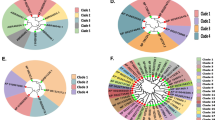
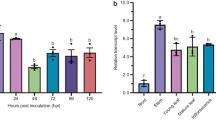
Abstract
The molecular interactions between grapevine and the obligate biotrophic fungus Erysiphe necator are not understood in depth. One reason for this is the recalcitrance of grapevine to genetic modifications. Using defense-related Arabidopsis mutants that are susceptible to pathogens, we were able to analyze key components in grapevine defense responses. We have examined the functions of defense genes associated with the salicylic acid (SA) pathway, including ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY 1 (EDS1), EDS1-LIKE 2 (EDL2), EDL5 and PHYTOALEXIN DEFICIENT 4 (PAD4) of two grapevine species, Vitis vinifera cv. Cabernet Sauvignon, which is susceptible to E. necator, and V. aestivalis cv. Norton, which is resistant. Both VaEDS1 and VvEDS1 were previously found to functionally complement the Arabidopsis eds1-1 mutant. Here we show that the promoters of both VaEDS1 and VvEDS1 were induced by SA, indicating that the heightened defense of Norton is related to its high SA level. Other than Va/VvEDS1, only VaEDL2 complemented Arabidopsis eds1-1, whereas Va/VvPAD4 did not complement Arabidopsis pad4-1. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation results indicated that Vitis EDS1 and EDL2 proteins interact with Vitis PAD4 and AtPAD4, suggesting that Vitis EDS1/EDL2 forms a complex with PAD4 to confer resistance, as is known from Arabidopsis. However, Vitis EDL5 and PAD4 did not interact with Arabidopsis EDS1 or PAD4, correlating with their inability to function in Arabidopsis. Together, our study suggests a more complicated EDS1/PAD4 module in grapevine and provides insight into molecular mechanisms that determine disease resistance levels in Vitis species native to the North American continent.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker CL, Donald T, Pauquet J, Ratnaparkhe MB, Bouquet A, Adam-Blondon AF, Thomas MR, Dry IB (2005) Genetic and physical mapping of the grapevine powdery mildew resistance gene, Run1, using a bacterial artificial chromosome library. Theor Appl Genet 111:370–377
Bhattacharjee S, Halane MK, Kim SH, Gassmann W (2011) Pathogen effectors target Arabidopsis EDS1 and alter its interactions with immune regulators. Science 334:1405–1408
Camps C, Kappel C, Lecomte P, Léon C, Gomès E, Coutos-Thévenot P, Delrot S (2010) A transcriptomic study of grapevine (Vitis vinifera cv. Cabernet-Sauvignon) interaction with the vascular ascomycete fungus Eutypa lata. J Exp Bot 61:1719–1737
Chandra-Shekara AC, Navarre D, Kachroo A, Kang H-G, Klessig D, Kachroo P (2004) Signaling requirements and role of salicylic acid in HRT- and rrt-mediated resistance to turnip crinkle virus in Arabidopsis. Plant J 40:647–659
Chong J, Le Henanff G, Bertsch C, Walter B (2008) Identification, expression analysis and characterization of defense and signaling genes in Vitis vinifera. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:469–481
Citovsky V, Lee LY, Vyas S, Glick E, Chen MH, Vainstein A, Gafni Y, Gelvin SB, Tzfira T (2006) Subcellular localization of interacting proteins by bimolecular fluorescence complementation in planta. J Mol Biol 362:1120–1131
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Coleman C, Copetti D, Cipriani G, Hoffmann S, Kozma P, Kovács L, Morgante M, Testolin R, Di Gaspero G (2009) The powdery mildew resistance gene REN1 co-segregates with an NBS-LRR gene cluster in two Central Asian grapevines. BMC Genet 10:89
Collins NC, Thordal-Christensen H, Lipka V, Bau S, Kombrink E, Qiu JL, Hückelhoven R, Stein M, Freialdenhoven A, Somerville SC, Schulze-Lefert P (2003) SNARE-protein-mediated disease resistance at the plant cell wall. Nature 425:973–977
Donald TM, Pellerone F, Adam-Blondon A-F, Bouquet A, Thomas MR, Dry IB (2002) Identification of resistance analogs linked to a powdery mildew resistance locus in grapevine. Theor Appl Genet 104:610–618
Eulgem T, Somssich IE (2007) Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:366–371
Falk A, Feys BJ, Frost LN, Jones JDG, Daniels MJ, Parker JE (1999) EDS1, an essential component of R gene-mediated disease resistance in Arabidopsis has homology to eukaryotic lipases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:3292–3297
Feechan A, Anderson C, Torregrosa L, Jermakow A, Mestre P, Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S, Merdinoglu D, Walker AR, Cadle-Davidson L, Reisch B, Aubourg S, Bentahar N, Shrestha B, Bouquet A, Adam-Blondon AF, Thomas MR, Dry IB (2013) Genetic dissection of a TIR-NB-LRR locus from the wild North American grapevine species Muscadinia rotundifolia identifies paralogous genes conferring resistance to major fungal and oomycete pathogens in cultivated grapevine. Plant J 76:661–674
Feys BJ, Moisan LJ, Newman MA, Parker JE (2001) Direct interaction between the Arabidopsis disease resistance signaling proteins, EDS1 and PAD4. EMBO J 20:5400–5411
Feys BJ, Wiermer M, Bhat RA, Moisan LJ, Medina-Escobar N, Neu C, Cabral A, Parker JE (2005) Arabidopsis SENESCENCE-ASSOCIATED GENE101 stabilizes and signals within an ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1 complex in plant innate immunity. Plant Cell 17:2601–2613
Fung RWM, Qiu WP, Su YC, Schachtman D, Huppert K, Fekete C, Kovacs LG (2007) Gene expression variation in grapevine species Vitis vinifera L. and Vitis aestivalis Michx. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:1541–1553
Fung RWM, Gonzalo M, Fekete C, Kovacs LG, He Y, Marsh E, McIntyre LM, Schachtman DP, Qiu W (2008) Powdery mildew induces defense-oriented reprogramming of the transcriptome in a susceptible but not in a resistant grapevine. Plant Physiol 146:236–249
Gamm M, Héloir MC, Kelloniemi J, Poinssot B, Wendehenne D, Adrian M (2011) Identification of reference genes suitable for qRT-PCR in grapevine and application for the study of the expression of genes involved in pterostilbene synthesis. Mol Genet Genomics 285:273–285
Gao F, Shu X, Ali MB, Howard S, Li N, Winterhagen P, Qiu W, Gassmann W (2010) A functional EDS1 ortholog is differentially regulated in powdery mildew-resistant and -susceptible grapevines and complements an Arabidopsis eds1 mutant. Planta 231:1037–1047
García AV, Blanvillain-Baufumé S, Huibers RP, Wiermer M, Li G, Gobbato E, Rietz S, Parker JE (2010) Balanced nuclear and cytoplasmic activities of EDS1 are required for a complete plant innate immune response. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000970
Gooding GV, Hewitt WB (1962) Grape yellow vein: symptomatology, identification, and the association of a mechanically transmissible virus with the disease. Am J Enol Vitic 13:196–203
Heidrich K, Wirthmueller L, Tasset C, Pouzet C, Deslandes L, Parker JE (2011) Arabidopsis EDS1 connects pathogen effector recognition to cell compartment-specific immune responses. Science 334:1401–1404
Hinsch M, Staskawicz BJ (1996) Identification of a new Arabidopsis disease resistance locus, RPS4, and cloning of the corresponding avirulence gene, avrRps4, from Pseudomonas syringae pv. pisi. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 9:55–61
Hoffmann S, Di Gaspero G, Kovacs LG, Howard S, Kiss E, Galbacs R, Testolin R, Kozma P (2008) Resistance to Erysiphe necator in the grapevine ‘Kishmish vatkana’ is controlled by a single locus through restriction of hyphal growth. Theor Appl Genet 116:427–438
Hu GS, deHart AKA, Li YS, Ustach C, Handley V, Navarre R, Hwang CF, Aegerter BJ, Williamson VM, Baker B (2005) EDS1 in tomato is required for resistance mediated by TIR-class R genes and the receptor-like R gene Ve. Plant J 42:376–391
Jaillon O, Aury JM, Noel B, Policriti A, Clepet C, Casagrande A, Choisne N, Aubourg S, Vitulo N, Jubin C, Vezzi A, Legeai F, Hugueney P, Dasilva C, Horner D, Mica E, Jublot D, Poulain J, Bruyere C, Billault A, Segurens B, Gouyvenoux M, Ugarte E, Cattonaro F, Anthouard V, Wincker P et al (2007) The grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature 449:463–467
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Jirage D, Tootle TL, Reuber TL, Frost LN, Feys BJ, Parker JE, Ausubel FM, Glazebrook J (1999) Arabidopsis thaliana PAD4 encodes a lipase-like gene that is important for salicylic acid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13583–13588
Kwon SI, Kim SH, Bhattacharjee S, Noh JJ, Gassmann W (2009) SRFR1, a suppressor of effector-triggered immunity, encodes a conserved tetratricopeptide repeat protein with similarity to transcriptional repressors. Plant J 57:109–119
Lipka V, Dittgen J, Bednarek P, Bhat R, Wiermer M, Stein M, Landtag J, Brandt W, Rosahl S, Scheel D, Llorente F, Molina A, Parker J, Somerville S, Schulze-Lefert P (2005) Pre- and postinvasion defenses both contribute to nonhost resistance in Arabidopsis. Science 310:1180–1183
Liu YL, Schiff M, Marathe R, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2002) Tobacco Rar1, EDS1 and NPR1/NIM1 like genes are required for N-mediated resistance to tobacco mosaic virus. Plant J 30:415–429
Moffett P, Farnham G, Peart J, Baulcombe DC (2002) Interaction between domains of a plant NBS-LRR protein in disease resistance-related cell death. EMBO J 21:4511–4519
Moroldo M, Paillard S, Marconi R, Fabrice L, Canaguier A, Cruaud C, De Berardinis V, Guichard C, Brunaud V, Le Clainche I, Scalabrin S, Testolin R, Di Gaspero G, Morgante M, Adam-Blondon AF (2008) A physical map of the heterozygous grapevine ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ allows mapping candidate genes for disease resistance. BMC Plant Biol 8:66
Ohad N, Shichrur K, Yalovsky S (2007) The analysis of protein–protein interactions in plants by bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Plant Physiol 145:1090–1099
Peart JR, Cook G, Feys BJ, Parker JE, Baulcombe DC (2002) An EDS1 orthologue is required for N-mediated resistance against tobacco mosaic virus. Plant J 29:569–579
Peirson SN, Butler JN, Foster RG (2003) Experimental validation of novel and conventional approaches to quantitative real-time PCR data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 31:e73
Pike S, Gao F, Kim MJ, Kim SH, Schachtman DP, Gassmann W (2014) Members of the NPF3 transporter family encode pathogen-inducible nitrate/nitrite transporters in grapevine and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 55:162–170
Rietz S, Stamm A, Malonek S, Wagner S, Becker D, Medina-Escobar N, Corina Vlot A, Feys BJ, Niefind K, Parker JE (2011) Different roles of enhanced disease susceptibility1 (EDS1) bound to and dissociated from phytoalexin deficient4 (PAD4) in Arabidopsis immunity. New Phytol 191:107–119
Rustérucci C, Aviv DH, Holt BF, Dangl JL, Parker JE (2001) The disease resistance signaling components EDS1 and PAD4 are essential regulators of the cell death pathway controlled by LSD1 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13:2211–2224
Shah J (2003) The salicylic acid loop in plant defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:365–371
Shirano Y, Kachroo P, Shah J, Klessig DF (2002) A gain-of-function mutation in an Arabidopsis toll interleukin-1 receptor-nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat type r gene triggers defense responses and results in enhanced disease resistance. Plant Cell 14:3149–3162
Stein M, Dittgen J, Sanchez-Rodriguez C, Hou BH, Molina A, Schulze-Lefert P, Lipka V, Somerville S (2006) Arabidopsis PEN3/PDR8, an ATP binding cassette transporter, contributes to nonhost resistance to inappropriate pathogens that enter by direct penetration. Plant Cell 18:731–746
Tang F, Yang S, Gao M, Zhu H (2013) Alternative splicing is required for RCT1-mediated disease resistance in Medicago truncatula. Plant Mol Biol 82:367–374
Vanacker H, Carver TL, Foyer CH (2000) Early H2O2 accumulation in mesophyll cells leads to induction of glutathione during the hyper-sensitive response in the barley-powdery mildew interaction. Plant Physiol 123:1289–1300
Wagner S, Stuttmann J, Rietz S, Guerois R, Brunstein E, Bautor J, Niefind K, Parker JE (2013) Structural basis for signaling by exclusive EDS1 heteromeric complexes with SAG101 or PAD4 in plant innate immunity. Cell Host Microbe 14:619–630
Wang J, Shine MB, Gao QM, Navarre D, Jiang W, Liu C, Chen Q, Hu G, Kachroo A (2014) Enhanced disease susceptibility1 mediates pathogen resistance and virulence function of a bacterial effector in soybean. Plant Physiol 165:1269–1284
Zhu S, Jeong RD, Venugopal SC, Lapchyk L, Navarre D, Kachroo A, Kachroo P (2011) SAG101 forms a ternary complex with EDS1 and PAD4 and is required for resistance signaling against turnip crinkle virus. PLoS Pathog 7:e1002318
Acknowledgments
We thank Paul Schulze-Lefert and Volker Lipka for providing pen2-1 pad4-1 sag101-2 Arabidopsis seeds, the MU Molecular Cytology Core for assistance with light and confocal microscopy, and Alissa Higgins for technical support. This work was supported by grants from the United States Department of Agriculture-National Institute of Food and Agriculture (2008-38901-19367, 2009-38901-19962, and 2010-38901-20939 to WG and WQ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, F., Dai, R., Pike, S.M. et al. Functions of EDS1-like and PAD4 genes in grapevine defenses against powdery mildew. Plant Mol Biol 86, 381–393 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-014-0235-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-014-0235-4