Abstract
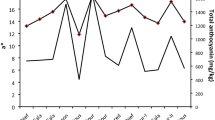
More than as a phenotypic marker for breeding, seed coat colour of soybean is gaining momentum as a nutraceutical marker owing to the multitude of medicinal effects provided by anthocyanins. The acute obstacle for large scale phenotyping is a rapid, reliable and accurate quantification which simultaneously determines various anthocyanins and hence, in this study, the modified method efficiently separated cyanidin-3-glucoside (C3G), delphinidin-3-glucoside (D3G) and petunidin-3-glucoside (Pt3G) forms by eluting through a RP-C18 column with an optimized isocratic mobile phase containing 18% solvent B (0.4% trifluoro acetic acid in acetonitrile) in solvent A (0.4% trifluoro acetic acid in water). The elution profile of anthocyanins were C3G > D3G > Pt3G, with C3G as the predominant (~ 85%) form. The modified method was validated in terms of linearity (R2 = 0.998), low limit of detection (LOD = 5.8 μg ml−1), limit of quantification (LOQ = 22.25 μg ml−1), precision, repeatability, stability and recovery. C3G dynamics was found increased in a linear trend from 30DAF to later developing stages until maturity. The investigation on characterization of exotic soybean genotypes revealed that, maximum C3G content of 4.9 mg g−1 was in UPSL496 and the least in EC471921 (3.56 mg g−1). There was a positive correlation observed among all the variables, like monomeric anthocyanin content (MAC), C3G, D3G and Pt3G. Clustering and heat map analysis information on this efficient method can be used for future research for germ plasm evaluation and for developing nutritionally C3G enriched high yielding varieties.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Satue-Gracia, I.M. Heinonen, E.N. Frankel, J. Agric. Food Chem. 45, 3362–3367 (1997)
S.H. Nam, S.P. Choi, M.Y. Kang, H.J. Koh, N. Kozukue, M. Friedman, Food Chem. 94, 613–620 (2006)
S. Kumari, M. Jolly, V. Krishnan, A. Dahuja, A. Sachdev, Afr. J. Biotechnol. 11, 16443–164544 (2012)
V. Krishnan, S. Gothwal, A. Dahuja, T. Vinutha, B. Singh, M. Jolly, A. Sachdev, Food Chem. 245, 246–253 (2018)
R.L. Bernard, M.G. Weiss, Qualitative genetics. Soybeans improvement, production, and uses. In: Caldwell BE, editor. Agronomy Monograph. Vol. 16. American Society of Agronomy; Madison, 117–154p (1973).
J.J. Todd, L.O. Vodkin, Plant Physiol. 102, 663–670 (1993)
V. Krishnan, A. Singh, V. Thimmegowda, B. Singh, D. Anil, D.R. Raj, S. Archana, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 307, 49 (2016)
J.M. Kong, L.S. Chia, N.K. Goh, T.F. Chia, R. Brouillard, Phytochemistry 64, 923–933 (2003)
M. Takikawa, S. Inoue, F. Horio, T. Tsuda, J. Nutr. 140, 527–533 (2010)
H. Kamei, Y. Hashimoto, T. Koide, T. Kojima, M. Hasegawa, Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 13, 447–452 (1998)
I. Nagai, Tokyo Univ. Coll. Agric. J. 8, 1–92 (1921)
C. Kuroda, M. Wada, Proc. Jpn. Acad. 9, 17 (1933)
T. Manabe, S. Kubo, M. Kodama, Y. Bessho, Nippon Shokuhin Kogyo Gakkaish 12, 472 (1965)
K. Yoshikura, Y. Hamaguchi, J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. 22, 367 (1969)
K. Yoshida, Y. Sato, R. Okuno, K. Kameda, M. Isobe, T. Kondo, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 60, 589–593 (1996)
M. Choung, B.I. Youl, S. Kang, W. Han, D. Shin, H. Moon, K. Kang, J. Agric. Food Chem. 49, 5848–5851 (2001)
G. Mazza, L. Gao, Blue and purple grains. In: Abdel-Aal E-SM, Peter PJ, editors. Specialty Grains for Food and Feed. St. Paul: American Association of Cereal Chemists, 45–67 (2005).
K. Koh, J. Youn, H. Kim, J. Food Sci. Technol. 51, 377–381 (2014)
K.J. Lee, J.R. Lee, K.H. Ma, Y.H. Cho, G.A. Lee, J.W. Chung, Plant Breed. Biotech. 4, 441–452 (2016)
B.H. Taylor, M.S. Thesis, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, AR (1976).
S. Abdel, J.C. Young, I. Rabalski, J. Agric. Food Chem. 54, 4696–4704 (2006)
V. Pandey, V. Krishnan, N. Basak, A. Hada, M. Punjabi, M. Jolly, S.K. Lal, S.B. Singh, A. Sachdev, J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 25, 367–374 (2016)
R Core Team, R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/ (2018).
L. Longo, G. Vasapollo, L. Rescio, J. Agric. Food Chem. 53, 1723–1727 (2005)
J. Sang, Q. Ma, C. Li, Anal. Methods 9, 2535–2545 (2017)
A. Castaneda-Ovando, M.L. Pacheo-Hernandez, E. Paez-Hernandez, J. Rodriguez, C. Galan-Vidal, Food Chem. 113, 859–871 (2009)
J.M. Awika, L.W. Rooney, R.D. Waniska, Food Chem. 90, 293–301 (2005)
K. Yoshida, D. Ma, C.P. Constabel, Plant Physiol. 167, 693–710 (2015)
E.H. Kim, H.M. Ro, S.L. Kim, H.S. Kim, I.M. Chung, J. Agric. Food Chem. 60, 6045–6055 (2012)
Y. Kim, H. Yoon, Y. Lee, D. Youn, T. Ha, H. Kim, J. Lee, Biomol. Ther. 20, 68–74 (2012)
L. Zhang, Q. Fu, Y. Zhang, Food Chem. 127, 1444–1449 (2011)
V. Reddy, K. Goud, R. Sharma, A. Reddy, Plant Physiol. 105, 1059–1066 (1994)
S.N. Ryu, S.Z. Park, C.T. Ho, J. Food Drug Anal. 6, 729–736 (1998)
N. Kovinich, A. Saleem, J.T. Arnason, B. Miki, BMC Genomics 12, 381 (2011)
A. Kasai, M. Watarai, S. Yumoto, S. Akada, R. Ishikawa, T. Harada, M. Niizeki, M. Senda, Breed. Sci. 54, 355–360 (2004)
S. Phommalath, M. Teraishi, T. Yoshikawa, H. Saito, T. Tsukiyama, T. Nakazaki, T. Tanisaka, Y. Okumoto, Breed. Sci. 64, 409–415 (2014)
Q. Wang, M. Xia, C. Liu, H. Guo, Q. Ye, Y. Hu, Y. Zhang, M. Hou, H. Zhu, J. Ma, W. Ling, Life Sci. 83, 176–184 (2008)
Z. Liu, M. Shi, D. Xie, Planta 239, 765 (2014)
S.Y. Park, S. Pak, S.J. Kang, N.Y. Kim, D.S. Kim, J.M. Kim, S.A. Kim, J.Y. Kim, S.Y. Park, S.H. Park, C.R. Youn, B.R. Lee, H.E. Lee, S.Y. Choi, H.W. Choi, J.Y. Heo, Y.A. Hwang, M.S. Lee, J. Nutr. Health Aging 48, 299–309 (2015)
S. Kumar, V. Krishnan, J. Phytochem. Biochem 1, 103 (2017)
M. Schwartz, B. Venables, gplots: Various R Programming Tools for Plotting Data. R package version 3.0.1.2. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=gplots (2020).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR), New Delhi for procuring the exotic collections of black soybean. This research was supported by ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnan, V., Rani, R., Pushkar, S. et al. Anthocyanin fingerprinting and dynamics in differentially pigmented exotic soybean genotypes using modified HPLC–DAD method. Food Measure 14, 1966–1975 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-020-00443-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-020-00443-y