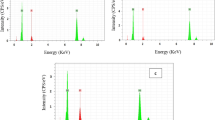
Abstract
The role of ferric oxide nanoparticles on the lubricating characteristics of passivating films formed on stainless steel (SS) was discussed in this study. The tribo-electrochemical behavior of mirror-like polished AISI 304 SS, used as an exemplary material, was evaluated in various electrolytes by means of a simulated chemical–mechanical polishing process in laboratory scale. It was clearly demonstrated that a suitable combination of abrasives (ferric oxide nanoparticles) and an oxidizer (nitric acid) can act as an effective lubricant that lowers the friction and wear of the AISI 304 SS surfaces. The excellent lubricating and anti-corrosion properties shown by a slurry containing a high content of ferric oxide nanoparticles at high nitric acid concentrations were attributed to the formation of a stable and robust passive film that was composed of chromium oxide and a mixture of iron oxides. The lack of ferric oxide nanoparticles in two solutions containing nitric acid of different concentrations led to pitting corrosion and abrasive wear. When low concentrations of both ferric oxide nanoparticles and nitric acid were used, wear-accelerated corrosion became the dominant mechanism that was caused by the presence of third-body wear particles in the contact zone.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landolt, D., Mischler, S., Stemp, M.: Electrochemical methods in tribocorrosion: a critical appraisal. Electrochim. Acta 46, 3913–3929 (2001)
Mischler, S., Ponthiaux, P.: A round robin on combined electrochemical and friction tests on alumina/stainless steel contacts in sulphuric acid. Wear 1–2, 211–225 (2001)
Assi, F., Bohni, H.: Study of wear–corrosion synergy with a new microelectrochemical technique. Wear 233–235, 505–514 (1999)
Watson, S.W., Friedersdorf, F.J., Madsen, B.W., Cramer, S.D.: Methods of measuring wear-corrosion synergism. Wear 181–183, 476–484 (1995)
Fang, C.K., Huang, C.C., Chuang, T.H.: Synergistic effects of wear and corrosion for Al2O3 particulate-reinforced 6061 aluminium matrix composites. Metall. Mater. Trans. 30A, 643–651A (1999)
Ponthiaux, P., Wenger, F., Drees, D., Celis, J.-P.: Electrochemical techniques for studying tribocorrosion processes. Wear 256, 459–468 (2004)
Mischler, S.: Triboelectrochemical techniques and interpretation methods in tribocorrosion: a comparative evaluation. Tribol. Int. 41, 573–583 (2008)
Wood, R.J.K.: Tribo-corrosion of coatings: a review. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 5502–5521 (2007)
Stack, M.M.: Mapping tribo-corrosion processes in dry and in aqueous conditions: some new directions for the new millennium. Tribol. Int. 35, 681–689 (2002)
Rimbert, J.F., Pagetti, J.: Repassivation kinetics studies on an austenitic stainless steel in chloride media. Corros. Sci. 20(2), 189–210 (1980)
Burstein, G.T., Marshall, P.I.: Growth of passivating films on scratched 304L stainless steel in alkaline solution. Corros. Sci. 23(2), 125–137 (1983)
Burstein, G.T., Gao, G.: Verification of the validity of peak bare surface current densities obtained from the scratched electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 138(9), 2627–2630 (1991)
Bastek, P., Newman, R., Kelly, R.: Measurement of passive film effects on scratched electrode behavior. J. Electrochem. Soc. 140, 1884–1889 (1993)
Xiulin, J., Biao, H., Yixian, L., Shuqi, W.: Sliding tribocorrosion behavior of bulk metallic glass against bearing steel in 3.5% NaCl solution. Tribol. Int. 91, 214–220 (2015)
Huttunen-Saarivirta, E., Kilpi, L., Hakala, T.J., Carpen, L., Ronkainen, H.: Tribocorrosion study of martensitic and austenitic stainless steels in 0.01 M NaCl solution. Tribol. Int. 95, 358–371 (2016)
Chen, J., Wang, J., Yan, F., Zhang, Q., Li, Q.: Effect of applied potential on the tribocorrosion behaviors of Monel K500 alloy in artificial seawater. Tribol. Int. 81, 1–8 (2015)
Hedayat, A., Yannacopoulos, S., Postlethwaite, J., Sangal, S.: Aqueous corrosion of plain carbon steel during sliding wear. Wear 154, 167–176 (1992)
Totolin, V., Pejakovic, V., Csanyi, T., Hekele, O., Huber, M., Ripoll, M.R.: Surface engineering of Ti6Al4 V surfaces for enhanced tribocorrosion performance in artificial seawater. Mater. Des. 104, 10–18 (2016)
Wu, P., Celis, J.P.: Electrochemical noise measurements on stainless steel during corrosion-wear in sliding contacts. Wear 256, 480–490 (2004)
Malfatti, C.F., Veit, H.M., Santos, C.B., Metzner, M., Hololeczek, H., Bonino, J.-P.: Heat treated NiP-SiC composite coatings: elaboration and tribocorrosion behaviour in NaCl solution. Tribol. Lett. 36, 165–173 (2009)
Bazzoni, A., Mischler, S., Espallargas, N.: Tribocorrosion of pulsed plasma-nitrided CoCrMo implant alloy. Tribol. Lett. 49, 157–167 (2013)
Yu, S.Y., Ishii, H., Chuang, T.H.: Corrosive wear of SiC whisker-and 6061 aluminum alloy composites particulate-reinforced. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 27A, 2653–2662 (1996)
Salasi, M., Stachowiak, G., Stachowiak, G.: Tribo-electrochemical behaviour of 316L stainless steel: the effects of contact configuration, tangential speed, and wear mechanism. Corros. Sci. 98, 20–32 (2015)
Salasi, M., Stachowiak, G., Stachowiak, G.: New experimental rig to investigate abrasive-corrosive characteristics of metals in aqueous media. Tribol. Lett. 40, 71–84 (2010)
Sun, D., Wharton, J.A., Wood, R.J.K.: Abrasive size and concentration effects on the tribo-corrosion of cast CoCrMo alloy in simulated body fluids. Tribol. Int. 42, 1595–1604 (2009)
Zu, J.B., Hutchings, I.M., Burstein, G.T.: Design of a slurry erosion test rig. Wear 140, 331–344 (1990)
Barik, R.C., Wharton, J.A., Wood, R.J.K., Stokes, K.R.: Electro-mechanical interactions during erosion-corrosion. Wear 267, 1900–1908 (2009)
Cheng, J., Wang, T., Chai, Z., Lu, X.: Tribocorrosion study of copper during chemical mechanical polishing in potassium periodate-based slurry. Tribol. Lett. 58, 8 (2015)
Li, J., Chai, Z., Liu, Y., Lu, X.: Tribo-chemical behavior of copper in chemical mechanical planarization. Tribol. Lett. 50, 177–184 (2013)
Zhao, D., Lu, X.: Chemical mechanical polishing: theory and experiment. Friction 1, 306–326 (2013)
Kao, M.J., Hsu, F.C., Peng, D.X.: Synthesis and characterization of SiO2 nanoparticles and their efficacy in chemical mechanical polishing steel substrate. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2014). doi:10.1155/2014/691967
Peng, D.-X.: Chemical mechanical polishing of steel substrate using aluminum nanoparticles abrasive slurry. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 66, 124–130 (2014)
Jiang, L., He, Y., Luo, J.: Chemical mechanical polishing of steel substrate using colloidal silica-based slurries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 330, 487–495 (2015)
Hu, X., Song, Z., Liu, W., Qin, F., Zhang, Z., Wan, H.: Chemical mechanical polishing of stainless steel foil as flexible substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 5798–5802 (2012)
Yun, D.-J., Lim, S.-H., Lee, T.-W., Rhee, S.-W.: Fabrication of the flexible pentacene thin-film transistors on 304 and 430 stainless steel (SS) substrate. Org. Electron. 10, 970–977 (2009)
Stojadinovic, J., Mischler, S., Bouvet, D., Declercq, M.: Tribocorrosion of tungsten: effect of potential on wear. Tribol. Ind. 29, 41–44 (2007)
Gao, F., Liang, H.: Material removal mechanisms in electrochemical-mechanical polishing of tantalum. Electrochim. Acta 54, 6808–6815 (2009)
Jang, K., Nam, E., Lee, C.-Y., Seok, J., Min, B.-K.: Mechanisms of synergistic material removal by electrochemical magnetorheological polishing. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf 70, 88–92 (2013)
Totolin, V., Göcerler, H., Rodríguez Ripoll, M., Jech, M.: Tribo-electrochemical study of stainless steel surfaces during chemical-mechanical polishing. Lubr. Sci. 28, 363–380 (2016)
Iida, S., Hidaka, Y.: Influence of the iron oxide layer on lubricating properties in seamless pipe hot rolling. Tetsu-to-Hagane 94, 244–250 (2008)
Hu, Z.S., Dong, J.X., Chen, G.X.: Study on antiwear and reducing friction additive of nanometer ferric oxide. Tribol. Int. 31, 355–360 (1998)
Inzelt, G.: Pseudo-reference electrodes, handbook of reference electrodes, pp. 331–332. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Kasem, K., Jones, S.: Platinum as a reference electrode in electrochemical measurements. Platin. Met. Rev. 52, 100–106 (2008)
Pejakovic, V., Totolin, V., Göcerler, H., Brenner, J., Rodriguez Ripoll, M.: Friction and wear behavior of selected titanium and zirconium based nitride coatings in Na2SO4 aqueous solution under low contact pressure. Tribol. Int. 91, 267–273 (2015)
Beverskog, B., Puigdomenech, I.: Pourbaix diagrams for the ternary system of iron-chromium-nickel. Corrosion 55, 1077–1087 (1999)
Bardwell, J.A., Sproule, G.I., MacDougall, B., Graham, M.J., Davenport, A.J., Isaacs, H.S.: In situ XANES detection of Cr(VI) in the passive film on Fe-26Cr. J. Electrochem. Soc. 139, 371–373 (1992)
Bojinov, M., Fabricius, G., Kinnunen, P., Laitinen, T., Makela, K., Saario, T., Sundholm, G.: The mechanism of transpassive dissolution of Ni–Cr alloys in sulphate solutions. Electrochim. Acta 45, 2791–2802 (2000)
Schmuki, P., Virtanen, S., Isaacs, H.S., Ryan, M.R., Davenport, A.J., Bohni, H., Stenberge, T.: Electrochemical behaviour of Cr2O3/Fe2O3 artificial passive films studied by in situ XANES. J. Electrochem. Soc. 145, 791–801 (1998)
Ningshen, S., Kamachi, M.U., Ramya, S., Raj, B.: Corrosion behavior of AISI type 304L stainless steel in nitric acid media containing oxidizing species. Corros. Sci. 53, 64–70 (2011)
Evans, U.R.: The corrosion and oxidation of metals: scientific principles and practical applications. Edward Arnold, London (1960)
Fauvet, P., Balbaud, F., Robin, R., Tran, Q.T., Mugnier, A., Espinoux, D.: Corrosion mechanisms of austenitic stainless steels in nitric media used in reprocessing plants. J. Nucl. Mater. 375, 52–64 (2008)
Ningshen, S., Kamachi, M.U., Amarendra, G., Raj, B.: Corrosion assessment of nitric acid grade austenitic stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 51, 322–329 (2009)
Godet, M.: 3rd-Bodies in tribology. Wear 136, 29–45 (1990)
Landolt, D., Mischler, S., Stemp, M., Barril, S.: Third body effects and material fluxes in tribocorrosion systems involving a sliding contact. Wear 256, 517–524 (2004)
Stachowiak, G.W., Batchelor, A.W.: Engineering tribology, 3rd edn. Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Amsterdam (2005)
Mohapatra, M., Anand, S.: Synthesis and applications of nano-structured iron oxides/hydroxides: a review. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2, 127–146 (2010)
Lorang, G., Cunha Belo, M.D., Simoes, A.M.P., Ferreira, M.G.S.: Chemical composition of passive films on AISI 304 stainless steel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 141, 3347–3356 (1994)
Husein, M.M., Zakaria, M.F., Hareland, G.: Use of nanoparticles as a lubricity additive in well fluids. WO Patent 2013116921 A1 (2013)
Freire, L., Catarino, M.A., Godinho, M.I., Ferreira, M.J., Ferreira, M.G.S., Simões, A.M.P., Montemor, M.F.: Electrochemical and analytical investigation of passive films formed on stainless steels in alkaline media. Cement Concr. Compos. 34, 1075–1081 (2012)
Milanti, A., Koivuluoto, H., Vuoristo, P., Bolelli, G., Bozza, F., Lusvarghi, L.: Microstructural characteristics and tribological behavior of HVOF-sprayed novel Fe-based alloy coatings. Coatings 4, 98–120 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Austrian COMET-Program (Project K2 XTribology, Grant No. 849109) and has been carried out within the Excellence Centre of Tribology. The authors would like to thank Christoph Gabler for performing the XPS analyses and Fjorda Xhiku for the topography measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Totolin, V., Göcerler, H., Rodríguez Ripoll, M. et al. The Role of Ferric Oxide Nanoparticles in Improving Lubricity and Tribo-Electrochemical Performance During Chemical–Mechanical Polishing. Tribol Lett 65, 20 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0806-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0806-4