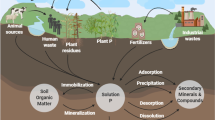
Abstract
The rapid development of nanomaterials has led to the unavoidable leakage and release of nanoparticles (NPs) into soil and the underlying groundwater. It is possible for chars and phosphate introduced into soil to improve crop soil properties by improving contact with NPs. In this study, the influences of hydrochar and/or phosphate on the anatase nTiO2 transport behaviors were investigated under different conditions. The breakthrough curves (BTCs) and retention profiles were obtained by the saturated sand column experiments. The additional analysis of zeta potentials, sedimentation kinetics, Raman mapping, and the two-site kinetic attachment model (TSKAM) was conducted to explore the possible underlying mechanisms. The simultaneous presence of phosphate and hydrochar acted in a synergetic fashion to enhance the transport of nTiO2 in a sand medium compared to the facilitated effect of single phosphate or hydrochar. The higher levels of hydrochar induce the more nTiO2 in the high IC solution passing through the saturated sand columns in the co-presence of phosphate. It was attributed to the competitive adsorption of hydrochar with nTiO2 to the sand site and the phosphate adsorption on nTiO2 occurred simultaneously through the sand columns. The fitting results of BTCs using TSKAM showed that the value of k2 for nTiO2 (the irreversible attachment coefficient at site 2) was smaller than that of k1d/k1 (the first-order reversible detachment and attachment coefficient at site 1, respectively), suggesting irreversible retention of anatase nTiO2 at site 1. The value of k1d/k1 could be better used to explain the retention of nTiO2 with combined phosphate and hydrochar. This study provides insight into the implications of phosphate and/or hydrochar for nTiO2 transport in crop soil environments.

ᅟ






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babakhani P, Bridge J, Doong RA, Phenrat T (2017) Continuum-based models and concepts for the transport of nanoparticles in saturated porous media: a state-of-the-science review. Adv Colloid Interfac 246:75–104
Babakhani P, Fagerlund F, Shamsai A, Lowry GV, Phenrat T (2018) Modified MODFLOW-based model for simulating the agglomeration and transport of polymer-modified Fe0 nanoparticles in saturated porous media. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:7180–7199
Bayat AE, Junin R, Derahman MN, Samad AA (2015) TiO2 nanoparticle transport and retention through saturated limestone porous media under various ionic strength conditions. Chemosphere 134:7–15
Chen G, Liu X, Su C (2012) Distinct effects of humic acid on transport and retention of TiO2 rutile nanoparticles in saturated sand columns. Environ Sci Technol 46:7142–7150
Chen M, Xu N, Cao X, Zhou K, Chen Z, Wang Y, Liu C (2015) Facilitated transport of anatase titanium dioxides nanoparticles in the presence of phosphate in saturated sands. J Colloid Interface Sci 451:134–143
Chowdhury I, Cwiertny DM, Walker SL (2012) Combined factors influencing the aggregation and deposition of nano-TiO2 in the presence of humic acid and bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 46:6968–6976
de Castro JA, Pereira BA, Tassi E, Pini R, Araujo A, Valadao I (2012) Modelling the transport phenomena of TiO2 nanoparticles into leachate of municipal landfills. Mater Sci Forum 727-728:1695–1700
Du W, Sun Y, Ji R, Zhu J, Wu J, Guo H (2011) TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles negatively affect wheat growth and soil enzyme activities in agricultural soil. J Environ Monit 13:822–828
Fang J, Shan XQ, Wen B, Lin JM, Owens G (2009) Stability of titania nanoparticles in soil suspensions and transport in saturated homogeneous soil columns. Environ Pollut 157:1101–1109
Fang J, Xu MJ, Wang DJ, Wen B, Han JY (2013) Modeling the transport of TiO2 nanoparticle aggregates in saturated and unsaturated granular media: effects of ionic strength and pH. Water Res 47:1399–1408
Fang J, Shijirbaatar A, Lin D, Wang D, Shen B, Sun P, Zhou Z (2017) Stability of co-existing ZnO and TiO2, nanomaterials in natural water: aggregation and sedimentation mechanisms. Chemosphere 184:1125–1133
Flory J, Kanel SR, Racz LA, Impellitteri CA, Silva RG, Goltz MN (2013) Influence of pH on the transport of silver nanoparticles in saturated porous media: laboratory experiments and modeling. J Nanopart Res 15:1–11
French RA, Jacobson AR, Kim B, Isley SL, Penn RL, Baveye PC (2009) Influence of ionic strength, pH, and cation valence on aggregation kinetics of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 43:1354–1359
Galinato SP, Yoder JK, Granatstein D (2011) The economic value of biochar in crop production and carbon sequestration. Energy Policy 39:6344–6350
Gentile GJ, Fidalgo de Cortalezzi MM (2016) Enhanced retention of bacteria by TiO2 nanoparticles in saturated porous media. J Contam Hydrol 191:66–75
Glaser B, Haumaier L, Guggenberger G, Zech W (2001) The ‘Terra Preta’ phenomenon: a model for sustainable agriculture in the humid tropics. Naturwissenschaften 88:37–41
Godinez IG, Darnault CJ (2011) Aggregation and transport of nano-TiO2 in saturated porous media: effects of pH, surfactants and flow velocity. Water Res 45:839–851
Godinez IG, Darnault CJ, Khodadoust AP, Bogdan D (2013) Deposition and release kinetics of nano-TiO2 in saturated porous media: effects of solution ionic strength and surfactants. Environ Pollut 174:106–113
Guggenberger G, Rodionov A, Shibistova O, Grabe M, Kasansky OA, Fuchs H, Mikheyeva N, Zrazhevskaya G, Flessa H (2008) Storage and mobility of black carbon in permafrost soils of the forest tundra ecotone in Northern Siberia. Glob Chang Biol 14:1367–1381
Han P, Wang X, Cai L, Tong M, Kim H (2014) Transport and retention behaviors of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in iron oxide-coated quartz sand: effects of pH, ionic strength, and humic acid. Colloid Surface A 454:119–127
He YT, Wan J, Tokunaga T (2008) Kinetic stability of hematite nanoparticles: the effect of particle sizes. J Nanopart Res 10:321–332
Hockaday WC, Grannas AM, Kim SH, Hatcher PG (2007) The transformation and mobility of charcoal in a fire-impacted watershed. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 71:3432–3445
Hotze EM, Phenrat T, Lowry GV (2010) Nanoparticle aggregation: challenges to understanding transport and reactivity in the environment. J Environ Qual 39:1909–1924
Kim HJ, Phenrat T, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2012) Effect of kaolinite, silica fines and pH on transport of polymer-modified zero valent iron nano-particles in heterogeneous porous media. J Colloid Interface Sci 370:1–10
Lehmann J (2007) A handful of carbon. Nature 447:143–144
Lehmann J, Gaunt J, Rondon M (2006) Bio-char sequestration in terrestrial ecosystems – a review. Mitig Adapt Strat Gl 11:395–419
Li X, Scheibe TD, Johnson WP (2004) Apparent decreases in colloid deposition rate coefficients with distance of transport under unfavorable deposition conditions: a general phenomenon. Environ Sci Technol 38:5616–5625
Liu C, Xu N, Feng G, Zhou D, Cheng X, Li Z (2017) Hydrochars and phosphate enhancing the transport of nanoparticle silica in saturated sands. Chemosphere 189:213–223
Major J, Lehmann J, Rondon M, Goodale C (2010) Fate of soilapplied black carbon: downward migration, leaching, and soil respiration. Glob Chang Biol 16:1366–1379
Meyer S, Glaser B, Quicker P (2011) Technical, economical, and climate-related aspects of biochar production technologies: a literature review. Environ Sci Technol 45:9473–9483
Nagaveni K, Sivalingam G, Hegde MS, Madras G (2004) Photocatalytic degradation of organic compounds over combustion-synthesized nano-TiO2. Environ Sci Technol 38:1600–1604
Phenrat T, Long TC, Lowry GV, Veronesi B (2009) Partial oxidation (“aging”) and surface modification decrease the toxicity of nanosized zerovalent iron. Environ Sci Technol 43:195–200
Phenrat T, Song JE, Cisneros CM, Schoenfelder DP, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2010) Estimating attachment of nano- and submicrometer-particles coated with organic macromolecules in porous media: development of an empirical model. Environ Sci Technol 44:4531–4538
Rahman T, George J, Shipley HJ (2013) Transport of aluminum oxide nanoparticles in saturated sand: effects of ionic strength, flow rate, and nanoparticle concentration. Sci Total Environ 463-464:565–571
Robichaud CO, Uyar AE, Darby MR, Zucker LG, Wiesner MR (2009) Estimates of upper bounds and trends in nano-TiO2 production as a basis for exposure assessment. Environ Sci Technol 43:4227–4233
Schmidt J, Vogelsberger W (2009) Aqueous long-term solubility of titania nanoparticles and titanium (IV) hydrolysis in a sodium chloride system studied by adsorptive stripping voltammetry. J Solut Chem 38:1267–1282
Scown TM, Aerle RV, Tyler CR (2010) Do engineered nanoparticles pose a significant threat to the aquatic environment? Crit Rev Toxicol 40:653–670
Šimůnek J, Šejna M, Saito H, Sakai M, Genuchten MTV (2008) The HYDRUS-1D software package for simulating the one-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably saturated media, 4th edn. Department of Environmental Science, University of California Riverside, Riverside
Sun P, Shijirbaatar A, Fang J, Owens G, Lin D, Zhang K (2015) Distinguishable transport behavior of zinc oxide nanoparticles in silica sand and soil columns. Sci Total Environ 505:189–198
Tassi E, Pini R, Gorini F, Valadao I, de Castro JA (2012) Chemical and physical soil properties influencing TiO2 nanoparticles availability in terrestrial ecosystems. J Environ Res Dev 6:1014–1018
Thio BJ, Zhou D, Keller AA (2011) Influence of natural organic matter on the aggregation and deposition of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 189:556–563
Tufenkji N, Elimelech M (2005) Breakdown of colloid filtration theory: role of the secondary energy minimum and surface charge heterogeneities. Langmuir 21:841–852
Wang L, Guo Y, Zhu Y, Li Y, Qu Y, Rong C, Ma X, Wang Z (2010) A new route for preparation of hydrochar from rice husk. Bioresour Technol 101:9807–9810
Wang D, Bradford SA, Harvey RW, Gao B, Cang L, Zhou D (2012) Humic acid facilitates the transport of ARS-labeled hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in iron oxyhydroxide-coated sand. Environ Sci Technol 46:2738–2745
Wang D, Su C, Zhang W, Hao X, Cang L, Wang Y, Zhou D (2014) Laboratory assessment of the mobility of water-dispersed engineered nanoparticles in a red soil (ultisol). J Hydrol 519:1677–1687
Wang D, Jin Y, Jaisi DP (2015) Effect of size selective retention on the cotransport of hydroxyapatite and goethite nanoparticles in saturated porous media. Environ Sci Technol 49(14):8461–8470
Wang D, Park CM, Masud A, Aich N, Su C (2017) Carboxymethylcellulose mediates the transport of carbon nanotubes-magnetite nanohybrid aggregates in water-saturated porous media. Environ Sci Technol 51:12405–12415. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b04037
Wiesner MR, Lowry GV, Alvarez P, Dionysiou D, Biswas P (2006) Assessing the risks of manufactured nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol 40:4336–4345
Xu N, Yin HW, Chen ZG, Chen M, Liu S (2013) Mechanisms of phosphate removal by synthesized calcite. Mater Sci Forum 744:597–602
Xu N, Cheng X, Zhou K, Xu X, Li Z, Chen J, Wang D, Li D (2017a) Facilitated transport of titanium dioxide nanoparticles via hydrochar in the presence of ammonium in saturated sands: effects of pH, ionic strength, and ionic composition. Sci Total Environ 612:1348–1357
Xu X, Xu N, Cheng X, Guo P, Chen Z, Wang D (2017b) Transport and aggregation of rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles in saturated porous media in the presence of ammonium. Chemosphere 169:9–17
Zhang W, Niu JZ, Morales VL, Chen XC, Hay AG, Lehmann J, Steenhuis TS (2010) Transport and retention of biochar particles in porous media: effect of pH, ionic strength, and particle size. Ecohydrology 3:497–508
Zheng H, Wang Z, Deng X, Herbert S, Xing B (2013) Impacts of adding biochar on nitrogen retention and bioavailability in agricultural soil. Geoderma 206:32–39
Zhu M, Wang H, Keller AA, Wang T, Li F (2014) The effect of humic acid on the aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles under different pH and ionic strengths. Sci Total Environ 487:375–380
Acknowledgements
The authors would also like to acknowledge the support from the Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center of Technology and Material for Water Treatment, and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Funding
This work has been financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (NSF) of China (grant Nos. 21377090 and 21777110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Thomas D. Bucheli
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 256 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, X., Xu, N., Huangfu, X. et al. Synergetic effect of hydrochar on the transport of anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles in the presence of phosphate in saturated quartz sand. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 28864–28874 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2795-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2795-3