Abstract
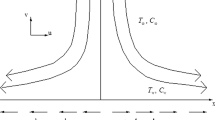
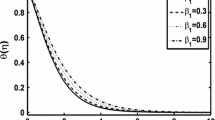
Present article provides an analytical investigation of the fluid flow and heat and mass transfer for the steady laminar MHD three-dimensional nanofluid flow over a bidirectional stretching sheet with convective surface boundary condition using optimal homotopy analysis method (OHAM) via Mathematica package BVPh2.0. In contrast to the conventional no-slip condition at the surface, Navier’s slip condition has been applied. The governing partial differential equations are transformed into a highly nonlinear coupled ordinary differential equations consisting the momentum, energy and concentration equations via appropriate similarity transformations. The current OHAM solution demonstrates very good correlation with those of the previously published studies in the especial cases. The influence of different physical parameters such as magnetic parameter (M), Prandtl number (\( \Pr \)), Brownian motion parameter (\( {\text{Nb}} \)), thermophoresis parameter (\( {\text{Nt}} \)), Lewis number (Le), velocity slip parameter (γ), stretching rate ratio parameter (λ), and Biot number (Bi) on all fluid velocity components \( \left( {f^{\prime}(\eta ),\,\,g^{\prime}(\eta )} \right) \), temperature distribution \( \left( {\theta \,(\eta )} \right) \) and concentration \( \left( {\phi \,(\eta )} \right) \) as well as the skin friction coefficients in x and y directions \( \left( {C_{\text{fx}} {\text{Re}}_{\text{x}}^{{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 2}} \right. \kern-0pt} 2}}} ,\,\,C_{\text{fy}} {\text{Re}}_{\text{x}}^{{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 2}} \right. \kern-0pt} 2}}} } \right), \) local Nusselt number \( \left( {{{{\text{Nu}}_{\text{x}} } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\text{Nu}}_{\text{x}} } {{\text{Re}}_{\text{x}}^{{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 2}} \right. \kern-0pt} 2}}} }}} \right. \kern-0pt} {{\text{Re}}_{\text{x}}^{{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 2}} \right. \kern-0pt} 2}}} }}} \right) \) and local Sherwood number \( \left( {{{{\text{Sh}}_{\text{x}} } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\text{Sh}}_{\text{x}} } {{\text{Re}}_{\text{x}}^{{\,{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 2}} \right. \kern-0pt} 2}}} }}} \right. \kern-0pt} {{\text{Re}}_{\text{x}}^{{\,{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 2}} \right. \kern-0pt} 2}}} }}} \right) \) are tabulated graphically and discussed in details. This study specifies that nanoparticles in the base fluid offer a potential in increasing the convective heat transfer performance of various liquids.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a, b:
-
Constants
- Bi:
-
Biot number
- \( B_{\text{o}} \) :
-
Constant magnetic field
- c :
-
Heat capacity
- C :
-
Nanoparticle concentration
- \( C_{\text{w}} \) :
-
Concentration of nanoparticle
- \( C_{\infty } \) :
-
Ambient concentration
- \( C_{\text{f}} \) :
-
Friction coefficient
- \( C_{\text{i}} \) :
-
Constant in Eq. (24)
- D :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- \( D_{\text{T}} \) :
-
Thermophoretic diffusion coefficient
- \( f(\eta ),\;g(\eta ) \) :
-
Velocity similarity functions
- h :
-
Convective heat transfer coefficient
- K :
-
Thermal conductivity
- k :
-
Constant
- \( {\text{Le}} \) :
-
Lewis number
- M :
-
Magnetic parameter
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- Nb:
-
Brownian motion parameter
- Nt:
-
Thermophoresis parameter
- n, m :
-
Constants
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- q :
- R :
-
Auxiliary function
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- Sh:
-
Sherwood number
- T:
-
Temperature
- \( T_{\text{f}} \) :
-
Convective surface temperature
- \( T_{\infty } \) :
-
Ambient temperature
- u, v, w :
-
Velocity components in x, y, z directions
- x, y, z :
-
Cartesian coordinates
- \( \alpha \) :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- \( \gamma \) :
-
Velocity slip parameter
- \( \gamma_{0} \) :
-
Slip length
- \( \varepsilon \) :
-
Total squared residual error
- \( \eta \) :
-
Similarity parameter
- \( \theta (\eta ) \) :
-
Temperature distribution
- \( \lambda \) :
-
Stretching rate ratio parameter
- \( \nu \) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- \( \rho \) :
-
Fluid density
- \( \sigma \) :
-
Electrical conductivity
- \( \tau \) :
-
Skin friction
- \( \phi (\eta ) \) :
-
Concentration
- \( \chi \) :
-
Auxiliary parameter
- \( {\mathcal{L}} \) :
-
Auxiliary linear operator
- \( {\mathcal{N}} \) :
References
Choi SUS, Eastman JA. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. Mater Sci. 1995;231:99–105.
Eastman JA, Choi SUS, Li S, Soyez G, Thompson LJ, DiMelfi RJ. Novel thermal properties of nanostructured materials. Mater Sci Forum. 1999;312–314:629–34.
Xuana Y, Roetzel W. Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2000;43:3701–7.
Masuda H, Ebata A, Teramae K, Hishinuma H. Alteration of Thermal conductivity and viscosity of liquid by dispersing ultra-fine particles (dispersion of 7-A1203, SiO2 and TiO2 ultra-fine particles). Netsu Bussei. 1993;4:227–33.
Xuan Y, Li Q. Investigation on convective heat transfer and flow features of nanofluids. J Heat Transf. 2003;125:151–5.
Hatami M, Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DDJ. Laminar flow and heat transfer of nanofluid between contracting and rotating disks by least square method. Powder Technol. 2014;253:769–79.
Khan WA, Pop I. Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2010;53:2477–83.
Rashidi MM, Abelman S, Freidoonimehr N. Entropy generation in steady MHD flow due to a rotating porous disk in a nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2013;62:515–25.
Rana P, Bhargava R, Bég OA. Numerical solution for mixed convection boundary layer flow of a nanofluid along an inclined plate embedded in a porous medium. Comput Math Appl. 2012;64:2816–32.
Rana P, Bhargava R. Flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a nonlinearly stretching sheet: a numerical study. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2012;17:212–26.
Sheikholeslami M, Gorji-Bandpy M, Ganji DDJ. Lattice Boltzmann method for MHD natural convection heat transfer using nanofluid. Powder Technol. 2014;254:82–93.
Toghraie D, Alempour SM, Afrand M. Experimental determination of viscosity of water based magnetite nanofluid for application in heating and cooling systems. J Magn Magn Mater. 2016;417:243–8.
Amani M, Amani P, Kasaeian A, Mahian O, Wongwises S. Thermal conductivity measurement of spinal-type ferrite MnFe2O4 nanofluids in the presence of a uniform magnetic field. J Mol Liq. 2017;230:121–8.
Amani M, Amani P, Kasaeian A, Mahian O, Kasaeian F, Wongwises S. Experimental study on viscosity of spinal-type manganese ferrite nanofluid in attendance of magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater. 2017;428:457–63.
Esfe MH, Ahangar MRH, Toghraie D, Hajmohammad MH, Rostamian H, Tourang H. Designing artificial neural network on thermal conductivity of Al2O3-water—EG (60–40%) nanofluid using experimental data. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126(2):837–43.
Ameri M, Amani M, Amani P. Thermal performance of nanofluids in metal foam tube: thermal dispersion model incorporating heterogeneous distribution of nanoparticles. Adv Powder Technol. 2017;28(10):2747–55.
Amani M, Amani P, Kasaeian A, Mahian O, Pop I, Wongwises S. Modelling and optimization of thermal conductivity and viscosity of MnFe2O4 nanofluid under magnetic field using an ANN. Sci Rep. 2017;7:Article number:17369.
Esfe MH, Afrand M, Rostamian SH, Toghraie D. Examination of rheological behavior of MWCNTs/ZnO-SAE40 hybrid nano-lubricants under various temperatures and solid volume fractions. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2017;80:384–90.
Esfe MH, Rostamian H, Toghraie D, Yan WM. Using artificial neural network to predict thermal conductivity of ethylene glycol with alumina nanoparticle. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126(2):643–8.
Amani M, Ameri M, Kasaeian A. The experimental study of convection Heat transfer characteristics and pressure drop of magnetic nanofluid in a porous metal foam tube. Transp Porous Media. 2017;16(2):959–74.
Sajadifar SA, Karimipour A, Toghraie D. Fluid flow and heat transfer of non- Newtonian nanofluid in a microtube considering slip velocity and temperature jump boundary conditions. Eur J Mech B Fluids. 2017;61:25–32.
Esfe MH, Razi P, Hajmohammad MH, Rostamian SH, Sarsam WS, Arani AA, Dahari M. Optimization, modeling and accurate prediction of thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of stabilized ethylene glycol and water mixture Al2O3 nanofluids by NSGA-II using ANN. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2017;82:154–60.
Amani M, Amani P, Mahian O, Estelle P. Multi objection optimization of thermophysical properties of eco-friendly organic nanofluid. J Clean Prod. 2017;166:350–9.
Esfahani MA, Toghraie D. Experimental investigation for developing a new model for the thermal conductivity of Silica/Water-Ethylene glycol (40%–60%) nanofluid at different temperatures and solid volume fractions. J Mol Liq. 2017;232:105–12.
Akbari OA, Afrouzi HH, Marzban A, Toghraie D, Malekzade H, Arabpour A. Investigation of volume fraction of nanoparticles effect and aspect ratio of the twisted tape in the tube. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;129:1–12.
Zadkhast M, Karimipour A, Toghraie D. Developing a new correlation to estimate the thermal conductivity of MWCNT-CuO/water hybrid nanofluid via an experimental investigation. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;129:859–67.
Sharma P, Baek IH, Cho T, Park S, Lee KB. Measurement of thermal conductivity of ZnO-TiO2/EG hybrid nanofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;125(1):527–35.
Toghraie D, Chaharsoghi VA, Afrand M. Measurement of thermal conductivity of ZnO–TiO2/EG hybrid nanofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;125(1):527–35.
Esfe MH, Saedodin S, Wongwises S, Toghraie D. An experimental study on the effect of diameter on thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of Fe/water nanofluids. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119(3):1817–24.
Esfe MH, Saedodin S, Bahiraei M, Toghraie D, Mahian O, Wongwises S. Thermal conductivity modeling of MgO/EG nanofluids using experimental data and artificial neural network. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;118(1):287–94.
Wang CY. Flow due to a stretching boundary with partial slip—an exact solution of the Navier-Stokes equations. Chem Eng Sci. 2002;57:3745–7.
Sparrow E, Beavers G, Hung L. Flow about a porous-surfaced rotating disk. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 1971;14:993–6.
Turkyilmazoglu M, Senel P. Heat and mass transfer of the flow due to a rotating rough and porous disk. Int J Therm Sci. 2013;63:146–58.
Sahoo B. Effects of partial slip, viscous dissipation and joule heating on von kármán flow and heat transfer of an electrically conducting non-newtonian fluid. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2009;14:2982–98.
Mohammadein AA, Gorla RSR. Heat transfer in a micropolar fluid over a stretching sheet with viscous dissipation and internal heat generation. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2001;11:50–8.
Rashidi MM, Mohimanianpour SA. Analytic approximate solutions for unsteady boundary-layer flow and heat transfer due to a stretching sheet by homotopy analysis method. Nonlinear Anal Model Control. 2010;15:83–95.
Bhargava R, Kumar L, Takhar HS. Finite element solution of mixed convection micropolar flow driven by a porous stretching sheet. Int J Eng Sci. 2003;41:2161–78.
Bachok N, Ishak A, Pop I. Boundary-layer flow of nanofluids over a moving surface in a flowing fluid. Int J Therm Sci. 2010;49:1663–8.
Rashidi MM, Freidoonimehr N, Hosseini A, Bég OA, Hung TK. Homotopy simulation of nanofluid dynamics from a non-linearly stretching isothermal permeable sheet with transpiration. Meccanica. 2013;49:1–14.
Freidoonimehr N, Rahimi AB. Investigation of MHD nano-fluid flow over a stretching surface with velocity slip and convective surface boundary conditions. Modares Mech Eng. 2015;15(3):208–18.
Liao SJ. An optimal homotopy-analysis approach for strongly nonlinear differential equations. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2010;15:2003–16.
http://numericaltank.sjtu.edu.cn/BVPh2_0.htm. Retrieved June 5,2015.
Hayat T, Shehzad SA, Qasim M, Asghar S. Three-dimensional stretched flow via convective boundary condition and heat generation/absorption. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2012;24:342–58.
Wang CY. The three-dimensional flow due to a stretching sheet. Phys Fluids. 1984;27:1915–7.
Hayat T, Shehzad TS, Alsaedi A. Three-dimensional flow of jeffrey fluid over a bidirectional stretching surface with heat source/sink. J Aerosp Eng. 2014;27:04014007.
Hayat T, Muhammad T, Alsaedi A, Ahmad AB. Three-dimensional flow of nano-fluid with Cattaneo-Christov double diffusion. Results Phys. 2016;6:897–903.
Rashidi MM, Freidoonimehr N, Hosseini A, Bég OA, Hung TK. Homotopy simulation of nanofluid dynamics from a non-linearly stretching isothermal permeable sheet with transpiration. Meccanica. 2014;49:469–82.
Khan JA, Mustafa M, Hayat T, Farooq MA, Alsaedi A, Liao SJ. On model for three-dimensional flow of nanofluid: an application to solar energy. J Mol Liq. 2014;194:41–7.
Acknowledgements
Financial support of Ferdowsi University of mashhad under Contract No. 2/40473 is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freidoonimehr, N., Rahimi, A.B. Brownian motion effect on heat transfer of a three-dimensional nanofluid flow over a stretched sheet with velocity slip. J Therm Anal Calorim 135, 207–222 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7060-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7060-y