K
Takenaka, K., & Setsuhara, Y. (2013). Plasma interactions with organic materials in liquid through plasma/liquid interface. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(11 PART 2), 11NE04. https://doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.52.11NE04/XML
Tappi, S., Gozzi, G., Vannini, L., Berardinelli, A., Romani, S., Ragni, L., & Rocculi, P. (2016). Cold plasma treatment for fresh-cut melon stabilization. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 33, 225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2015.12.022
Tendero, C., Tixier, C., Tristant, P., Desmaison, J., & Leprince, P. (2006). Atmospheric pressure plasmas: A review. Spectrochimica Acta - Part B Atomic Spectroscopy, 61(1), 2–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2005.10.003
Tiban, N. N., Šimović, M., Polović, M., Šarić, A., Tomac, I., Matić, P., & Jakobek, L. (2022). The effect of high voltage electrical discharge on the physicochemical properties and the microbiological safety of rose hip nectars. Foods, 11(5), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/FOODS11050651/S1
Tolouie, H., Mohammadifar, M. A., Ghomi, H., & Hashemi, M. (2021). Argon and nitrogen cold plasma effects on wheat germ lipolytic enzymes: Comparison to thermal treatment. Food Chemistry, 346(December 2020), 128974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128974
Ulbin-Figlewicz, N., Brychcy, E., & Jarmoluk, A. (2015). Effect of low-pressure cold plasma on surface microflora of meat and quality attributes. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(2), 1228–1232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1108-6
Umair, M., Jabbar, S., Senan, A. M., Sultana, T., Nasiru, M. M., Shah, A. A., & Jianhao, Z. (2019). Influence of combined effect of ultra-sonication and high-voltage cold plasma treatment on quality parameters of carrot juice. Foods, 8(11), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8110593
Umair, M., Jabbar, S., Nasiru, M. M., Senan, A. M., Zhuang, H., & Zhang, J. (2021). Sequential application of high-voltage electric field cold plasma treatment and acid blanching improves the quality of fresh carrot juice (Daucus carota L.). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c03470
Wan, Z., Misra, N. N., Li, G., & Keener, K. M. (2021). High voltage atmospheric cold plasma treatment of Listeria innocua and Escherichia coli K-12 on Queso Fresco (fresh cheese). Lwt, 146(November 2020), 111406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111406
Wang, J., Fu, T., Wang, Y., & Zhang, J. (2022a). Effects of high-voltage atmospheric cold plasma treatment on microbiological and quality characters of tilapia fillets. Foods, 11(16), 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11162398
Wang, J., Xing, C., Xia, J., Chen, H., Zhang, J., & Yan, W. (2023). Degradation of carbendazim in aqueous solution by dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma: Identification and toxicity of degradation products. Food Chemistry, 403, 134329. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2022.134329
Wang, Q., Pal, R. K., Yen, H.-W., Naik, S. P., Orzeszko, M. K., Mazzeo, A., & Salvi, D. (2022b). Cold plasma from flexible and conformable paper-based electrodes for fresh produce sanitation: Evaluation of microbial inactivation and quality changes. Food Control, 137, 108915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.108915
Wang, R. X., Nian, W. F., Wu, H. Y., Feng, H. Q., Zhang, K., Zhang, J., Zhu, W. D., Becker, K. H., & Fang, J. (2012). Atmospheric-pressure cold plasma treatment of contaminated fresh fruit and vegetable slices: Inactivation and physiochemical properties evaluation. European Physical Journal D, 66(10), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2012-30053-1
Wang, X., Han, Y., Niu, H., Zhang, L. H., Xiang, Q., & Zong, W. (2022c). Alternaria mycotoxin degradation and quality evaluation of jujube juice by cold plasma treatment. Food Control, 137, 108926. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCONT.2022.108926
Wang, X., Wang, Z., Zhuang, H., Nasiru, M. M., Yuan, Y., Zhang, J., & Yan, W. (2021). Changes in color, myoglobin, and lipid oxidation in beef patties treated by dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma during storage. Meat Science, 176(February), 108456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2021.108456
Wang, Z., Zhao, Q., Gan, Y., Fan, Q., Hu, Z., Wang, Z., Cai, R., Yue, T., & Yuan, Y. (2023). Inactivation of Alicyclobacillus contaminans spores by dielectric barrier discharge plasma and its biological mechanism. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 87, 103415. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2023.103415
Wei, W., Yang, S., Yang, F., Hu, X., Wang, Y., Guo, W., Yang, B., Xiao, X., & Zhu, L. (2023). Cold plasma controls nitrite hazards by modulating microbial communities in pickled radish. Foods, 12(13), 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/FOODS12132550
Wohlt, D., Schwarz, E., Schieber, A., & Bader-Mittermaier, S. (2021). Effects of extraction conditions on banana peel polyphenol oxidase activity and insights into inactivation kinetics using thermal and cold plasma treatment. Foods, 10(5), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051022
Won, M. Y., Lee, S. J., & Min, S. C. (2017). Mandarin preservation by microwave-powered cold plasma treatment. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 39, 25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2016.10.021
Wu, Q., Shen, C., Li, J., Wu, D., & Chen, K. (2022a). Application of indirect plasma-processed air on microbial inactivation and quality of yellow peaches during storage. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 79, 103044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2022.103044
Wu, Y., Cheng, J.-H., & Sun, D.-W. (2022b). Subcellular damages of Colletotrichum asianum and inhibition of mango anthracnose by dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Food Chemistry, 381, 132197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132197
Wu, Y., Cheng, J. H., Keener, K. M., & Sun, D. W. (2023). Inhibitory effects of dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma on pathogenic enzymes and anthracnose for mango postharvest preservation. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 196, 112181. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.POSTHARVBIO.2022.112181
Xiang, Q., Liu, X., Li, J., Liu, S., Zhang, H., & Bai, Y. (2018). Effects of dielectric barrier discharge plasma on the inactivation of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii and quality of apple juice. Food Chemistry, 254(136), 201–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.02.008
Xu, L., Garner, A. L., Tao, B., & Keener, K. M. (2017). Microbial inactivation and quality changes in orange juice treated by high voltage atmospheric cold plasma. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10(10), 1778–1791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1947-7
Xu, Y., Tian, Y., Ma, R., Liu, Q., & Zhang, J. (2016). Effect of plasma activated water on the postharvest quality of button mushrooms, Agaricus bisporus. Food Chemistry, 197, 436–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.10.144
Yadav, B., & Roopesh, M. S. (2022). Synergistically enhanced Salmonella Typhimurium reduction by sequential treatment of organic acids and atmospheric cold plasma and the mechanism study. Food Microbiology, 104, 103976. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FM.2021.103976
Yang, X., Chang, X., Tei, R., & Nagatsu, M. (2016). Effect of excited nitrogen atoms on inactivation of spore-forming microorganisms in low pressure N2/O2 surface-wave plasma. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 49(23), 235205. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/49/23/235205
Yang, Z., Wu, Q., Jiang, F., Zheng, D., Wu, D., & Chen, K. (2023). Indirect treatment of plasma-processed air to decrease decay and microbiota of strawberry fruit caused by mechanical damage. Food Chemistry, 408, 135225. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2022.135225
Yi, F., Wang, J., Xiang, Y., Yun, Z., Pan, Y., Jiang, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2022). Physiological and quality changes in fresh-cut mango fruit as influenced by cold plasma. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 194, 112105. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.POSTHARVBIO.2022.112105
Yinxin, L., Can, Z., Menglu, H., Cui, S., Jinping, C., Jingyu, W., & Huang, L. (2022). Effect of cold atmospheric plasma on the gray mold rot of postharvest mulberry fruit. Food Control, 137, 108906. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCONT.2022.108906
Yong, H. I., Han, M., Kim, H. J., Suh, J. Y., & Jo, C. (2018). Mechanism underlying green discolouration of myoglobin induced by atmospheric pressure plasma. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28096-4
Zeng, Z., Wang, Y., Xu, G., Zhou, L., Liu, C., & Luo, S. (2023). Peroxidase inactivation by cold plasma and its effects on the storage, physicochemical and bioactive properties of brown rice. Food Bioscience, 52, 102383. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FBIO.2023.102383
Zeraatpisheh, F., Tabatabaei Yazdi, F., & Shahidi, F. (2022). Investigation of effect of cold plasma on microbial load and physicochemical properties of ready-to-eat sliced chicken sausage. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 59(10), 3928–3937. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13197-022-05422-3/TABLES/1
Zhang, H., Xu, Z., Shen, J., Li, X., Ding, L., Ma, J., Lan, Y., Xia, W., Cheng, C., Sun, Q., Zhang, Z., & Chu, P. K. (2015). Effects and mechanism of atmospheric-pressure dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma on lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) enzyme. Scientific Reports, 5(May), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10031
Zhang, Y., Lei, Y., Huang, S., Dong, X., Huang, J., & Huang, M. (2022). In-package cold plasma treatment of braised chicken: Voltage effect. Food Science and Human Wellness, 11(4), 845–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FSHW.2022.03.006
Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Hu, H., Luo, S., Zhang, L., Zhou, H., & Li, P. (2021). Effects of in-package atmospheric cold plasma treatment on the qualitative, metabolic and microbial stability of fresh-cut pears. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, January. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.11085
Zhao, Y., Meng, Z., Shao, L., Dai, R., Li, X., & Jia, F. (2022). Employment of cold atmospheric plasma in chilled chicken breasts and the analysis of microbial diversity after the shelf-life storage. Food Research International, 162, 111934. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2022.111934
Zhao, Y., Shao, L., Jia, L., Meng, Z., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Zou, B., Dai, R., Li, X., & Jia, F. (2022). Subcellular inactivation mechanisms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa treated by cold atmospheric plasma and application on chicken breasts. Food Research International, 160, 111720. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2022.111720
Zhao, Y., Shao, L., Jia, L., Zou, B., Dai, R., Li, X., & Jia, F. (2022). Inactivation effects, kinetics and mechanisms of air- and nitrogen-based cold atmospheric plasma on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 79, 103051. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2022.103051
Zheng, Z., Niu, L., Yang, W., Chen, Y., Huang, Y., & Li, C. (2023). Degradation of zearalenone by dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma and its effect on maize quality. Foods, 12(6), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/FOODS12061129
Zhou, D., Li, T., Cong, K., Suo, A., & Wu, C. (2022). Influence of cold plasma on quality attributes and aroma compounds in fresh-cut cantaloupe during low temperature storage. LWT, 154, 112893. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LWT.2021.112893
Zhou, R., Zhou, R., Zhuang, J., Zong, Z., Zhang, X., Liu, D., Bazaka, K., & Ostrikov, K. (2016). Interaction of atmospheric-pressure air microplasmas with amino acids as fundamental processes in aqueous solution. PLoS ONE, 11(5), e0155584. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0155584
Zhu, H., Cheng, J. H., Han, Z., & Han, Z. (2023). Cold plasma enhanced natural edible materials for future food packaging: Structure and property of polysaccharides and proteins-based films. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 63(20), 4450–4466. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.2002258
Zhu, Y., Elliot, M., Zheng, Y., Chen, J., Chen, D., & Deng, S. (2022). Aggregation and conformational change of mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) polyphenol oxidase subjected to atmospheric cold plasma treatment. Food Chemistry, 386, 132707. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2022.132707
Zielinska, S., Cybulska, J., Pieczywek, P., Zdunek, A., Kurzyna-Szklarek, M., Staniszewska, I., Liu, Z. L., Pan, Z., Xiao, H. W., & Zielinska, M. (2022a). Structural morphology and rheological properties of pectin fractions extracted from okra pods subjected to cold plasma treatment. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(5), 1168–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11947-022-02798-0/FIGURES/3
Zielinska, S., Staniszewska, I., Cybulska, J., Zdunek, A., Szymanska-Chargot, M., Zielinska, D., Liu, Z.-L., Pan, Z., Xiao, H.-W., & Zielinska, M. (2022b). Modification of the cell wall polysaccharides and phytochemicals of okra pods by cold plasma treatment. Food Hydrocolloids, 131, 107763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107763
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kharagpur, West Bengal, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SK: conceptualization, methodology, software, and writing- original draft preparation; SP: visualization, investigation, and editing; PPS and BS: reviewing, validation, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Pipliya, S., Srivastav, P.P. et al. Exploring the Role of Various Feed Gases in Cold Plasma Technology: A Comprehensive Review. Food Bioprocess Technol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03229-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03229-4