Abstract
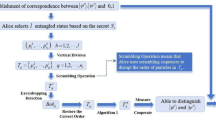
Initially, we address two issues that exist in multiparty quantum private comparison protocols. One among those arises when XOR operation is used in the multiparty comparison. The other issue occurs due to the poor implementation of multiparty computation, which leads to semi-honest third-party to access private data of the participants. Then, we propose a multiparty quantum private comparison protocol based on quantum walks on a circle. The protocol checks whether all parties (participants) hold the same value or not with the help of a semi-honest third-party (TP). Finally, we prove the correctness and security of the proposed system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Yao, A.C.: for secure computations. In: 23rd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (sfcs 1982), pp. 160–164 (1982). IEEE
Goldreich, O., Micali, S., Wigderson, A.: How to play any mental game, or a completeness theorem for protocols with honest majority. In: Providing Sound Foundations for Cryptography: On the Work of Shafi Goldwasser and Silvio Micali, pp. 307–328 (2019)
Ben-Or, M., Goldwasser, S., Wigderson, A.: Completeness theorems for non-cryptographic fault-tolerant distributed computation. In: Providing Sound Foundations for Cryptography: On the Work of Shafi Goldwasser and Silvio Micali, pp. 351–371 (2019)
Beaver, D., Micali, S., Rogaway, P.: The round complexity of secure protocols. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-second Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 503–513 (1990)
Kolesnikov, V.: Gate evaluation secret sharing and secure one-round two-party computation. In: International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, pp. 136–155 (2005). Springer
Bennett, C., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: Public key cryptography and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of International Conference Computer Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, pp. 175–179 (1984)
Hillery, M., Bužek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59(3), 1829 (1999)
Shimizu, K., Imoto, N.: Communication channels secured from eavesdropping via transmission of photonic bell states. Phys. Rev. A 60(1), 157 (1999)
Yang, Y.-G., Wen, Q.-Y.: An efficient two-party quantum private comparison protocol with decoy photons and two-photon entanglement. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 42(5), 055305 (2009)
Yang, Y.-G., Cao, W.-F., Wen, Q.-Y.: Secure quantum private comparison. Phys. Scr. 80(6), 065002 (2009)
Huang, S.-L., Hwang, T., Gope, P.: Multi-party quantum private comparison protocol with an almost-dishonest third party using ghz states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(6), 2969–2976 (2016)
Jia, H.-Y., Wen, Q.-Y., Li, Y.-B., Gao, F.: Quantum private comparison using genuine four-particle entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51(4), 1187–1194 (2012)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.-B., Jiang, Z.-T., Cao, Y.-Z.: A protocol for the quantum private comparison of equality with \(\chi \)-type state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51(1), 69–77 (2012)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.-B., Jiang, Z.-T., Cao, Y.-Z., Cui, W.: New quantum private comparison protocol using \(\chi \)-type state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51(6), 1953–1960 (2012)
Liu, W.-J., Liu, C., Wang, H.-B., Liu, J.-F., Wang, F., Yuan, X.-M.: Secure quantum private comparison of equality based on asymmetric w state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(6), 1804–1813 (2014)
Zhang, H., Ji, Z., Wang, H., Wu, W.: Survey on quantum information security. China Commun. 16(10), 1–36 (2019). https://doi.org/10.23919/JCC.2019.10.001
Chang, Y.-J., Tsai, C.-W., Hwang, T.: Multi-user private comparison protocol using ghz class states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(2), 1077–1088 (2013)
Aharonov, Y., Davidovich, L., Zagury, N.: Quantum random walks. Phys. Rev. A 48(2), 1687 (1993)
Chen, F.-L., Zhang, H., Chen, S.-G., Cheng, W.-T.: Novel two-party quantum private comparison via quantum walks on circle. Quant. Inf. Process. 20(5), 1–19 (2021)
Chongqiang, Y., Jian, L., Zheng-wen, C.: A class of protocols for multi-party quantum private comparison based on traveling mode. Quant. Inf. Process. 20(2), 1–18 (2021)
Ye, T.-Y.: Multi-party quantum private comparison protocol based on entanglement swapping of bell entangled states. Commun. Theor. Phys. 66(3), 280 (2016)
Ye, T.-Y., Hu, J.-L.: Multi-party quantum private comparison based on entanglement swapping of bell entangled states within d-level quantum system. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 60(4), 1471–1480 (2021)
Yan-Feng, L.: Improvement of multi-party quantum private comparison protocol using d-dimensional basis states without entanglement swapping. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59(9), 2773–2780 (2020)
Lo, H.-K., Chau, H.F.: Is quantum bit commitment really possible? Phys. Rev. Lett. 78(17), 3410 (1997)
Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Mayers, D., Salvail, L.: A brief review on the impossibility of quantum bit commitment. arXiv:quant-ph/9712023 (1997)
Farhi, E., Gutmann, S.: Quantum computation and decision trees. Phys. Rev. A 58(2), 915 (1998)
Ming-Yi, D.: Multi-party quantum private comparison with qudit shifting operation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59(10), 3079–3085 (2020)
Du, G., Zhang, F., Ma, C.: A new multi-party quantum private comparison protocol based on circle model. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(10), 3225–3233 (2019)
Cao, H., Ma, W., Lü, L., He, Y., Liu, G.: Multi-party quantum privacy comparison of size based on d-level ghz states. Quant. Inf. Process. 18(9), 1–14 (2019)
Zhao-Xu, J., Tian-Yu, Y.: Multi-party quantum private comparison based on the entanglement swapping of d-level cat states and d-level bell states. Quant. Inf. Process. 16(7), 1–20 (2017)
Funding
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors made contributions to the conception or design of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
I, the undersigned, give my consent for the publication of identifiable details, which can include photograph(s) and/or videos and/or case history and/or details within the text (“Material”) to be published in the above Journal and Article.
Code availability
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, J., Ali, S.T. Multiparty quantum private comparison based on quantum walks. Quantum Inf Process 22, 17 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03758-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03758-5