Abstract
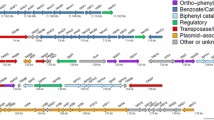
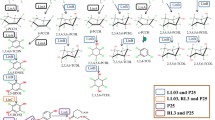
In order to study the mechanisms regulating the phenanthrene degradation pathway and the intermediate-metabolite accumulation in strain S. paucimobilis 20006FA, we sequenced the genome and compared the genome-based predictions to experimental proteomic analyses. Physiological studies indicated that the degradation involved the salicylate and protocatechuate pathways, reaching 56.3% after 15 days. Furthermore, the strain degraded other polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) such as anthracene (13.1%), dibenzothiophene (76.3%), and fluoranthene. The intermediate metabolite 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid (HNA) accumulated during phenanthrene catabolism and inhibited both bacterial growth and phenanthrene degradation, but exogenous-HNA addition did not affect further degradation. Genomic analysis predicted 126 putative genes encoding enzymes for all the steps of phenanthrene degradation, which loci could also participate in the metabolism of other PAH. Proteomic analysis identified enzymes involved in 19 of the 23 steps needed for the transformation of phenanthrene to trichloroacetic-acid intermediates that were upregulated in phenanthrene cultures relative to the levels in glucose cultures. Moreover, the protein-induction pattern was temporal, varying between 24 and 96 h during phenanthrene degradation, with most catabolic proteins being overexpressed at 96 h—e. g., the biphenyl dioxygenase and a multispecies (2Fe–2S)-binding protein. These results provided the first clues about regulation of expression of phenanthrene degradative enzymes in strain 20006FA and enabled an elucidation of the metabolic pathway utilized by the bacterium. To our knowledge the present work represents the first investigation of genomic, proteomic, and physiological studies of a PAH-degrading Sphingomonas strain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armengaud J (2013) Microbiology and proteomics, getting the best of both worlds! Environ Microbiol 15(1):12–23
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom 9(1):75
Basta T, Keck A, Klein J, Stolz A (2004) Detection and characterization of conjugative degradative plasmids in xenobiotic-degrading Sphingomonas strains. J Bacteriol 186(12):3862–3872
Basta T, Buerger S, Stolz A (2005) Structural and replicative diversity of large plasmids from sphingomonads that degrade polycyclic aromatic compounds and xenobiotics. Microbiology 151(Pt 6):2025–2037
Cavalca L, Guerrieri N, Colombo M, Pagani S, Andreoni V (2007) Enzymatic and genetic profiles in environmental strains grown on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 91(4):315–325
Cerniglia C, Yang S (1984) Stereoselective metabolism of anthracene and phenanthrene by the fungus Cunninghamella elegans. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:119–124
Cho O, Choi KY, Zylstra GJ, Kim YS, Kim SK, Lee JH, Sohn HY, Kwon GS, Kim YM, Kim E (2005) Catabolic role of a three-component salicylate oxygenase from Sphingomonas yanoikuyae B1 in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327(3):656–662
Coppotelli BM, Ibarrolaza A, Del Panno MT, Morelli IS (2008) Effects of the inoculant strain Sphingomonas paucimobilis 20006FA on soil bacterial community and biodegradation in phenanthrene-contaminated soil. Microb Ecol 55(2):173–183
Coppotelli BM, Ibarrolaza A, Dias RL, Del Panno MT, Berthe-Corti L, Morelli IS (2010) Study of the degradation activity and the strategies to promote the bioavailability of phenanthrene by Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain 20006FA. Microb Ecol 59:266–276
Demaneche S, Meyer C, Micoud J, Louwagie M, Willison JC, Jouanneau Y (2004) Identification and functional analysis of two aromatic-ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases from a Sphingomonas strain that degrades various polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(11):6714–6725
Desai AM, Autenrieth RL, Dimitriou-Christidis P, McDonald TJ (2008) Biodegradation kinetics of select polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) mixtures by Sphingomonas paucimobilis EPA505. Biodegradation 19 (2):223–233
Dong C, Bai X, Lai Q, Xie Y, Chen X, Shao Z (2014) Draft Genome sequence of Sphingobium sp. strain C100, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium from the deep-sea sediment of the Arctic Ocean. Genome Announc 2(1):e01210–e01213
Favaloro B, Tamburro A, Trofino M, Bologna L, Rotilio D, Heipieper H (2000) Modulation of the glutathione S-transferase in Ochrobactrum anthropi: function of xenobiotic substrates and other forms of stress. Biochem J 346(2):553–559
Fernandez S, Shingler V, De Lorenzo V (1994) Cross-regulation by XylR and DmpR activators of Pseudomonas putida suggests that transcriptional control of biodegradative operons evolves independently of catabolic genes. J Bacteriol 176(16):5052–5058
Fernandez-Luqueno F, Valenzuela-Encinas C, Marsch R, Martinez-Suarez C, Vazquez-Nunez E, Dendooven L (2011) Microbial communities to mitigate contamination of PAHs in soil-possibilities and challenges: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 18(1):12–30
Festa S, Coppotelli BM, Madueño L, Loviso CL, Macchi M, Tauil RMN, Valacco MP, Morelli IS (2017) Assigning ecological roles to the populations belonging to a phenanthrene-degrading bacterial consortium using omic approaches. PLoS ONE 12(9):e0184505
Fialho AM, Moreira LM, Granja AT, Popescu AO, Hoffmann K, Sa-Correia I (2008) Occurrence, production, and applications of gellan: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(6):889–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1496-0
Fulekar M, Sharma J (2008) Bioinformatics applied in bioremediation. Innov Rom Food Biotechnol 3:28
Gibson DT (1984) Microbial degradation of aromatic hydrocabons. Microb Degrad Org Compd 31:181–252
Johnsen AR, Karlson U (2005) PAH degradation capacity of soil microbial communities–does it depend on PAH exposure? Microb Ecol 50(4):488–495
Jouanneau Y, Micoud J, Meyer C (2007) Purification and characterization of a three-component salicylate 1-hydroxylase from Sphingomonas sp. strain CHY-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(23):7515–7521
Khara P, Roy M, Chakraborty J, Ghosal D, Dutta TK (2014) Functional characterization of diverse ring-hydroxylating oxygenases and induction of complex aromatic catabolic gene clusters in Sphingobium sp. PNB FEBS Open Bio 4:290–300
Pao SS, Paulsen IT, Saier MH (1998) Major facilitator superfamily. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62(1):1–34
Peng RH, Xiong AS, Xue Y, Fu XY, Gao F, Zhao W, Tian YS, Yao QH (2008) Microbial biodegradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32(6):927–955
Perez Vidakovics ML, Paba J, Lamberti Y, Ricart CA, Valle de Sousa M, Rodriguez ME (2007) Profiling the Bordetella pertussis proteome during iron starvation. J Proteome Res 6(7):2518–2528
Pieper DH, Reineke W (2000) Engineering bacteria for bioremediation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11(3):262–270
Romine MF, Stillwell LC, Wong K-K, Thurston SJ, Sisk EC, Sensen C, Gaasterland T, Fredrickson JK, Saffer JD (1999) Complete sequence of a 184-kilobase catabolic plasmid from Sphingomonas aromaticivorans F199. J Bacteriol 181(5):1585–1602
Rutherford K, Parkhill J, Crook J, Horsnell T, Rice P, Rajandream M-A, Barrell B (2000) Artemis: sequence visualization and annotation. Bioinformatics 16:944–945
Sanchez J-C, Hochstrasser D, Rabilloud T (1999) In-gel sample rehydration of immobilized pH gradient. In: Link AJ (ed) 2-D proteome analysis protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 221–225
Stolz A (2009) Molecular characteristics of xenobiotic-degrading sphingomonads. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81(5):793–811
Story S, Kline E, Hughes T, Riley M, Hayasaka S (2004) Degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain EPA505. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 47(2):168–176
Tritt A, Eisen JA, Facciotti MT, Darling AE (2012) An integrated pipeline for de novo assembly of microbial genomes. PLoS ONE 7:e42304
Vandermeer KD, Daugulis AJ (2007) Enhanced degradation of a mixture of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a defined microbial consortium in a two-phase partitioning bioreactor. Biodegradation 18(2):211–221
Vandermeersch G, Lourenco HM, Alvarez-Munoz D, Cunha S, Diogene J, Cano-Sancho G, Sloth JJ, Kwadijk C, Barcelo D, Allegaert W, Bekaert K, Fernandes JO, Marques A, Robbens J (2015) Environmental contaminants of emerging concern in seafood—European database on contaminant levels. Environ Res 143:29–45
Waigi MG, Kang F, Goikavi C, Ling W, Gao Y (2015) Phenanthrene biodegradation by sphingomonads and its application in the contaminated soils and sediments: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 104:333–349
Xia Y, Min H, Rao G, Lv Z-m, Liu J, Ye Y-f, Duan X-j (2005) Isolation and characterization of phenanthrene-degrading Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain ZX4. Biodegradation 16(5):393–402
Yuan SY, Wei SH, Chang BV (2000) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a mixed culture. Chemosphere 41(9):1463–1468
Zafra G, Absalón ÁE, Anducho-Reyes M, Fernandez FJ, Cortés-Espinosa DV (2017) Construction of PAH-degrading mixed microbial consortia by induced selection in soil. Chemosphere 172:120–126
Zhang H, Wang DZ, Xie ZX, Zhang SF, Wang MH, Lin L (2015) Comparative proteomics reveals highly and differentially expressed proteins in field-collected and laboratory-cultured blooming cells of the diatom Skeletonema costatum. Environ Microbiol 17:3976–3991
Zhao HP, Wang L, Ren JR, Li Z, Li M, Gao HW (2008) Isolation and characterization of phenanthrene-degrading strains Sphingomonas sp. ZP1 and Tistrella sp. ZP5. J Hazard Mater 152(3):1293–1300
Zhao Q, Hu H, Wang W, Peng H, Zhang X (2015) Genome sequence of Sphingobium yanoikuyae B1, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading strain. Genome Announc 3(1):e01522–e01514
Zhao Q, Yue S, Bilal M, Hu H, Wang W, Zhang X (2017) Comparative genomic analysis of 26 Sphingomonas and Sphingobium strains: dissemination of bioremediation capabilities, biodegradation potential and horizontal gene transfer. Sci Total Environ 609:1238–1247
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (PICT 2013-0103 and 2010-1983). Macchi M. has a doctoral fellowship supported by CONICET. Morelli I.S. is a research member of CIC-PBA. Coppotelli B.M. and Valacco MP are research members of CONICET. Dr. Donald F. Haggerty, a retired academic career investigator and native English speaker, edited the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Macchi, M., Martinez, M., Tauil, R.M.N. et al. Insights into the genome and proteome of Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain 20006FA involved in the regulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34, 7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2391-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2391-6