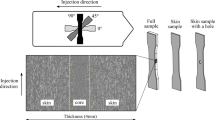
A structural model of a highly porous cellular plastic reinforced with short fibers is developed for calculating its linearly elastic characteristics. By means of orientationally averaging the stiffness tensors of structural elements, whose dimensions and properties also depend on their spatial orientation, relationships for the stiffness tensor of entire cellular plastic are derived. It is shown that they allowed us to describe experimental data for the elastic moduli of a transversely isotropic nanoclay-filled foam plastic reinforced with short carbon fibers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Yakushin, U. Stirna, L. Bel’kova, L. Deme, and I. Sevastyanova, “Properties of rigid polyurethane foams filled with milled carbon fibers,” Mech. Compos. Mater., 46, No. 6, 679-688 (2011).
S. Hussain and M. T. Kortschot, “Polyurethane foam mechanical reinforcement by low-aspect ratio micro-crystalline cellulose and glass fibers,” J. of Cellular Plastics, 51, No. 1, 59-73 (2015).
L. J. Lee, C. Zeng, X. Cao, X. Han, J. Shen, and G. Xu, “Polymer nanocomposite foams,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 65, 2344-2363 (2005).
S. Pardo-Alonso, E. Solórzano, L. Brabant, P. Vanderniepen, M. Dierick, L. Van Hoorebeke, and M. A. Rodríguez-Pérez, “3D analysis of the progressive modification of the cellular architecture in polyurethane nanocomposite foams via X-ray microtomography,” Europ. Polymer J., 49, 999-1006 (2013).
P. Mondal and D. V. Khakhar, “Rigid polyurethane-clay nanocomposite foams: preparation and properties,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 103, 2802-2809 (2007).
S. Chuayjuljit, A. Maungchareon, and O. Saravari, “Preparation and properties of palm oil-based rigid polyurethane nanocomposite foams,” J. of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 29, 218-225 (2010).
N. N. P. Nik Pauzi, R. A. Majid, M. H. Dzulkifli, and M. Y. Yahya, “Development of rigid bio-based polyurethane foam reinforced with nanoclay,” Composites: Part B, 67, 521-526 (2014).
U. Cabulis, I. Sevastyanova, J. Andersons, and I. Beverte, “Rapeseed oil-based rigid polyisocyanurate foams modified with nanoparticles of various type,” Polimery, 59, 207-212 (2014).
A. Lagzdins, A. Zilaucs, I. Beverte, and J. Andersons, “A refined strut model for calculating the elastic constants of highly porous cellular plastics by the method of orientational averaging,” Mech. Compos. Mater., 47, No. 6, 589-596 (2011).
A. Lagzdins, A. Zilaucs, I. Beverte, and J. Andersons, “Calculating the elastic constants of highly porous cellular plastics with an oriented structure,” Mech. Compos. Mater., 49, No. 2, 121-128 (2013).
A. Lagzdins, A. Zilaucs, I. Beverte, and J. Andersons, “Estimation of the elastic constants of highly porous cellular plastics reinforced with fibers embedded in foam struts,” J. Compos. Mater., 50, 1169-1180 (2016).
J.-J. Luo and I. M. Daniel, “Characterization and modeling of the mechanical behavior of polymer/clay nanocomposites,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 63, 1607-1616 (2003).
S. Gaidukov, R. D. Maksimov, U. Cabulis, E. Plume, and A. Stunda-Zujeva, “Mechanical properties of a rigid polyurethane/montmorillonite composite prepared by using a biopolyol,” Mech. Compos. Mater., 49, 333-344 (2013).
W. Xu, Q. Zeng, and A. Yu, “Prediction of the overall Young’s moduli of clay-based polymer nanocomposites,” J. Compos. Mater., 49, 3459-3469 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 53, No. 3, pp. 459-476, May-June, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lagzdins, A., Zilaucs, A., Beverte, I. et al. A Refined Strut Model for Describing the Elastic Properties of Highly Porous Cellular Polymers Reinforced with Short Fibers. Mech Compos Mater 53, 321–334 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-017-9664-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-017-9664-x