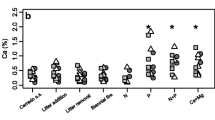
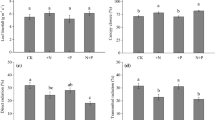
Abstract
Aims
To assess the fertility island effect of Prosopis pallida in the North Peruvian dry forests and analyze if it is influenced by tree size and structural and/or chemical leaf traits.
Methods
We measured the soil nutrient concentrations under and outside the tree canopy in five populations that differ in mean annual temperature and annual rainfall in North Peru. We also measured tree size (height, stem diameter, and crown area), leaf structure (leaf mass per area (LMA) and leaf dry matter content), and leaf nutrient concentrations (C, N, P, Mn, Fe, Cu, and Zn).
Results
The concentration of most soil nutrients was higher under the P. pallida canopy. Tree size affected positively the soil C, N, and P concentrations, while leaf structural traits such as LMA were negatively related to the soil C, N, and P concentrations. The relationships between the nutrient concentrations in the leaf and soil were only significant for P and Mn. The tree size effect was greater in those populations where the temperature was lower, suggesting the fertility island effect can be increased or weakened by climatic factors.
Conclusions
P. pallida have a significant though limited fertility island effect regulated by plant traits and influenced by climatic factors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abril A, Villagra P, Noe L (2009) Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of soil fertility in the Central Monte desert (Argentina). J Arid Environ 73:901–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2009.04.019
Aguiar MR, Sala OE (1999) Patch structure, dynamics and implications for the functioning of arid ecosystems. Trends Ecol Evol 14:273–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-5347(99)01612-2
Alameda D, Villar R, Iriondo JM (2012) Forest ecology and management spatial pattern of soil compaction: trees’ footprint on soil physical properties. For Ecol Manag 283:128–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2012.07.018
Allison SD, Vitousek PM (2004) Rapid nutrient cycling in leaf litter from invasive plants in Hawai’i. Oecologia 141:612–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-004-1679-z
Aponte C, García LV, Pérez-Ramos IM, Gutiérrez E, Marañón T (2011) Oak trees and soil interactions in Mediterranean forests: a positive feedback model. J Veg Sci 22:856–867. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1654-1103.2011.01298.x
Austin AT, Yahdjian L, Schaeffer SM et al (2004) Water pulses and biogeochemical cycles in arid and semiarid ecosystems. Oecologia 141:221–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-004-1519-1
Bashan Y, Davis EA, Carrillo-Garcia A, Linderman RG (2000) Assessment of VA mycorrhizal inoculum potential in relation to the establishment of cactus seedlings under mesquite nurse-trees in the Sonoran Desert. Appl Soil Ecol 14:165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0929-1393(00)00050-0
Bates BC, Kundzewicz ZW, Wu S, Palutikof JP (2008) Climate change and water. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Secretariat, Geneva
Berdugo M, Maestre FT, Kéfi S, Gross N, le Bagousse-Pinguet Y, Soliveres S (2018) Aridity preferences alter the relative importance of abiotic and biotic drivers on plant species abundance in global drylands. J Ecol 84:293–295. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.13006
Berry R, Livesley SJ, Aye L (2013) Tree canopy shade impacts on solar irradiance received by building walls and their surface temperature. Build Environ 69:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2013.07.009.This
Bolker BM, Brooks ME, Clark CJ, Geange SW, Poulsen JR, Stevens MHH, White JSS (2009) Generalized linear mixed models: a practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol Evol 24:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2008.10.008
Bongers FJ, Olmo M, Lopez-iglesias B et al (2017) Drought responses, phenotypic plasticity and survival of Mediterranean species in two different microclimatic sites. Plant Biol 38:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijlh.12426
Bravo M, Rodriguez M, De los Heros M (2003) Mapa de bosques secos del departamento de Piura. Memoria Descriptiva, Piura
Bretz F, Westfall P, Hothorn T (2016) Multiple comparisons using R. Chapman and Hall/CRC
Briceño-Zuluaga F, Castagna A, Rutllant JA, Flores-Aqueveque V, Caquineau S, Sifeddine A, Velazco F, Gutierrez D, Cardich J (2017) Paracas dust storms: sources, trajectories and associated meteorological conditions. Atmos Environ 165:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.06.019
Buendía-González L, Orozco-Villafuerte J, Cruz-Sosa F, Barrera-Díaz CE, Vernon-Carter EJ (2010) Prosopis laevigata a potential chromium (VI) and cadmium (II) hyperaccumulator desert plant. Bioresour Technol 101:5862–5867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.03.027
Burnell JN (1988) The biochemistry of manganese in plants. In: Manganese in soils and plants. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 125–137
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference. Springer New York, New York, NY
Buschiazzo DE, Hevia GG, Hepper EN, Urioste A, Bono AA, Babinec F (2001) Organic C, N and P in size fractions of virgin and cultivated soils of the semi-arid pampa of Argentina. J Arid Environ 48:501–508. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2000.0775
Callaway RM, Brooker RW, Choler P, Kikvidze Z, Lortie CJ, Michalet R, Paolini L, Pugnaire FI, Newingham B, Aschehoug ET, Armas C, Kikodze D, Cook BJ (2002) Positive interactions among alpine plants increase with stress. Nature 417:844–848. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00812
Canadell J, Jackson R, Ehleringer J et al (1996) Maximum rooting depth of vegetation types at the global scale. Oecologia 108:583–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00329030
Catenazzi A, Donnelly MA (2007) Distribution of geckos in northern Peru: long-term effect of strong ENSO events. J Arid Environ 71:327–332
Charley JL, West NE (1975) Plant-induced soil chemical patterns in some shrub-dominated semi-desert ecosystems of Utah. J Ecol 63:945. https://doi.org/10.2307/2258613
Cornelissen JHC, Lavorel S, Garnier E, Díaz S, Buchmann N, Gurvich DE, Reich PB, Steege H, Morgan HD, Heijden MGA, Pausas JG, Poorter H (2003) A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust J Bot 51:335. https://doi.org/10.1071/BT02124
Cornelissen JHC, Thompson K (1997) Functional leaf attributes predict litter decomposition rate in herbaceous plants. New Phytol 135:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.1997.00628.x
Cross AF, Schlesinger WH (1999) Plant regulation of soil nutrient distribution in the northern Chihuahuan Desert. Plant Ecol 145:11–25. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009865020145
Curiel Yuste J, Baldocchi DD, Gershenson A et al (2007) Microbial soil respiration and its dependency on carbon inputs, soil temperature and moisture. Glob Chang Biol 13:2018–2035. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01415.x
de la Riva EG, Olmo M, Poorter H, Ubera JL, Villar R (2016) Leaf mass per area (LMA) and its relationship with leaf structure and anatomy in 34 Mediterranean woody species along a water availability gradient. PLoS One 11:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148788
Deans JD, Diagne O, Nizinski J, Lindley DK (2003) Comparative growth, biomass production, nutrient use and soil amelioration by nitrogen-fixing tree species in semi-arid Senegal. For Ecol Manag 176:253–264
Díaz S, Kattge J, Cornelissen JHC, Wright IJ, Lavorel S, Dray S, Reu B, Kleyer M, Wirth C, Colin Prentice I, Garnier E, Bönisch G, Westoby M, Poorter H, Reich PB, Moles AT, Dickie J, Gillison AN, Zanne AE, Chave J, Joseph Wright S, Sheremet’ev SN, Jactel H, Baraloto C, Cerabolini B, Pierce S, Shipley B, Kirkup D, Casanoves F, Joswig JS, Günther A, Falczuk V, Rüger N, Mahecha MD, Gorné LD (2016) The global spectrum of plant form and function. Nature 529:167–171. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16489
Domínguez MT, Aponte C, Pérez-Ramos IM, García LV, Villar R, Marañón T (2012) Relationships between leaf morphological traits, nutrient concentrations and isotopic signatures for Mediterranean woody plant species and communities. Plant Soil 357:407–424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1214-7
Fan H, Wu J, Liu W, Yuan Y, Hu L, Cai Q (2015) Linkages of plant and soil C:N:P stoichiometry and their relationships to forest growth in subtropical plantations. Plant Soil 392:127–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2444-2
Fang X, Zhao L, Zhou G, Huang W, Liu J (2015) Increased litter input increases litter decomposition and soil respiration but has minor effects on soil organic carbon in subtropical forests. Plant Soil 392:139–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2450-4
Ffolliott PF (1995) Dryland forestry: planning and management. John Wiley & Sons
Forbes GS, Whitford WG, Van Zee JW, Smith W (2005) Desert grassland canopy arthropod species richness: temporal patterns and effects of intense, short-duration livestock grazing. J Arid Environ 60:627–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2004.07.004
Fraisse CW, Hu Z, Simonne EH (2010) Effect of El Niño–southern oscillation on the number of leaching rain events in Florida and implications on nutrient management for tomato. Horttechnology 20:120–132
Gallaher T, Merlin M (2010) Biology and impacts of Pacific Island invasive species. 6. Prosopis pallida and Prosopis juliflora (Algarroba, Mesquite, Kiawe ) (Fabaceae). Pac Sci 64:489–526. https://doi.org/10.2984/64.4.489
Gallardo A (2003) Effect of tree canopy on the spatial distribution of soil nutrients in a Mediterranean Dehesa. Pedobiologia (Jena) 47:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1078/0031-4056-00175
Geesing D, Felker P, Bingham RL (2000) Influence of mesquite (Prosopis glandulosa) on soil nitrogen and carbon development: implications for global carbon sequestration. J Arid Environ 46:157–180. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2000.0661
Gómez-Aparicio L, Canham C (2008) Neighborhood models of the effects of invasive. Ecol Monogr 78:69–86
Grace JB, Schoolmaster DR, Guntenspergen GR et al (2012) Guidelines for a graph-theoretic implementation of structural equation modeling. Ecosphere 3:art73. https://doi.org/10.1890/ES12-00048.1
Harris I, Jones PD, Osborn TJ, Lister DH (2014) Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations - the CRU TS3.10 dataset. Int J Climatol 34:623–642. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3711
Herrera-Arreola G, Herrera Y, Reyes-Reyes BG, Dendooven L (2007) Mesquite (Prosopis juliflora (Sw.) DC.), huisache (Acacia farnesiana (L.) Willd.) and catclaw (Mimosa biuncifera Benth.) and their effect on dynamics of carbon and nitrogen in soils of the semi-arid highlands of Durango Mexico. J Arid Environ 69:583–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2006.11.014
Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int J Climatol 25:1965–1978. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1276
Hollister EB, Schadt CW, Palumbo AV, James Ansley R, Boutton TW (2010) Structural and functional diversity of soil bacterial and fungal communities following woody plant encroachment in the southern Great Plains. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1816–1824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.06.022
Holmgren M, Scheffer M, Ezcurra E, Gutiérrez JR, Mohren GMJ (2001) El Niño effects on the dynamics of terrestrial ecosystems. Trends Ecol Evol 16:89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-5347(00)02052-8
Holmgren M, Stapp P, Dickman CR, Gracia C, Graham S, Gutiérrez JR, Hice C, Jaksic F, Kelt DA, Letnic M, Lima M, López BC, Meserve PL, Milstead WB, Polis GA, Previtali MA, Richter M, Sabaté S, Squeo FA (2006) Extreme climatic events shape arid and semiarid ecosystems. Front Ecol Environ 4:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1890/1540-9295(2006)004[0087:ECESAA]2.0.CO;2
Jarrell WM, Virginia RA (1990) Response of mesquite to nitrate and salinity in a simulated phreatic environment: water use, dry matter and mineral nutrient accumulation. Plant Soil 125:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010656
Kahi CH, Ngugi RK, Mureithi SM, Ng’ethe J (2009) The canopy effects of Prosopis juliflora (dc.) and Acacia tortilis (hayne) trees on herbaceous plants species and soil physico-chemical properties in Njemps, Kenya. Trop Subtrop Agroecosystems 10:441–449
Kazakou E, Vile D, Shipley B et al (2006) Co-variations in litter decomposition, leaf traits and plant growth in species from a Mediterranean old-field succession. Funct Ecol 20:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2006.01080.x
Kemp PR, Reynolds JF, Virginia RA, Whitford WG (2003) Decomposition of leaf and root litter of Chihuahuan desert shrubs: effects of three years of summer drought. J Arid Environ 53:21–39. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2002.1025
Kilchenmann JAR, Manso AF, Rodríguez F (2009) DendroFlexómetro©: dendrómetro económico de libre utilización y autoconstrucción para la medición de árboles y masas forestales. In: 5o Congreso forestal español. pp 1–10
Lambers H, Hayes PE, Laliberté E, Oliveira RS, Turner BL (2015) Leaf manganese accumulation and phosphorus-acquisition efficiency. Trends Plant Sci 20:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.10.007
Li J, Okin GS, Alvarez L, Epstein H (2008) Effects of wind erosion on the spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients in two desert grassland communities. Biogeochemistry 88:73–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-008-9195-6
Linares-Palomino R, Alvarez SIP (2005) Tree community patterns in seasonally dry tropical forests in the Cerros de Amotape Cordillera, Tumbes, Peru. For Ecol Manag 209:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2005.02.003
Lü XT, Kong DL, Pan QM, Simmons ME, Han XG (2012) Nitrogen and water availability interact to affect leaf stoichiometry in a semi-arid grassland. Oecologia 168:301–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-011-2097-7
Mazía N, Moyano J, Perez L, Aguiar S, Garibaldi LA, Schlichter T (2016) The sign and magnitude of tree-grass interaction along a global environmental gradient. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 25:1510–1519. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12518
Michalet R, Brooker RW, Cavieres LA, Kikvidze Z, Lortie CJ, Pugnaire FI, Valiente-Banuet A, Callaway RM (2006) Do biotic interactions shape both sides of the humped-back model of species richness in plant communities? Ecol Lett 9:767–773. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00935.x
Muenchow J, von Wehrden H, Rodríguez EF, Rodriguez Arisméndiz R, Bayer F, Richter M (2013) Woody vegetation of a Peruvian tropical dry forest along a climatic gradient depends more on soil than annual precipitation. Erdkunde 67:241–248. https://doi.org/10.3112/erdkunde.2013.03.03
Murphy J, Riley J (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chem ACTA 27:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
Olsen SR, Sommers LE, Page AL (1982) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chem Microbiol Prop Phosphorus ASA Monogr 403–430
Ordoñez JC, Van Bodegom PM, Witte JPM et al (2009) A global study of relationships between leaf traits, climate and soil measures of nutrient fertility. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 18:137–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2008.00441.x
Poorter H, Niinemets U, Poorter L, Wright IJ, Villar R (2009) Causes and consequences of variation in leaf mass per area (LMA): a meta-analysis. New Phytol 182:565–588
Purohit U, Mehar SK, Sundaramoorthy S (2002) Role of Prosopis cineraria on the ecology of soil fungi in Indian desert. J Arid Environ 52:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2002.0977
Qi Y-C, Dong Y-S, Jin Z et al (2010) Spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients and respiration in the desertified grasslands of Inner Mongolia, China. Pedosphere 20:655–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(10)60055-0
R Development Core Team (2013) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing
Ravi S, D’Odorico P, Okin GS (2007) Hydrologic and aeolian controls on vegetation patterns in arid landscapes. Geophys Res Lett 34:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL031023
Reyes-Reyes BG, Alcántara-Hernández R, Rodríguez V, Olalde-Portugal V, Dendooven L (2007) Microbial biomass in a semi arid soil of the central highlands of Mexico cultivated with maize or under natural vegetation. Eur J Soil Biol 43:180–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2007.02.001
Reyes-Reyes G, Baron-Ocampo L, Cuali-Alvarez I, Frias-Hernandez JT, Olalde-Portugal V, Varela Fregoso L, Dendooven L (2002) C and N dynamics in soil from the central highlands of Mexico as affected by mesquite (Prosopis spp.) and huizache (Acacia tortuoso): a laboratory investigation. Appl Soil Ecol 19:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0929-1393(01)00169-X
Rodríguez R, Mabres A, Luckman B, Evans M, Masiokas M, Ektvedt TM (2005) “El Niño” events recorded in dry-forest species of the lowlands of northwest Peru. Dendrochronologia 22:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dendro.2005.05.002
Rollenbeck R, Bayer F, Münchow J, Richter M, Rodriguez R, Atarama N (2015) Climatic cycles and gradients of the El Niño Core region in North Peru. Adv Meteorol 2015:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/750181
Rosseel Y (2012) Lavaan: an R package for structural equation modeling. J Stat Softw 48:1–21. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v048.i02
Ruiz TG, Zaragoza SR, Cerrato RF (2008) Fertility islands around Prosopis laevigata and Pachycereus hollianus in the drylands of Zapotitlán Salinas, México. J Arid Environ 72:1202–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2007.12.008
Salazar PC, Navarro-Cerrillo RM, Ancajima E, Duque Lazo J, Rodríguez R, Ghezzi I, Mabres A (2018a) Effect of climate and ENSO events on Prosopis pallida forests along a climatic gradient. For An Int J For Res 91:552–562. https://doi.org/10.1093/forestry/cpy014
Salazar PC, Navarro-Cerrillo RM, Cruz G, Villar R (2018b) Intraspecific leaf functional trait variability of eight Prosopis pallida tree populations along a climatic gradient of the dry forests of northern Peru. J Arid Environ 152:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2018.01.010
Schade JD, Sponseller R, Collins SL, Stiles A (2003) The influence of Prosopis canopies on understorey vegetation: effects of landscape position. J Veg Sci 14:743–750. https://doi.org/10.1658/1100-9233(2003)014[0743:TIOPCO]2.0.CO;2
Schlesinger WH, Raikes JA, Hartley AE, Cross AF (1996) On spatial pattern of soil nutrients in desert ecosystems. Ecology 77:364–374
Senthilkumar P, Prince WSPM, Sivakumar S, Subbhuraam CV (2005) Prosopis juliflora - a green solution to decontaminate heavy metal (Cu and Cd) contaminated soils. Chemosphere 60:1493–1496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.022
Simmons MT, Archer SR, Teague WR, Ansley RJ (2008) Tree (Prosopis glandulosa) effects on grass growth: an experimental assessment of above- and belowground interactions in a temperate savanna. J Arid Environ 72:314–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2007.07.008
Tongway D, Ludwig J (1994) Small-scale resource heterogeneity in semi-arid landscapes. Pac Conserv Biol 1:201. https://doi.org/10.1071/PC940201
Uriarte M, Turner BL, Thompson J, Zimmerman JK (2015) Linking spatial patterns of leaf litterfall and soil nutrients in a tropical forest: a neighborhood approach. Ecol Appl 25:2022–2034
Vallejo VE, Arbeli Z, Terán W, Lorenz N, Dick RP, Roldan F (2012) Effect of land management and Prosopis juliflora (Sw.) DC trees on soil microbial community and enzymatic activities in intensive silvopastoral systems of Colombia. Agric Ecosyst Environ 150:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2012.01.022
van Breemen N, Finzi AC (1998) Plant-soil interactions: ecological aspects and evolutionary implications. Biogeochemistry 42:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005996009413
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157:423–447. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00695.x
Vásquez-Méndez R, Ventura-Ramos E, Oleschko K, Hernández-Sandoval L, Parrot JF, Nearing MA (2010) Soil erosion and runoff in different vegetation patches from semiarid Central Mexico. Catena 80:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2009.11.003
Villar R, Ruiz-Benito P, de la Riva EG et al (2017) Growth and growth-related traits for a range of Quercus species grown as seedlings under controlled conditions and for adult plants from the field. In: Gil-Pelegrín E, Peguero-Pina JJ, Sancho-Knapik D (eds) Oaks physiological ecology. Exploring the functional diversity of genus Quercus L. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 393–417
Villegas JC, Breshears DD, Zou CB, Law DJ (2010) Ecohydrological controls of soil evaporation in deciduous drylands: how the hierarchical effects of litter, patch and vegetation mosaic cover interact with phenology and season. J Arid Environ 74:595–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2009.09.028
Wang B, Zha TS, Jia X, Wu B, Zhang YQ, Qin SG (2014) Soil moisture modifies the response of soil respiration to temperature in a desert shrub ecosystem. Biogeosciences 11:259–268. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-11-259-2014
Wang G, Cai W, Gan B, Wu L, Santoso A, Lin X, Chen Z, McPhaden MJ (2017) Continued increase of extreme El Niño frequency long after 1.5 °C warming stabilization. Nat Clim Chang 7:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3351
Warton D, Duursma R, Falster D, Taskinen S (2013) (Standardised) major axis estimation and testing routines
White DA, Welty-Bernard A, Rasmussen C, Schwartz E (2009) Vegetation controls on soil organic carbon dynamics in an arid, hyperthermic ecosystem. Geoderma 150:214–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.02.011
Whitford W (2002) Ecology of dessert systems. Elsevier science, Las Cruces USA
Wright IJ, Reich PB, Cornelissen JHC, Falster DS, Groom PK, Hikosaka K, Lee W, Lusk CH, Niinemets Ü, Oleksyn J, Osada N, Poorter H, Warton DI, Westoby M (2005) Modulation of leaf economic traits and trait relationships by climate. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 14:411–421. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-822x.2005.00172.x
Wright IJ, Reich PB, Westoby M, Ackerly DD, Baruch Z, Bongers F, Cavender-Bares J, Chapin T, Cornelissen JHC, Diemer M, Flexas J, Garnier E, Groom PK, Gulias J, Hikosaka K, Lamont BB, Lee T, Lee W, Lusk C, Midgley JJ, Navas ML, Niinemets Ü, Oleksyn J, Osada N, Poorter H, Poot P, Prior L, Pyankov VI, Roumet C, Thomas SC, Tjoelker MG, Veneklaas EJ, Villar R (2004) The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature 428:821–827. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02403
Zavala-Hurtado J (2000) Influence of leaf-cutting ants (Atta mexicana) on performance and dispersion patterns of perennial desert shrubs in an inter-tropical region of Central Mexico. J Arid Environ 46:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2000.0655
Acknowledgments
We thank the biologist Luis Urbina and the bachelor students Marco Balcazar and Lorena Huiman for their help during field data acquisition.
Funding
This research was funded by Fondo para la Innovación, Ciencia y Tecnología (146-FINCyT-IB-2013), currently known as Programa Nacional de Innovación para la Competitividad y Productividad INNOVATE PERU. RV was supported by the Spanish MEC project DIVERBOS (CGL2011-30285-C02-02) and ECO-MEDIT (CGL2014-53236-R) and European FEDER funds. RMNC was supported by the Spanish MEC project DIVERBOS (CGL2011-30285-C02-02) and QUERCUSAT (CLG2013-40790-R).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declarations of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Honghua He.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 20 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salazar, P.C., Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M., Grados, N. et al. Tree size and leaf traits determine the fertility island effect in Prosopis pallida dryland forest in Northern Peru. Plant Soil 437, 117–135 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-03965-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-03965-7