Abstract
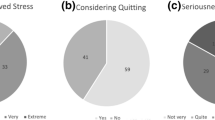
The fears of pre-service teachers, particularly Teach for America (TFA) teachers. about working in urban classroom settings are framed as racial stress. Racial stress is the threat of well-being when one is unprepared to negotiate a race-related interpersonal encounter. Currently, there exist no measures on racial stress, socialization, and coping for teachers of African American and Latino students. Findings reveal that newly developed and reliable measures of teacher appraisal of racial/ethnic stressful interactions, socialization and coping are related to classroom management self-efficacy and school collegial racial conversations. These findings have implications for racial stress management as key to developing high quality teacher-student relationships.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiba, M. (2011). Identifying program characteristics for preparing pre-service teachers for diversity. Teachers College Record, 113(3), 658–697.
Alexander, K. L., Entwisle, D. R., & Herman, R. (1999). In the eye of the beholder: Parents’ and teachers’ ratings of children’s behavioral style. In C. L. Shenan (Ed.), Contemporary perspectives on family research (Vol. 1, pp. 225–245). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Allen, Q. (2015). Race, culture and agency: Examining the ideologies and practices of U.S. teachers of Black male students. Teaching and Teacher Education, 47, 71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2014.12.010.
Anderson, A. (2013). Teach for America and symbolic violence: A bourdieuian analysis of education's next quick-fix. The Urban Review, 45(5), 684–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11256-013-0241-x.
Anderson, R. E., & Stevenson, H. C. (2019). RECASTing racial stress and trauma: Theorizing the healing potential of racial socialization in families. American Psychologist, 74(1), 63–75. https://doi.org/10.1037/amp0000392.
Arrington, E. G., Hall, D. M., & Stevenson, H. C. (2003). The success of African-American students in independent schools. Independent School, 62(Summer), 10–21.
Banks, J. A., & Banks, C. A. M. (1993). Multicultural education: Issues and perspectives. Allyn and Bacon.
Bartoli, E., Bentley-Edwards, K. L., García, A. M., Michael, A., & Ervin, A. (2015). What do white counselors and psychotherapists need to know about race? White racial socialization in counseling and psychotherapy training programs. Women and Therapy, 38(3–4), 246–262. https://doi.org/10.1080/02703149.2015.1059206.
Bentley-Edwards, K. L., & Stevenson, H. C. (2016). The multidimensionality of racial/ethnic socialization: Scale construction for the cultural and racial experiences of socialization (CARES). Journal of Child and Family Studies, 25(1), 96–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-015-0214-7.
Bentley-Edwards, K. L., Thomas, D. E., & Stevenson, H. C. (2013). Raising consciousness: Promoting healthy coping among African American boys at school. In C. Clauss-Ehlers, Z. Serpell, & M. Weist (Eds.), Handbook of culturally responsive school mental health: advancing research, training, practice, and policy (pp. 121–133). New York: Springer.
Bennett, C. I. (2016). Preparing teachers for cultural diversity and national standards of academic excellence. Journal of Teacher Education, 46(4), 259–265.
Bergin, C., & Bergin, D. (2009). Attachment in the classroom. Educational Psychology Review, 21, 141–170.
Blumenreich, M., & Gupta, A. (2015). The globalization of Teach for America: An analysis of the institutional discourses of Teach for America and Teach for India within local contexts. Teaching and Teacher Education, 48, 87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2015.01.017.
Boyle, G. J., Borg, M. G., Falzon, J. M., & Baglioni, A. J. (1995). A structural model of the dimensions of teacher stress. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 65(1), 49–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8279.1995.tb01130.x.
Brewer, T. J. (2014). Accelerated burnout: How teach For America's academic impact model and theoretical culture of accountability can foster disillusionment among its corps members. Educational Studies, 50(3), 246–263. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131946.2014.907163.
Brouwers, A., & Tomic, W. (2001). The factorial validity of scores on the teacher Interpersonal self-efficacy scale. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 61, 433–445.
Casteel, C. A. (1998). Teacher–student interactions and race in integrated classrooms. The Journal of Educational Research, 92, 115–120.
Casteel, C. A. (2000). African American students! perceptions of their treatment by Caucasian teachers. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 27, 143–148.
Castro, A. J. (2010). Themes in the research on preservice teachers' views of cultural diversity: Implications for researching millennial preservice teachers. Educational Researcher, 39(3), 198–210. https://doi.org/10.2307/27764583.
Coleman, S., & Stevenson, H. C. (2013). The racial stress of membership: Development of the faculty inventory of racialized experiences in schools. Psychology in the Schools, 50(6), 548–566. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.21693.
Costello, A. B., & Osborne, J. W. (2005). Best practices in exploratory factor analysis: four recommendations for getting the most from your analysis. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 10(7), 1–9.
Crawford-Garrett, K. (2017). “The problem is bigger than us”: Grappling with educational inequity in TeachFirst New Zealand. Teaching and Teacher Education, 68, 91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2017.08.010.
Dee, T. S. (2004). The race connection: Are teachers more effective with students who share their ethnicity? Education Next, 4, 52.
DeVellis, R. F. (2003). Scale development: Theory and applications (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Disare, M. (2018). How diverse is the teaching force in your district? A new analysis highlights the gap between students and teachers of color. Diversity & Equity Retrieved June 25, 2020, from https://ny.chalkbeat.org/2018/1/8/21104225/how-diverse-is-the-teaching-force-in-your-district-a-new-analysis-highlights-the-gap-between-student.
Douglas, B., Lewis, C. B., Douglas, A., Scott, M. E., & Garrison-Wade, D. (2008). The impact of White teachers on the academic achievement of Black students: An exploratory qualitative analysis. Educational Foundations, Winter-Spring, 22, 47–62.
Downey, D. B., & Pribesh, S. (2016). When race matters: Teachers’ evaluations of students' classroom behavior. Sociology of Education, 77(4), 267–282.
Dworkin, A. G., Haney, C. A., & Telschow, R. L. (1988). Fear, victimization, and stress among urban public school teachers. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 9(2), 159–171.
Exley, S. (2014). The unstoppable rise of Teach for All. TES: Times Educational Supplement (5076), pp. 24–28.
Fabrigar, L. R., Wegener, D. T., MacCallum, R. C., & Strahan, E. J. (1999). Evaluating the use of exploratory factor analysis in psychological research. Psychological Methods, 4(3), 272–299.
Ferguson, R. F. (1998). Teachers' perceptions and expectations and the black–white test score gap. In C. Jencks & M. Phillips (Eds.), The black–white test score gap (pp. 273–317). Washington, DC: Brookings Institution Press.
Fimian, M. J., & Fastenau, P. S. (1990). The validity and reliability of the teacher stress inventory: A re-analysis of aggregate data. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 11(2), 151–157. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.4030110206.
Fimian, M. J., Lieberman, R. J., & Fastenau, P. S. (1991). Development and validation of an instrument to measure occupational stress in speech-language pathologists. Journal of Speech & Hearing Research, 34(2), 439–446.
Friedrich, D., Walter, M., & Colmenares, E. (2015). Making All children count: Teach for all and the universalizing appeal of data. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 23(48), 48.
Gilliam, W. S. (2008). Implementing policies to reduce the likelihood of preschool expulsion. Foundation for Child Development Policy Brief, 7, 2–10.
Gregory, A., Skiba, R., & Noguera, P. (2010). The achievement gap and the discipline gap: Two sides of the same coin? Educational Researcher, 39, 59–68.
Gudykunst, W. B., & Kim, Y. Y. (1984). Communicating with strangers: An approach to intercultural communication. Addison Wesley Publishing Company.
Halim, L., Samsudin, M. A., Meerah, T. S. M., & Osman, K. (2006). Measuring science teachers' stress level triggered by multiple stressful conditions. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 4(4), 727–739.
Hammen, C., & deMayo, R. (1982). Cognitive correlates of teacher stress and depressive symptoms: Implications for attributional models of depression. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 91(2), 96–101.
Harrell, S. P. (2000). A multidimensional conceptualization of racism-related stress: Implications for the well-being of people of color. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 70(1), 42–57.
Hinojosa, M. (2008). Black-white differences in school suspension: Effect of student beliefs about teachers. Sociological Spectrum, 28, 175–193.
Hootnick, A. (2014). Teach for America's growing pains. Nation, 298(18), 22–25.
Hoy, W. K., & Woolfolk, A. E. (1990). Socialization of student teachers. American Educational Research Journal, 27, 279–300.
Hughes, J. N., Gleason, K. A., & Zhang, D. (2005). Relationship influences on teachers’ perceptions of academic competence in academically at-risk minority and majority first-grade students. Journal of School Psychology, 43, 303–320.
Johnson, R. S., & Avelar La Salle, R. (2010). Data strategies to uncover and eliminate hidden inequities: The wallpaper effect. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Karp, S. & Harris, R. (2011). Teacher colleges emphasizing ‘Cultural Competence’. Education Week, 30, 26, https://www.edweek.org/ew/articles/2011/03/15/26catalyst_culturalcomp.h30.html.
Kavanaugh, K. M., & Dunn, A. H. (2013). Teach for America and the political spectacle of recruiting the "Best and the Brightest". Critical Education, 4(11), 48–66. https://doi.org/10.14288/ce.v4i11.183941.
Klassen, R., Wilson, E., Siu, A. F. Y., Hannok, W., Wong, M. W., Wongsri, N., et al. (2013). Preservice teachers’ work stress, self-efficacy, and occupational commitment in four countries. European Journal of Psychology of Education - EJPE, 28(4), 1289–1309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-012-0166-x.
Labaree, D. (2010). Teach for America and Teacher Education: Heads they win, tails we lose. Journal of Teacher Education, 61, 48–55.
Ladson-Billings, G. (2001). Teaching and cultural competence. Rethinking Schools, 15, 4, Summer.
Lazarus, R. S., & Folkman, S. (1984). Stress, appraisal and coping. New York: Springer.
Liu, L. (2018). A portrait in datat of the typical Philadephia teacher, Keystone Crossroads. Retrieved from https://whyy.org/articles/a-portrait-in-data-of-the-typical-philadelphia-teacher/.
Marcus, G., Gross, S., & Seefeldt, C. (1991). Black and white students’ perceptions of teacher treatment. Journal of Educational Research, 84(6), 363–367.
Mattison, E., & Aber, M. S. (2007). Closing the achievement gap: The association of racial climate with achievement and behavioral outcomes. American Journal of Community Psychology, 40(1–2), 1–12.
McAllister, G., & Irvine, J. J. (2016). Cross cultural competency and multicultural teacher education. Review of Educational Research, 70(1), 3–24.
McKown, C., & Weinstein, R. S. (2002). Modeling the role of child ethnicity and gender in children's differential response to teacher expectations. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 32, 159–184.
Michael, A. (2014). Raising race questions: Whiteness, education and inquiry. New York: Teachers College Press.
Michael, A., Coleman-King, C., Lee, S., Ramirez, C., & Bentley-Edwards, K. L. (2017). Naming the Unnamed: White Culture in Relief. In S. D. Hancock & C. A. Warren (Eds.), White woman’s work: Examining the intersectionality of cultural norms, teaching, and identity formation in urban schools (pp. 19–43). Charlotte: Information Age Publishing.
Milner, H. R., Flowers, L. A., Moore, E., Moore, J. L., & Flowers, T. A. (2003). Preservice teachers' awareness of multiculturalism and diversity. The High School Journal, 87(1), 63–70.
Minor, L. C., Onwugbuzie, A. J., Witcher, A. E., & James, T. L. (2002). Preservice teachers' educational beliefs and their perceptions of characteristics of effective teachers. The Journal of Educational Research, 96(2), 116–127.
National Academy of Sciences. (2004). Engaging Schools: Fostering High School Students Motivation to Learn: Executive Summary.https://books.nap.edu/catalog/10421.html.
National Center for Education Statistics. (2020). The conditions of education 2020 (p. 348). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education.
Neal, L. V. I., McCray, A. D., Webb-Johnson, G., & Bridgest, S. T. (2016). The effects of African American movement styles on teachers' perceptions and reactions. The Journal of Special Education, 37(1), 49–57.
Oates, G. L. (2003). Teacher-student racial congruence, teacher perceptions, and test performance. Social Science Quarterly, 84(3), 508–525.
O’Connor, E., & McCartney, K. (2007). Examining teacher-child relationships and achievement as part of an ecological model of development. American Educational Research Journal., 44(2), 340–369. https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831207302172c2007AERA.
Okonofua, J. A., & Eberhardt, J. L. (2015). Two strikes. Psychological Science, 26(5), 617–624.
Onchwari, J. (2010). Early childhood inservice and preservice teachers’ perceived levels of preparedness to handle stress in their students. Early Childhood Education Journal, 37(5), 391–400.
Parker, L., & Hood, S. (1995). Minority students vs. majority faculty and administrators in teacher education: Perspectives on the clash of cultures. Urban Review, 27(2), 159–174.
Pianta, R. C. (1999). Enhancing relationships between children and teachers. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Pianta, R. (2011). Getting traction on enhancing teachers' impacts on student learning. Teachers College Record, Vol. 113(1).
Robinson, J. P., Shaver, P. R., & Wrightsman, L. S. (1991). Measures of personality and social psychological attitudes (Vol. 1). San Diego: Academic Press.
Ross, J. A., Cousins, J. B., & Gadalla, T. (1996). Within-teacher predictors of teacher efficacy. Teacher and Teacher Education, 12, 385–400.
Rowley, A. A., Roesch, S. C., Jurica, B. J., & Vaughn, A. A. (2005). Developing and validating a stress appraisal measure for minority adolescents. Journal of Adolescence, 28, 547–557.
Sawchuk, S. (2016). 25 years In, TFA faces tensions, Courts Change. Education Week, 35(18), 1–13.
Skaalvik, E. M., & Skaalvik, S. (2017). Motivated for teaching? Associations with school goal structure, teacher self-efficacy, job satisfaction and emotional exhaustion. Teaching and Teacher Education, 67, 152–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2017.06.006.
Skaalvik, E. M., & Skaalvik, S. (2010). Teacher self-efficacy and teacher burnout: A study of relations. Teaching and Teacher Education, 26, 1059–1069.
Skiba, R., Eckes, S., & Brown, K. (2010). African American disproportionality in school discipline: The divide between best evidence and legal remedy. New York Law School Law Review, 54, 1071–1112.
Skiba, R., Michael, R. S., Nardo, A. C., & Peterson, R. (2002). The color of discipline: Sources of racial and gender disproportionality in school punishment. Urban Review, 34, 317–342. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021320817372.
Sleeter, C. E. (2001). Preparing teachers for culturally diverse schools: Research and the overwhelming presence of Whiteness. Journal of Teacher Education, 52(2), 94–106.
Sorenson, R. D. (2007). Stress management in education: Warnings signs and coping mechanisms. Management in Education, 21(3), 10–13.
Spencer, M. (2005). Crafting identities and accessing opportunities post-brown. American Psychologist, 60, 821–830.
Stevens, P. A., & Dworkin, A. G. (2019). The Palgrave handbook of race and ethnic inequalities in education. Berlin: Springer.
Stevenson, H. C. (2003). Playing with anger: teaching coping skills to African American boys through athletics and culture. Westport, CT: Praeger.
Stevenson, H. C. (2014). Promoting racial literacy in schools: Differences that make a difference. New York: Teachers College Press.
Sue, D. W., Capodilupo, C. M., Torino, G. C., Bucceri, J. M., Holder, A. B. M., Nadal, K. L., et al. (2007). Racial microaggressions in everyday life: Implications for clinical practice. American Psychologist, 62(4), 271–286.
Sue, D. W., Lin, A. I., Torino, G. C., Capodilupo, C. M., & Rivera, D. P. (2009). Racial microaggressions and difficult dialogues on race in the classroom. Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority Psychology, 15(2), 183–190.
Swartz, E. (2003). Teaching White preservice teachers: pedagogy for change. Urban Education, 38(3), 255–278.
Tschannen-Moran, M., Hoy, A. W., & Hoy, W. K. (1998). Teacher efficacy: Its meaning and measure. Review of Educational Research, Summer, 68, 202–248.
Tschannen-Moran, M., & Woolfolk Hoy, A. (2001). Teacher efficacy: Capturing an elusive construct. Teaching and Teacher Education, 17, 783–805.
Vellanki, V. (2014). Teach for India and education reform some preliminary reflections. Contemporary Education Dialogue, 11(1), 137–147.
Veltri, B. T. (2010). Learning on other people’s kids: Becoming a teach for America teacher. Charlotte, NC: Information Age Publishing Inc.
Veltri, B. T. (2012). Teach for America: It's more about leading than teaching. Educational Leadership, 69(8), 62–65.
Weinstein, C., Curran, M., & Tomlinson-Clarke, S. (2003). Culturally responsive classroom management: Awareness into action. Theory Into Practice, 42(4), 269–276.
Welter, P. (2011). Some resentments and fears of pre-service teachers. Journal of Humanistic Counseling (Online Journal), (1971) SPATE, Student Personal Association for Teacher Education, 9, 81–87.
Wolters, C. A., & Daugherty, S. G. (2007). Goal structures and teachers' sense of efficacy: Their relation and association to teaching experience and academic level. Journal of Educational Psychology, 99(1), 181–193.
Wubbels, T. (2005). Student perceptions of teacher-student relationships in class. International Journal of Educational Research, 43(2), 1–5.
Yates, T. M., & Marcelo, A. K. (2014). Through race-colored glasses: Preschoolers’ pretend play and teachers’ ratings of preschooler adjustment. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 29(1), 1–11.
Zirkel, S. (2004). What will you think of me? Racial integration, peer relationships and achievement among White students and students of color. Journal of Social Issues, 60, 57–74.
Zirkel, S. (2005). Ongoing issues of racial and ethnic stigma in education 50 years after Brown v. Board. Urban Review, 37(2), 107–126.
Acknowledgements
This article was partially funded by a Grant from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, NICHD is 1-R21-HD-058206-01A1 University of Penn #- 553073.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bentley-Edwards, K.L., Stevenson, H.C., Thomas, D.E. et al. Teaching scared: pre-service teacher appraisals of racial stress, socialization and classroom management self-efficacy. Soc Psychol Educ 23, 1233–1257 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-020-09578-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-020-09578-8