Abstract
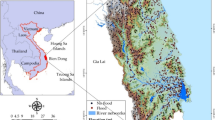
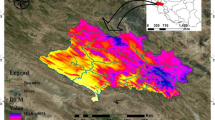
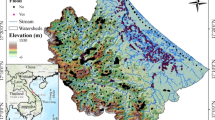
Floods are arguably the most impactful of natural hazards. The increasing magnitude of their effects on the environment, human life, and economic activities calls for improved management of water resources. Flood susceptibility modeling has been used around the world to reduce the damage caused by flooding, although the extrapolation problem still presents a significant challenge. This study develops a machine learning (ML) model utilizing deep neural network (DNN) and optimization algorithms, namely earthworm optimization algorithm (EOA), wildebeest herd optimization (WHO), biogeography-based optimization (BBO), satin bowerbird optimizer (SBO), grasshopper optimization algorithm (GOA), and particle swarm optimization (PSO), to solve the extrapolation problem in the construction of flood susceptibility models. Quang Nam Province was chosen as a case study as it is subject to the significant impact of intense flooding, and Nghe An Province was selected as the region for extrapolation of the flood susceptibility model. Root mean square error (RMSE), receiver operating characteristic (ROC), the area under the ROC curve (AUC), and accuracy (ACC) were applied to assess and compare the fit of each of the models. The results indicated that the models in this study are a good fit in establishing flood susceptibility maps, all with AUC > 0.9. The deep neural network (DNN)-BBO model enjoyed the best results (AUC = 0.99), followed by DNN-WHO (AUC = 0.99), DNN-SBO (AUC = 0.98), DNN-EOA (AUC = 0.96), DNN-GOA (AUC = 0.95), and finally, DNN-PSO (AUC = 0.92). In addition, the models successfully solved the extrapolation problem. These new models can modify their behavior to evaluate flood susceptibility in different regions of the world. The models in this study distribute a first point of reference for debate on the solution to the extrapolation problem, which can support urban planners and other decision-makers in other coastal regions in Vietnam and other countries.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdessamed D, Abderrazak B (2019) Coupling HEC-RAS and HEC-HMS in rainfall–runoff modeling and evaluating floodplain inundation maps in arid environments: case study of Ain Sefra City, Ksour Mountain. SW of Algeria. Environ Earth Sci 78:1–17
Ahmadlou M, Karimi M, Alizadeh S, Shirzadi A, Parvinnejhad D, Shahabi H, Panahi M (2019) Flood susceptibility assessment using integration of adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and biogeography-based optimization (BBO) and BAT algorithms (BA). Geocarto Int 34:1252–1272
Ahmadlou M, Ak A-F, Al-Shabeeb AR, Arora A, Al-Adamat R, Pham QB, Al-Ansari N, Linh NTT, Sajedi H (2021) Flood susceptibility mapping and assessment using a novel deep learning model combining multilayer perceptron and autoencoder neural networks. J Flood Risk Manag 14:e12683
Ahmed N, Hoque MA-A, Arabameri A, Pal SC, Chakrabortty R, Jui J (2021) Flood susceptibility mapping in Brahmaputra floodplain of Bangladesh using deep boost, deep learning neural network, and artificial neural network. Geocarto Int 37(25):8770–8791
Ali SA, Parvin F, Pham QB, Vojtek M, Vojteková J, Costache R, Linh NTT, Nguyen HQ, Ahmad A, Ghorbani MA (2020) GIS-based comparative assessment of flood susceptibility mapping using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making approach, naïve Bayes tree, bivariate statistics and logistic regression: a case of Topľa basin, Slovakia. Ecol Ind 117:106620
Amali D, Dinakaran M (2019) Wildebeest herd optimization: a new global optimization algorithm inspired by wildebeest herding behaviour. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 37:8063–8076
Anusha N, Bharathi B (2020) Flood detection and flood mapping using multi-temporal synthetic aperture radar and optical data. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 23:207–219
Arora A, Arabameri A, Pandey M, Siddiqui MA, Shukla U, Bui DT, Mishra VN, Bhardwaj A (2021) Optimization of state-of-the-art fuzzy-metaheuristic ANFIS-based machine learning models for flood susceptibility prediction mapping in the Middle Ganga Plain, India. Sci Total Environ 750:141565
Askar S, Zeraat Peyma S, Yousef MM, Prodanova NA, Muda I, Elsahabi M, Hatamiafkoueieh J (2022) Flood susceptibility mapping using remote sensing and integration of decision table classifier and metaheuristic algorithms. Water 14:3062
Bedient PB, Holder A, Benavides JA, Vieux BE (2003) Radar-based flood warning system applied to Tropical Storm Allison. J Hydrol Eng 8:308–318
Bui DT, Bui Q-T, Nguyen Q-P, Pradhan B, Nampak H, Trinh PT (2017) A hybrid artificial intelligence approach using GIS-based neural-fuzzy inference system and particle swarm optimization for forest fire susceptibility modeling at a tropical area. Agric for Meteorol 233:32–44
Bui DT, Ngo P-TT, Pham TD, Jaafari A, Minh NQ, Hoa PV, Samui P (2019) A novel hybrid approach based on a swarm intelligence optimized extreme learning machine for flash flood susceptibility mapping. CATENA 179:184–196
Bui DT, Hoang N-D, Martínez-Álvarez F, Ngo P-TT, Hoa PV, Pham TD, Samui P, Costache R (2020a) A novel deep learning neural network approach for predicting flash flood susceptibility: a case study at a high frequency tropical storm area. Sci Total Environ 701:134413
Bui Q-T, Nguyen Q-H, Nguyen XL, Pham VD, Nguyen HD, Pham V-M (2020b) Verification of novel integrations of swarm intelligence algorithms into deep learning neural network for flood susceptibility mapping. J Hydrol 581:124379
Chaouch N, Temimi M, Hagen S, Weishampel J, Medeiros S, Khanbilvardi R (2012) A synergetic use of satellite imagery from SAR and optical sensors to improve coastal flood mapping in the Gulf of Mexico. Hydrol Process 26:1617–1628
Chen W, Li Y, Xue W, Shahabi H, Li S, Hong H, Wang X, Bian H, Zhang S, Pradhan B (2020) Modeling flood susceptibility using data-driven approaches of naïve bayes tree, alternating decision tree, and random forest methods. Sci Total Environ 701:134979
Chen W, Chen X, Peng J, Panahi M, Lee S (2021) Landslide susceptibility modeling based on ANFIS with teaching-learning-based optimization and satin bowerbird optimizer. Geosci Front 12:93–107
Choubin B, Moradi E, Golshan M, Adamowski J, Sajedi-Hosseini F, Mosavi A (2019) An ensemble prediction of flood susceptibility using multivariate discriminant analysis, classification and regression trees, and support vector machines. Sci Total Environ 651:2087–2096
Costache R, Zaharia L (2017) Flash-flood potential assessment and mapping by integrating the weights-of-evidence and frequency ratio statistical methods in GIS environment–case study: Bâsca Chiojdului River catchment (Romania). J Earth Syst Sci 126:1–19
Costache R (2019a) Flash-flood Potential Index mapping using weights of evidence, decision Trees models and their novel hybrid integration. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 33:1375–1402
Costache R (2019b) Flood susceptibility assessment by using bivariate statistics and machine learning models-a useful tool for flood risk management. Water Resour Manag 33:3239–3256
Das S (2018) Geographic information system and AHP-based flood hazard zonation of Vaitarna basin, Maharashtra, India. Arab J Geosci 11:1–13
Dodangeh E, Choubin B, Eigdir AN, Nabipour N, Panahi M, Shamshirband S, Mosavi A (2020) Integrated machine learning methods with resampling algorithms for flood susceptibility prediction. Sci Total Environ 705:135983
Duan Y, Liu T, Meng F, Luo M, Frankl A, De Maeyer P, Bao A, Kurban A, Feng X (2018) Inclusion of modified snow melting and flood processes in the SWAT model. Water 10:1715
Ekmekcioğlu Ö, Koc K, Özger M (2021) Stakeholder perceptions in flood risk assessment: a hybrid fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS approach for Istanbul, Turkey. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 60:102327
El-Haddad BA, Youssef AM, Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, El-Shater A-H, El-Khashab MH (2020) Flood susceptibility prediction using four machine learning techniques and comparison of their performance at Wadi Qena Basin. Egypt Nat Hazards 105(1):83–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04296-y
El-Hay E, El-Hameed M, El-Fergany A (2018) Steady-state and dynamic models of solid oxide fuel cells based on satin bowerbird optimizer. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43:14751–14761
Emami M, Nazif S, Mousavi S-F, Karami H, Daccache A (2021) A hybrid constrained coral reefs optimization algorithm with machine learning for optimizing multi-reservoir systems operation. J Environ Manag 286:112250
Ghorbanzadeh O, Shahabi H, Mirchooli F, Valizadeh Kamran K, Lim S, Aryal J, Jarihani B, Blaschke T (2020) Gully erosion susceptibility mapping (GESM) using machine learning methods optimized by the multi-collinearity analysis and K-fold cross-validation. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 11:1653–1678
Ghosh A, Dey P, Ghosh T (2022a) Integration of RS-GIS with frequency ratio, fuzzy logic, logistic regression and decision tree models for flood susceptibility prediction in lower gangetic plain: a study on Malda District of West Bengal, India. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 50:1725–1745
Ghosh S, Saha S, Bera B (2022b) Flood susceptibility zonation using advanced ensemble machine learning models within Himalayan foreland basin. Nat Hazards Res
Guo W, Chen M, Wang L, Mao Y, Wu Q (2017) A survey of biogeography-based optimization. Neural Comput Appl 28:1909–1926
Hammami S, Zouhri L, Souissi D, Souei A, Zghibi A, Marzougui A, Dlala M (2019) Application of the GIS based multi-criteria decision analysis and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) in the flood susceptibility mapping (Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 12:1–16
He Y, Ma D, Xiong J, Cheng W, Jia H, Wang N, Guo L, Duan Y, Liu J, Yang G (2022) Flash flood vulnerability assessment of roads in China based on support vector machine. Geocarto Int 37:6141–6164
Hong H, Panahi M, Shirzadi A, Ma T, Liu J, Zhu A-X, Chen W, Kougias I, Kazakis N (2018) Flood susceptibility assessment in Hengfeng area coupling adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system with genetic algorithm and differential evolution. Sci Total Environ 621:1124–1141
Hosseini FS, Choubin B, Mosavi A, Nabipour N, Shamshirband S, Darabi H, Haghighi AT (2020) Flash-flood hazard assessment using ensembles and Bayesian-based machine learning models: application of the simulated annealing feature selection method. Sci Total Environ 711:135161
Hosseini Rad M, Abdolrazzagh-Nezhad M (2020) A new hybridization of DBSCAN and fuzzy earthworm optimization algorithm for data cube clustering. Soft Comput 24:15529–15549
Huang C, Chen Y, Zhang S, Wu J (2018) Detecting, extracting, and monitoring surface water from space using optical sensors: a review. Rev Geophys 56:333–360
Irawan L, Panoto D, Pradana I, Darmansyah A (2021) Combination of machine learning model (LR-FR) for flash flood susceptibility assessment in Dawuan Sub watershed Mojokerto Regency, East Java. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 739(1):012017
Islam ARMT, Talukdar S, Mahato S, Kundu S, Eibek KU, Pham QB, Kuriqi A, Linh NTT (2021) Flood susceptibility modelling using advanced ensemble machine learning models. Geosci Front 12:101075
Kadam P, Sen D (2012) Flood inundation simulation in Ajoy River using MIKE-FLOOD. ISH J Hydraul Eng 18:129–141
Kanna SR, Sivakumar K, Lingaraj N (2021) Development of deer hunting linked earthworm optimization algorithm for solving large scale traveling salesman problem. Knowl-Based Syst 227:107199
Kennedy J (1942–1948) Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization, Proceedings of ICNN'95-international conference on neural networks. IEEE, Perth. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Khan A, Mushtaq N, Faraz SH, Khan OA, Sarwar MA, Javaid N (2017) Genetic algorithm and earthworm optimization algorithm for energy management in smart grid. In: International conference on P2P, parallel, grid, cloud and internet computing. 3PGCIC 2017. Lecture notes on data engineering and communications technologies, vol 13. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-69835-9_42
Khoirunisa N, Ku C-Y, Liu C-Y (2021) A GIS-based artificial neural network model for flood susceptibility assessment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:1072
Khosravi K, Pham BT, Chapi K, Shirzadi A, Shahabi H, Revhaug I, Prakash I, Bui DT (2018) A comparative assessment of decision trees algorithms for flash flood susceptibility modeling at Haraz watershed, Northern Iran. Sci Total Environ 627:744–755
Kim TH, Kim B, Han K-Y (2019) Application of fuzzy TOPSIS to flood hazard mapping for levee failure. Water 11:592
Liu D, Fan Z, Fu Q, Li M, Faiz MA, Ali S, Li T, Zhang L, Khan MI (2020) Random forest regression evaluation model of regional flood disaster resilience based on the whale optimization algorithm. J Clean Prod 250:119468
Liu J, Xiong J, Cheng W, Li Y, Cao Y, He Y, Duan Y, He W, Yang G (2021) Assessment of flood susceptibility using support vector machine in the belt and road region. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci Discuss 2021:1–37. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-2021-80
Liu X, Sahli H, Meng Y, Huang Q, Lin L (2017) Flood inundation mapping from optical satellite images using spatiotemporal context learning and modest AdaBoost. Remote Sens 9:617
Liu X, Yang M, Meng X, Wen F, Sun G (2019) Assessing the impact of reservoir parameters on runoff in the Yalong River Basin using the SWAT model. Water 11:643
Luu C, Von Meding J, Kanjanabootra S (2018) Assessing flood hazard using flood marks and analytic hierarchy process approach: a case study for the 2013 flood event in Quang Nam, Vietnam. Nat Hazards 90:1031–1050
Luu C, Pham BT, Van Phong T, Costache R, Nguyen HD, Amiri M, Bui QD, Nguyen LT, Van Le H, Prakash I (2021) GIS-based ensemble computational models for flood susceptibility prediction in the Quang Binh Province, Vietnam. J Hydrol 599:126500
Ma H, Simon D, Siarry P, Yang Z, Fei M (2017) Biogeography-based optimization: a 10-year review. IEEE Trans Emerg Top Comput Intell 1:391–407
Mirzaei S, Vafakhah M, Pradhan B, Alavi SJ (2021) Flood susceptibility assessment using extreme gradient boosting (EGB), Iran. Earth Sci Inform 14:51–67
Moosavi SHS, Bardsiri VK (2017) Satin bowerbird optimizer: a new optimization algorithm to optimize ANFIS for software development effort estimation. Eng Appl Artif Intell 60:1–15
Msabi MM, Makonyo M (2021) Flood susceptibility mapping using GIS and multi-criteria decision analysis: a case of Dodoma region, central Tanzania. Remote Sens Appl: Soc Environ 21:100445
Nachappa TG, Piralilou ST, Gholamnia K, Ghorbanzadeh O, Rahmati O, Blaschke T (2020) Flood susceptibility mapping with machine learning, multi-criteria decision analysis and ensemble using Dempster Shafer theory. J Hydrol 590:125275
Narimani R, Jun C, Shahzad S, Oh J, Park K (2021) Application of a novel hybrid method for flood susceptibility mapping with satellite images: a case study of Seoul, Korea. Remote Sens 13:2786
Nguyen HD, Ardillier-Carras F, Touchart L (2018) Les paysages de rizières et leur évolution récente dans le delta du fleuve Gianh. Cybergeo: Eur J Geogr 876. https://doi.org/10.4000/cybergeo.29826
Nguyen HD, Nguyen Q-H, Du QVV, Nguyen THT, Nguyen TG, Bui Q-T (2021a) A novel combination of deep neural network and manta ray foraging optimization for flood susceptibility mapping in Quang Ngai Province. Vietnam. Geocarto Int 37(25):7531–7555
Nguyen Q-H, Chou T-Y, Yeh M-L, Hoang T-V, Nguyen H-D, Bui Q-T (2021b) Henry’s gas solubility optimization algorithm in formulating deep neural network for landslide susceptibility assessment in mountainous areas. Environ Earth Sci 80:1–10
Nguyen HD (2022a) GIS-based hybrid machine learning for flood susceptibility prediction in the Nhat Le–Kien Giang watershed. Vietnam. Earth Sci Inform 15:2369–2386
Nguyen HD (2022b) Flood susceptibility assessment using hybrid machine learning and remote sensing in Quang Tri Province. Vietnam. Trans GIS 27(6):2776–2801
Nguyen HD, Dang DK, Nguyen Q-H, Bui Q-T, Petrisor A-I (2022a) Evaluating the effects of climate and land use change on the future flood susceptibility in the central region of Vietnam by integrating land change modeler, machine learning methods. Geocarto Int 37(26):12810–12845
Nguyen HD, Nguyen Q-H, Du QVV, Nguyen THT, Nguyen TG, Bui Q-T (2022b) A novel combination of deep neural network and manta ray foraging optimization for flood susceptibility mapping in Quang Ngai Province, Vietnam. Geocarto Int 37:7531–7555
Nguyen HD, Quang-Thanh B, Nguyen Q-H, Nguyen TG, Pham LT, Nguyen XL, Vu PL, Thanh Nguyen TH, Nguyen AT, Petrisor A-I (2022c) A novel hybrid approach to flood susceptibility assessment based on machine learning and land use change. Case study: a river watershed in Vietnam. Hydrol Sci J 67:1065–1083
Nguyen HD, Quang-Thanh B, Nguyen Q-H, Nguyen TG, Pham LT, Nguyen XL, Vu PL, Thanh Nguyen TH, Nguyen AT, Petrisor A-I (2022d) A novel hybrid approach to flood susceptibility assessment based on machine learning and land use change. Case study: a river watershed in Vietnam. Hydrol Sci J 67(7):1065–1083
Nguyen HD (2023) Spatial modeling of flood hazard using machine learning and GIS in Ha Tinh Province, Vietnam. J Water Clim Change 14:200–222
Nguyen HD, Dang DK, Nguyen YN, Van CP, Truong Q-H, Bui Q-T, Petrisor A-I (2023a) A framework for flood depth using hydrodynamic modeling and machine learning in the coastal province of Vietnam. Vietnam J Earth Sci 45(4):456–478
Nguyen HD, Van CP, Do AD (2023b) Application of hybrid model-based deep learning and swarm-based optimizers for flood susceptibility prediction in Binh Dinh Province, Vietnam. Earth Sci Inform 16:1173–1193
Oleyiblo JO, Li Z-j (2010) Application of HEC-HMS for flood forecasting in Misai and Wan’an catchments in China. Water Sci Eng 3:14–22
Pal SC, Chowdhuri I, Das B, Chakrabortty R, Roy P, Saha A, Shit M (2022) Threats of climate change and land use patterns enhance the susceptibility of future floods in India. J Environ Manag 305:114317
Panahi M, Dodangeh E, Rezaie F, Khosravi K, Van Le H, Lee M-J, Lee S, Pham BT (2021) Flood spatial prediction modeling using a hybrid of meta-optimization and support vector regression modeling. CATENA 199:105114
Parsa P, Naderpour H (2021) Shear strength estimation of reinforced concrete walls using support vector regression improved by teaching–learning-based optimization, particle swarm optimization, and Harris hawks optimization algorithms. J Build Eng 44:102593
Patro S, Chatterjee C, Mohanty S, Singh R, Raghuwanshi N (2009) Flood inundation modeling using MIKE FLOOD and remote sensing data. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 37:107–118
Paul P, Sarkar R (2022) Flood susceptible surface detection using geospatial multi-criteria framework for management practices. Nat Hazards 14:3015–3041
Pham BT, Luu C, Van Phong T, Trinh PT, Shirzadi A, Renoud S, Asadi S, Van Le H, von Meding J, Clague JJ (2021) Can deep learning algorithms outperform benchmark machine learning algorithms in flood susceptibility modeling? J Hydrol 592:125615
Pham MH, Do TH, Pham V-M, Bui Q-T (2020) Mangrove forest classification and aboveground biomass estimation using an atom search algorithm and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. PLoS One 15:e0233110
Prasad P, Loveson VJ, Das B, Kotha M (2022) Novel ensemble machine learning models in flood susceptibility mapping. Geocarto Int 37:4571–4593
Pulvirenti L, Pierdicca N, Chini M, Guerriero L (2011) An algorithm for operational flood mapping from synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data using fuzzy logic. Nat Hazard 11:529–540
Rahmati O, Pourghasemi HR, Zeinivand H (2016) Flood susceptibility mapping using frequency ratio and weights-of-evidence models in the Golastan Province, Iran. Geocarto Int 31:42–70
Razavi-Termeh SV, Shirani K, Pasandi M (2021) Mapping of landslide susceptibility using the combination of neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), ant colony (ANFIS-ACOR), and differential evolution (ANFIS-DE) models. Bull Eng Geol Env 80:2045–2067
Ren X, Zhao Y, Hao D, Sun Y, Chen S, Gholinia F (2021) Predicting optimal hydropower generation with help optimal management of water resources by developed wildebeest herd optimization (DWHO). Energy Rep 7:968–980
Saha TK, Pal S, Talukdar S, Debanshi S, Khatun R, Singha P, Mandal I (2021) How far spatial resolution affects the ensemble machine learning based flood susceptibility prediction in data sparse region. J Environ Manag 297:113344
Sahana M, Patel PP (2019) A comparison of frequency ratio and fuzzy logic models for flood susceptibility assessment of the lower Kosi River Basin in India. Environ Earth Sci 78:1–27
Saremi S, Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2017) Grasshopper optimisation algorithm: theory and application. Adv Eng Softw 105:30–47
Shahabi H, Shirzadi A, Ronoud S, Asadi S, Pham BT, Mansouripour F, Geertsema M, Clague JJ, Bui DT (2021) Flash flood susceptibility mapping using a novel deep learning model based on deep belief network, back propagation and genetic algorithm. Geosci Front 12:101100
Siahkamari S, Haghizadeh A, Zeinivand H, Tahmasebipour N, Rahmati O (2018) Spatial prediction of flood-susceptible areas using frequency ratio and maximum entropy models. Geocarto Int 33:927–941
Simon D (2008) Biogeography-based optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 12:702–713
Talukdar S, Ghose B, Salam R, Mahato S, Pham QB, Linh NTT, Costache R, Avand M (2020) Flood susceptibility modeling in Teesta River basin, Bangladesh using novel ensembles of bagging algorithms. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 34:2277–2300
Tang X, Machimura T, Liu W, Li J, Hong H (2021) A novel index to evaluate discretization methods: a case study of flood susceptibility assessment based on random forest. Geosci Front 12:101253
Tien Bui D, Khosravi K, Li S, Shahabi H, Panahi M, Singh VP, Chapi K, Shirzadi A, Panahi S, Chen W (2018) New hybrids of anfis with several optimization algorithms for flood susceptibility modeling. Water 10:1210
Towfiqul Islam ARM, Talukdar S, Mahato S, Kundu S, Eibek KU, Pham QB, Kuriqi A, Linh NTT (2021) Flood susceptibility modelling using advanced ensemble machine learning models. Geosci Front 12:101075
Tran VN, Kim J (2022) Robust and efficient uncertainty quantification for extreme events that deviate significantly from the training dataset using polynomial chaos-kriging. J Hydrol 609:127716
Wang G-G, Deb S, Coelho LDS (2018) Earthworm optimisation algorithm: a bio-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimisation problems. Int J Bio-Inspired Comput 12:1–22
Wang Z, Lai C, Chen X, Yang B, Zhao S, Bai X (2015) Flood hazard risk assessment model based on random forest. J Hydrol 527:1130–1141
Waqas H, Lu L, Tariq A, Li Q, Baqa MF, Xing J, Sajjad A (2021) Flash flood susceptibility assessment and zonation using an integrating analytic hierarchy process and frequency ratio model for the Chitral District, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Water 13:1650
Xie S, Wu W, Mooser S, Wang Q, Nathan R, Huang Y (2021) Artificial neural network based hybrid modeling approach for flood inundation modeling. J Hydrol 592:125605
Xu L, Wang X, Liu J, He Y, Tang J, Nguyen M, Cui S (2019) Identifying the trade-offs between climate change mitigation and adaptation in urban land use planning: an empirical study in a coastal city. Environ Int 133:105162
Yao J, Zhang X, Luo W, Liu C, Ren L (2022) Applications of stacking/blending ensemble learning approaches for evaluating flash flood susceptibility. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 112:102932
Yariyan P, Janizadeh S, Van Phong T, Nguyen HD, Costache R, Van Le H, Pham BT, Pradhan B, Tiefenbacher JP (2020) Improvement of best first decision trees using bagging and dagging ensembles for flood probability mapping. Water Resour Manag 34:3037–3053
Yaseen A, Lu J, Chen X (2022) Flood susceptibility mapping in an arid region of Pakistan through ensemble machine learning model. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 36:3041–3061
Youssef AM, Pourghasemi HR, El-Haddad BA (2022) Advanced machine learning algorithms for flood susceptibility modeling—performance comparison: Red Sea. Egypt. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:66768–66792
Funding
Huu Duy Nguyen was funded by the Postdoctoral Scholarship Programme of Vingroup Innovation Foundation (VINIF), code VINIF.2022.STS.24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huu Duy Nguyen: conceptualization, methodology, material preparation, validation, analysis, writing of original draft, and writing including review and editing. Quang-Thanh Bui: conceptualization, methodology, material preparation, and writing including review and editing. Quoc-Huy Nguyen: conceptualization, methodology, material preparation, and data collection. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, H.D., Nguyen, QH. & Bui, QT. Solving the spatial extrapolation problem in flood susceptibility using hybrid machine learning, remote sensing, and GIS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 18701–18722 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32163-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32163-x