Abstract
Background
Seeds of super basmati were mutagenized with different ethyl methane sulphonate (EMS) doses for creating genetic variability.
Methods and results
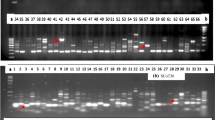
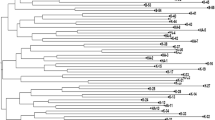
A total of 48 randomly selected putative EMS mutants of super basmati were analyzed to dissect the genetic diversity by using 25 SSR primers located on twelve chromosomes of rice. SSRs analysis revealed that wide-range of genetic diversity is present among mutants of super basmati. A sum of 91 alleles were identified, out of these, 82 alleles were polymorphic and the rest of nine alleles were monomorphic in nature. The range of allele number was 2–10 with mean of 3.64 alleles/locus. The value of polymorphic information content was range between 0.039 (RM5) and 0.878 (RM44) with mean of 0.439 for each locus. A number of polymorphic markers showed unique bands of various sizes ranges from 75 to 1000 bp, during genetic dissection of mutant population. Dendrogram divided whole mutant population into four major groups. Phylogenic analyses revealed that 40–96%genetic similarity is present among individuals of mutant population.
Conclusion
It is concluded that EMS induced genetic variability and SSRs markers (RM44, RM154, RM1, RM252, RM334, RM487, RM110 and RM257) could be handy for the selection of rice mutants as parents for functional genomic and molecular breeding program.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari MR, Shaheen T, Bukhari SA, Husnain T (2015) Genetic improvement of rice for biotic and abiotic stress tolerance. Turk J Bot 39:911–919
Naeem M, Ghouri F, Shahid MQ, Iqbal M, Baloch FS, Chen L, Allah S, Babar M, Rana M (2015) Genetic diversity genetic diversity in mutated and non mutated rice varieties. Genet Mol Res 14:17109–17123
Awan FS, Sadia B, Altaf J, Habib M, Hameed K, Hussain S (2021) Genetic variability through induced mutation. Genetic variation. IntechOpen
Botticella E, Sestili F, Hernandez-Lopez A, Phillips A, Lafiandra D (2011) High resolution melting analysis for the detection of EMS induced mutations in wheat SbeIIagenes. BMC Plant Biol 11:156
Raza A, Shaukat H, Ali Q, Habib M (2018) Assessment of RAPD markers to analyse the genetic diversity among sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) genotypes. TURJAF 6(1):107–111
Matin S, Ashrafuzzaman M, Islam MM, Sikdar SU, Zobayer N (2012) Molecular marker based (SSR) genetic diversity analysis in deep water rice germplasms of Bangladesh. Int J Biosci 2:64–72
Hussain S, Habib M, Ahmed Z, Sadia B, Bernardo A, Amand PS, Maqbool R (2022) Genotyping-by-sequencing based molecular genetic diversity of Pakistani bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) accessions. Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.772517
Senior ML, Murphy JP, Goodman MM, Stuber CW (1998) Utility of SSRs for determining genetic similarities and relationships in maize using an agarose gel system. Crop Sci 38:1088–1098
Liu S, Cantrell RG, McCarty JC, Stewart JMD (2000) Simple sequence repeat-based assessment of genetic diversity in cotton race stock accessions. Crop Sci 40:1459–1469
Zhu Y, Hu J, Han R, Wang Y, Zhu S (2011) Fingerprinting and identification of closely related wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars using ISSR and fluorescence-labeled TP-M13-SSR markers. Afric J Crop Sci 5(7):846–860
Shamim MZ, Manzar H, Sharma VK, Kumar P (2016) Microsateliite marker based characterization and divergence analysis among rice varieties. Indian J Biotechnol 15:182–189
Li W, Wu J, Weng S, Zhang D, Zhang Y, Shi C (2010) Characterization and fine mapping of the glabrous leaf and hull mutants (gl1) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant cell Rep 29:617–627
Pervaiz ZH, Rabbani MA, Khaliq I, Pearce SR, Malik SA (2010) Genetic diversity associated with agronomic traits using microsatellite markers in Pakistani rice landraces. Electron J Biotechnol 13(3):4–5
Guo Y, Cheng B, Hong D (2010) Construction of SSR linkage map and analysis of QTLs for rolled leaf in japonica rice. Rice Sci 17:28–34
Thomson MJ, Polato NR, Prasetiyono J, Trijatmiko KR, Silitonga TS, McCouch SR (2009) Genetic diversity of isolated populations of Indonesian landraces of rice (Oryza sativa L.) collected in East Kalimantan on the island of Borneo. Rice 2:80–92
Sweeney MT, Thomson MJ, Cho YG, Park YJ, Williamson SH, Bustamante CD, McCouch SR (2007) Global dissemination of a single mutation conferring white pericarp in rice. PLoS Genet 3(8):e133
Vikash K, Bhagwat SG (2012) Microsatellite (SSR) based assessment of genetic diversity among the semi-dwarf mutants of elite rice variety WL112. Int Plant Breed Genet 6(4):195–205
Gul Z (2013) Genetic diversity of important rice cultivars of Kashmir valley using microsatellite markers. Afr J Biotechnol 12(7):658–664
Yesmin N, Elias SM, Rahman M, Haque T, Mahbub Hasan AKM, Seraj ZI (2014) Unique genotypic differences discovered among indigenous Bangladeshi rice landraces. Int J Genom. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/210328
Ni J, Colowit PM, Mackill DJ (2002) Evaluation of genetic diversity in rice subspecies using microsatellite markers. Crop Sci 42:601–607
Chauhan RA, Patel DH, Rajkumar BK, Parmar PR, Sejal R (2018) Induction genetic variability using ems and its molecular analysis using RAPD, ISSR and SSR markers in cotton. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 7(2):591–594
Hameed K, Khan MS, Sadaqat HA, Awan FS (2019) Phenotypic characterization of super basmati ethyl methane sulfonate (EMS) induced mutants. PakJAS 56(2):10
Zheng KL, Huang N, Bennett J, Khush GS (1995) PCR-based phylogenetic analysis of wide compatibility varieties in Oryza sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 88:65–69
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
Pal S, Jain S, Saini N, Aarti JRK (2004) Identification of microsatellite markers for differentiating some basmati and non-basmati rice varieties. Indian J Biotechnol 3:519–526
Mahalingam A, Saraswathi R, Ramalingam J (2013) Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers for assessing genetic diversity among the parental lines of hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.). Afric J Biotechnol 12(33):5105–5116
Nagaraju J, Kathirvel M, Kumar RR, Siddiq EA, Hasnain SE (2002) Genetic analysis of traditional and evolves basmati and non-basmati rice varieties by using flouresence—based ISSR-PCR and SSR markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:5836–5841
Allhgholipour M, Farshdfar E, Rabiei B (2014) Molecular characterization and genetic diversity analysis of different rice cultivars by microsatellite markers. Genetika 46:187–198
Berilus SR, Pattanayak A, Ram G (2013) Analysis of genetic variability in rice cultivars of Arunachal Pradesh (India) using microsatellite marker. Afr J Biotechnol 12(8):1–8
Babu BK, Meena V, Agarwal V, Agrawal PK (2014) Population structure and genetic diversity analysis of Indian and exotic rice (Oryza sativa L.) accessions using SSR markers. Mol Biol Rep 41:4329–4339
Lee HH, Neoh PPN, Bong WST, Puvaneswaran J, Wong SC, Yiu PH, Rajan A (2011) Genotyping of Sarawak rice cultivars using microsatellite markers. Pertanika J Trop Agri Sci 34:123–136
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: an intregrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21:2128–2129
Yeh FC, Yang RC, Boyle T (1999) POPGENE Version 1.32: Microsoft window-based freeware for population genetics analysis. University of Alberta, Edmonton
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model of studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:s5269-5276
Page RDM (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Rahman L, Islam MN, Rahman MS, Islam MS, Shah-e-Alam M, Bashar MK (2008) Characterization of 94 rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties of Bangladesh based on microsatellite loci. Bangladesh J Agril Sci 35(1):97–112
Rahman MS, Sohag MKH, Rahman L (2010) Microsatellite based DNA fingerprinting of 28 local rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties of Bangladesh. J Bangaladesh Agri Univ 8:7–17
Taheri S, Abdullah TL, Ahmad Z, Sahebi M, Azizi P (2016) Phenotypic and molecular effects of chronic gamma irradiation on curcuma alismatifolia. Eur J Horti Sci 81:137–147
Kumar GR, Sakthivel K, Sundaram RM, Neeraja CN, Balachandran SM, Rani NS, Viraktamath BC, Madhav MS (2010) Allele mining in crops: prospects and potentials. Biotechnol Adv 28:451–461
Patel S, Ravikiran R, Chakraborty S, Macwana S, Sasidharan N, Trivedi R, Aher B (2014) Genetic diversity analysis of colored and white rice genotypes using microsatellite (SSR) and insertion-deletion (INDEL) markers. J Food Agri 26:497–507
Sahu VK, Sunil NK, Vishwakarma AK, Verulkar SB, Chandel G (2017) QTL hotspots detected for yield contributing traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using composite interval mapping analysis. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia 14:329–341
Jain S, Mitchell SE, Jain RK, Kresovich S, McCouch SR (2003) DNA fingerprinting and phylogenetic analysis of Indian aromatic high-quality rice germplasm using panels of fluorescent-labeled microsatellite markers. Advances in rice genetics. World Scientific, pp 162–166
Choudhary N, Ahuja U, Chawla V, Jain RK, Kumari P, Batan KR (2011) Morphological and molecular variability in weedy rice of Haryana. Asian J Agri Res 5:250–259
Chen LJ, Lee DS, Song ZP, Shu HS, Lu BR (2004) Gene flow from cultivated rice (Oryza sativa) to its weedy and wild relatives. Ann Bot 93:67–73
Kawai T (1965) Studies on artificial induction of mutations in rice by chemicals. 1. Chlorophyll mutations by ethyl imine and ethylene oxide treatments. Bull Nat Inst Agr Sci Ser D 13:133–162
Wu JL, Wu C, Lei C, Baraoidan M, Bordeos A, Madamba MRS, Ramos-Pamplona M, Mauleon R, Portugal A, Ulat VJ, Bruskiewich R, Wang G, Leach J, Khush G, Leung H (2005) Chemical and irradiation-induced mutants of indica rice IR64 for forward and reverse genetics. Plant Mol Biol 59:85–97
Ghneim Herrera T, Posso Duque P, Perez Alemeida I, Torrealba Núñez G, Pieters AJ, Masrtinez CP, Tohme JM (2008) Assessment of genetic diversity in Venezuelan rice cultivar using simple sequence repeats markers. Electron J Biotechnol 11(5):3–4
Arif M, Kousar S, Bajwa MA, Arif A, Zafar Y (2005) Genetic diversity among rice genotypes of Pakistan through random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis. Pak J Bot 37(3):585–592
Tu M, Lu BR, Zhu Y, Wang Y (2007) Abundant within-varietal genetic diversity in rice germplasm from Yunnan Province of China revealed by SSR fingerprints. Biochem Genet 45:789–801
Wong SC, Yiu PH, Bong STW, Lee HH, Neoh PNP, Rajan A (2009) Analysis of Sarawak Bario rice diversity using microsatellite markers. Am J Agri Biol Sci 4:298–304
Oladosu Y, Rafii MY, Abdullah N, Malek MA, Rahim HA, Hussin G, Ismail MR, Latif MA, Kareem I (2015) Genetic variability and diversity of mutant rice revealed by quantitative traits and molecular markers. Agrociencia 49(3):249–266
Domingo C, Andrés F, Talón M (2007) Rice cv. Bahia mutagenized population: a new resource for rice breeding in the Mediterranean basin. Spanish J Agri Res 5:341–347
Shehata SM, Ammar MH, Abdelkalik AF, Zayed BA (2009) Morphological, molecular and biochemical evaluation of Egyptian jasmine rice variety and its M5 derived mutants. Afr J Biotechnol 8:6110–6116
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Higher Education Commission (HEC), Islamabad, Pakistan for providing funds for this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization by [FSA]; manuscript writing data collection and analysis was done by [KH] and [MH]; Supervision of research activity was done by [FSA] and [ZQ]; draft was reviewed and edited by [BS], [SH] and [HASA]. All authors offered suggestions in preparation of the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Responsible editor: Feng Zhou.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hameed, K., Habib, M., Awan, F.S. et al. Detection of genetic divergence among putative ethyl methane sulfonate mutants of super basmati using microsatellite markers. Mol Biol Rep 50, 8799–8808 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08425-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08425-1