Abstract
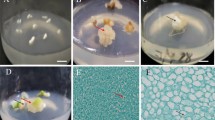
The low efficiency of somatic embryo induction, proliferation, germination, and conversion to plantlets is a major problem in walnut. In this study, we used the cotyledons of immature embryos of apomictic seeds in walnut plus trees ‘Y17’ as explants. The optimum medium and culture conditions of somatic embryo induction, proliferation, and germination were tested through comparative experiments. The results showed that the optimum formula for somatic embryo induction, proliferation, and germination medium was DKW medium with 1.0 mg L−1 6-BA, 2.0 mg L−1 KT, and 0.01 mg L−1 IBA, DKW medium with 30–40 g L−1 sucrose and 7–8 g L−1 agar, and DKW medium with 2.0 mg L−1 concentrations of GA3, respectively. Meanwhile, the optimum time of seedling training was 36 h, and the substrate ratio was perlite: peat soil: vermiculite (1: 2: 1) after plant transplanting. The inter simple sequence repeat marker banding patterns of the primary embryo, secondary embryo and regenerated plants were all identical to that of the mother plant and proved the genetic stability of regenerated plants. An excellent walnut tissue culture system from walnut somatic embryo to the whole plant was formed, which can accelerate the speed of walnut genetic improvement.
Key message
An excellent walnut tissue culture system from walnut somatic embryo to the whole plant was formed, which can accelerate the speed of walnut genetic improvement.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DKW:
-
Driver and kuniyuki walnut
- 6-BA:
-
6-Benzylaminopruine
- KT:
-
Kinetin
- IBA:
-
Indole-3-butyric acid
- GA3 :
-
Gibberellic acid (3)
- WPM:
-
Wood plant medium
- MS:
-
Murashige and skoog medium
- ISSR:
-
Inter simple sequence repeats
References
Al-Snafi AE (2018) Chemical constituents, nutritional, pharmacological and therapeutic importance of Juglans regia-a review. IOSR J Pharm 8(11):1–21
Arnold S, Sabala I, Bozhkov P, Dyachok J, Filonova L (2002) Developmental pathways of somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 69:233–249
Bernard A, Lheureux F, Dirlewanger E (2018) Walnut: past and future of geneticim provement. Tree Genet Genomes 14(1):1
Chen X, Lai HG, Sun Q, Liu JP, Chen SB, Zhu WL (2018) Induction of apomixis by dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and genetic identification of apomictic plants in cassava. Breed Sci 68(2):227–232
Deng MD, Cornu D (1992) Maturation and germination of walnut somatic emryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 28:195–202
Feng S, Fang H, Liu X, Dong Y, Yang KQ (2021) Genome-wide identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs conferring resistance to Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in walnut (Juglans regia). BMC Genomics 22(1):15
Harada JJ (1999) Signaling in plant embryogenesis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:23–27
Jalali MA, Sirmandi HB, Hatamzadeh A (2017) Effects of carbohydrate source and polyethylene glycol on maturation and germination of somatic embryos in walnut (Juglans regia L.). J Crop Sci Biotechnol 20(1):29–35
Jariteh M, Ebrahimzadeh H, Niknam V, Mirmasoumi M, Vahdati K (2015) Developmental changes of protein, proline and some antioxidant enzymes activities in somatic and zygotic embryos of Persian walnut (Juglans regia L.). Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Culture 122(1):101–115
Koltunow AM, Grossniklaus U (2003) Apomixis: a developmental perspective. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:547–574
Long LM, Preece JE, Sambeek JWV (1995) Adventitious regeneration of Juglans nigra L (eastern black walnut). Plant Cell Rep 14(12):799–803
Lopes MA, Larkins BA (1993) Endosperm origin, development, and function. Plant Cell 5:1383–1399
McGranahan G, Leslie C, Uratsu S, Dandekar A (1990) Improve defficiency of the walnut somatic embryo gene transfer system. Plant Cell Rep 8:512–516
Oh MJ, Na HR, Choi HK, Liu JR, Kim SW (2010) High frequency plant regeneration system for Nymphoides coreana via somatic embryogenesis from zygotic embryoderived embryogenic cell suspension cultures. Plant Biotech Rep 4:125–128
Potter D, Gao F, Aiello G, Leslie C, McGranahan G (2002) Intersimple sequence repeat markers for fingerprinting and determining genetic relationships of walnut (Juglans regia) cultivars. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 127(1):75–81
Quiroz-Figueroa FR, Rojas-Herrera R, Galaz-Avalos RM, Loyola-Vargas VM (2006) Embryo production through somatic embryogenesis can be used to study cell differentiation in plants. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 86:285–301
Rodriguez-Leal D, Vielle-Calzada JP (2012) Regulation of apomixis: learning from sexual experience. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15:549–555
Solar A, Smole J, Simoncic S (1995) The ability of apomictic fruit setting in five walnut cultivars (Juglands regia L.). Kmetijstvo
Stasolla C, Yeung EC (2003) Recent advances in conifer somatic embryogenesis: improving somatic embryo quality. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 74:15–35
Tang H, Ren Z, Reustle G, Krczal G, Germaine E (2001) Optimizing secondary somatic embryo production in English walnut (Juglans regia L.). Acta Hort 544:187–194
Tautorus TE, Fowke LC, Dunstan DI (1991) Somatic embryogenesis in conifers. Can J Bot 69:1873–1899
Tulecke W, McGranahan G (1985) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from cotyledons of walnut, Juglans regia L. Plant Sci 40:57–63
Vahdati K, Jariteh M, Niknam V, Mirmasoumi M, Ebrahimzadeh H (2006) Somatic embryogenesis and embryo maturation in Persian walnut. Acta Hortic 705:199–205
Vahdati K, Bayat SH, Ebrahimzadeh H, Jariteh M, Mirmasoumi M (2008) Effect of exogenous ABA on somatic embryo maturationand germination in Persian walnut (Juglans regia L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 93:163–171
van Dijk PJ, Rigola D, Schauer SE (2016) Plant breeding: surprisingly, less sex is better. Curr Biol 26:R122-124
Wu G, Yang J, Zhang P, Liu Q, Song Y (2010) Study on the apomixis in Shanxi Mianhetao walnut. J Fruit Sci 27(2):221–226
Yang X, Zhang X (2010) Regulation of somatic embryogenesis in higher plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 29(1):36–57
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32001340), the Improved Variety Program of Shandong Province of China (2020LZGC090102), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2020QC169).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RC and KY contributed the conception, design, and final revision. HF and YD contributed to design and drafting the manuscript. YB, SX, XL, SG, QW and QD analyzed and interpreted the data. RZ and CW contributed to supervise and revise the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Francisco de Assis Alves Mourão Filho.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, H., Dong, Y., Zhou, R. et al. Optimization of the induction, germination, and plant regeneration system for somatic embryos in apomictic walnut (Juglans regia L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 150, 289–297 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-022-02266-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-022-02266-9