Abstract
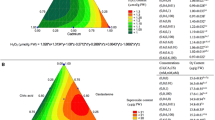
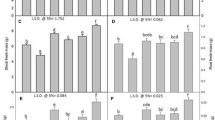
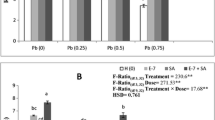
Plant growth regulator-assisted phytoremediation has been assessed as a novel strategy to improve phytoremediation potential of plants. In the present work, potential of castasterone, a plant growth regulator, combined with citric acid was explored for phytoremediation of cadmium in Brassica juncea seedlings. The seedlings were raised under controlled laboratory conditions for 7 days. Results revealed that 0.6 mM cadmium exposure induced toxicity in the seedlings, which was reflected through root growth inhibition, accumulation of hydrogen peroxide and malondialdehyde, and loss of cell viability. Pre-sowing treatment of castasterone supplemented with citric acid enhanced cadmium accumulation in the roots (from 752 μg/g DW to 1192 μg/g DW) and shoots (from 88 μg/g DW to 311 μg/g DW) and also improved root length, shoot length, fresh weight, and dry weight of seedlings by 81, 17, 39, and 35 %, respectively. The co-application reduced malondialdehyde accumulation by 39 % and reduced oxidative stress by enhancing the activities of antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase, guaiacol peroxidase, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, dehydroascorbate, glutathione reductase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione-S-transferase, polyphenol oxidase), maximum enhancement (82 %) being in polyphenol oxidase. Similarly, the contents of water- and lipid-soluble antioxidants were found to increase by 31 and 4 %, respectively. Confocal microscopy revealed enhanced content of NO. Results suggested that binary combination of castasterone and citric acid is helpful in improving cadmium accumulation and ameliorating metal toxicity in B. juncea seedlings.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- PPB:
-
Potassium phosphate buffer
- TEMED:
-
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylethane-1,2-diamine
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- NADPH:
-
Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- nM:
-
Nanomole/liter
- mM:
-
Millimole/liter
- DW:
-
Dry weight
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- MLR:
-
Multiple linear regression
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Afshan S, Ali S, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Farid M, Abbas F, Ibrahim M, Mehmood MA, Abbasi GH (2015) Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus. L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(15):11679–11689. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4396-8
Ahammed GJ, Choudhary SP, Chen S, Xia X, Shi K, Zhou Y, Yu J (2013) Role of brassinosteroids in alleviation of phenanthrene-cadmium co-contamination-induced photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress in tomato. J Exp Bot 64(1):199–213. doi:10.1093/jxb/ers323
Ali N, Hadi F (2015) Phytoremediation of cadmium improved with the high production of endogenous phenolics and free proline contents in Parthenium hysterophorus plant treated exogenously with plant growth regulator and chelating agent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(17):13305–13318. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4595-3
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881
Ali B, Rafaqat A, Gill RA, Yang S, Gill MB, Farooq MA, Liu D, Daud MK, Ali S, Zhou W (2015) Regulation of cadmium-induced proteomic and metabolic changes by 5-aminolevulinic acid in leaves of Brassica napus L. PLoS One 10(4):e0123328. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0123328
Allen SE, Grimshaw HM, Parkinson JA, Quarmby C, Roberts JD (1976) Chemical analysis. In: Chapman SB (ed) Methods in plant ecology. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, London, pp. 424–426
Andresen E, Kupper H (2013) Cadmium toxicity in plants. In: Sigel A, Sigel H, Sigel KO (eds) Cadmium: from toxicity to essentiality. Metal science in life sciences. Springer, New York, pp. 395–413. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-5179-8_13
Anuradha S, Rao SSR (2007) The effect of brassinosteroids on radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seedlings growing under cadmium stress. Plant Soil Environ 53:465–472
Asgher M, Khan MIR, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2015) Minimising toxicity of cadmium in plants—role of plant growth regulators. Protoplasma 252:399–413. doi:10.1007/s00709-014-0710-4
Bajguz A, Piotrowska-Niczyporuk A (2014) Brassinosteroids implicated in growth and stress responses. In: Tran LSP, Pal S (eds) Phytohormones: a window to metabolism, signaling and biotechnological applications. Springer Science + Business Media, New York, pp. 163–190
Barbafieri M, Tassi E (2011) Brassinosteroids for phytoremediation application. In: Hayat S, Ahmad A (eds) Brassinosteroids: a class of plant hormone. Springer Science + Business Media B.V, Heidelberg, Germany, pp. 403–438
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287
Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro M (2005) Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:21–34
Blaylock MJ, Salt DE, Dushenkov S, Zakharova O, Gussman C, Kapulnik Y, Ensley BD, Raskin I (1997) Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environ Sci Technol 31(3):860–865
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bulak P, Walkiewicz A, Brzezińska M (2014) Plant growth regulators-assisted phytoextraction. Biol Plantarum 58(1):1–8
Cao F, Liu L, Ibrahim W, Cai Y, Wu F (2013) Alleviating effects of exogenous glutathione, glycinebetaine, brassinosteroids and salicylic acid on cadmium toxicity in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa). Agrotechnology 2:107. doi:10.4172/2168-9881.1000107
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1975) Purification and characterization of the flavoenzyme glutathione reductase from rat liver. J Biol Chem 250:5475–5480
Cassina L, Tassi E, Morelli E, Giorgetti L, Remorini D, Chaney RL, Barbafieri M (2011) Exogenous cytokinin treatments of an Ni hyper-accumulator, Alyssum murale, grown in a serpentine soil: implications for phytoextraction. Int J Phytoremediation 1:90–101
Cassina L, Tassi E, Pedron F, Petruzzelli G, Ambrosini P, Barbafieri M (2012) Using a plant hormone and a thioligand to improve phytoremediation of Hg-contaminated soil from a petrochemical plant. J Hazard Mater 231–232:36–42
Chen F, Wang F, Wu F, Mao W, Zhang G, Zhou M (2010) Modulation of exogenous glutathione in antioxidant defense system against Cd stress in the two barley genotypes differing in Cd tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(8):663–672. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.05.001
Chen X, Wang J, Shi Y, Zhaq MQ, Chi GY (2011) Effects of cadmium on growth and photosynthetic activities in pakchoi and mustard. Bot Stud 52:41–46
Choudhary SP, Kanwar M, Bhardwaj R, Yu JQ, Tran LS (2012) Chromium stress mitigation by polyamine-brassinosteroid application involves phytohormonal and physiological strategies in Raphanus sativus L. PLoS One 7(3):e33210. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033210
Cui JX, Zhou YH, Ding JG, Xia XJ, Shi K, Chen SC, Asami T, Chen ZX, Yu JQ (2011) Role of nitric oxide in hydrogen peroxide-dependent induction of abiotic stress tolerance by brassinosteroids in cucumber. Plant Cell Environ 34:347–358
Dalton DA, Russell SA, Hanus FJ, Pascoe GA, Evans HJ (1986) Enzymatic reactions of ascorbate and glutathione that prevent peroxide damage in soybean root nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci 83:3811–3815
Divi UK, Krishna P (2009) Brassinosteroid: a biotechnological target for enhancing crop yield and stress tolerance. New Biotechnol 26(3–4):131–136. doi:10.1016/j.nbt.2009.07.006
Duarte B, Delgado M, Caçador I (2007) The role of citric acid in cadmium and nickel uptake and translocation, in Halimione portulacoides. Chemosphere 69:836–840
Ehsan S, Ali S, Noureen S, Mahmood K, Farid M, Ishaque W, Shakoor MB, Rizwan M (2014) Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of cadmium by Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 106:164–172. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.03.007
Fancy NN, Bahlmann AK, Loake GJ (2016) Nitric oxide function in plant abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ. doi:10.1111/pce.12707
Fassler E, Evangelou MW, Robinson BH, Schulin R (2010) Effects of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) on sunflower growth and heavy metal uptake in combination with ethylene diamine disuccinic acid (EDDS). Chemosphere 80:901–907
Fielding JL, Hall JL (1978) A biochemical and cytological study of peroxidase activity in roots of Pisum sativum. J Exp Bot 29:969–981
Flohe L, Gunzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121
Foyer CH, Rennenberg H (2000) Regulation of glutathione synthesis and its role in abiotic and biotic stress. In: Rennenberg H, Brunold C, De Kok LJ, Stulen I (eds) Sulfur nutrition and sulfur assimilation in higher plants. SPB Academic Publishing, The Hague, The Netherlands, pp. 127–153
Gall JE, Boyd RS, Rajakaruna N (2015) Transfer of heavy metals through terrestrial food webs: a review. Environ Monit Assess 187(4):201. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4436-3
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Lannone MF, Rosalesa EP, Zawoznika MS, Groppaa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46
Gao Y, Miao C, Mao L, Zhou P, Jin Z, Shi W (2010) Improvement of phytoextraction and antioxidative defense in Solanum nigrum L. under cadmium stress by application of cadmium-resistant strain and citric acid. J Hazard Mater 181(1–3):771–777. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.080
Gao Y, Miao C, Xia J, Luo C, Mao L, Zhou P, Shi W (2012) Effect of citric acid on phytoextraction and antioxidative defense in Solanum nigrum L. as a hyperaccumulator under Cd and Pb combined pollution. Environ Earth Sci 65:1923–1932
Garbisu C, Alkorta I (2001) Phytoextraction: a cost-effective plant-based technology for the removal of metals from the environment. Bioresour Technol 77(3):229–236
Ghosh S, Chakraborty R, Raychaudhuri U (2015) Determination of pH-dependent antioxidant activity of palm (Borassus flabellifer) polyphenol compounds by photoluminol and DPPH methods: a comparison of redox reaction sensitivity. 3. Biotech 5(5):633–640
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(12):909–930
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2011) Cadmium stress tolerance in crop plants: probing the role of sulfur. Plant Signal Behav 6(2):215–222. doi:10.4161/psb.6.2.14880
Gill SS, Khan NA, Tuteja N (2011) Differential cadmium stress tolerance in five Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) cultivars an evaluation of the role of antioxidant machinery. Plant Signal Behav 6:293–300
Goswami S, Das S (2015) A study on cadmium phytoremediation potential of Indian mustard, Brassica juncea. Int J Phytoremediation 17(1–6):583–588. doi:10.1080/15226514.2014.935289
Habiba U, Ali S, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbasi GH, Hayat T, Ali B (2015) EDTA enhanced plant growth, antioxidant defence system and phytoextraction of copper by Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1534–1544
Habig WH, Jakoby WB (1981) Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-transferases. Methods Enzymol 77:398–405
Hartmann TN, Fricker MD, Rennenberg H, Meyer AJ (2003) Cell-specific measurement of cytosolic glutathione in poplar leaves. Plant Cell Environ 26(6):965–975
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hsiao KH, Kao PH, Hseu ZY (2007) Effects of chelators on chromium and nickel uptake by Brassica juncea on serpentine-mine tailings for phytoextraction. J Hazard Mater 148:366–376
Jakubowska D, Janicka-Russak M, Kabała K, Migocka M, Reda M (2015) Modification of plasma membrane NADPH oxidase activity in cucumber seedling roots in response to cadmium stress. Plant Sci 234:50–59. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.02.005
Kapoor D, Kaur S, Bhardwaj R (2014) Physiological and biochemical changes in Brassica juncea plants under Cd-induced stress. Biomed Res Int 2014:726070. doi:10.1155/2014/726070
Kaur G, Sharma A, Guruprasad K, Pati PK (2014) Versatile roles of plant NADPH oxidases and emerging concepts. Biotechnol Adv 32(3):551–563. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.02.002
Kim BK, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Tsujimoto M, Choe S (2008) Castasterone is a likely end product of brassinosteroid biosynthetic pathway in rice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374:614–619
Kono Y (1978) Generation of superoxide radical during autooxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys 186:189–195
Kumar KB, Khan PA (1982) Peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase in excised ragi (Eleusine coracana cv. PR 202) leaves during senescence. Indian J Exp Biol 20:412–416
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Laspina NV, Groppa MD, Tomaro ML, Benavides MP (2005) Nitric oxide protects sunflower leaves against Cd-induced oxidative stress. Plant Sci 169:323–330
Liao BH, Liu HY, Zeng QR, Yu PZ, Probst A, Probst JL (2005) Complex toxic effects of Cd2+, Zn2+, and acid rain on growth of kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Environ Int 31:891–895
Liu S, Yang R, Pan Y, Ma M, Pan J, Zhao Y, Cheng Q, Wu M, Wang M, Zhang L (2015) Nitric oxide contributes to minerals absorption, proton pumps and hormone equilibrium under cadmium excess in Trifolium repens L. plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 119:35–46. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.04.053
Lu LL, Tian SK, Yang XE, Peng HY, Li TQ (2013) Improved cadmium uptake and accumulation in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii: the impact of citric acid and tartaric acid. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 14(2):106–114. doi:10.1631/jzus.B1200211
McGrath SP (1998) Phytoextraction for soil remediation. In: Brooks RR (ed) Plants that hyperaccumulate heavy metals: their role in phytoremediation, microbiology, archeology, mineral exploration and Phytomining. CAN International, New York, pp. 261–288
Mohamed AA, Castagna A, Ranieri A, Sanità di Toppi L (2012) Cadmium tolerance in Brassica juncea roots and shoots is affected by antioxidant status and phytochelatin biosynthesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 57:15–22
Najeeb U, Jilani G, Ali S, Sarwar M, Xu L, Zhou W (2011) Insights into cadmium induced physiological and ultra-structural disorders in Juncus effusus L. and its remediation through exogenous citric acid. J Hazard Mater 186:565–574
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate specific-peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22(5):867–880
Nazar R, Iqbal N, Masood A, Khan MIR, Syeed S, Khan NA (2012) Cadmium toxicity in plants and role of mineral nutrients in its alleviation. Am J Plant Sci 3(10):1476–1489
Neill SJ, Desikan R, Hancock JT (2003) Nitric oxide signaling in plants. New Phytol 159:11–35
Noctor G, Mhamdi A, Foyer CH (2014) The roles of reactive oxygen metabolism in drought: not so cut and dried. Plant Physiol 164(4):1636–1648. doi:10.1104/pp.113.233478
Poonam KR, Bhardwaj R, Sirhindi G (2015) Castasterone regulated polyphenolic metabolism and photosynthetic system in Brassica juncea plants under copper stress. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 4(4):282–289
Putter J (1974) Peroxidase. In: Bergmeyer, H.U. (Ed.), Methods of enzymatic analysis. vol 2 Weinhan, Verlag Chemie, pp 685–690
Qadir S, Jamshieed S, Rasool S, Ashraf M, Akram NA, Ahmad P (2014) Modulation of plant growth and metabolism in cadmium-enriched environments. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 229:51–88. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-03777-6_4
Quartacci MF, Baker AJM, Navari-Izzo F (2005) Nitrilotriacetate- and citric acid-assisted phytoextraction of cadmium by Indian mustard (Brassica juncea (L.) Czernj, Brassicaceae). Chemosphere 59:1249–1255
Rascio N, Navari-Izzo F (2011) Heavy metal hyperaccumulating plants: how and why do they do it? And what makes them so interesting? Plant Sci 180(2):169–181. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.08.016
Rodriguez-Serrano M, Romero-Puertas MC, Pazmino DM, Testillano PS, Risueno MC, del Rio LA, Sandalio LM (2009) Cellular response of pea plants to cadmium toxicity: cross talk between reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, and calcium. Plant Physiol 150:229–243
Romero-Puertas MC, Corpas FJ, Rodriguez-Serrano M, Gomez M, del Río LA, Sandalio LM (2007) Differential expression and regulation of antioxidative enzymes by Cd in pea plants. J Plant Physiol 164:1346–1357
Saxena I, Shekhawat GS (2013) Nitric oxide (NO) in alleviation of heavy metal induced phytotoxicity and its role in protein nitration. Nitric Oxide 32:13–20. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2013.03.004
Seth CS, Remans T, Keunen E, Jozefczak M, Gielen H, Opdenakker K, Weyens N, Vangronsveld J, Cuypers A (2012) Phytoextraction of toxic metals: a central role for glutathione. Plant Cell Environ 35(2):334–346. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02338.x
Sharma I, Pati PK, Bhardwaj R (2010) Regulation of growth and antioxidant enzyme activities by 28-homobrassinolide in seedlings of Raphanus sativus L. under cadmium stress. Indian J Biochem Biophys 47(3):172–177
Sharma I, Pati PK, Bhardwaj R (2011a) Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on oxidative stress markers induced by nickel-ion in Raphanus sativus L. Acta Physiol Plant 33:1723–1735. doi:10.1007/s11738-010-0709-1
Sharma A, Sharma I, Pati PK (2011b) Post-infectional changes associated with the progression of leaf spot disease in Withania somnifera. J Plant Pathol 93(2):397–405
Sharma P, Jha AB, Dubey RS, Pessarakli M (2012) Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J Bot 217037:26. doi:10.1155/2012/217037
Sharma A, Vats SK, Pati PK (2014) Post-infectional dynamics of leaf spot disease in Withania somnifera. Ann Appl Biol 165:429–440
Tran TA, Popova LP (2013) Functions and toxicity of cadmium in plants: recent advances and future prospects. Turk J Bot 37:1–13. doi:10.3906/bot-1112-16
Vázquez MN, Guerrero YR, González LM, de la Noval WT (2013) Brassinosteroids and plant responses to heavy metal stress. An overview. O J Metal 3:34–41. doi:10.4236/ojmetal.2013.32A1005
Verma K, Shekhawat GS, Sharma A, Mehta SK, Sharma V (2008) Cadmium induced oxidative stress and changes in soluble and ionically bound cell wall peroxidase activities in roots of seedling and 3-4 leaf stage plants of Brassica juncea (L.) czern. Plant Cell Rep 27(7):1261–1269. doi:10.1007/s00299-008-0552-7
Woodbury W, Spencer AK, Stahmann MA (1971) An improved procedure using ferricyanide for detecting catalase isozymes. Anal Biochem 443:301–305
Xiong J, Lu H, Lu K, Duan Y, An L, Zhu C (2009) Cadmium decreases crown root number by decreasing endogenous nitric oxide, which is indispensable for crown root primordia initiation in rice seedlings. Planta 230(4):599–610. doi:10.1007/s00425-009-0970-y
Xu L, Dong Y, Kong J, Liu S (2014) Effects of root and foliar applications of exogenous NO on alleviating cadmium toxicity in lettuce seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 72:39–50
Yeh TY, Pan CT (2012) Effect of chelating agents on copper, zinc, and lead uptake by sunflower, Chinese cabbage, cattail, and reed for different organic contents of soils. J Environ Anal Toxicol 2(5):1000145. doi:10.4172/2161-0525.1000145
Zhang L, Chen Z, Zhu C (2012) Endogenous nitric oxide mediates alleviation of cadmium toxicity induced by calcium in rice seedlings. J Environ Sci 24(5):940–948
Zhao Y, Peralta-Videa JR, Lopez-Moreno ML, Ren M, Saupe G, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2011) Kinetin increases chromium absorption, modulates its distribution, and changes the activity of catalase and ascorbate peroxidase in Mexican Palo Verde. Environ Sci Technol 45(3):1082–1087. doi:10.1021/es102647w
Zheng G, Lv HP, Gao S, Wang SR (2010) Effects of cadmium on growth and antioxidant responses in Glycyrrhiza uralensis seedlings. Plant Soil Environ 56:508–515
Acknowledgment
Research fellowship to the first author was provided by the Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, under the INSPIRE scheme. The authors are thankful to the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, for establishing sophisticated instrumentation facilities in the university campus under the universities with potential for excellence (UPE) scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Highlights
• Co-application of castasterone and citric acid reduced cadmium-induced oxidative stress in B. juncea by enhancing the activities of antioxidative enzymes and antioxidant content.
• Application of castasterone and citric acid restored cell viability and endogenous nitric oxide content of cadmium-stressed seedlings.
• Binary treatment of castasterone and citric acid enhanced cadmium phytoextraction in the seedlings.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, R., Yadav, P., Thukral, A.K. et al. Co-application of 6-ketone type brassinosteroid and metal chelator alleviates cadmium toxicity in B. juncea L.. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 685–700 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7864-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7864-x