Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effect of Fuzheng Kang’ai Formula (扶正抗癌方, FZKA) plus gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations.
Methods
A randomized controlled trial was conducted from 2009 to 2012 in South China. Seventy chemotherapynaive patients diagnosed with stage IIIB/IV non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR mutations were randomly assigned to GF group [gefitinib (250 mg/day orally) plus FZKA (250 mL, twice per day, orally); 35 cases] or G group (gefitinib 250 mg/day orally; 35 cases) according to the random number table and received treatment until progression of the disease, or development of unacceptable toxicities. The primary endpoint [progression-free survival (PFS)] and secondary endpoints [median survival time (MST), objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR) and safety] were observed.
Results
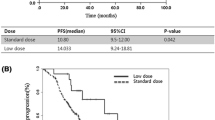
No patient was excluded after randomization. GF group had significantly longer PFS and MST compared with the G group, with median PFS of 12.5 months (95% CI 3.30–21.69) vs. 8.4 months (95% CI 6.30–10.50; log-rank P<0.01), MST of 21.5 months (95% CI 17.28–25.73) vs. 18.3 months (95% CI 17.97–18.63; log-rank P<0.01). ORR and DCR in GF group and G group were 65.7% vs. 57.1%, 94.3% vs. 80.0%, respectively (P>0.05). The most common toxic effects in the GF group and G group were rash or acne (42.8% vs. 57.1%, P>0.05), diarrhea (11.5% vs. 31.4%, P<0.05), and stomatitis (2.9% vs. 8.7%, P>0.05).
Conclusion
Patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer selected by EGFR mutations have longer PFS, MST with less toxicity treated with gefitinib plus FZKA than gefitinib alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 2010;60:277–300.
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2002;346:92–98.
Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM. Lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1367–1380.
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Douillard JY, et al. Multi-institutional randomized phase ? trial of gefi tinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (the IDEAL 1 Trial). J Clin Oncol 2003;21:2237–2246.
Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ Jr, Prager D, Belani CP, et al. Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA 2003;290:2149–2158.
Kim ES, Hirsh V, Mok T, Socinski MA, Gervais R, Wu YL, et al. Gefi tinib versus docetaxel in previously treated nonsmall cell lung cancer (INTEREST): a randomized phase ? trial. Lancet 2008;372:1809–1818.
Maruyama R, Nishiwaki Y, Tamura T, Yamamoto N, Tsuboi M, Nakagawa K, et al. Phase III study, V-15-32, of gefitinib versus docetaxel in previously treated Japanese patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:4244–4252.
Thatcher N, Chang A, Parikh P, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, von Pawel J, et al. Gefi tinib plus best supportive care in previously treated patients with refractory advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from a randomised, placebo-controlled, multi-centre study (Iressa Survival Evaluation in Lung Cancer). Lancet 2005;366:1527–1537.
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 2009;361:947–957.
Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C, Porta R, Cardenal F, Camps C, et al. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2009;361:958–967.
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefi tinib. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2129–2139.
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004;304:1497–1500.
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, Kuwano H, Takahashi T, Mitsudomi T. Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in lung cancer: biological and clinical implications. Cancer Res 2004;64:8919–8923.
Tamura K, Okamoto I, Kashii T, Negoro S, Hirashima T, Kudoh S, et al. Multicentre prospective phase II trial of gefitinib for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: results of the West Japan Thoracic Oncology Group trial (WJTOG0403). Br J Cancer 2008;98:907–914.
Morita S, Okamoto I, Kobayashi K, Yamazaki K, Asahina H, Inoue A, et al. Combined survival analysis of prospective clinical trials of gefi tinib for non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR mutations. Clin Cancer Res 2009;5:4493–4498.
Jackman DM, Miller VA, Cioffredi LA, Yeap BY, Jänne PA, Riely GJ, et al. Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor and KRAS mutations on clinical outcomes in previously untreated non-small cell lung cancer patients: results of an online tumor registry of clinical trials. Clin Cancer Res 2009;15:5267–5273.
Hyodo I, Amano N, Eguchi K, Narabayashi M, Imanishi J, Hirai M, et al. Nationwide survey on complementary and alternative medicine in cancer patients in Japan. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:2645–2654.
Swarup AB, Barrett W, Jazieh AR. The use of complementary and alternative medicine by cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy. Am J Clin Oncol 2006;29:468–473.
Ezeome ER, Anarado AN. Use of complementary and alternative medicine by cancer patients at the University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Enugu, Nigeria. BMC Complement Altern Med 2007;7:28.
Chan KK, Yao TJ, Jones B, Zhao JF, Ma FK, Leung CY, et al. The use of Chinese herbal medicine to improve quality of life in women undergoing chemotherapy for ovarian cancer: a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial with immunological monitoring. Ann Oncol 2011;22:2241–2249.
Liu ML, Chien LY, Tai CJ, Lin KC. Effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine for liver protection and chemotherapy completion among cancer patients. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011;2011:291843.
Yamamoto K, Hoshiai H, Noda K. Effects of Shakuyakukanzo-to on muscle pain from combination chemotherapy with paclitaxel and carboplatin. Gynecol Oncol 2001;81:333–334.
Mori K, Kondo T, Kamiyama Y, Kano Y, Tominaga K. Preventive effect of Kampo medicine (Hangeshashinto) against irinotecan-induced diarrhea in advanced nonsmall- cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2003;51:403–406.
Zheng F, Wu JJ, Li X, Tang Q, Yang LJ, Yang XB, et al. Chinese herbal medicine Fuzheng Kang-Ai Decoction inhibited lung cancer cell growth through AMPKa-mediated induction and interplay of IGFBP1 and FOXO3a. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016;2016:5060757.
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000;92:205–216.
Newton CR, Graham A, Heptinstall LE, Powell SJ, Summers C, Kalsheker N, et al. Analysis of any point mutation in DNA: the amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS). Nucleic Acids Res 1989;17:2503–2516.
Whitcombe D, Theaker J, Guy SP, Brown T, Little S. Detection of PCR products using self-probing amplicons and fluorescence. Nat Biotechnol 1999;17:804–807.
Wu WY, Yang XB, Deng H, Long SQ, Sun LS, He WF, et al. Treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer with extracorporeal high frequency thermotherapy plus traditional Chinese medicine. Chin J Integr Med 2010;16:406–410.
Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program. Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE) v3.0. National Cancer Institute. Accessed July 10, 2013. Available at http://ctep. cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/ctcaev3.pdf.
Pfi ster DG, Johnson DH, Azzoli CG, Sause W, Smith TJ, Baker S Jr, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology treatment of unresectable non-small cell lung cancer guideline: update 2003. J Clin Oncol 2004;22:330–353.
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, et al. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2002;346:92–98.
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, et al. Gefi tinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2010;11:121–128.
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for nonsmall- cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 2010;362:2380–2388.
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Jänne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 2005;352:786–792.
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007;316:1039–1043.
Sequist LV, von Pawel J, Garmey EG, Akerley WL, Brugger W, Ferrari D, et al. Randomized phase II study of erlotinib plus tivantinib versus erlotinib plus placebo in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2011;29:3307–3315.
Xu L, Li H, Xu Z, Wang Z, Liu L, Tian J, et al. Multi-center randomized double-blind controlled clinical study of chemotherapy combined with or without traditional Chinese medicine on quality of life of postoperative non-small cell lung cancer patients. BMC Complement Altern Med 2012;12:112.
Ma JJ, Liu HP. Effi cacy of Aidi Injection on overexpression of P-glycoprotein induced by vinorelbine and cisplatin regimen in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Integr Med 2017;23:504–509.
Sima L. The assessment of randomized controlled clinical trial of Banxia Xiexin Prescription in treating erlotinib-induced skin rash in NSCLC patients. Ann Oncol 2009;20:43–46.
Hwang SW, Han HS, Lim KY, Han JY. Drug interaction between complementary herbal medicines and gefi tinib. J Thorac Oncol 2008;3:942–943.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Dr. OU Ai-hua in Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine for managing the statistic analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81273965, 81503507) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2015A030310245)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Xb., Chai, Xs., Wu, Wy. et al. Gefitinib plus Fuzheng Kang’ai Formula (扶正抗癌方) in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 24, 734–740 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2819-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2819-8